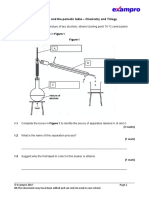
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chem 2010 - 3 Periodic Trends
Enviado por
penguinpowerrrrTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chem 2010 - 3 Periodic Trends
Enviado por
penguinpowerrrrDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Periodic
Trends
Periodic Trends
Moving across the Periodic Table from left to right, the elements
chemical and physical properties change from those of metals to those
of metalloids (or semi-metals) and finally to those of non-metals:
Metals Metalloids Non-metals
Magnesium Silicon Sulphur
Periodic Trends
Question:
What are the typical chemical and physical properties of metals?
Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Tend to have high melting points and boiling points.
Tend to be hard and strong.
Tend to have a high density.
Have a metallic lustre (are shiny).
Malleable and ductile (shape can be changed without breaking).
Sonorous (ring when struck).
React by losing their valence electrons.
Oxides are basic.
Periodic Trends
Question:
What are the typical chemical and physical properties of
non-metals?
Poor conductors of heat and electricity (insulators).
Tend to have low melting points and boiling points.
Tend to be soft.
Tend to have a low density.
Surface is dull (unless crystalline).
Tend to be brittle.
Not sonorous.
React by gaining valence electrons.
Oxides are acidic.
Periodic Trends
Question:
What are the typical chemical and physical properties of
metalloids?
Semiconductors (electrical conductivity varies greatly depending
upon the conditions that they are subject to).
Oxides are amphoteric (oxides can be either acidic or basic
depending upon the conditions that they are subject to).
1 2 Group 3 4 5 6 7 0
1
H He
2
Li Be B C N O F Ne
3
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
4
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
5
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
6
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
7
Fr Ra Ac
P
e
r
i
o
d
Periodic Trends
The dividing line
between metals (left)
and non-metals (right).
1 2 Group 3 4 5 6 7 0
1
H He
2
Li Be B C N O F Ne
3
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
4
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
5
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
6
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
7
Fr Ra Ac
P
e
r
i
o
d
Periodic Trends
Metals!
1 2 Group 3 4 5 6 7 0
1
H He
2
Li Be B C N O F Ne
3
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
4
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
5
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
6
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
7
Fr Ra Ac
P
e
r
i
o
d
Periodic Trends
Metalloids!
1 2 Group 3 4 5 6 7 0
1
H He
2
Li Be B C N O F Ne
3
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
4
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
5
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
6
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
7
Fr Ra Ac
P
e
r
i
o
d
Periodic Trends
Non-metals!
1 2 Group 3 4 5 6 7 0
1
H He
2
Li Be B C N O F Ne
3
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
4
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
5
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
6
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
7
Fr Ra Ac
P
e
r
i
o
d
Periodic Trends
Summary!
Periodic Trends
Question:
Lithium and sodium are both elements from Group 1 of the Periodic
Table.
Draw the electron configurations of lithium (atomic number = 3) and
sodium (atomic number = 11):
Periodic Trends
Question:
What do the electron configurations of the Group 1 metals have in
common?
Periodic Trends
Answer:
The Group 1 metals all have 1 electron in their valence shell.
Periodic Trends
Question:
How do the Group 1 metals react to obtain a complete valence
shell?
Periodic Trends
Answer:
The Group 1 metals all react by losing their single valence electron to
form an ion with a complete valence shell and a single positive
charge. Because the Group 1 metals all react in this way, they are
said to have similar chemical properties.
Periodic Trends
Question:
Sodium (symbol Na) and caesium (symbol Cs) are both in
Group 1 of the Periodic Table.
The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl. The formula of sodium
carbonate is Na
2
CO
3
. The formula of sodium sulphate is Na
2
SO
4
.
Using this information, predict the formulae of caesium chloride,
caesium carbonate and caesium sulphate.
Answer:
Caesium chloride CsCl.
Caesium carbonate Cs
2
CO
3
.
Caesium sulphate Cs
2
SO
4
.
Periodic Trends
Question:
Some information about the Group 1 metals is given in the table
below:
Element Melting Point / C Metallic Radius / nm
Lithium Li 180.0 0.152
Sodium Na 97.8 0.186
Potassium K ? ?
Rubidium Rb 38.9 0.244
Caesium Cs 28.7 0.262
Predict the melting point and metallic radius of potassium.
Periodic Trends
Answer:
Some information about the Group 1 metals is given in the table
below:
Element Melting Point / C Metallic Radius / nm
Lithium Li 180.0 0.152
Sodium Na 97.8 0.186
Potassium K 63.7 0.231
Rubidium Rb 38.9 0.244
Caesium Cs 28.7 0.262
Periodic Trends
Question:
Fluorine and chlorine are both elements from Group 7 of the
Periodic Table.
Draw the electron configurations of fluorine (atomic number = 9)
and chlorine (atomic number = 17):
Periodic Trends
Question:
What do the electron configurations of the Group 7 elements have
in common?
Periodic Trends
Answer:
The Group 7 elements all have 7 electrons in their valence shell.
Periodic Trends
Question:
How do the Group 7 elements react to obtain a complete valence
shell?
Periodic Trends
Answer:
The Group 7 elements all react by gaining a single valence electron to
form an ion with a complete valence shell and a single negative
charge. Because the Group 7 elements all react in this way, they are
said to have similar chemical properties.
Periodic Trends
Question:
Chlorine (symbol Cl) and astatine (symbol At) are both in
Group 7 of the Periodic Table.
The formula of sodium chloride is NaCl. The formula of magnesium
chloride is MgCl
2
. The formula of aluminium chloride is AlCl
3
. Using
this information, predict the formulae of sodium astatide,
magnesium astatide and aluminium astatide.
Answer:
Sodium astatide NaAt.
Magnesium astatide MgAt
2
.
Aluminium astatide AlAt
3
.
Periodic Trends
Question:
Some information about the Group 7 elements is given in the table
below:
Element Melting Point / C Covalent Radius / nm
Fluorine F 220 0.072
Chlorine Cl ? ?
Bromine Br 7.2 0.114
Iodine I 114 0.133
Astatine At 302 0.140
Predict the melting point and covalent radius of chlorine.
Periodic Trends
Answer:
Some information about the Group 7 elements is given in the table
below:
Element Melting Point / C Covalent Radius / nm
Fluorine F 220 0.072
Chlorine Cl 101 0.099
Bromine Br 7.2 0.114
Iodine I 114 0.133
Astatine At 302 0.140
Periodic Trends
Question:
Elements in the same Group of the Periodic Table have similar
chemical properties because they lose or gain the same number of
electrons to fill their valence shells. In what way do the elements in
the same Group of the Periodic Table differ from each other?
Answer:
The reactivity of the elements in the same Group varies. On
descending a Group of metals, the elements become more reactive.
On descending a Group of non-metals, the elements become less
reactive. In addition, the physical properties of the elements in the
same Group varies. On descending a Group of metals, their melting
points tends to decrease. On descending a Group of non-metals,
their melting points tends to increase.
Periodic Trends
Question:
Sodium and chlorine are both in the same Period of the
Periodic Table. Draw the electron configurations of sodium
(atomic number = 11) and chlorine (atomic number = 17) and
state in what way their electron configurations are similar to
each other.
Periodic Trends
Answer:
Sodium and chlorine are both in the third Period of the Periodic Table
and so both atoms have three electron shells:
Periodic Trends
Question:
Complete the table below to show how the properties of the elements
changes across the Periodic Table:
Group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
Element Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
Metal / Non-metal
Number of
Valence
Electrons
Number of
Electrons Lost /
Gained
Charge on Ion
Valency
Periodic Trends
Question:
Complete the table below to show how the properties of the elements
changes across the Periodic Table:
Group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
Element Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
Metal / Non-metal Metal Metal Metal
Semi-
metal
Non-
metal
Non-
metal
Non-
metal
Non-
metal
Number of
Valence
Electrons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Number of
Electrons Lost /
Gained
1 Lost 2 Lost 3 Lost
4
Gained
3
Gained
2
Gained
1
Gained
0 Lost
or
Gained
Charge on Ion +1 +2 +3 4 3 2 1 0
Valency 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 0
Periodic Trends
Summary:
Moving across the Periodic Table from left to right, the elements
chemical and physical properties change from those of metals to
those of metalloids and finally to those of non-metals.
Elements in the same Group have the same number of valence
electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties.
Elements from the same Group form compounds with the same
formulae.
On descending a Group of elements, there is a gradual change in
their chemical and physical properties. Metals become more
reactive and their melting points decrease. Non-metals become less
reactive and their melting points increase.
Elements in the same Period have the same number of electron
shells.
Periodic Trends
Enrichment:
Consider the elements of the third Period, sodium to chlorine.
How does the size (atomic radius) of an atom vary from left
to right across the Periodic Table?
How does the ease with which an atom loses an electron
from its valence shell (first ionization energy) vary from left to
right across the Periodic Table?
Clue consider how atomic number changer across the
Periodic Table from sodium to chlorine. Remember what the
atomic number of an element represents.
Periodic Trends
Symbol
of
Element
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
Atomic
Number
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Atomic
Radius /
nm
0.157 0.136 0.125 0.117 0.110 0.104 0.099
First
Ionization
Energy /
kJ mol
-1
494 736 577 786 1060 1000 1260
Periodic Trends
Symbol
of
Element
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
Atomic
Number
Number of protons within the nucleus of the atom increases.
Positive charge within the nucleus of the atom increases.
Force of attraction between the positive nucleus and negative electrons orbiting
the nucleus increases.
Atomic
Radius /
nm
0.157 0.136 0.125 0.117 0.110 0.104 0.099
First
Ionization
Energy /
kJ mol
-1
494 736 577 786 1060 1000 1260
Periodic Trends
As the force of attraction between the positive nucleus and
negative electrons that are orbiting the nucleus increases, the
electrons are pulled in closer to the nucleus and the size of
the atom (atomic radius) decreases.
As the force of attraction between the positive nucleus and
negative electrons that are orbiting the nucleus increases, the
amount of energy required to remove an electron from the
valence shell of an atom (first ionization energy) increases.
Periodic Trends
A Note on First Ionization Energy
The ease with which an atom of a particular element
loses a single electron from its valence shell is given by
its first ionization energy. This is the energy required to
convert one mole of gaseous atoms to one mole of
gaseous ions, each with a single positive charge. It can
be summarised by the following equation:
E
(g)
E
+
(g)
+ e
Você também pode gostar
- Senior Moot 2012 Competitors' GuideDocumento10 páginasSenior Moot 2012 Competitors' GuidepenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation of Accounting Statements: VA (18) JDDocumento39 páginasPreparation of Accounting Statements: VA (18) JDpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- International Law Crash CourseDocumento12 páginasInternational Law Crash CoursepenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- ANigeria V Home SecretaryDocumento3 páginasANigeria V Home SecretarypenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- IC558954-Newsletterpubs-10. Final Bench MemoDocumento24 páginasIC558954-Newsletterpubs-10. Final Bench MemoA HAinda não há avaliações
- (Good) ICJ Study Guide - Finalized - 17may13Documento28 páginas(Good) ICJ Study Guide - Finalized - 17may13penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- The Wadham Law Student'S: Michaelmas 2014Documento22 páginasThe Wadham Law Student'S: Michaelmas 2014penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Job DescriptionDocumento3 páginasJob DescriptionpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- The House of Lords' Decision in Fiona TrustDocumento2 páginasThe House of Lords' Decision in Fiona TrustRajatAgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- 9769 Y08 SP 1Documento606 páginas9769 Y08 SP 1penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Relevant Legal Training 2015 and Training Contracts 2016 Job Descr...Documento2 páginasRelevant Legal Training 2015 and Training Contracts 2016 Job Descr...penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- 1pound Off Almond Breeze PDFDocumento1 página1pound Off Almond Breeze PDFpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Sand Gcybilj2Documento25 páginasSand Gcybilj2penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- All Marriages Are Equal - 163 NLJ 7570, PDocumento2 páginasAll Marriages Are Equal - 163 NLJ 7570, PpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Christmas 2015 Shopping Party TicketDocumento2 páginasChristmas 2015 Shopping Party TicketpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- RP13 31Documento42 páginasRP13 31penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Graduate Recruitment Brochure AsiaDocumento23 páginasGraduate Recruitment Brochure AsiapenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Graduate Recruitment Brochure AsiaDocumento23 páginasGraduate Recruitment Brochure AsiapenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Approximately 800-1000 Words: Re: SEO London Investment Banking Summer Internship ProgrammeDocumento2 páginasApproximately 800-1000 Words: Re: SEO London Investment Banking Summer Internship ProgrammepenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Andrew Beale - Essential Constitutional and Administrative LawDocumento123 páginasAndrew Beale - Essential Constitutional and Administrative LawPop Rem100% (4)
- (2015) SGHC 217Documento22 páginas(2015) SGHC 217penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Same-Sex Marriage and Civil Partnership DifferencesDocumento6 páginasSame-Sex Marriage and Civil Partnership DifferencesTterram IjnusAinda não há avaliações
- ArbitrationDocumento57 páginasArbitrationpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- 9095645Documento13 páginas9095645penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Mercouri Speech Oxford UnionDocumento6 páginasMercouri Speech Oxford UnionpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Nutshells Constitutional Law 9e Judicial Review Topic GuideDocumento28 páginasNutshells Constitutional Law 9e Judicial Review Topic Guidepenguinpowerrrr100% (1)
- 9769 Y08 SP 1Documento606 páginas9769 Y08 SP 1penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- 9095645Documento13 páginas9095645penguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Proportionality and Deference: The Importance of A Structured ApproachDocumento19 páginasProportionality and Deference: The Importance of A Structured ApproachpenguinpowerrrrAinda não há avaliações
- Moore V Regents T08Documento40 páginasMoore V Regents T08Davide RossettoAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- TJC Chemistry H2 Y1 2009Documento21 páginasTJC Chemistry H2 Y1 2009OccamsRazor100% (1)
- Systems Operationc - Best Practice GuidelinesDocumento44 páginasSystems Operationc - Best Practice GuidelinesNguyen Van Dzung75% (4)
- Parametric Studies of Ethylene Dichloride Purification ProcessDocumento4 páginasParametric Studies of Ethylene Dichloride Purification ProcessArsalan QadirAinda não há avaliações
- Discussion Exp 1 CHM 301 Alcohol TestDocumento4 páginasDiscussion Exp 1 CHM 301 Alcohol TestCik Mira YusoffAinda não há avaliações
- Water Filters Everpure CatalogDocumento42 páginasWater Filters Everpure CatalogSinergroup Water Filters Water Purifiers Water SoftenersAinda não há avaliações
- Moles and EquationsDocumento16 páginasMoles and EquationssksksksAinda não há avaliações
- Astm Methods WATER22Documento40 páginasAstm Methods WATER22rizwan chAinda não há avaliações
- Chlorine Dioxide Health and SafetyDocumento3 páginasChlorine Dioxide Health and SafetyNavaneetha KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- M4 Check in ActivityDocumento2 páginasM4 Check in Activityjelly fishAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS Sodium Hypochlorite CoatzaDocumento3 páginasMSDS Sodium Hypochlorite CoatzaDefenceDogAinda não há avaliações
- Best-Practises RO PlantDocumento25 páginasBest-Practises RO PlantjdadhaAinda não há avaliações
- Text 3Documento3 páginasText 3Hana AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Jsa Jis B 8701Documento25 páginasJsa Jis B 8701farhad100% (1)
- Stoichiometry PracticeDocumento7 páginasStoichiometry PracticecdddeAinda não há avaliações
- Organ BiochemistryDocumento158 páginasOrgan Biochemistryyodi2801Ainda não há avaliações
- Review Test - 2Documento16 páginasReview Test - 2vishal110085100% (2)
- Chemistry Module f5 AnswersDocumento210 páginasChemistry Module f5 AnswersFarah Adibah RozaimyAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocumento15 páginasChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableRenee DisaAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible Balflex - Hoses - Catalogue - 2019Documento181 páginasFlexible Balflex - Hoses - Catalogue - 2019zephyrinAinda não há avaliações
- Conservation - of - Matter Test From Problem AtticDocumento12 páginasConservation - of - Matter Test From Problem AtticMystAinda não há avaliações
- ChemistryTestfinal - LASTDocumento30 páginasChemistryTestfinal - LASTpurpleasma64Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocumento8 páginasChemistry Investigatory Projectrithika praveenAinda não há avaliações
- PDS - Sunchlor Tcca 90%Documento1 páginaPDS - Sunchlor Tcca 90%tito rahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaDocumento1 páginaChemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaMouli MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Aqa CHM4 W QP Jun06Documento20 páginasAqa CHM4 W QP Jun06branavan93Ainda não há avaliações
- Science BukletDocumento69 páginasScience BukletManu GoelAinda não há avaliações
- Microorganisms 09 00136 v2Documento19 páginasMicroorganisms 09 00136 v2elalaoui25Ainda não há avaliações
- 5070 w02 QP 1Documento16 páginas5070 w02 QP 1mstudy123456100% (1)
- Water Treatment Math DocsDocumento12 páginasWater Treatment Math DocsPruthaviraj BAinda não há avaliações
- Important Reagents For Organic ChemistryDocumento2 páginasImportant Reagents For Organic ChemistryRohan NewaskarAinda não há avaliações