Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Thoracic Vertebrae Anatomy
Enviado por
Nourhan JamalDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Thoracic Vertebrae Anatomy
Enviado por
Nourhan JamalDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3/1/2014 Cervical Vertebrae Print Page: Unlabeled Diagram (Image) and Text
http://www.getbodysmart.com/ap/skeletalsystem/skeleton/axial/vertebrae/thoracic_vertebrae/print2.html 1/3
PRINT PAGE
Return to Print Previews
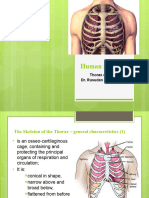
Thoracic Vertebrae
The twelve thoracic vertebrae are located in the middle of the vertebral column and
each articulates with a pair of ribs.
Most of the thoracic vertebrae share the anatomical characteristics described below.
However, the upper and lower thoracic vertebrae vary slightly in their appearance.
T1 somewhat resembles the last cervical vertebra (C7) and T9 - T12 progressively look
3/1/2014 Cervical Vertebrae Print Page: Unlabeled Diagram (Image) and Text
http://www.getbodysmart.com/ap/skeletalsystem/skeleton/axial/vertebrae/thoracic_vertebrae/print2.html 2/3
more like the lumbar vertebrae.
Bone Markings:
a. Body (or centrum):
(Corpus vertebrae) - a heart-shaped cylindrical mass on the anterior side of the
vertebra. It articulates with vertebral bodies (or centrums) above and below.
b. Superior costal demifacet:
(Fovea costalis superior) - a depression on the superiolateral surface of the body. It
serves as the lower half of a facet (= demifacet) that articulates with the head of the rib.
The upper half of the facet is found on the body of the thoracic vertebra above.
c. Inferior costal demifacet:
(Fovea costalis inferior) - a depression on the inferiolateral surface of the body. It
serves as the upper half of a facet (= demifacet) that articulates with the head of the rib.
The lower half of the facet is found on the body of the thoracic vertebra below.
d. Vertebral (spinal) foramen:
(Foramen vertebrale) - a large opening in the center of the bone that forms a
passageway for the spinal cord.
e. Vertebral (or neural) arch:
(Arcus vertebrae) - a bony posterior arch made up of two pedicles, two laminae, and a
spinous process. The arch encloses the posterior portion of the vertebral foramen and
protects the spinal cord from damage.
f. Pedicle of the vertebral arch:
(Pediculus arcus vertebrae) - a posterior extension from the body. The left and right
pedicles form the bases of the vertebral arch (L., pediculus, a little foot; stalk).
g. Lamina of the vertebral arch:
(Lamina archus vertebrae) - a plate of bone that extends from the pedicle to the
spinous process. The left and right laminae form the dorsal portion of the vertebral arch.
h. Spinous process:
(Processus spinosus) - a narrow, posterior extension from the junction of the two
laminae. The downward projecting processes are long and narrow and have an
expanded (tuberculated) tip. They are the attachment points for ligaments and muscles
that move the vertebral column.
i. Transverse process:
(Processus transversus) - a thick, elongated projection that extends lateroposteriorly
from the junction of pedicle and lamina. It serves as an attachment point for several
back muscles.
j.Transverse costal facet:
(Fovea costalis transversalis) - a slightly concave surface on the lateral aspect of the
3/1/2014 Cervical Vertebrae Print Page: Unlabeled Diagram (Image) and Text
http://www.getbodysmart.com/ap/skeletalsystem/skeleton/axial/vertebrae/thoracic_vertebrae/print2.html 3/3
transverse process, which is also called the transverse costal fovea (L., costa, rib). It
serves as an area of articulation with the tubercle of the rib.
k. Superior articular facet:
(Facies articularis superior) - a posterior facing, flattened surface on the superior
articular process. It is located near the junction of the pedicles and laminae and
articulates with the inferior articular facet on the vertebra above.
l. Superior vertebral notch:
(Incisura vertebralis superior) - a slight indentation on the superior surface of the
pedicle.
m. Inferior vertebral notch:
(Incisura vertebralis inferior) - a large indentation on the inferior surface of the pedicle.
n. Intervertebral foramen:
(Foramina intervertebralia) - a large opening formed by the inferior vertebral notch on
the vertebra above and the superior vertebral notch on the vertebra below. The opening,
which is also called the neural foramen or lateral foramen, serves as a passageway
for a spinal nerve and a pair of spinal nerve roots.
Você também pode gostar
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocumento3 páginasPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeAinda não há avaliações
- Osteology BonesDocumento48 páginasOsteology BonesÂhmęd ĐoolaAinda não há avaliações
- The anatomy and features of thoracic vertebraeDocumento32 páginasThe anatomy and features of thoracic vertebraeAbhishek SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Relevance of Clavicle FracturesDocumento11 páginasClinical Relevance of Clavicle FracturesShuvashishSunuwarAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy VertebraDocumento3 páginasAnatomy VertebraRichard PierAinda não há avaliações
- OSTEOLOGY MaketDocumento22 páginasOSTEOLOGY MaketFemiAinda não há avaliações
- Osteology of The Upper Limb 2Documento71 páginasOsteology of The Upper Limb 2obehi4rAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento4 páginasAnatomy and PhysiologyAnnileighjeanAinda não há avaliações
- Bones of the Back and Upper Limbscapulait is the longest border of the scapula; it is a site of attachmentfor the serratus anterior mDocumento38 páginasBones of the Back and Upper Limbscapulait is the longest border of the scapula; it is a site of attachmentfor the serratus anterior mshahera rosdiAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Limb Anatomy 1Documento6 páginasUpper Limb Anatomy 1shahab shamsiAinda não há avaliações
- Vertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaDocumento39 páginasVertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaT CAinda não há avaliações
- ST - Paulos Hospital Millennium Medical College: Gross Anatomy:Upper LimbDocumento256 páginasST - Paulos Hospital Millennium Medical College: Gross Anatomy:Upper LimbetAinda não há avaliações
- 1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGDocumento129 páginas1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGReath Gatkuoth DuothAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding the Appendicular SkeletonDocumento23 páginasUnderstanding the Appendicular SkeletonFachriza Effendi100% (1)
- Bones and LimbsDocumento147 páginasBones and LimbsDana IonescuAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Fibula and FootDocumento11 páginas3 Fibula and Footطه طارقAinda não há avaliações
- Upperlimbbones 181202102428Documento32 páginasUpperlimbbones 181202102428qaziafifa404Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivesDocumento18 páginasAnatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivespoAinda não há avaliações
- Bones of Lower Limb: 1. Pelvic Bone (Hip Bone)Documento9 páginasBones of Lower Limb: 1. Pelvic Bone (Hip Bone)Zaid AbdulqadirAinda não há avaliações
- Snell Lower LimbDocumento44 páginasSnell Lower LimbBen100% (3)
- Bones of The Back RegionDocumento9 páginasBones of The Back Regionyachiru121Ainda não há avaliações
- 4 ThoraxDocumento35 páginas4 Thoraxpreetam912002.22Ainda não há avaliações
- Shoulder Blade Bone: The ScapulaDocumento7 páginasShoulder Blade Bone: The ScapulasujsamAinda não há avaliações
- 4.thoracic WallDocumento20 páginas4.thoracic WallAmrith LordAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of the hip bone and hip jointDocumento8 páginasAnatomy of the hip bone and hip jointBeGie MamBaAinda não há avaliações
- ThoraxDocumento54 páginasThoraxfalz0012kAinda não há avaliações
- Vertebral ColumnDocumento8 páginasVertebral ColumnNaium Uddin BPTAinda não há avaliações
- BIOMECHANICS OF THE CERVICAL SPINEDocumento25 páginasBIOMECHANICS OF THE CERVICAL SPINENithya NithyaAinda não há avaliações
- Vertebra: StructureDocumento9 páginasVertebra: StructureayudhyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Anatomy of the ThoraxDocumento237 páginasThe Anatomy of the ThoraxAbel Belete100% (1)
- Exp 12 PDFDocumento16 páginasExp 12 PDFKath BarcelonaAinda não há avaliações
- SkeletalDocumento8 páginasSkeletalJeanina BuenaventuraAinda não há avaliações
- Clavicle - WikipediaDocumento8 páginasClavicle - WikipediaVaishnavi TradersAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Femur, Patella and TibiaDocumento10 páginas2 Femur, Patella and Tibiaطه طارقAinda não há avaliações
- Lower LimbpostgDocumento79 páginasLower LimbpostgBuya kasahunAinda não há avaliações
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDocumento16 páginas2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Part 1 - The Upper LimbDocumento27 páginasAnatomy Part 1 - The Upper LimbSolange AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- Clavicle - WikipediaDocumento15 páginasClavicle - WikipediaBalaji BscRTAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Vertebral Column: Supervisor: DR - Younis ZandyDocumento36 páginasAnatomy of The Vertebral Column: Supervisor: DR - Younis ZandyZA IDAinda não há avaliações
- Spaces.: TH TH TH THDocumento4 páginasSpaces.: TH TH TH THbarbacumlaudeAinda não há avaliações
- Appendicular Body - Bones (Lower Limb)Documento10 páginasAppendicular Body - Bones (Lower Limb)Rodmar GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomylec 2Documento43 páginasAnatomylec 2n gautamAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Lac.1Documento43 páginasAnatomy Lac.1minayayoongi2004Ainda não há avaliações
- MSK Lab 2Documento13 páginasMSK Lab 2mohammedalfadhil333Ainda não há avaliações
- 18 MSK Arm and HandDocumento27 páginas18 MSK Arm and HandNTRisforthinkersAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy PcketDocumento16 páginasAnatomy PcketHanya BelajarAinda não há avaliações
- Prepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)Documento43 páginasPrepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)AmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1Documento49 páginasAnatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1ffAinda não há avaliações
- Hip joint anatomy guideDocumento4 páginasHip joint anatomy guideshash82Ainda não há avaliações
- L1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmDocumento8 páginasL1 Anatomy of The Lungs, Pleural Cavities and Respiratory Muscles - L4 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and DiaphragmAurora TamAinda não há avaliações
- Verterbral Column Assingment Takunda MakondoDocumento58 páginasVerterbral Column Assingment Takunda MakondomakondotakundaAinda não há avaliações
- Spine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Documento11 páginasSpine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Sarah Magdy100% (1)
- Appendicular SkeletonDocumento6 páginasAppendicular SkeletonJohn Snow1Ainda não há avaliações
- Headandneck SkullDocumento27 páginasHeadandneck SkullKarla PappaAinda não há avaliações
- 36 Reading RapoffDocumento11 páginas36 Reading RapoffFanica ScarlatAinda não há avaliações
- So It Has Three Part:: Called Hyglossus Which Extend From Hyoid Bone Toward The TonguDocumento14 páginasSo It Has Three Part:: Called Hyglossus Which Extend From Hyoid Bone Toward The TonguHeba S RadaidehAinda não há avaliações
- Upper LimbDocumento17 páginasUpper LimbPapadoveAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnDocumento44 páginasBiomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnVijay PradeepAinda não há avaliações
- BY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)Documento52 páginasBY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)DCRUZAinda não há avaliações
- MCQsDocumento1 páginaMCQsNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- General Pathology Extra 6 QuestionsDocumento14 páginasGeneral Pathology Extra 6 QuestionsNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific CrimeDocumento2 páginasScientific CrimeNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- RahmanDocumento5 páginasRahmanNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Step 1 Classroom Anywhere Prep: March 17, 2014 - June 22, 2014Documento2 páginasStep 1 Classroom Anywhere Prep: March 17, 2014 - June 22, 2014Nourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Mnemonics 2Documento50 páginasAnatomy Mnemonics 2Nourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- The IcebreakerDocumento89 páginasThe IcebreakerNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines On Travel-Related Venous Thrombosis: GuidelineDocumento4 páginasGuidelines On Travel-Related Venous Thrombosis: GuidelineNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- MalariaDocumento20 páginasMalariaNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Association Problem SolvingDocumento3 páginasAssociation Problem SolvingNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Happy Ben To Lunch CaddyDocumento9 páginasHappy Ben To Lunch CaddyNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Questions 01Documento103 páginasInteractive Questions 01ngole_96Ainda não há avaliações
- Barbie Winter Princess Dress - Cogaroo CraftsDocumento6 páginasBarbie Winter Princess Dress - Cogaroo CraftsNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Brachial Plexus Part 1 AnatomyDocumento3 páginasBrachial Plexus Part 1 AnatomyNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Blood 1998 May 91 (10) 3527-61, Fig. 1Documento1 páginaBlood 1998 May 91 (10) 3527-61, Fig. 1Nourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- 8 in 1 Crochet Barbie ClothesDocumento3 páginas8 in 1 Crochet Barbie ClothesNourhan Jamal89% (9)
- Upper Limb ArteriesDocumento1 páginaUpper Limb ArteriesNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Histology Slides EpitheliumDocumento3 páginasHistology Slides EpitheliumNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- CPK isoenzyme test clinical usesDocumento5 páginasCPK isoenzyme test clinical usesNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Classy Continental HatDocumento0 páginaClassy Continental HatNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write A Good Ucas Personal StatementDocumento5 páginasHow To Write A Good Ucas Personal StatementNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Crayon KeeperDocumento0 páginaCrayon KeeperNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Bunny BasketDocumento10 páginasBunny BasketNourhan Jamal100% (1)
- Birthday Cake Box Pattern by MoonScDocumento5 páginasBirthday Cake Box Pattern by MoonScNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- The Ultimate Craft Guide 25 Projects For Every CrafterDocumento67 páginasThe Ultimate Craft Guide 25 Projects For Every CrafterNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- LW3182Documento1 páginaLW3182Nourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Birthday Cake Box Pattern by MoonScDocumento5 páginasBirthday Cake Box Pattern by MoonScNourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- SN0121Documento2 páginasSN0121Nourhan JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Fall Leaves CoasterDocumento2 páginasFall Leaves Coastern_yusaf3707100% (2)
- Upper Cross Syndrome Dr. Jeff Luebbe 2-05-12Documento9 páginasUpper Cross Syndrome Dr. Jeff Luebbe 2-05-12Simo AsterAinda não há avaliações
- ANATOMI SISTEM PENCERNAAN by Dr. RifalDocumento97 páginasANATOMI SISTEM PENCERNAAN by Dr. RifalSusi ErawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Kyusho Points and Martial Arts TechniquesDocumento2 páginasKyusho Points and Martial Arts Techniquescoucou0505100% (1)
- Core Stability - A Pilates WorkoutDocumento26 páginasCore Stability - A Pilates WorkoutJelena VivodaAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Facts About the Temporomandibular JointDocumento6 páginas100 Facts About the Temporomandibular JointArjun Narang100% (1)
- II - 4.anterior Cranial FossaDocumento2 páginasII - 4.anterior Cranial FossaalllexissssAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Oral Cavity, Abdominal and Inguinal Region PDFDocumento50 páginas05 Oral Cavity, Abdominal and Inguinal Region PDFShaira Aquino VerzosaAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER III Physical AssessmentDocumento3 páginasCHAPTER III Physical AssessmentDenise DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Barefoot Shiatsu: (Oriental Foot Massage)Documento23 páginasBarefoot Shiatsu: (Oriental Foot Massage)familiazeleAinda não há avaliações
- 125 - 208 Homework 4 SolutionsDocumento18 páginas125 - 208 Homework 4 SolutionsdfgdfgdfgaaAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Manual Ligament Therapy - FoundationDocumento38 páginasRevised Manual Ligament Therapy - FoundationKleberBattaglia100% (4)
- Muscles of MasticationDocumento50 páginasMuscles of MasticationKaran AroraAinda não há avaliações
- AAB Human Skull Anatomy ActivityDocumento2 páginasAAB Human Skull Anatomy ActivityCamila VorkapicAinda não há avaliações
- Cefalometria ActualDocumento55 páginasCefalometria Actualmateo bravo0% (1)
- Differences between identical and fraternal twinsDocumento55 páginasDifferences between identical and fraternal twinsOverRush AmareshAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional Status 1Documento13 páginasNutritional Status 1Rochelle Mae G. IrincoAinda não há avaliações
- The NeckDocumento36 páginasThe NeckJefri SandikaAinda não há avaliações
- Istezanje Nakon SpavanjaDocumento6 páginasIstezanje Nakon SpavanjaLaza UrosevicAinda não há avaliações
- Biomekanik ElbowDocumento14 páginasBiomekanik Elbowdadakan16Ainda não há avaliações
- BA Basic Fitness Part 4Documento7 páginasBA Basic Fitness Part 4concussion100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Disorders - AuriculotherapyDocumento3 páginasCardiovascular Disorders - AuriculotherapyCarissa Nichols100% (2)
- Head Neck MCQ ChaptersDocumento17 páginasHead Neck MCQ ChaptersMohamed GhabrunAinda não há avaliações
- Lower Leg and FootDocumento40 páginasLower Leg and Footapi-295870055Ainda não há avaliações
- APTA Combined Sections Meeting 2008: Fugl-Meyer AssessmentDocumento17 páginasAPTA Combined Sections Meeting 2008: Fugl-Meyer AssessmentDaniele Bertolo100% (1)
- Anatomi Fisiologi HidungDocumento29 páginasAnatomi Fisiologi HidungRomanna100% (1)
- Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDocumento13 páginasEssentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDani AnyikaAinda não há avaliações
- Anterior Compartment of Cubital Fossa and ArmDocumento22 páginasAnterior Compartment of Cubital Fossa and ArmMedicosNotesAinda não há avaliações
- Body For Life - Abs TrainingDocumento9 páginasBody For Life - Abs Trainingzulu22Ainda não há avaliações
- Approaches in NeurosurgeryDocumento226 páginasApproaches in NeurosurgeryJavier Andres Jacobo100% (2)
- PDLDocumento2 páginasPDLKathleen Cay Medrano PanopioAinda não há avaliações
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNo EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (515)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNo EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeAinda não há avaliações
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindNo EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (93)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondNo EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyNo EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (31)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNo EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (811)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNo EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorAinda não há avaliações
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldNo EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (18)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNo EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNo EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (44)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineNo EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (17)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishNo EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (30)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesNo EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (56)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceAinda não há avaliações
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesNo EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (347)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsAinda não há avaliações
- Younger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationNo EverandYounger for Life: Feel Great and Look Your Best with the New Science of AutojuvenationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Darwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeNo EverandDarwin's Dangerous Idea: Evolution and the Meaning of LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (523)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsNo EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2083)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthNo EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (13)