Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum Hemorrhage
Enviado por
Patricia FrancoTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum Hemorrhage
Enviado por
Patricia FrancoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
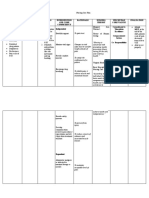
Fluid Volume Deficit secondary to Post Partum Hemorrhage
Cues and
Clues
Analysis Goals/Objectives Nursing
Intervention
Rationale Evaluation
Blood loss of
500mL
Heavy Lochia
flow
Elevation of
pulse rate
indicating
hypovolemia
Sudden drop
in blood
pressure
implying
hemorrhage
Soft uterus
Uterus not
well
contracted
Decreased
urine output
Drop in
hemoglobin
laboratory
results
Postpartum
hemorrhage is
defined as any
loss of blood
from the
uterus more
than 500 ml
within a 24
hour period. It
may be
immediate or
late occurring
from the first
24 hours of
delivery up to
the remaining
days of the 6-
week
puerperium.
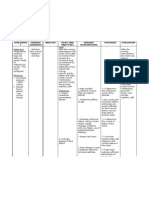
Short Term Goal:
Long Term Goal:
Client will
maintain fluid
volume at a
functional level
as evidenced by
individually
adequate
hemoglobin,
hematocrit
laboratory
results, stable
vital signs,
adequate urine
output, good
uterine
contractility,
good skin turgor
and capillary
refill after one
week
1.Assess vital
signs and note
for peripheral
pulses
2.Assess uterine
contraction and
lochia flow
every two hours
3. Note clients
physiological
response to
blood loss
4. Keep
accurate record
of the blood
products during
replacement
therapy
5. Maintain bed
rest and
schedule
activities to
provide
undisturbed
rest periods
6.Keep fluids
within reach of
client
1.Changes in BP
and pulse may
be used for
estimating
amount of blood
loss
2.To note how
much blood loss
the client is
experiencing
and to prompt
for immediate
intervention
3.
Symptomatology
May be useful in
gauging severity
of bleeding
episode
4. Potential
exists for over
transfusion of
fluids
5.Activity may
predispose to
further bleeding
6. To encourage
fluid intake
7.Administer
fluids/volume
expanders as
indicated
8.Replace blood
products as
ordered by the
physician
9.Administer
oxytocin as
prescribed by
the physician
10.Monitor
laboratory
studies
(hemoglobin,
hematocrit,
creatinine/BUN)
11.Encourage
client to do
Kegels
exercises every
4 hours
12.Teach client
perineal self-
care
7.Fluid
replacement
with isotonic
crystalloids
solutions
depends on the
degree of
hypovolemia
and duration of
bleeding
8.Fresh whole
blood, platelets
and fresh frozen
plasma are
usually given to
patients
depending on
severity of blood
loss
9.This drug helps
in the
contraction of
the uterus
10.Helps in
monitoring the
effectiveness of
the therapy;
malfunction in
the kidneys may
indicate major
bleeding
episodes
11.It helps
improve the
blood supply in
the perineal
area
12.To prevent
development of
perineal
infections
13.Assist in the
preparation for
surgery
specifically
hysterectomy
13.It is the most
effective in
halting bleeding
especially an
extremely atonic
uterus
Você também pode gostar
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (33)
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento4 páginasBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliAinda não há avaliações
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Documento6 páginasPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocumento8 páginasFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocumento2 páginasAbruptio Placenta NCPNichole Audrey Saavedra100% (1)
- Hemorrhage NCPDocumento4 páginasHemorrhage NCPElishaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PPHDocumento2 páginasNCP PPHmikee-berredo-9975Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaDocumento13 páginasNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- Abruptio NCPDocumento4 páginasAbruptio NCPShien Samalea Vasquez100% (1)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocumento7 páginasCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Documento26 páginasNursing Diagnosis: May Be Related To: Fluid Volume Deficit (Isotonic)Ric Nacional75% (4)
- Placenta Previa (NCP)Documento2 páginasPlacenta Previa (NCP)jonna casumpangAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocumento2 páginasNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- NCP Post PartumDocumento2 páginasNCP Post PartumsteffiAinda não há avaliações
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsDocumento3 páginasAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For EclampsiaDocumento6 páginasNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- NCP Risk For Bleeding 3Documento2 páginasNCP Risk For Bleeding 3Jayson Olile100% (1)
- NCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Documento3 páginasNCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Anne DyAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- NCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocumento3 páginasNCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping PatternAlma Gobaleza100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalDocumento19 páginasAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationDocumento2 páginasSubjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationKyla Castro100% (1)
- Pre EclampsiaDocumento3 páginasPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- NCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNDocumento2 páginasNCP Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Fluid Loss DHNMa. Elaine Carla Tating38% (8)
- NCP CSDocumento9 páginasNCP CSFreida Marie PiczonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Knowledge DeficientDocumento4 páginasNCP For Knowledge DeficientLeanne Joie LozanoAinda não há avaliações
- (NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaDocumento3 páginas(NCP) Deficient Fluid Volume - HypovolemiaMacaRonie PepeRownie del Rio100% (4)
- Ineffective Fetal Tissue Perfusion Related To Impaired Gas Exchange During Labor and DeliveryDocumento3 páginasIneffective Fetal Tissue Perfusion Related To Impaired Gas Exchange During Labor and DeliveryRenetria Drake75% (4)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento9 páginasImpaired Skin IntegrityJamila Angeli Valle100% (2)
- NCP For Delivery RoomDocumento4 páginasNCP For Delivery RoomGiselle EstoquiaAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPGian Arlo Hilario Castro100% (6)
- NCP Gestational HypertensionDocumento2 páginasNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Placenta PreviaDocumento2 páginasNCP Placenta PreviaCathy CnlsAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPRachel PerandoAinda não há avaliações
- Care Plan PostpartumDocumento2 páginasCare Plan Postpartumteokie082483% (6)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocumento6 páginasDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- NCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeDocumento23 páginasNCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeKath100% (2)
- CA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocumento13 páginasCA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismRodelen Maraño100% (2)
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Documento1 páginaNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Eclampsia)Jenny AjocAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For InfectionDocumento3 páginasRisk For InfectioncamziiiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP DysuriaDocumento1 páginaNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutAinda não há avaliações
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocumento5 páginasAbruptio Placenta NCPTinAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaLei Ortega0% (1)
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 páginaNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8Ainda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPmimingdot33Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP For PCAPCDocumento6 páginasNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- Risk For Hypothermia of New BornDocumento2 páginasRisk For Hypothermia of New BornjenspryAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageLei Ortega95% (21)
- OxytocinDocumento1 páginaOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP UtiDocumento1 páginaNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento14 páginasNCPkristapot80% (10)
- Fluid Vol Deficit Secondary To Postpartum Hemorrhage Care PlanDocumento3 páginasFluid Vol Deficit Secondary To Postpartum Hemorrhage Care PlanEllie GartungAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Blood TransfusionDocumento10 páginasUnit 5 Blood TransfusionMarianne Gonzales-HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Select All That Apply SATADocumento67 páginasSelect All That Apply SATAHermie Joy Maglaqui100% (1)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento3 páginasPostpartum HemorrhageClaire Canapi BattadAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing InterventionsDocumento2 páginasNursing InterventionsAaron Paul Romualdez100% (4)
- Thomasian Resume FormatDocumento4 páginasThomasian Resume FormatPatricia AngelaAinda não há avaliações
- DischargeDocumento4 páginasDischargePatricia Franco100% (1)
- The Basics of OncologyDocumento15 páginasThe Basics of OncologyPatricia FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- Bls SchedueDocumento3 páginasBls ScheduePatricia FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- Postpartum NCPDocumento20 páginasPostpartum NCPapi-370148988% (34)
- What Is Manipulative Behavior, Anyway?: Nancy Nyquist Potter, PHDDocumento19 páginasWhat Is Manipulative Behavior, Anyway?: Nancy Nyquist Potter, PHDPatricia FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- MS ReportDocumento6 páginasMS ReportPatricia FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- Deve-Milestones Page 2Documento1 páginaDeve-Milestones Page 2Patricia FrancoAinda não há avaliações
- AABB Pediatric Transfusion - Risks and GuidelinesDocumento57 páginasAABB Pediatric Transfusion - Risks and GuidelinesDR.RAJESWARI SUBRAMANIYANAinda não há avaliações
- Poch 100i Operating Procedure PDFDocumento11 páginasPoch 100i Operating Procedure PDFTeguh Setyo Nugroho0% (2)
- Trombopoiesis (3) - 1Documento10 páginasTrombopoiesis (3) - 1Vannisa Dwi NovianaAinda não há avaliações
- Complete Blood CountDocumento5 páginasComplete Blood Counttharaka100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion in Hemorrhagic ShockDocumento28 páginasBlood Transfusion in Hemorrhagic Shocklas100% (2)
- Artikel Jurnal IbnuDocumento4 páginasArtikel Jurnal Ibnuibnu rifaldiAinda não há avaliações
- Test Report: Mrs - UMA (46/F)Documento3 páginasTest Report: Mrs - UMA (46/F)KanjamAinda não há avaliações
- Perbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorDocumento7 páginasPerbedaan Kadar Hbsag Sampel Serum Dan Plasma Metode Clia Pada PendonorAAK DHGRiski MaulanaAinda não há avaliações
- Hematologic Disorders and PregnancyDocumento12 páginasHematologic Disorders and PregnancyAngelie RojasAinda não há avaliações
- ABO-RH IncompatiilityDocumento6 páginasABO-RH IncompatiilitymarisonaningatAinda não há avaliações
- Hemolytic Uremic SyndromeDocumento3 páginasHemolytic Uremic SyndromeEliDavid100% (1)
- Skripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFDocumento64 páginasSkripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFBillyDwiSaputraAinda não há avaliações
- Coagulation of BloodDocumento16 páginasCoagulation of BloodMoner ManushAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingDocumento18 páginasMechanism of Blood Clotting Extensic Pathway Factors Affecting Blood ClottingRaunak TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- CTK-USA (Aria) : End User Price List-Rapid TestDocumento2 páginasCTK-USA (Aria) : End User Price List-Rapid TestAbdalazeez AlsayedAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Cells: By, Shobhana PandianDocumento60 páginasBlood Cells: By, Shobhana PandianhrishikeshanandAinda não há avaliações
- APPENDIX B-Comparative HematologyDocumento30 páginasAPPENDIX B-Comparative HematologySultan AlexandruAinda não há avaliações
- AnaemiaDocumento7 páginasAnaemiaYousef El3alameyAinda não há avaliações
- Buenafe, Sebastien Andrei - (Block - H - SGD6)Documento2 páginasBuenafe, Sebastien Andrei - (Block - H - SGD6)SEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFEAinda não há avaliações
- Transfusion Medicine - RK SaranDocumento80 páginasTransfusion Medicine - RK SaranAvinashAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocumento3 páginasStandard Operating ProcedureMamunur Rasid100% (1)
- Hemostasis ReviewerDocumento14 páginasHemostasis ReviewerDayledaniel SorvetoAinda não há avaliações
- Red Blood Cell Phenotyping of Blood Donors in Islamabad, PakistanDocumento5 páginasRed Blood Cell Phenotyping of Blood Donors in Islamabad, PakistanAHNS123Ainda não há avaliações
- Blood and Bloodstains: Harry Danny L. Aspillaga Instructor Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyDocumento50 páginasBlood and Bloodstains: Harry Danny L. Aspillaga Instructor Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyHarry Danny AspillagaAinda não há avaliações
- Advisory Comittee Meeting 06-03-21Documento24 páginasAdvisory Comittee Meeting 06-03-21SarwarAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical and Etiological Profile of Unprovoked Thrombosis in Young Patients Admitted at A Tertiary Care HospitalDocumento5 páginasClinical and Etiological Profile of Unprovoked Thrombosis in Young Patients Admitted at A Tertiary Care HospitalfarhanomeAinda não há avaliações
- Bleeding DisordersDocumento92 páginasBleeding DisordersIsaac MwangiAinda não há avaliações
- Finals FundaDocumento82 páginasFinals FundaNecesario BanaagAinda não há avaliações
- Pengaruh Event Dan Kesadaran Masyarakat Karawang Terhadap Minat Donor Darah Di Pmi Kabupaten KarawangDocumento7 páginasPengaruh Event Dan Kesadaran Masyarakat Karawang Terhadap Minat Donor Darah Di Pmi Kabupaten KarawangDwi Septia RiniAinda não há avaliações
- Platelet Count Direct Method Activity (MANALO)Documento3 páginasPlatelet Count Direct Method Activity (MANALO)Rose ValerieAinda não há avaliações