Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
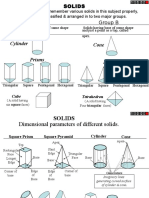
Projection of Solids: Engineering Graphics
Enviado por
GPFanTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Projection of Solids: Engineering Graphics
Enviado por
GPFanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 10
Projection of solids
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
(TA C111)
Contd
Contd
.
.
Last class
Classification of solids
Projection of solids (in simple positions)
Axis perpendicular to one reference plane
Transfer of points from one view to the other view
Axis inclined to one reference plane and parallel to
the other
Projections drawn in two stages:
STAGE I: Solid is assumed to be in simple position i.e. its
axis perpendicular to one of the planes
STAGE II: Alteration of axis orientation i.e. the orientation of
the axis is altered as required and the other view projected
from it
The 1
The 1
st st
stage should be such that we should be
stage should be such that we should be
able to draw the
able to draw the
true views
true views
from the top and
from the top and
front easily
front easily
Axis perpendicular w.r.t. which plane??
If the axis is inclined to the ground i.e the H.P.
It is assumed to be perpendicular to the H.P. in STAGE I
If the axis is inclined to the V.P.
It is assumed to be perpendicular to the V.P. in STAGE I
While drawing the TS of the base (STAGE I) consider the given
rest condition in the problem. If it is resting on:
Base-edge: Draw that base-edge perpendicular to x-y line.
Base-corner: Draw the line joining the base-corner and center of
base parallel to XY line.
Slant face (PYRAMID)/rectangular face (PRISM): Draw the base-
edge of that slant face perpendicular to x-y line.
Slant/vertical edge: Draw the line joining the base-corner of that
slant/vertical edge and center of base parallel to x-y line.
Orientations of the base (rest condition)
Visibility of points
The highest parts of the object are visible in the view
from TOP. The view from the front gives a clue
regarding this.
The front faces, the front edges and the front corners
nearest to the observer are visible in the view from
front. These can also be determined from the view
from TOP.
Example:
When the object is resting on BASE EDGE
A hexagonal pyramid, A hexagonal pyramid,
base 100 mm and height base 100 mm and height
175 mm, has an edge of 175 mm, has an edge of
its base on the ground. its base on the ground.
Its axis is inclined at 30 Its axis is inclined at 30
to the ground and to the ground and
parallel to the V.P. Draw parallel to the V.P. Draw
its projections. its projections.
1 1
2 2
4 4
3 3
6 6
5 5
View OK?
Example:
When the object is resting on BASE EDGE
A hexagonal pyramid, A hexagonal pyramid,
base 100 mm and height base 100 mm and height
175 mm, has an edge of 175 mm, has an edge of
its base on the ground. its base on the ground.
Its axis is inclined at 30 Its axis is inclined at 30
to the ground and to the ground and
parallel to the V.P. Draw parallel to the V.P. Draw
its projections. its projections.
Example:
When the object is resting on a BASE CORNER
Draw the projections of a Draw the projections of a
cube of 100 mm long cube of 100 mm long
edges resting on the edges resting on the
ground on one of its ground on one of its
corners with a body corners with a body
diagonal passing through diagonal passing through
that corner perpendicular that corner perpendicular
to the H.P. to the H.P.
b
b
Example:
When the object is resting on SLANT
FACE/RECTANGULAR FACE
Draw the projections Draw the projections
of a pentagonal of a pentagonal
prism, base edge prism, base edge
100 mm and height 100 mm and height
175 mm, resting on 175 mm, resting on
one of its one of its
rectangular faces on rectangular faces on
the ground, with the the ground, with the
axis inclined at 45 axis inclined at 45
to the V.P. to the V.P.
Example:
When the object is resting on SLANT
FACE/RECTANGULAR FACE
Draw the projections Draw the projections
of a pentagonal of a pentagonal
prism, base edge prism, base edge
100 mm and height 100 mm and height
175 mm, resting on 175 mm, resting on
one of its one of its
rectangular faces on rectangular faces on
the ground, with the the ground, with the
axis inclined at 45 axis inclined at 45
to the V.P. to the V.P.
Example:
When the object is resting on SLANT/ VERTICAL
EDGE
A hexagonal A hexagonal
pyramid, base 100 pyramid, base 100
mm and height 175 mm and height 175
mm, has one of its mm, has one of its
slant edges on the slant edges on the
ground. A plane ground. A plane
containing that containing that
edge and the axis edge and the axis
is perpendicular to is perpendicular to
the ground and the ground and
also perpendicular also perpendicular
to VP. Draw its to VP. Draw its
projections when projections when
the apex is nearer the apex is nearer
to the observer. to the observer.
Example:
Projections of a cylinder
Example:
Projections of a cone
Você também pode gostar
- Projectionsofsolids 111202014535 Phpapp02Documento58 páginasProjectionsofsolids 111202014535 Phpapp02Priyanka RamanAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Projection of SolidsDocumento40 páginasLecture Projection of SolidsarunAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento6 páginasProjection of SolidsMahesh J. UmaAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solids (Revised)Documento26 páginasProjection of Solids (Revised)21AIB316 ABHINAV GUPTAAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento58 páginasProjection of SolidsSachi DhanandamAinda não há avaliações
- Projections of SolidsDocumento55 páginasProjections of SolidsFaizal.P.M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Projections of SolidsDocumento20 páginasProjections of SolidsSuneel Kumar MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Projections of Solids & Sections of SolidsDocumento34 páginasProjections of Solids & Sections of SolidsQudartullah MonibAinda não há avaliações
- Section of Solids1Documento38 páginasSection of Solids1Vikas ChaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solids - CompleteDocumento100 páginasProjection of Solids - CompleteSyed Waqar AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Engg Graphics Viva Question AnswersDocumento12 páginasEngg Graphics Viva Question AnswersaswinAinda não há avaliações
- EG Unit 3..Documento18 páginasEG Unit 3..Damotharan Sathesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- GE2111 Engineering Graphics Notes 2013Documento271 páginasGE2111 Engineering Graphics Notes 2013Mahesh KannanAinda não há avaliações
- 7proj PlanesDocumento15 páginas7proj Planesmanishjangid9869Ainda não há avaliações
- 04 - Projection of SolidsDocumento33 páginas04 - Projection of SolidsCreative ThinkerAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing AND Graphics: BS (EE) - 17 Class NotesDocumento32 páginasEngineering Drawing AND Graphics: BS (EE) - 17 Class NotesMichael JacksonAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solid - ClassDocumento37 páginasProjection of Solid - Classrcora69Ainda não há avaliações
- Group A Group B .: Cylinder ConeDocumento23 páginasGroup A Group B .: Cylinder Conehotnili0% (1)
- Projection of SolidsDocumento81 páginasProjection of SolidsHarshit SolankiAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing: Projection of SolidsDocumento221 páginasEngineering Drawing: Projection of SolidsOdhiambo MeshackAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solids ProblemsDocumento31 páginasProjection of Solids ProblemsFaria KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento23 páginasProjection of SolidsSatya Shivani50% (2)
- Projection of PlanesDocumento18 páginasProjection of PlanesTariqAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics - PlanesDocumento6 páginasEngineering Graphics - Planesnishanth87Ainda não há avaliações
- Section of SolidsDocumento49 páginasSection of SolidsRavi Kiran NandyalaAinda não há avaliações
- 05 - Section of SolidDocumento37 páginas05 - Section of SolidVinay SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solids 1Documento27 páginasProjection of Solids 1saketh.s.tandigeAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics: (BITS F110)Documento14 páginasEngineering Graphics: (BITS F110)vivekanandtAinda não há avaliações
- ALP ENGINEERING DRAWING - pdf-61Documento7 páginasALP ENGINEERING DRAWING - pdf-61Tara Chandra PanjiyarAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento23 páginasProjection of SolidsSrinu ArnuriAinda não há avaliações
- SHEET No 1 (Section of Solids)Documento5 páginasSHEET No 1 (Section of Solids)Ayush Ranjan100% (1)
- SolidsDocumento11 páginasSolidsPanduranga HulihalliAinda não há avaliações
- Analytic Geometry PrismsDocumento17 páginasAnalytic Geometry PrismsCarl Kristopher Pelonia100% (1)
- Ge3251 Unit 3 Projection of Solids PDFDocumento41 páginasGe3251 Unit 3 Projection of Solids PDFNaveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Sections of Solids & Development of SurfaceDocumento12 páginasSections of Solids & Development of SurfaceAnonymous p8bHAAxAinda não há avaliações
- A Few Unnecessary Things.Documento6 páginasA Few Unnecessary Things.CocmyloveAinda não há avaliações
- EG QuestionsDocumento6 páginasEG QuestionsHariprasath VisvanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento18 páginasSolid MensurationLlorente Dante Jr. M - AAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-3 BT-1005 EGDocumento29 páginasUnit-3 BT-1005 EGSagar DhruvaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing ReviewerDocumento5 páginasEngineering Drawing ReviewerAngelo GranadaAinda não há avaliações
- (Reverse Development Problems) : Exercise BDocumento14 páginas(Reverse Development Problems) : Exercise BVikas ChaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento5 páginasSolid MensurationDelfin MendezAinda não há avaliações
- Projection (Solid Geometry)Documento20 páginasProjection (Solid Geometry)dhileepan kumarasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Projection (Solid Geometry) PDFDocumento20 páginasProjection (Solid Geometry) PDFsilberksouzaAinda não há avaliações
- Solids Problem StatementsDocumento38 páginasSolids Problem StatementsShailaja VijayAinda não há avaliações
- Group A Group B .: Cylinder ConeDocumento11 páginasGroup A Group B .: Cylinder ConeTanmayAinda não há avaliações
- Interpenetration - 2 Full Practice SessionDocumento11 páginasInterpenetration - 2 Full Practice SessionTanmay Singh ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento22 páginasProjection of SolidsWarren RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Solid MensurationDocumento13 páginasSolid MensurationJann Michael Carpio100% (1)
- Course Name and Code: Engineering Drawing EE-105 Roll Number: Reg. Number: Name of Student: Degree Program: DateDocumento16 páginasCourse Name and Code: Engineering Drawing EE-105 Roll Number: Reg. Number: Name of Student: Degree Program: DateAttaUrRahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Development Lecture 1-1Documento20 páginasDevelopment Lecture 1-1Jackson SichingaAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento27 páginasProjection of SolidsAYUSH ACHARYAAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of SolidsDocumento23 páginasProjection of SolidspradeepAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Solids - Question Bank and Solutions PDFDocumento4 páginas3 Solids - Question Bank and Solutions PDFTejas RandiveAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5Documento13 páginasUnit 5gansumaaAinda não há avaliações
- Spherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesNo EverandSpherical Trigonometry, For The Use Of Colleges And Schools, With Numerous ExamplesAinda não há avaliações
- Dik Bal of GrahasDocumento2 páginasDik Bal of GrahasGPFan100% (1)
- KoppulingesDocumento35 páginasKoppulingesGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Ganga StotramDocumento3 páginasGanga StotramDarshAna PaulaAinda não há avaliações
- Makingprecisepredictions 110925102058 Phpapp01Documento28 páginasMakingprecisepredictions 110925102058 Phpapp01GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Hybris SAPDocumento32 páginasHybris SAPGPFan40% (5)
- EarthquakesDocumento74 páginasEarthquakesNitish BahlAinda não há avaliações
- Talent ManagementDocumento200 páginasTalent ManagementGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Solids1 PDFDocumento17 páginasSolids1 PDFGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Solutions On VMware Best Practices GuideDocumento32 páginasSAP Solutions On VMware Best Practices Guideahm3d16nAinda não há avaliações
- Vaastu Questions and AnswersDocumento38 páginasVaastu Questions and AnswersGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Diploma in Light Music-1st YearDocumento2 páginasDiploma in Light Music-1st YearGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- MA Sanskrit-2nd Year Nov 2013Documento8 páginasMA Sanskrit-2nd Year Nov 2013GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Diploma in Light Music-2nd Year PSR TU Nov 2013Documento1 páginaDiploma in Light Music-2nd Year PSR TU Nov 2013GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Diploma - Film Writing PSR TU Nov 2013Documento3 páginasDiploma - Film Writing PSR TU Nov 2013GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- MA Sanskrit - 1st Year Nov 2013Documento8 páginasMA Sanskrit - 1st Year Nov 2013GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Parashara Smriti Sanskrit, Hindi, English)Documento129 páginasParashara Smriti Sanskrit, Hindi, English)nss1234567890100% (1)
- Devp SurfacesDocumento17 páginasDevp SurfacesGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Data Manager PDFDocumento122 páginasData Manager PDFGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Children and Vedic AstrologyDocumento24 páginasChildren and Vedic AstrologyGPFan100% (1)
- MGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra7Documento6 páginasMGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra7GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Hora AnubhavaDocumento4 páginasHora AnubhavaGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Jata KaRajeeYamDocumento43 páginasJata KaRajeeYamGPFan100% (3)
- Jyotishi - Prospect of Acquiring EducationDocumento16 páginasJyotishi - Prospect of Acquiring EducationGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Arthashastra 2Documento7 páginasArthashastra 2api-3719593Ainda não há avaliações
- Transit Results of Jupiter WRT Name SignDocumento4 páginasTransit Results of Jupiter WRT Name SignGPFanAinda não há avaliações
- MGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra6Documento6 páginasMGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra6GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Arthashastra 5Documento6 páginasArthashastra 5api-3719593100% (1)
- MGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra3Documento6 páginasMGMNT Fundas in Arthashastra3GPFanAinda não há avaliações
- Arthashastra 1Documento6 páginasArthashastra 1api-3719593100% (1)
- Maths NotesDocumento57 páginasMaths NotesMireille Attard100% (2)
- Quiz 2: ObjectivesDocumento12 páginasQuiz 2: ObjectivesChristian M. MortelAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry Cheat Sheet 3d Shape FormulasDocumento2 páginasGeometry Cheat Sheet 3d Shape FormulasMT100% (2)
- Math 6Documento9 páginasMath 6Daniela Erika Beredo InandanAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Math Worksheets31 1Documento21 páginasGrade 10 Math Worksheets31 1Jaymar SarvidaAinda não há avaliações
- Periodical Test in Math 6 With TOS and Answer KeyDocumento6 páginasPeriodical Test in Math 6 With TOS and Answer KeyRey Mark Ramos93% (14)
- 3d Object Lesson - AndieDocumento5 páginas3d Object Lesson - Andieapi-463860120Ainda não há avaliações
- Plane and Solid Geometry 2Documento3 páginasPlane and Solid Geometry 2ARNOLD MORANAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Solid GeometryDocumento2 páginas4 Solid GeometryNeo GarceraAinda não há avaliações
- Projection of Solids ProblemsDocumento31 páginasProjection of Solids ProblemsFaria KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Geometry: Simple Geometric FiguresDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 - Geometry: Simple Geometric Figuresrica portuguezAinda não há avaliações
- Technical LetteringDocumento12 páginasTechnical LetteringMaverick Timbol50% (2)
- m106 Solid GeometryDocumento8 páginasm106 Solid GeometryMarjorie MalvedaAinda não há avaliações
- Cot - DLP - Math 5Documento7 páginasCot - DLP - Math 5MYLEEN P. GONZALESAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Problems Involving Polynomial FunctionsDocumento6 páginasSolving Problems Involving Polynomial FunctionsEmelyAinda não há avaliações
- PT - Math 6 - Q4Documento4 páginasPT - Math 6 - Q4Joan Eve GagapAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry and ConstructionsDocumento46 páginasGeometry and ConstructionsAuthachai Gokla Chaysang100% (2)
- Descriptive Geometry 1 Lecture NotesDocumento63 páginasDescriptive Geometry 1 Lecture NotesGrigor Ciko100% (1)
- Ge 8152-Engineering Graphics Answer All QuestionsDocumento4 páginasGe 8152-Engineering Graphics Answer All Questionsm anbumaniAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Chapter 16 Notebook WorkDocumento3 páginasMaths Chapter 16 Notebook Workjaisurya14107Ainda não há avaliações
- Properties of 2D Shapes and 3D Objects: Terms Illustrations DefinitionsDocumento11 páginasProperties of 2D Shapes and 3D Objects: Terms Illustrations DefinitionsChoukri SaoudiAinda não há avaliações
- Area and Volume of Similar Shapes Worksheet 1Documento4 páginasArea and Volume of Similar Shapes Worksheet 1Taha YousafAinda não há avaliações
- ECE 2101 ENGINEERING DRAWING II NotesDocumento7 páginasECE 2101 ENGINEERING DRAWING II NotesJohn Ng'ang'aAinda não há avaliações
- Hodder Cambridge Primary Maths Learner's Book 2 PDFDocumento178 páginasHodder Cambridge Primary Maths Learner's Book 2 PDFabdullah vaseem94% (18)
- ENGGMATH 1 - Module 3 Solid MensurationDocumento28 páginasENGGMATH 1 - Module 3 Solid MensurationScottie YanesAinda não há avaliações
- Notes: Chapter 9 Mensuration: CircleDocumento4 páginasNotes: Chapter 9 Mensuration: CircleST Electrical & ConstructionAinda não há avaliações
- EQAO Grade 3 Questions Sorted by Strand - Google SlidesDocumento94 páginasEQAO Grade 3 Questions Sorted by Strand - Google SlidesAKASH MINTO PRABHUAinda não há avaliações
- DLP Gr. 6 Module 54 Identifying The Faces Edges, and Vertices of Solids PDFDocumento12 páginasDLP Gr. 6 Module 54 Identifying The Faces Edges, and Vertices of Solids PDFCyrell Castroverde PapauranAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Cube, Cuboid, Prism and PyramidDocumento11 páginasLesson Plan Cube, Cuboid, Prism and PyramidAbkarin Tara NadhiraAinda não há avaliações
- Review Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Documento3 páginasReview Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Mina, KhristineAinda não há avaliações