Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Drug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)
Enviado por
Angelica Cassandra Villena0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
46 visualizações2 páginasThis document contains a drug study for a patient named JN who was admitted on August 7, 2014 for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). The drug cefuroxime is prescribed to treat the patient's infection. Cefuroxime is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that works by binding to bacterial cell walls and causing cell death. It is prescribed for respiratory, skin, bone, joint, urinary, and gynecological infections. The document outlines the dosage, effects, contraindications, nursing responsibilities, and patient teaching for cefuroxime administration and monitoring.
Descrição original:
drug study
Título original
Ce Fur Oxime
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document contains a drug study for a patient named JN who was admitted on August 7, 2014 for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). The drug cefuroxime is prescribed to treat the patient's infection. Cefuroxime is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that works by binding to bacterial cell walls and causing cell death. It is prescribed for respiratory, skin, bone, joint, urinary, and gynecological infections. The document outlines the dosage, effects, contraindications, nursing responsibilities, and patient teaching for cefuroxime administration and monitoring.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
46 visualizações2 páginasDrug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)
Enviado por
Angelica Cassandra VillenaThis document contains a drug study for a patient named JN who was admitted on August 7, 2014 for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). The drug cefuroxime is prescribed to treat the patient's infection. Cefuroxime is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that works by binding to bacterial cell walls and causing cell death. It is prescribed for respiratory, skin, bone, joint, urinary, and gynecological infections. The document outlines the dosage, effects, contraindications, nursing responsibilities, and patient teaching for cefuroxime administration and monitoring.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
Republic of the Philippines
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
(CvSU)
Don Severino Delas Alas Campus
Indang, Cavite
(046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012
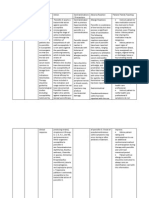
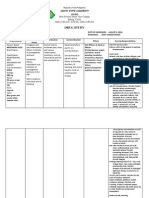
DRUG STUDY
NAME OF PATIENT: JN DATE OF ADMISSION: AUGUST 7, 2014
AGE: 33 YEARS OLD DIAGNOSIS: PTB
SEX: FEMALE
Drug Features
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name:
Cefuroxime
Brand Name:
none
Classification:
anti-infectives
Sub Classification:
second-generation
cephalosporins
Dosage:
500 mg 1 tab
Route:
PO
Frequency:
BID
Form:
Film coated tablet
Binds to
bacterial cell
wall membrane,
causing cell
death.
Therapeutic
Effects:
Bactericidal
action against
susceptible
bacteria.
Spectrum:
Similar to that of
first-generation
cephalosporins
but has
increased
activity against
several other
gram-negative
pathogens
including:
Haemophilus
Treatment of:
Respiratory tract
infections, Skin and
skin structure
infections, Bone
and joint infections
(IV), Urinary tract
infections,
Gynecological
infections,
Septicemia (IV),
Otitis media (PO),
Meningitis (IV),
Lyme disease (PO).
Perioperative
prophylaxis (IV).
Contraindicated in:
Hypersensitivity to
cephalosporins;
Serious
hypersensitivity to
penicillins.
Use Cautiously in:
Renal impairment
(dose
reduction/increase
d dosing interval
recommended if
CCr 20 mL/min);
History of GI
disease, especially
colitis; Geriatric
patients (dose
adjustment may be
required due to
Side Effects &Adverse
Effects
CNS: SEIZURES (HIGH
DOSES). GI:
PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS
COLITIS, diarrhea,
nausea, vomiting,
cramps. Derm: rashes,
urticaria, diaper
dermatitis. Hemat:
bleeding, eosinophilia,
hemolytic anemia,
leukopenia. Local: pain
at IM site, phlebitis at IV
site. Misc: ALLERGIC
REACTIONS INCLUDING
ANAPHYLAXIS,
superinfection.
Check for doctors order
Carefully read product packaging to note
strength of solution, dosage/ route of
administration.
Observe 10 Rs in medicine
administration
Assessment:
Assess for infection (vital signs;
appearance of wound, sputum, urine,
and stool; WBC) at beginning of and
throughout therapy.
Before initiating therapy, obtain a history
to determine previous use of and
reactions to penicillins or
cephalosporins. Persons with a negative
history of penicillin sensitivity may still
have an allergic response.
Obtain specimens for culture and
sensitivity before initiating therapy. First
dose may be given before receiving
results.
Observe patient for signs and symptoms
of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal
edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug
and notify health care professional
immediately if these symptoms occur.
Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and
resuscitation equipment close by in the
event of an anaphylactic reaction.
influenzae
(including -
lactamase-
producing
strains),
Haemophilus
parainfluenzae,
Escherichia coli,
Klebsiella
pneumoniae,
Neisseria ,
Proteus,
Moraxella
catarrhalis,
Borrelia
burgdorferi. Not
active against
methicillin-
resistant
staphylococci or
enterococci.
age-related in
renal function);
Pregnancy and
lactation (has been
used safely).
Monitor bowel function. Diarrhea,
abdominal cramping, fever, and bloody
stools should be reported to health care
professional promptly as a sign of
pseudomembranous colitis. May begin
up to several weeks following cessation
of therapy.
Lab Test Considerations: May cause
positive results for Coombs' test.
May cause serum AST, ALT, alkaline
phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, BUN, and
creatinine.
May rarely cause leukopenia,
neutropenia, and eosinophilia.
Patient/Family Teaching:
Instruct patient to take medication
around the clock at evenly spaced times
and to finish the medication completely,
even if feeling better. Missed doses
should be taken as soon as possible
unless almost time for next dose; do not
double doses. Advise patient that sharing
of this medication may be dangerous.
Pedi: Tell parents or cargeivers to use
calibrated measuring device with liquid
preparations.
Advise patient to report signs of
superinfection (furry overgrowth on the
tongue, vaginal itching or discharge,
loose or foul-smelling stools) and allergy.
Instruct patient to notify health care
professional if fever and diarrhea
develop, especially if stool contains
blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not
to treat diarrhea without consulting
health care professional.
SUBMITTED BY: ANGELICA CASSANDRA P. VILLENA CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR: EDERLYN P. DESTURA RN, MAN
YEAR & SEC. GRP: BSN 3 1 GRP 1
DATE: AUGUST 15, 2014
Você também pode gostar
- Gastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2No EverandGastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2Ainda não há avaliações
- CEFRADINEDocumento2 páginasCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- CefoxitinDocumento3 páginasCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- CefazolinDocumento3 páginasCefazolinDanielle Marie SamblacenoAinda não há avaliações
- Medication Card AncefDocumento2 páginasMedication Card AncefEllieAinda não há avaliações
- ZegenDocumento2 páginasZegenianecunar100% (3)
- Document - Drug Card OneDocumento3 páginasDocument - Drug Card OneLinda AdamsonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug Studym100% (1)
- CefazolinDocumento2 páginasCefazolinConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocumento2 páginasCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Generic NameDocumento2 páginasGeneric NamePei BartolomeAinda não há avaliações
- CephalexinDocumento1 páginaCephalexinJehadadAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study EditedDocumento5 páginasDrug Study EditedfabtaciousVeelaAinda não há avaliações
- Generic NameDocumento8 páginasGeneric Namemel aquinoAinda não há avaliações
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasAmpicillin Drug Studymilkv92% (12)
- Oral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Documento1 páginaOral Suspension: 125 mg/5 Powder For Injection: 750 Premixed Containers: 750Diane Grace PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - CefuroximeDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - CefuroximeSiergs Smith GervacioAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisDocumento6 páginasWhat Is The Appendix?: Symptoms of AppendicitisVonn Bryan CalumiaAinda não há avaliações
- CeftazidimeDocumento1 páginaCeftazidimePaulineAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocumento2 páginasDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenAinda não há avaliações
- Cefixime Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasCefixime Drug StudyJonalin Magbanua100% (12)
- CefuroximeDocumento1 páginaCefuroximeRox SanAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study NCP - San LazaroDocumento9 páginasDrug Study NCP - San LazaroLynne CammayoAinda não há avaliações
- CeftriaxoneDocumento1 páginaCeftriaxoneJanine Erika Julom BrillantesAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyRyan BancoloAinda não há avaliações
- NR at MADocumento4 páginasNR at MAAngie MandeoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study On CloxacillinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study On CloxacillinRoanne LaguaAinda não há avaliações
- Cephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)Documento3 páginasCephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)HannaAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Documento9 páginasAntibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Kath TagamolilaAinda não há avaliações
- CeftriaxoneDocumento5 páginasCeftriaxoneCastillo MikaellaAinda não há avaliações
- Augmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Documento2 páginasAugmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Adrianne BazoAinda não há avaliações
- DrugsDocumento11 páginasDrugsElisa Libo-onAinda não há avaliações
- Albuterol Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaAinda não há avaliações
- CEPHALOSPORINSDocumento8 páginasCEPHALOSPORINSShreyas WalvekarAinda não há avaliações
- Drug AmpicillinDocumento2 páginasDrug AmpicillinRenz Ivan FuntilonAinda não há avaliações
- Pat 2 sd-1Documento22 páginasPat 2 sd-1api-283672381Ainda não há avaliações
- RocephinDocumento2 páginasRocephinianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Card Grid: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion)Documento2 páginasDrug Card Grid: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion)Khaleel BalogunAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study OrthoDocumento17 páginasDrug Study OrthoMc Crister SilangAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study FinalDocumento5 páginasDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatAinda não há avaliações
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDocumento23 páginasV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesAinda não há avaliações
- Brand NameDocumento2 páginasBrand NameAshley AleaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. ClassificationDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Drug Name: Ceftriaxone A. ClassificationMark BarengAinda não há avaliações
- Mefenamic AcidDocumento3 páginasMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- CeftriaxoneDocumento1 páginaCeftriaxoneleroux2890100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueAinda não há avaliações
- AmpicillinDocumento1 páginaAmpicillinMichael KuzbytAinda não há avaliações
- Invanz (Ertapenem)Documento2 páginasInvanz (Ertapenem)E100% (1)
- Antibiotic Penicillin: Ampicillin Ampicillin Sodium AmpicillinDocumento3 páginasAntibiotic Penicillin: Ampicillin Ampicillin Sodium AmpicillinMaria Delia SalvadoAinda não há avaliações
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocumento4 páginasTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 9 Drugs To Know: Penicillin (Amoxicillin), Cephalosporin, Macrolides (Azithromycin), AminoglycosidesDocumento8 páginasUnit 9 Drugs To Know: Penicillin (Amoxicillin), Cephalosporin, Macrolides (Azithromycin), AminoglycosidestriciaAinda não há avaliações
- History of Present Illness: Magno, Corisette Corsino Flores C C C C C C C CDocumento4 páginasHistory of Present Illness: Magno, Corisette Corsino Flores C C C C C C C CDaniele Katrina PimentelAinda não há avaliações
- Classification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseDocumento3 páginasClassification: Cefditoren, As This Agent May CauseHavier EsparagueraAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDavid VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento9 páginasDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloAinda não há avaliações
- 8 G/day: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: SourceDocumento1 página8 G/day: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: SourcefairwoodsAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasDrug StudyJuliana LegarteAinda não há avaliações
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNo EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- USMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsNo EverandUSMLE Step 3 Lecture Notes 2021-2022: Internal Medicine, Psychiatry, EthicsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (9)
- Marcos Administration: Capv, Bsa 2-6Documento2 páginasMarcos Administration: Capv, Bsa 2-6Angelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainability in NursingDocumento18 páginasSustainability in NursingAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocumento4 páginasAppendicitis PathophysiologyAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- 8.-ANATOMY and Physiology GIDocumento12 páginas8.-ANATOMY and Physiology GIAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- F Table 1Documento8 páginasF Table 1Talha IdreesAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Activity: Key FactsDocumento4 páginasPhysical Activity: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Mental Health ActDocumento9 páginasMental Health ActAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (1)
- CETIRIZINEDocumento2 páginasCETIRIZINEAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (10)
- BibliographyDocumento2 páginasBibliographyAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Lcohol: Key FactsDocumento4 páginasLcohol: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Lcohol: Key FactsDocumento4 páginasLcohol: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Health: History, Policy, Budget, Programs For HealthDocumento57 páginasDepartment of Health: History, Policy, Budget, Programs For HealthAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Art 8Documento27 páginasArt 8Angelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Mefenamic AcidDocumento3 páginasMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Cavite (046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012Documento1 páginaDrug Study: Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Cavite (046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012Angelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Community NCP Personal HygieneDocumento2 páginasCommunity NCP Personal HygieneAngelica Cassandra Villena67% (3)
- GenogramDocumento1 páginaGenogramAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Reader ResponseDocumento2 páginasReader ResponseAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Typology of A Problem and Family Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 páginasTypology of A Problem and Family Nursing Care PlanAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (1)
- Patricia Benner: From Novice To ExpertDocumento25 páginasPatricia Benner: From Novice To ExpertAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- EcomapDocumento1 páginaEcomapAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection NCPDocumento2 páginasUpper Respiratory Tract Infection NCPAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (2)
- Prioritization of Health ProblemDocumento1 páginaPrioritization of Health ProblemAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Physical HazardsDocumento2 páginasPhysical HazardsAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism of Drug Action-1Documento46 páginasMechanism of Drug Action-1Sameer HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Reverse TsaDocumento4 páginasReverse Tsaprwill00Ainda não há avaliações
- Anesthesia For in Vitro Fertilization: Review ArticleDocumento11 páginasAnesthesia For in Vitro Fertilization: Review ArticleSumangala MagiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Additives in FoodDocumento21 páginasLesson Plan Additives in FoodZahra AlkhansaAinda não há avaliações
- Andre Tan UPDATED M3 Surgical NotesDocumento285 páginasAndre Tan UPDATED M3 Surgical Noteskenyandoctor2880% (5)
- Neuro-Ophthalmology: DR Jusuf Wijaya, SPM FK - Uki CawangDocumento65 páginasNeuro-Ophthalmology: DR Jusuf Wijaya, SPM FK - Uki CawanggeorgyAinda não há avaliações
- Ulcerative ColitisDocumento30 páginasUlcerative ColitisAndika SulistianAinda não há avaliações
- CT Public v82 8 9Documento2 páginasCT Public v82 8 9Dida HermaAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Pharma (NLE)Documento2 páginasApplied Pharma (NLE)Maginalyn CangasAinda não há avaliações
- 11.21 - Maternal Health Status in The PhilippinesDocumento7 páginas11.21 - Maternal Health Status in The PhilippinesJøshua CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Management of PPHDocumento24 páginasManagement of PPHMutabazi SharifAinda não há avaliações
- Cuscuta AssignmentDocumento12 páginasCuscuta AssignmentAshfaq Hussain KharalAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Day Fast by Bo Sanchez PDFDocumento14 páginas5 Day Fast by Bo Sanchez PDFBelle100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Factors Affecting Performance: Training Purpose OnlyDocumento19 páginasChapter 4 Factors Affecting Performance: Training Purpose OnlySajjad ShamimAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperspectral Plant Disease Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial NetworksDocumento4 páginasHyperspectral Plant Disease Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial NetworksaAinda não há avaliações
- More Reading Power PP 160-180Documento21 páginasMore Reading Power PP 160-180kenken2Ainda não há avaliações
- Genu Valgum Treatment & SurgeryDocumento17 páginasGenu Valgum Treatment & SurgeryRanadaPrasadSahaAinda não há avaliações
- LCB Surgical Technique - 2022 Update v3Documento24 páginasLCB Surgical Technique - 2022 Update v3Samuel SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- VirologyDocumento27 páginasVirologyAgus Nurul HidayahAinda não há avaliações
- Metabolic Encephalopathies in The Critical Care Unit: Review ArticleDocumento29 páginasMetabolic Encephalopathies in The Critical Care Unit: Review ArticleFernando Dueñas MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- MNT-Dislipidemia-Unja 20022019 PDFDocumento48 páginasMNT-Dislipidemia-Unja 20022019 PDFAnonymous o3Q3QXEAinda não há avaliações
- 0226.OPWDD Letter From MembersDocumento2 páginas0226.OPWDD Letter From MembersZacharyEJWilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Imaging in Transplantation PDFDocumento259 páginasImaging in Transplantation PDFAnca MehedintuAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology: United StatesDocumento11 páginasPathophysiology: United StatesNurullia RahmawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Atlas of Cystoscopy: Jan SchönebeckDocumento48 páginasDigital Atlas of Cystoscopy: Jan SchönebeckdemisAinda não há avaliações
- SIgE Conjugate 02.17Documento4 páginasSIgE Conjugate 02.17Clodagh WhelanAinda não há avaliações
- Myanmar Translation Blog, Vol-1, Issue-14Documento24 páginasMyanmar Translation Blog, Vol-1, Issue-14ane lwanAinda não há avaliações
- Kevin Moon Proposed DoH Maintenance StandardsDocumento35 páginasKevin Moon Proposed DoH Maintenance StandardsKarthik RajaAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal FibrosarcomaDocumento12 páginasJurnal FibrosarcomaanugrahAinda não há avaliações
- Aids ProjectDocumento7 páginasAids Projectapi-270625016Ainda não há avaliações