Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP Excess Fluid Volume
Enviado por
Trixia Camporedondo0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
4K visualizações4 páginasNursing Care Plan
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoNursing Care Plan
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
4K visualizações4 páginasNCP Excess Fluid Volume
Enviado por
Trixia CamporedondoNursing Care Plan
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
Trixia T.
Camporedondo 4AN2 Intensive Care Unit August 26-27, 2014
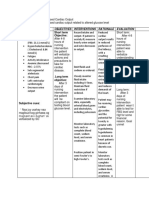
Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
Patient is in ET and
unconscious.
Objective:
Hypotension
90/70 mmHg
Tachycardia 114
bpm
Anasarca
Decreased
urinary output
100cc
Lethargic
Excess Fluid
Volume
related to
compromised
regulatory
mechanism
as evidenced
y edema.
HASCVD
Decreased
Ventricular
contraction
Ventricular
overload
Tachycardia
Ventricular
Dilatation
Myocardial
Hypertrophy
Decreased
cardiac
output
Short Term:
After 30
minutes of
nursing
intervention
patients vital
signs will be in
normal range.
Long Term:
After of 5
hours
of nursing
interventions,
the patient
will be able to
stabilize fluid
volume as
evidenced by:
a.
Balance intake
and output;
b. Drain at
least 1liter of
urine and
foley catheter
Independent:
Monitor vital
signs.
Auscultate
lungs and
heart sound.
Assess for
presence/
location of
edema.
Note for
presence of
neck and
peripheral
vein
distention.
Tachycardia
and
hypertension
are common
manifestation.
Adventitous
sounds
(crackles) and
extra heart
sound(s3) are
indicative of
fluid excess.
Edema can be
either a cause
or a result of
various
pathologic.
Signs of cardiac
decompensatio
n
Short Term:
After 30
minutes of
nursing
intervention
patients vital
signs was in
normal range.
Long Term:
After of 5 hours
of nursing
interventions,
the patient was
able to
stabilize fluid
volume as
evidenced by:
a.
Balanced intake
and output;
b. Drain at
least 1liter of
urine and foley
catheter
Trixia T. Camporedondo 4AN2 Intensive Care Unit August 26-27, 2014
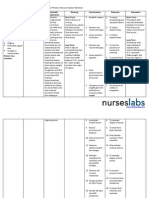
Decreased
renal
perfusion
Increased
sodium
retention
Increased
osmotic
pressure
Increased
antidiuretic
hormone
Increased
water
reabsorption
Fluid
overload
Edema
Maintain
accurate I and
O. Note
Decreased
urinary
output.
Weigh as
indicated. Be
alert for acute
or sudden
weight gain.
Monitor
infusion rate
or parenteral
fluids closely;
administer via
control
device/
infusion pump
as necessary.
Maintain a
Semi-Folwer
position.
Decreased
renal perfusion,
cardiac
insufficiency,
and fluid shifts
may cause
decreased
urinary output
and edema
formation.
One liter of
fluid retention
equals a weight
gain of 2.2 lbs.
Sudden fluid
bolus/
prolonged
excessive
administration
potentiates
volume
overload or risk
of cardiac
decompensatio
n.
Gravity
improves lung
expansion by
Trixia T. Camporedondo 4AN2 Intensive Care Unit August 26-27, 2014
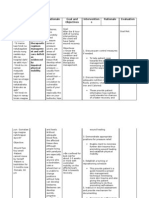
Turn,
reposition,
and provide
skin care at
regular
intervals.
Provide safety
precautions;
raise the side
rails and self
restraint.
Collaborative:
Monitor
laboratory
includes BUN,
ABG's and
electrolytes.
Administer
lowering
diaphragm and
shifting fluids
lower
abdominal
cavity.
Reduces
pressure and
friction in
edematous
tissue.
Note: Use of
restraint may
increase
agitation and
can pose a
safety threat.
Extracellular
fluid shifts,
sodium/ water
restriction and
renal function
all affect serum
sodium levels.
To achieve
Trixia T. Camporedondo 4AN2 Intensive Care Unit August 26-27, 2014
diuretics as
ordered by
the physician:
loop diuretics
e.g.,
Furosemide
(Lasix).
excretion of
fluid.
Você também pode gostar
- Pediatric Shelf NotesDocumento20 páginasPediatric Shelf NotesRajanAinda não há avaliações
- Resident On Call PDFDocumento143 páginasResident On Call PDFMuhammad RezaAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Transfusion 2Documento11 páginasBlood Transfusion 2Anusha VergheseAinda não há avaliações
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocumento5 páginasAltered Renal Perfusion CRFGen Ramos- SolisAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento3 páginasNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis of Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento4 páginasNursing Diagnosis of Fluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- NCP Ischemic StrokeDocumento3 páginasNCP Ischemic StrokeEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- List of The PhobiaDocumento8 páginasList of The PhobiaRjvm Net Ca FeAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento2 páginasFluid Volume ExcessRodel Yacas100% (5)
- 1. Assist with ambulation, as toleratedDocumento2 páginas1. Assist with ambulation, as toleratedIngrid Sasha Fong100% (4)
- NCP EsrdDocumento9 páginasNCP EsrdWilmar AngeloAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- 6 Urinary EliminationDocumento5 páginas6 Urinary EliminationkhautedameAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureKian Herrera100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing DiagnosisDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing DiagnosisJoehoney BarreraAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormal Labour: Perceptor: Dr. Nurul Islamy, M. Kes., Sp. OGDocumento54 páginasAbnormal Labour: Perceptor: Dr. Nurul Islamy, M. Kes., Sp. OGramadhiena destia100% (1)
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 páginasNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP HemoDocumento2 páginasNCP HemoJigs HechAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue Perfusionderic83% (29)
- NoncomplianceDocumento3 páginasNoncomplianceChristy BerryAinda não há avaliações
- NCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento5 páginasNCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputJillian AmponinAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute PainDocumento4 páginasNCP Acute PainSj 斗力上Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP Cardiogenic ShockDocumento3 páginasNCP Cardiogenic ShockTrixia Camporedondo100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionDocumento6 páginasFluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionKristel Abe100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento4 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionClariz Basco100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDocumento2 páginasNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFNoel Cabamongan88% (8)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Generalized Edema and Fluid Volume Excess (38Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan for Generalized Edema and Fluid Volume Excess (38Angel Moorer92% (12)
- Fluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsDocumento5 páginasFluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsMerrill HansAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDocumento2 páginasRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPAlbean DelojeroAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Documento3 páginasNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- Assessing Fluid Volume Status and Renal FunctionDocumento2 páginasAssessing Fluid Volume Status and Renal FunctionMei Payumo100% (1)
- Braun Neurology Endoscope SystemDocumento132 páginasBraun Neurology Endoscope SystemMārcis RancānsAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocumento2 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocumento4 páginasNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocumento3 páginasFluid Volume Excess NCPƦя de GuzмѧN80% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocumento5 páginasNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento1 páginaIneffective Tissue PerfusionEuanne Orellano85% (13)
- Esrd NCPDocumento7 páginasEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Hemodialysis NCPDocumento2 páginasHemodialysis NCPAfia Tawiah33% (3)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocumento4 páginasFluid Volume ExcessChristine Quirona100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocumento3 páginasNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Essential Newborn CareDocumento104 páginasEssential Newborn CareNacel Celeste100% (11)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 páginasNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputDheza Rodis Santos0% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocumento3 páginasFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahAinda não há avaliações
- NCP AfDocumento3 páginasNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotAinda não há avaliações
- Independent nurse midwifery practitioner issuesDocumento8 páginasIndependent nurse midwifery practitioner issuesKrishnaveni Murugesh100% (3)
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrAinda não há avaliações
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeDocumento4 páginasNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanAinda não há avaliações
- Pt Pain Relief Prostate EnlargementDocumento2 páginasPt Pain Relief Prostate EnlargementBobby Valencerina100% (1)
- NCPDocumento6 páginasNCPKyla Carbonel100% (1)
- NCP HypertensionDocumento1 páginaNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocumento1 páginaActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Pleural EffusionDocumento3 páginasNCP Pleural EffusionEli Xma100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocumento1 páginaNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For FrostbiteDocumento2 páginasNCP For FrostbiteRommar RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocumento3 páginasFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocumento2 páginasRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocumento1 páginaCritical Thinking ExerciseMaye ArugayAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento2 páginasImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 páginasNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocumento5 páginasNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Priorities for Hemodialysis PatientsDocumento6 páginasNursing Care Plan Priorities for Hemodialysis PatientsPauling FrezAinda não há avaliações
- HemodialysisDocumento4 páginasHemodialysisJon Adam Bermudez SamatraAinda não há avaliações
- Comparing blood donation knowledge among science and non-science studentsDocumento10 páginasComparing blood donation knowledge among science and non-science studentsGaoudam NatarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Quality and Safety Guidelines of Postanaesthesia CareDocumento7 páginasQuality and Safety Guidelines of Postanaesthesia CareAdi CărbunaruAinda não há avaliações
- General Anesthetic.: Presented by Jayesh Doke (S.Y B Pharm) S.G.D.C.P, JalgaonDocumento54 páginasGeneral Anesthetic.: Presented by Jayesh Doke (S.Y B Pharm) S.G.D.C.P, JalgaonJayesh DokeAinda não há avaliações
- Name:Putri Al Zahra Prodi:S1 Keperawatan Semester: 2: Tugas Individu B. InggrisDocumento6 páginasName:Putri Al Zahra Prodi:S1 Keperawatan Semester: 2: Tugas Individu B. InggrisPutri Al ZahraAinda não há avaliações
- Mindanao Medical Foundation College: P. Villanueva ST., Agdao, Davao City Tel. No. (082) 221-6225Documento5 páginasMindanao Medical Foundation College: P. Villanueva ST., Agdao, Davao City Tel. No. (082) 221-6225Miles Asia DieroAinda não há avaliações
- TOG 2007 983-87 Review Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Part 2 AcquiredDocumento5 páginasTOG 2007 983-87 Review Cardiac Disease in Pregnancy Part 2 Acquiredsaeed hasan saeedAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation Otitis ExternaDocumento24 páginasPresentation Otitis ExternaRichard GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Intensive Revision Course in Paediatrics (Poster)Documento2 páginasIntensive Revision Course in Paediatrics (Poster)Chris Jardine LiAinda não há avaliações
- Sde105 PDFDocumento37 páginasSde105 PDFMahaManthraAinda não há avaliações
- History of Urolithiasis: Garabed EknoyanDocumento9 páginasHistory of Urolithiasis: Garabed EknoyanErwin WibowoAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Surgical Clinical Pathway For Patient For AppendectomyDocumento70 páginasIntegrated Surgical Clinical Pathway For Patient For AppendectomyAllein Antonio-GeganteAinda não há avaliações
- Educational Preparation: Jones Marina N.V Associate Professor Meenakshi College of NursingDocumento63 páginasEducational Preparation: Jones Marina N.V Associate Professor Meenakshi College of NursingjonesmarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Rodriguez2005-Cognitive Dysfunction After Total Knee Arthroplasty - Effects of Intraoperative Cerebral Embolization and Postoperative ComplicationsDocumento9 páginasRodriguez2005-Cognitive Dysfunction After Total Knee Arthroplasty - Effects of Intraoperative Cerebral Embolization and Postoperative ComplicationsSyahpikal SahanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy and HeartDocumento53 páginasPregnancy and HeartgibreilAinda não há avaliações
- Ectopic Pregnancy GuideDocumento27 páginasEctopic Pregnancy GuideuunuunuunAinda não há avaliações
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento16 páginasPostpartum HemorrhageLuayon FrancisAinda não há avaliações
- Joni DialogDocumento3 páginasJoni DialogJoni TriliwijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS)Documento2 páginasIndian Public Health Standards (IPHS)Nikcy N M NicklavoseAinda não há avaliações
- Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy PDFDocumento13 páginasTrigeminal Nerve Anatomy PDFvinaykishore0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PainDocumento51 páginasPathophysiology of PainSujatha J JayabalAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Regression AnalysisDocumento10 páginasMultiple Regression AnalysisRishi DograAinda não há avaliações