Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2B - Electroforesis Moleculas Individuales de DNA - DG - BMC2014
Enviado por
Alissa Jara BulejeTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
2B - Electroforesis Moleculas Individuales de DNA - DG - BMC2014
Enviado por
Alissa Jara BulejeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
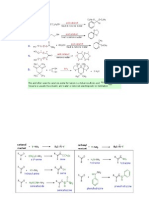
Electroforesis
TODOS LO HACEN
Radio de giro vs.
tamao de poro
Flexibilidad vs.
tamao
,
Donde R es el radio de giro del polmero, N es el nmero de
segmentos de enlace (igual al grado de polimerizacin) de la cadena.
Para un buen disolvente, v = 3/5 ;
para un mal disolvente, v = 1/3 .
Por tanto un polmero en buen disolvente tiene un tamao mayor. En un
mal disolvente se comporta como una esfera slida.
Dependencia
N. C. Stellwagen and E. Stellwagen, Effect of the matrix on
DNA electrophoretic mobility, Journal of Chromatography A,
vol. 1216, no. 10, pp. 1917-1929, Mar. 2009.
Cuando el radio de giro de la molcula es
menor al tamao promedio de los poros.
0.5,
1.6,
3.1,
6.1,
9.2,
12.2 kbp
Dependencia
0.5,
1.6,
3.1,
6.1,
9.2,
12.2 kbp
N. C. Stellwagen and E. Stellwagen, Effect of the matrix on
DNA electrophoretic mobility, Journal of Chromatography A,
vol. 1216, no. 10, pp. 1917-1929, Mar. 2009.
Concentracin de
agarosa
En solucin
movilidad
Fraccin
disponible
del
volumen
En gel
Retardamiento
segn tamao
Cuando el radio de giro de la molcula es
menor al tamao promedio de los poros.
Dependencia
1.5%
1.25%,
0.9%,
0.6%,
0.4%,
0.2%,
N. C. Stellwagen and E. Stellwagen, Effect of the matrix on
DNA electrophoretic mobility, Journal of Chromatography A,
vol. 1216, no. 10, pp. 1917-1929, Mar. 2009.
Dependencia se pierde
D
i
s
t
a
n
c
i
a
r
e
c
o
r
r
i
d
a
e
n
u
n
t
i
e
m
p
o
t
Tamao en Kbp
Cuando el radio de giro de la molcula es
mayor al tamao promedio de los poros,
la molcula repta.
Reptar se divide en
Fase sin orientacin y
Fase con orientacin
for DNA chains approaching ~1020 kb the
electrophoretic mobility m becomes
increasingly independent of
molecular size
Elongated states form
because the molecules
remain hooked around gel
fibers, extending
both of the arms downfield,
here named U-shapes
The leading end is usually
bunched up, appearing
brighter than other parts of the
molecule, since it has to find
its
way through the gel pores
the molecules never stretch
totally to their theoretical
contour length. This is due to
the intrinsic entropic elasticity
of the molecules and also to
the zig-zag path through the
agarose network that they are
constrained to follow.
chain retardation is not
controlled by the time required
to form and slip out of the U-
shapes, but by the sieving of
the leading end through the
gel pores.
Gurrieri S, Smith SB, Wells KS, Johnson ID, Bustamante C. Real-time imaging of
the reorientation mechanisms of YOYO-labelled DNA molecules during 90 degrees
and 120 degrees pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec
1;24(23):4759-4767.
Truco: campo pulsado
Se aplica un campo elctrico de ~10 V/cm,
o en ocasiones ms bajo, en forma
intermitente en dos direcciones.
La duracin ideal del pulso puede variar
desde menos de un segundo hasta varios
minutos, dependiendo del tamao de las
molculas a discriminar.
Se ha logrado la separacin de molculas
de hasta ~5 Mbp.
in DNA molecules undergoing 90 PFGE, the head of the
chain (that is bunched) usually remains the leading end of the
molecule and turns the corners in the direction of the new field,
entering new gel pores.
kinks (Fig. 4BC) (where
the molecule is doubled
over on itself) are
observed at the
beginning of the
reorientation, and these
disappear very rapidly.
leading end keeps driving the chain
both ends of the molecule
can extend and turn in the
new direction
Gurrieri S, Smith SB, Wells KS, Johnson ID, Bustamante C. Real-time imaging of
the reorientation mechanisms of YOYO-labelled DNA molecules during 90 degrees
and 120 degrees pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec
1;24(23):4759-4767.
When the field is switched by an angle of 120 (or any other angle
.90o) the component of the new electric field along the previous
orientation of the molecule is now in a direction opposite to the
one along which the molecule was moving before and, therefore,
the molecules are pulled back along their previous paths.
Gurrieri S, Smith SB, Wells KS, Johnson ID, Bustamante C. Real-time imaging of
the reorientation mechanisms of YOYO-labelled DNA molecules during 90 degrees
and 120 degrees pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec
1;24(23):4759-4767.
Gurrieri S, Smith SB, Wells KS, Johnson ID, Bustamante C. Real-time imaging of
the reorientation mechanisms of YOYO-labelled DNA molecules during 90 degrees
and 120 degrees pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec
1;24(23):4759-4767.
Gurrieri S, Smith SB, Wells KS, Johnson ID, Bustamante C. Real-time imaging of
the reorientation mechanisms of YOYO-labelled DNA molecules during 90 degrees
and 120 degrees pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec
1;24(23):4759-4767.
Molculas individuales de
ADN
Caracterizacin mecnica con pinzas
pticas
Deposicin y comportamiento en superficie
observado con AFM
MICROSCOPIO DE PINZAS PTICAS
Tecnologa para estudiar
nanomquinas
Tecnologa para estudiar
nanomquinas
Manipulacin con pinzas lser
Principio de la deteccin de fuerza.
La aplicacin de una fuerza externa provocar un desplazamiento
fuera del centro de la trampa.
La desviacin del rayo difractado es medida por un fotodetector y
usada para calcular el valor de la fuerza aplicada sobre la
microesfera atrapada.
strep
anti-dig
Succin via
pipeta de vidrio
Trampa ptica
biotina
digoxigenina
DNA, 3-15 Kbp
strep
Succin via
pipeta de vidrio
Trampa ptica
DNA, 3-15 Kbp
anti-dig
strep
Succin via
pipeta de vidrio
Trampa
ptica
DNA, 3-15 Kbp
anti-dig
r
Lc
Modelo cadena vermiforme
(worm-like chain model)
Modelo cadena vermiforme
(worm-like chain model)
r
Lc
Does transition 3D2D affect
molecular conformation?
Free diffusion
Equilibrium is reached
Limited diffusion
(kinetical trap)
No equilibrium
Projection 3D
Analysis of the DNA end-to-end
distance distributions
8
fragmentos
pixel 4nm
(12pb)
DNA Fragment
(bp)
N
molecules
Contour Length
(nm)
Theoretical <R
2
>
(nm
2
)
Experimental <R
2
>
(nm
2
)
278 64 84 7 5533 4312 1235
731 101 218 16 26110 24727 11366
1450 110 404 32 63010 67332 37354
278bp 731bp 1450bp
Rivetti, 1996
Você também pode gostar
- Autorizacion Sanitaria de Funcionamiento de Droguerias PDFDocumento60 páginasAutorizacion Sanitaria de Funcionamiento de Droguerias PDFAlissa Jara Buleje100% (2)
- Curso Taller "Manual de Buenas Prácticas de Laboratorio para El Control de Calidad de Productos Farmacéuticos"Documento41 páginasCurso Taller "Manual de Buenas Prácticas de Laboratorio para El Control de Calidad de Productos Farmacéuticos"Alissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Destilacic 3 B 3 N 1Documento27 páginasDestilacic 3 B 3 N 1Abraham Noe Lozoya RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Requisitos para Certificacion en BpaDocumento1 páginaRequisitos para Certificacion en BpaAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Cromatografía de GasesDocumento4 páginasCromatografía de GasesAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Taller 1 VSM LatfarDocumento7 páginasTaller 1 VSM LatfarAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- LectClase3 - OR y RRDocumento4 páginasLectClase3 - OR y RRAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- El Síndrome Del Condenado A Fracasar 2Documento16 páginasEl Síndrome Del Condenado A Fracasar 2Alissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- 6 DNA Recombinante BMC2014Documento40 páginas6 DNA Recombinante BMC2014Alissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- CR Acido Retinoico Hidroquinona Vitamina CDocumento1 páginaCR Acido Retinoico Hidroquinona Vitamina CAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- ParasitologiaDocumento57 páginasParasitologiaAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- ParasitologiaDocumento57 páginasParasitologiaAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- CoprocultivoDocumento47 páginasCoprocultivoAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Lectura Síndrome Codenado A Fracasar Preguntas Vía MailDocumento1 páginaLectura Síndrome Codenado A Fracasar Preguntas Vía MailAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Plaquetas y ProteinasDocumento12 páginasPlaquetas y ProteinasAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- La Ciudad de Los Reyes Los Chavez y Los Quispes ExpopDocumento21 páginasLa Ciudad de Los Reyes Los Chavez y Los Quispes ExpopAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Farmacologia de La DiarreaDocumento50 páginasFarmacologia de La DiarreaAlissa Jara Buleje100% (1)
- 6 DNA Recombinante BMC2014Documento40 páginas6 DNA Recombinante BMC2014Alissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- LecturaDocumento3 páginasLecturaAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Carbohidratos NutricionDocumento152 páginasCarbohidratos NutricionAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Carboni LosDocumento4 páginasCarboni LosAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Fisiologia y Energetica MuscularDocumento33 páginasFisiologia y Energetica MuscularAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis ConformacionalDocumento28 páginasAnalisis ConformacionalAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Avances en El Tratamiento de La ObesidadDocumento32 páginasAvances en El Tratamiento de La ObesidadAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 7 AlimentosDocumento4 páginasLab 7 AlimentosAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- La Oleoresina AmazónicaDel Árbol de Copaiba Utilizado Durante Largo Tiempo Por Los Nativos de Las Regiones AmazónicasDocumento3 páginasLa Oleoresina AmazónicaDel Árbol de Copaiba Utilizado Durante Largo Tiempo Por Los Nativos de Las Regiones AmazónicasAlissa Jara BulejeAinda não há avaliações
- Grados de Libertad HenleyDocumento7 páginasGrados de Libertad HenleyDavid M GaytanAinda não há avaliações
- Biol4433l - Microbiologia Industrial - 202310Documento2 páginasBiol4433l - Microbiologia Industrial - 202310Ashley GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Trabajo QuimicaDocumento26 páginasTrabajo QuimicaFred PérezAinda não há avaliações
- PRACTICA 3 Esterilizacion y Medios de CultivoDocumento6 páginasPRACTICA 3 Esterilizacion y Medios de CultivoRonmel AlejandroAinda não há avaliações
- Marcha Análisis Instrumental I Ciclo IiDocumento1 páginaMarcha Análisis Instrumental I Ciclo IiEliannys GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Hans Christian Joachim GramDocumento5 páginasHans Christian Joachim GramAispuro OscarAinda não há avaliações
- Practica de Laboratorio 6 FiltracionDocumento12 páginasPractica de Laboratorio 6 FiltracionNel Paitampoma OsoresAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory - Supplies - 09 Eqp Tem DissipaçãoDocumento119 páginasLaboratory - Supplies - 09 Eqp Tem Dissipaçãoarln_605551822Ainda não há avaliações
- Nmin y Rmin Ponchon EjemploDocumento38 páginasNmin y Rmin Ponchon EjemploJOSE LUIS GUTIERREZ RODRIGUEZAinda não há avaliações
- Equipo 2 - Reporte de Práctica 2Documento8 páginasEquipo 2 - Reporte de Práctica 2Gloria FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Equipos Auxiliares Ponchon-SavaritDocumento7 páginasEquipos Auxiliares Ponchon-Savaritlucas navarroAinda não há avaliações
- Análisis Granulométrico Por TamizadoDocumento6 páginasAnálisis Granulométrico Por TamizadoJeyson Mo Tongo AlejandroAinda não há avaliações
- Exposicion PCRDocumento6 páginasExposicion PCRJUAN JOSE ZULETA BLANCHARAinda não há avaliações
- Practica 5 OptimizacionDocumento24 páginasPractica 5 OptimizacionDaniel AmadorAinda não há avaliações
- Reactores Cataliticos Heterogeneos DisenDocumento43 páginasReactores Cataliticos Heterogeneos DisenM PAinda não há avaliações
- Filtro Prensa y Centrífuga FinalDocumento12 páginasFiltro Prensa y Centrífuga FinalDaniel EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagrama Y Vs X (Metanol-Agua) : Recuperacion X D ZFDocumento3 páginasDiagrama Y Vs X (Metanol-Agua) : Recuperacion X D ZFDaniel GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Sanchez Taller8Documento3 páginasSanchez Taller8ALVARO MIGUEL SANCHEZ GOMEZAinda não há avaliações
- HOJA DE PRÁCTICA 2 y 3Documento3 páginasHOJA DE PRÁCTICA 2 y 3Leslie MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- Reporte de Laboratorio No 1Documento11 páginasReporte de Laboratorio No 1Ruisdael MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- LISTA DE ENSAYOS A REVISAR-AUDITORÍA INTERNA - KateDocumento4 páginasLISTA DE ENSAYOS A REVISAR-AUDITORÍA INTERNA - KatediegoAinda não há avaliações
- 20210630i0017-Carla MagallanesDocumento1 página20210630i0017-Carla MagallanesCarla Nicolle Magallanes ZambranoAinda não há avaliações
- Promociones Marzo Mayo San FranciscoDocumento24 páginasPromociones Marzo Mayo San FranciscoGerardo BravoAinda não há avaliações
- Metodo DSC en Excel (Davies Swann y Campey)Documento6 páginasMetodo DSC en Excel (Davies Swann y Campey)ALeDuckBoanergesAinda não há avaliações
- Limpieza de Material de LaboratorioDocumento19 páginasLimpieza de Material de LaboratorioErick Ismael Nemesio RoblesAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamina E50 (dl-α Tocoferyl Acetato)Documento4 páginasVitamina E50 (dl-α Tocoferyl Acetato)Rusbel Andres RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Presentación Ud 1Documento20 páginasPresentación Ud 1neyca neycaAinda não há avaliações
- Informe-Doc 25983406-ESTEBAN KESSELMAN-Consulta 1130265Documento1 páginaInforme-Doc 25983406-ESTEBAN KESSELMAN-Consulta 1130265Pablo CanavesAinda não há avaliações
- Reflujo TotalDocumento20 páginasReflujo TotallauraAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentos de Laboratorio de QuímicaDocumento8 páginasInstrumentos de Laboratorio de QuímicaAnay SandovalAinda não há avaliações