Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The Large Intestine Channel of Hand Yangming
Enviado por
ray72roTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The Large Intestine Channel of Hand Yangming
Enviado por
ray72roDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Large Intestine Channel
1
THE LARGE INTESTINE
CHANNEL OF
HAND YANGMI NG
Large Intestine Channel
2
THE LARGE INTESTINE CHANNEL OF HAND YANGMING
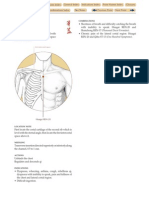
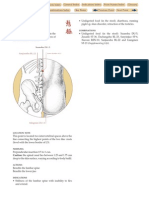
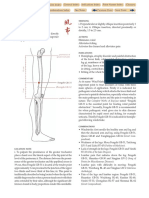
The Large Intestine primary channel
passes through
Bingfeng SI-12 to
Dazhui DU-14
connects with
the Lung and
descends to the
Large Intestine
passes through the
cheek and enters
the lower gums
descends to the lower he-sea
point of the Large Intestine at
Shangjuxu ST-37
crosses to the opposite
side of the face at
Renzhong DU-26 and
joins the Stomach
channel at Yingxiang
L.I.-20
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Large Intestine Channel
3
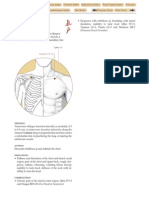
The Large Intestine luo-connecting channel
Note: i. According to descriptions of the Lung primary
channel pathway, a branch of the channel runs from
Lieque LU-7 to Shangyang L.I.-1. This latter point
however is not classified as a meeting point of the
Large Intestine and Lung channels. ii. Chengjiang
REN-24 is classified as a meeting point of the
Conception vessel with the Large Intestine channel.
This connection is not conventionally mentioned
however, in descriptions of the pathway of the Large
Intestine primary channel.
THE LARGE INTESTINE LUO-CONNECTING CHANNEL
begins at Pianli L.I.-6,
joins with its interiorly-exteriorly associated Lung
channel three cun above the wrist,
ascends the arm through Jianyu L.I.-15 to the jaw
and cheek, where it divides, one branch connecting
with the teeth, the other entering the ear to join the
zong mai (where the channels of the Large
Intestine, Stomach, Small Intestine, Gall Bladder and
Sanjiao gather and collect at the ear).
THE LARGE INTESTINE PRIMARY CHANNEL
begins at the radial side of the tip of the index
finger,
runs proximally along the radial side of the index
finger and passes through the interspace between
the first and second metacarpal bones at Hegu L.I.-4,
reaches the depression between the tendons of
extensor pollicis longus and brevis (anatomical
snuff-box) where Yangxi L.I.-5 is situated,
continues along the lateral aspect of the forearm to
the lateral aspect of the elbow at Quchi L.I.-11,
rises along the lateral aspect of the upper arm to the
shoulder joint at Jianyu L.I.-15,
crosses behind the shoulder to the depression
between the scapular spine and the lateral extremity
of the clavicle (Jugu L.I.-16),
travels in a medial direction, passing through
Bingfeng SI-12 (in the centre of the suprascapular
fossa) to Dazhui DU-14 (just below the spinous
process of the vertebra of C7) where it meets with
the other five yang channels of the hand and foot,
from Dazhui DU-14 it enters the supraclavicular
fossa in the region of Quepen ST-12 and connects
with the Lung before descending through the
diaphragm to join with the Large Intestine,
another branch ascends from the supraclavicular
fossa along the lateral aspect of the neck, passes
through the cheek, and enters the lower gums.
from the gums the channel passes through Dicang
ST-4, curves around the upper lip and crosses to the
opposite side of the body at Renzhong DU-26, at the
philtrum,
from Renzhong DU-26, the left channel travels to the
right and the right channel travels to the left to
terminate either side of the nose at Yingxiang L.I.-20,
at Yingxiang L.I.-20 the Large Intestine channel joins
with the Stomach channel.
According to the Spiritual Pivot
1
a branch of the
Large Intestine primary channel descends to
Shangjuxu ST-37.
The Large Intestine primary channel connects with the
following zangfu: Large Intestine, Lung.
The Large Intestine primary channel meets with other
channels at the following points: Dicang ST-4, Quepen
ST-12, Bingfeng SI-12, Dazhui DU-14, Renzhong
DU-26, Chengjiang REN-24. Note that although
Xuanlu GB-5, Xuanli GB-6 and Yangbai GB-14 are
classically listed as meeting points with the Large
Intestine channel, illustrations of the channel do not
normally show these connections.
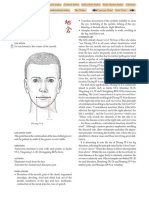
divides on the cheek,
one branch entering
the ear and the other branch
connecting with the teeth
separates from the primary
channel at Pianli L.I.-6 and
joins the Lung channel
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Large Intestine Channel
4
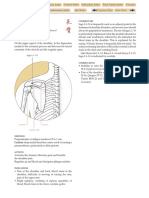
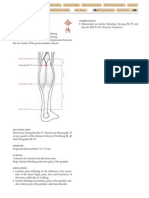
travels medially to
the spinal column,
descends to the
thorax, breast, Lung
and Large Intestine
and ascends along
the throat
The Large Intestine Divergent channel
THE LARGE INTESTINE DIVERGENT CHANNEL
separates from the Large Intestine primary channel
on the hand,
ascends the arm to the shoulder at Jianyu L.I.-15,
travels medially to the spinal column,
crosses to the supraclavicular fossa and descends to
the thorax, breast, Lung and Large Intestine,
a branch ascends from the supraclavicular fossa
along the throat and unites with the Large Intestine
primary channel.
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Large Intestine Channel
5
The Large Intestine sinew channel
attaches to the
upper thoracic spine
crosses over the top of the head to
connect with the opposite mandible
binds at the
side of the nose
THE LARGE INTESTINE SINEW CHANNEL
begins at the tip of the index finger at Shangyang
L.I.-1 and binds at the dorsum of the wrist,
ascends the forearm and binds at the lateral aspect of
the elbow,
ascends the upper arm to bind at the shoulder,
a branch winds around the scapula and attaches to
the upper thoracic spine,
from the shoulder the main channel ascends to the
neck from where a branch ascends across the cheeks
to bind at the side of the nose, whilst,
the main channel ascends anterior to the Small
Intestine sinew channel, crosses the temple to the
corner of the forehead, and crosses over the top of
the head to connect with the mandible on the
opposite side.
Pathological symptoms of the Large Intestine sinew channel
Cramping and pain along the course of the channel,
inability to raise the shoulder, inability to turn the neck
to the left or to the right.
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Large Intestine Channel
6
DISCUSSION
The Large Intestine channel of hand yangming is interiorly-
exteriorly coupled with the Lung channel of hand taiyin,
and paired with the Stomach channel of foot yangming
according to six channel theory. The Large Intestine-Lung
relationship is further strengthened by the fact that:
both the interior pathway of the Large Intestine
channel as well as the Large Intestine divergent
channel enter the Lung zang.
the Large Intestine luo-connecting channel from
Pianli L.I.-6 joins with the Lung channel.
In addition it is clinically valuable to note that:
the Large Intestine primary channel enters the gums
of the lower teeth.
the Large Intestine primary channel crosses to the
contralateral side of the face at Renzhong DU-26.
the Large Intestine sinew channel ascends to the
corner of the forehead and crosses over the top of the
head to connect with the opposite mandible.
the Large Intestine luo-connecting channel enters the
ear as well as the teeth.
the Large Intestine divergent channel descends to the
breast.
the Large Intestine sinew channel attaches to the
upper thoracic spine and the divergent channel
travels medially to the spinal column.
The function of the Large Intestine fu is to receive waste
material sent down from the Small Intestine, absorb its
fluid content and form the remainder into faeces to be
excreted. Despite this, although several points of the
Large Intestine channel have an action on the intestines
and lower abdomen (particularly in the treatment of
borborygmus and diarrhoea), in clinical practice they are
considerably less used than points of the Spleen and
Stomach channels. Also there is no Large Intestine chan-
nel point indicated for difficult defecation or constipation.
This paucity of Large Intestine indications is not surpris-
ing in view of the fact that whilst the channel traverses the
upper body, the fu lies in the lower abdomen.
According to the Spiritual Pivot
2
Yangming channel is
abundant in qi and blood. Points of both the arm and leg
portions of yangming channel are therefore much used
clinically to regulate qi and blood in the limbs and treat
atrophy disorder and painful obstruction, hemiplegia
and pain of all kinds.
In the Chinese tradition the sage faces South and thus the
light and warmth of the sun fall on the front of the body.
The yangming channels, on the anterior of the limbs,
receive the full intensity of the sun, as does the abdominal
and chest portion of the foot yangming Stomach channel,
the only yang channel to run along the anterior of the
body. For this reason, yangming or yang brightness is
considered to be particularly replete with yang qi. Points
of the Large Intestine channel, therefore, are among the
most important points to clear excess of yang in the form
of heat and fever, notably Hegu L.I.-4 and Quchi L.I.-11.
Apart from the above, the primary actions and indications
of the points of the Large Intestine channel can be summa-
rised as:
treating all disorders of the yangming channel in the
head; this area includes the face and cheeks, fore-
head, eyes, nose, lips, gums and teeth.
treating disorders of the ear (Large Intestine luo-
connecting channel).
expelling wind, cold and heat from the exterior
portion of the body.
clearing wind-heat, interior heat and fire poison from
the areas traversed by the channel, especially in the
head.
clearing yangming fire which disturbs the Heart and
spirit.
assisting the Lung in its function of opening the
water passages.
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Você também pode gostar
- The Spleen Channel of Foot TaiyinDocumento6 páginasThe Spleen Channel of Foot Taiyinray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Lung Channel of Hand TaiyinDocumento4 páginasThe Lung Channel of Hand Taiyinray72ro100% (1)
- Intestinal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandIntestinal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- STIntroDocumento6 páginasSTIntroa_steri_x2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Small Intestine Channel GuideDocumento5 páginasSmall Intestine Channel Guidea_steri_x2000Ainda não há avaliações
- The Liver Channel of Foot JueyinDocumento5 páginasThe Liver Channel of Foot Jueyinray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Conception Vessel 1Documento4 páginasThe Conception Vessel 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Channels of AcupunctureDocumento18 páginasThe Channels of AcupunctureFonnie OnesixthreeAinda não há avaliações
- Ren 20Documento1 páginaRen 20ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- ST 14 PDFDocumento1 páginaST 14 PDFsorinAinda não há avaliações
- L. Intestine Channel Points for Chest Pain ReliefDocumento1 páginaL. Intestine Channel Points for Chest Pain ReliefsorinAinda não há avaliações
- ST 13 PDFDocumento1 páginaST 13 PDFsorinAinda não há avaliações
- Liv 11Documento1 páginaLiv 11ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Shanglian L.I.-9: Large Intestine Channel 1Documento1 páginaShanglian L.I.-9: Large Intestine Channel 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Channels - ComprehensiveDocumento9 páginasChannels - Comprehensivetito zambranoAinda não há avaliações
- Shouwuli L.I.-13: Arm Five MilesDocumento1 páginaShouwuli L.I.-13: Arm Five Milesray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Pathway: Heart Primary Channel (Shou Shao Yin Jing)Documento3 páginasPathway: Heart Primary Channel (Shou Shao Yin Jing)uda2013Ainda não há avaliações
- ST 13Documento1 páginaST 13ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi NDocumento5 páginasThe Pericardium Channel of Hand Jueyi Nray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Tianxi Sp-18: Heavenly StreamDocumento1 páginaTianxi Sp-18: Heavenly Streamray72roAinda não há avaliações
- שלושת היינים של היד - מיקום אנטומיDocumento1 páginaשלושת היינים של היד - מיקום אנטומיyesgustejAinda não há avaliações
- Jimen Sp-11: Spleen Channel 1Documento1 páginaJimen Sp-11: Spleen Channel 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- SP 19Documento1 páginaSP 19ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- SP 16Documento1 páginaSP 16ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Luo-Connecting Deadman ArticlDocumento7 páginasThe Luo-Connecting Deadman ArticlavaAinda não há avaliações
- ST 10Documento1 páginaST 10ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Wenliu L.I.-7: Warm FlowDocumento1 páginaWenliu L.I.-7: Warm Flowray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Pianli L.I.-6: Veering PassageDocumento1 páginaPianli L.I.-6: Veering Passageray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Jizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineDocumento1 páginaJizhong Du-6: Centre of The SpineBDI92Ainda não há avaliações
- Acupuncture PointsDocumento46 páginasAcupuncture PointsM. P. Schaefer100% (1)
- Channels and Collaterals Guide to Acupoint Quchai BL-4Documento1 páginaChannels and Collaterals Guide to Acupoint Quchai BL-4ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Du 26Documento2 páginasDu 26BDI92Ainda não há avaliações
- ST 14Documento1 páginaST 14ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Book of The Acupuncture StudentDocumento350 páginasBook of The Acupuncture Studentmatt100% (5)
- Li 3Documento2 páginasLi 3ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Jianli Ren-11: Strengthen The InteriorDocumento1 páginaJianli Ren-11: Strengthen The Interiorray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Lu 9Documento2 páginasLu 9ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- ST 41 PDFDocumento2 páginasST 41 PDFsorinAinda não há avaliações
- L. Intestine Channel Point Jugu L.I.-16Documento1 páginaL. Intestine Channel Point Jugu L.I.-16Juan Gabriel CunhaAinda não há avaliações
- L. Intestine: Guide to Acupuncture Point Rugen ST-18Documento1 páginaL. Intestine: Guide to Acupuncture Point Rugen ST-18sorinAinda não há avaliações
- Point Selection Methods 1Documento5 páginasPoint Selection Methods 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- L. Intestine Channel Points for Headaches and Nasal IssuesDocumento1 páginaL. Intestine Channel Points for Headaches and Nasal IssuesJuan Gabriel CunhaAinda não há avaliações
- The Small Intestine Channel of Hand TaiyangDocumento165 páginasThe Small Intestine Channel of Hand TaiyangGeeta SajjanAinda não há avaliações
- SP 5Documento2 páginasSP 5ray72ro100% (1)
- Fushe Sp-13: Abode of The FuDocumento1 páginaFushe Sp-13: Abode of The Furay72roAinda não há avaliações
- Self TestDocumento91 páginasSelf Testray72roAinda não há avaliações
- ST 44 PDFDocumento2 páginasST 44 PDFsorinAinda não há avaliações
- Li 1Documento2 páginasLi 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Du 5Documento1 páginaDu 5BDI92Ainda não há avaliações
- Abdomen exam guide under 40 charsDocumento5 páginasAbdomen exam guide under 40 charsdidutza91Ainda não há avaliações
- Huatuojiaji (M-Bw-35) : Hua Tuo's Paravertebral PointsDocumento1 páginaHuatuojiaji (M-Bw-35) : Hua Tuo's Paravertebral Pointsray72ro100% (1)
- Scroll Three: Ling Shu, The Spiritual Pivot. Wu Jing-NuanDocumento30 páginasScroll Three: Ling Shu, The Spiritual Pivot. Wu Jing-NuanAnonymous RY91UFyQ100% (2)
- Anatomi EsofagusDocumento14 páginasAnatomi EsofagusSandy PranadaAinda não há avaliações
- ST 4 PDFDocumento2 páginasST 4 PDFsorinAinda não há avaliações
- Heyang Bl-55: Confluence of YangDocumento1 páginaHeyang Bl-55: Confluence of YangBDI92Ainda não há avaliações
- Raja ReddyDocumento41 páginasRaja Reddymanda YogeshAinda não há avaliações
- Li 15Documento2 páginasLi 15ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- SP 8Documento2 páginasSP 8ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Emotions Essential Oils 6th EnlightenDocumento271 páginasEmotions Essential Oils 6th Enlightenray72roAinda não há avaliações
- FourSacredSeasons EbookDocumento19 páginasFourSacredSeasons EbookLouis Lee Hires100% (3)
- Instructions Ffmpeg WinDocumento3 páginasInstructions Ffmpeg Winray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Instructions Ffmpeg MacDocumento3 páginasInstructions Ffmpeg Macray72roAinda não há avaliações
- GB 34Documento3 páginasGB 34ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Yi Notes PDFDocumento19 páginasYi Notes PDFEe6803100% (1)
- Da Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year SpiritsDocumento2 páginasDa Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year Spiritsray72roAinda não há avaliações
- DLR 2021 04 18 14 00Documento3 páginasDLR 2021 04 18 14 00ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- DLR 2021 04 18 10 00Documento3 páginasDLR 2021 04 18 10 00ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Yang Earth Joye Yap PDFDocumento18 páginasYang Earth Joye Yap PDFSerenity Serenity100% (3)
- DLR 2021 04 18 06 00Documento3 páginasDLR 2021 04 18 06 00ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocumento6 páginasThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roAinda não há avaliações
- DLR 2021 04 18 08 00Documento3 páginasDLR 2021 04 18 08 00ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- DLR 2021 04 18 02 00Documento3 páginasDLR 2021 04 18 02 00ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Jiang Notes PDFDocumento19 páginasJiang Notes PDFffmbdrngAinda não há avaliações
- Gui NotesDocumento18 páginasGui Notesffmbdrng100% (8)
- Notes: Gall Bladder ChannelDocumento1 páginaNotes: Gall Bladder Channelray72roAinda não há avaliações
- BaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengDocumento18 páginasBaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengMoses YeeAinda não há avaliações
- GB 39Documento2 páginasGB 39ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- GB 36Documento1 páginaGB 36ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDocumento2 páginasZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Zhongdu Gb-32: Middle DitchDocumento1 páginaZhongdu Gb-32: Middle Ditchray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Zulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of TearsDocumento2 páginasZulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of Tearsray72roAinda não há avaliações
- GB 38 PDFDocumento2 páginasGB 38 PDFray72roAinda não há avaliações
- GB 31Documento2 páginasGB 31ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Guangming Gb-37: Bright LightDocumento2 páginasGuangming Gb-37: Bright Lightray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Yangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1Documento1 páginaYangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- GB 30Documento2 páginasGB 30ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Toulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1Documento1 páginaToulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Juliao Gb-29: Stationary CreviceDocumento1 páginaJuliao Gb-29: Stationary Creviceray72roAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling mass transfer in fluidized bedsDocumento5 páginasModeling mass transfer in fluidized bedsSmrutiAinda não há avaliações
- QC ABO RH BloodDocumento62 páginasQC ABO RH BloodrhoderickAinda não há avaliações
- Eustress and Distress: Neither Good Nor Bad, But Rather The Same?Documento5 páginasEustress and Distress: Neither Good Nor Bad, But Rather The Same?Cosmin LazaroiuAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure For MapehDocumento4 páginasBrochure For MapehKarl Anthony SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- P. 134-149Documento16 páginasP. 134-149biblioagroAinda não há avaliações
- Secondary Immunodeficiency in ChildrenDocumento16 páginasSecondary Immunodeficiency in Childrenryan20eAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1 BI 602Documento6 páginasAssignment 1 BI 602Eneah NaicavacavaAinda não há avaliações
- Different Types of VaccinesDocumento2 páginasDifferent Types of VaccinesBhuvaneshAinda não há avaliações
- Shellfish Morphology GuideDocumento9 páginasShellfish Morphology GuideParimita SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Taruka Mammalian SpeciesDocumento12 páginas2013 Taruka Mammalian SpeciesabrunomirandacAinda não há avaliações
- 3 5 18 950 PDFDocumento3 páginas3 5 18 950 PDFBang AthanAinda não há avaliações
- Lionex LIOFeronTB LTBIDocumento2 páginasLionex LIOFeronTB LTBIBilgi KurumsalAinda não há avaliações
- NEBOSH 2007 Jul AllDocumento17 páginasNEBOSH 2007 Jul AllRobertProsser19100% (8)
- GEN3051 Lecture 1: Human Genes and Human Genetic DisordersDocumento5 páginasGEN3051 Lecture 1: Human Genes and Human Genetic DisordersAlessander Leyendecker JuniorAinda não há avaliações
- Etiologji Dhe Epidemiologjia e StrokeDocumento7 páginasEtiologji Dhe Epidemiologjia e StrokegranitAinda não há avaliações
- Kung Et Al. (2018)Documento14 páginasKung Et Al. (2018)Henry Daniel Ruiz AlbaAinda não há avaliações
- Happ Chapter 8 TransesDocumento13 páginasHapp Chapter 8 TransesFrencess Kaye SimonAinda não há avaliações
- B VIDAS T4 enDocumento7 páginasB VIDAS T4 enInn MironAinda não há avaliações
- English 2 Class 02Documento23 páginasEnglish 2 Class 02Bill YohanesAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous System Assessment GuideDocumento11 páginasNervous System Assessment Guideaderonke bello100% (2)
- General Biology 1 Module 6Documento19 páginasGeneral Biology 1 Module 6Vienne MonroidAinda não há avaliações
- Frances Boa Methodology QuestionDocumento39 páginasFrances Boa Methodology Questionmonday125Ainda não há avaliações
- B0 29palms 01 31 2017Documento148 páginasB0 29palms 01 31 2017The Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Toxicology and Toxicogenomics 2021Documento360 páginasEnvironmental Toxicology and Toxicogenomics 2021ancuta.lupaescuAinda não há avaliações
- Pforams@Mikrotax - Globigerinoides ConglobatusDocumento2 páginasPforams@Mikrotax - Globigerinoides ConglobatusAhmad Lumban GaolAinda não há avaliações
- Hurdle TechnologyDocumento5 páginasHurdle TechnologyDavid UribeAinda não há avaliações
- Brain-Computer Interface - Braingate Chip: Hillary Grimes Iii Homework 6 Comp 4640Documento12 páginasBrain-Computer Interface - Braingate Chip: Hillary Grimes Iii Homework 6 Comp 4640Amarjeet DasAinda não há avaliações
- Navy Weed Control & Plant Growth RegDocumento179 páginasNavy Weed Control & Plant Growth RegSpace_Hulker100% (1)
- General Biology 2 NotesDocumento97 páginasGeneral Biology 2 NotesMacky NohayAinda não há avaliações