Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CN Topic 3
Enviado por
Sarge Chisanga0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
29 visualizações27 páginasecture 09 Exceptions
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoecture 09 Exceptions
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
29 visualizações27 páginasCN Topic 3
Enviado por
Sarge Chisangaecture 09 Exceptions
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 27
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 1
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Computer Networks
Topic 3:
Wireless Networking Standards
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Computer Networks
Topic 3 Lecture 1:
Wireless Devices
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.3
Scope and Coverage
This topic will cover:
Wireless devices
Wireless networking standards
Issues for wireless networks
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Issues for wireless networks
Wireless networking protocols
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 2
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.4
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this topic, students will be able to:
Explain the function and rationale of wireless
networking standards
Explain a range of contemporarywireless
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Explain a range of contemporary wireless
standards and their relevant applications
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.5
Wireless Networks
Wireless Networks are networks in which
electromagnetic waves carry the signal over part or
all of the communication path.
This is in contrast to networks that utilise physical
NCC Education Limited V1.0
media, such as fibre-optic cable, coaxial cable, etc.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.6
Advantages of Wireless
Increased mobility
Increased flexibility
Convenience
Opportunities to provide newservices
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Opportunities to provide new services
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 3
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.7
History of Wireless
Wireless technology has been around for a few
decades.
Take up was initially slow:
Low data transfer rates
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Little interoperability between different devices
High cost
Great increase in number of wireless networks due
to standardisation, greater speeds and reduced
costs
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.8
Wireless Devices
Computer peripherals
Wireless LANs
Bluetooth devices
RFID
NCC Education Limited V1.0
RFID
Many others, e.g. mobile telephones, TV remote
control, GPS, etc.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.9
Wireless Computer Peripherals - 1
Devices include mouse, printer, keyboard, scanner,
etc.
Can allow multiple devices to use the same
peripheral
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Removes the need for cumbersome cables
Limited flexibility by operating a little distance away
from the PC
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 4
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.10
Wireless Computer Peripherals - 2
Use two technologies:
Infrared (IR) is cheaper, has less interference, but
requires direct optical contact between the
peripheral and receiver.
R di f (RF) k i ll l l ti
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Radio frequency (RF) works in all angles relative
to the receiver, even with objects between the
peripheral and receiver, but it is more expensive.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.11
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
Wireless networking relies on a broadcast signal.
Suitably configured devices contain receivers that
pick up and understand the broadcast signal.
Devices can process data and broadcast signals as
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p g
well.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.12
WLAN Components - 1
Wireless Adapters (WA)
Capable of transmitting and receiving wireless
digital signals and are usually contained in the user
device
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Modern PCs, laptops, smartphones, etc. all come
with a wireless adapter.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 5
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.13
WLAN Components - 2
Access Points (AP)
Acts as a base station that receives and transmits
signals via radio waves
It provides the link between the devices and the
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p
network.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.14
Hotspots
A wireless client may be any device (computer or
peripheral) designed to use the same wireless
protocol as the access point.
A client must be in range of the access point.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
The area within range of an AP is known as a
hotspot.
Overlapping hotspots allow a wireless network to
cover a wide area.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.15
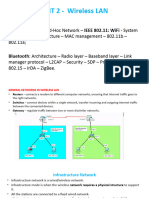
Bluetooth
A short range radio link with a range of around 10
metres
Allows a number of devices to link together in an
ad-hoc network
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Does not require line of sight
Can provide communication links between phones,
PDAs, computers, peripherals, etc
Can transmit voice and data
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 6
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.16
Piconets
The Bluetooth ad-hoc networks
Can have up to eight devices on the same piconet
Each piconet is synchronised to the clock of one
device on it (the master).
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Other devices are slaves
Several piconets may be active in the same
location.
Each device can be a part of several piconets, but
only master of one.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.17
RFID Tags
A radio frequency identification tag is a small object
that is attached to another object in order to identify
it via radio waves
Has two main components:
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Has two main components:
An integrated circuit that modulates and
demodulates a radio signal, stores data and
processes information
Antenna for transmitting/receiving
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.18
RFID Tag Uses
A wide range of uses including:
Passports
Travel cards
Wildlife tracking
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wildlife tracking
Stocktaking in shops
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 7
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.19
Other Wireless Devices
There are many devices in common use that are
wireless:
Mobile telephones
TV
Satellite communications
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Pagers (e.g. hospital)
Remote alarms
GPS
Remote controls (TV, model aircraft)
Two-way radio ..
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Computer Networks
Topic 3 Lecture 2:
Wireless Networking Standards
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.21
Wireless Standards
IEEE 802.11 series Wireless LAN
Bluetooth/IEEE 802.15 - Wireless Personal Area
Network
IEEE 802.16 - Wireless Metropolitan Area
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p
Networks
IEEE 802.20 - Mobile Broadband Wireless
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 8
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.22
Why Do We Need Standards?
There are a number of key reasons for creating
and adhering to standards for wireless networking.
Interoperability
Different devices work together
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Many equipment manufacturers
Customers can switch for better price or features
Allocation of frequencies
The radio wave spectrum is used for many
applications
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.23
The IEEE 802.11 standards
WLAN or WiFi
Wireless LAN Media Access Control and Physical
Layer specification
Contains a number of revisions and interpretations:
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p
802.11a,b,g,etc. are amendments to the original
802.11 standard
Products that implement 802.11 standards must
pass tests and are referred to as "Wi-Fi certified.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.24
The Original IEEE 802.11
Data rates of up to 2 Mbps
Uses Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS) or Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
(DSSS) signalling techniques
NCC Education Limited V1.0
2.4 GHz frequency range
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 9
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.25
IEEE 802.11 Revisions - 1
802.11a
Uses Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing
(OFDM)
Enhanced data speed to 54 Mbps
5 GHz frequency range
NCC Education Limited V1.0
802.11b
Added higher data rate modes to DSSS
Data speeds up to 11 Mbps
22 MHz Bandwidth yields 3 non-overlapping channels
in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz frequency band.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.26
IEEE 802.11 Revisions - 2
802.11d
Enhancement to 802.11a and 802.11b allows for
global roaming
Particulars can be set at Media Access Control
(MAC) layer
NCC Education Limited V1.0
(MAC) layer
802.11e
Enhancement to 802.11 includes quality of service
features
Facilitates prioritisation of data, voice, and video
transmissions
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.27
IEEE 802.11 Revisions - 3
802.11g
Extends the maximum data rate in the 2.4 GHz
band, permits interoperation with 802.11b devices
Uses OFDM
54 Mbps, with fall-back speeds that include the b
NCC Education Limited V1.0
speed
802.11h
Deals with interference
802.11i
Deals with security
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 10
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.28
IEEE 802.11 Revisions - 4
802.11n
High speed WLAN
Can theoretically operate at bandwidths up to 600
Mbps
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Applications supporting 100 Mbps using the TCP/IP
protocol are available.
Uses Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO)
technology
Uses 5 GHz band
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.29
Which Version?
Most modern wireless routers will support 802.11n
plus 802.11b and 802.11g
Older routers may only support 802.11b and
NCC Education Limited V1.0
y y pp
802.11g
Higher speed networks should use 802.11n
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.30
IEEE 802.15/Bluetooth
IEEE 802.15 covers Wireless Personal Area
Networks (WPAN).
Working Group1 (IEEE 802.15.1) is a standard
based upon Bluetooth version 1.1.
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) is a
NCC Education Limited V1.0
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) is a
separate non-profit organisation that oversees the
Bluetooth standards.
The Bluetooth SIG and IEEE are not related
No IEEE standards match recent Bluetooth
standards
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 11
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.31
Bluetooth
Openwireless technology standard
Exchanges data over short distances
Uses short wavelength radio transmissions
Usedin fixed and mobile devices
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Used in fixed and mobile devices
Creates Personal Area Networks (PANs)
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.32
Bluetooth Range
The range is specific to the application.
The Core Specification states a minimum range of
10 metres or 30 feet.
However, there is no set limit.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
,
Manufacturers are allowed to tune their devices to
provide the range they require.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.33
Bluetooth Spectrum
Operates in the unlicensed industrial, scientific and
medical (ISM) band
Frequencies 2.4 to 2.485 GHz are used
Uses a spread spectrum, frequency hopping, full-
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p p , q y pp g,
duplex signal at a nominal rate of 1600 hops/sec.
The 2.4 GHz ISM band is available and unlicensed
in most countries.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 12
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.34
Bluetooth Interference
Adaptive frequency hopping (AFH) reduces
interference between wireless technologies sharing
the 2.4 GHz spectrum.
The technology detects other devices in the
NCC Education Limited V1.0
spectrum and avoids the frequencies they are
using.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.35
Bluetooth Range
Range depends on class of radio used:
Class 3 radios have a range of up to 1 metre or 3
feet
Class 2 radios, most commonly found in mobile
NCC Education Limited V1.0
y
devices, have a range of 10 metres or 33 feet
Class 1 radios, used primarily in industrial devices,
have a range of 100 metres or 300 feet
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.36
IEEE 802.16
Mobile Broadband Wireless Access
Also known as WiMAX (from "Worldwide
Interoperability for Microwave Access")
Provides up to 40 Mbps
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p p
Currently working on the IEEE 802.16mupdate
Expected to offer up to 1 Gbps fixed speed
Required for 4G networks
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 13
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.37
WiMAX Usage
Provides mobile broadband or at-home broadband
connectivity across whole cities or countries.
Deploying a WiMAX network has low cost in
comparisonto DSL or Fibre-Optic
NCC Education Limited V1.0
comparison to DSL or Fibre Optic.
Can provide broadband in remote locations
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.38
Comparison with WiFi
WiMAX covers many km and uses an unlicensed
spectrum to provide access to a local network.
Wi-Fi is more popular in end user devices.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
802.11 supports direct, ad hoc or peer-to-peer
networking between end user devices without an
access point, while 802.16 end user devices must
be in range of the base station.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.39
IEEE 802.20
Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA)
Aims to enable worldwide deployment of
interoperable mobile broadband wireless access
networks, including:
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Mobile and ubiquitous Internet access
Transparent support of Internet applications
Access to enterprise intranet services
Transparent access to infotainment and location
services
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 14
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.40
IEEE 802.20 Detail
Bandwidths of 5, 10, and 20 MHz
Peak data rates of 80 Mbps
Uses MIMO
Supports low-bit rates efficiently carrying up to 100
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Supports lowbit rates efficiently, carrying up to 100
phone calls per MHz
Allows network access whilst travelling at speeds
of 250 km/h
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Computer Networks
Topic 3 Lecture 3:
Issues for Wireless Networks
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.42
Wireless Issues
There are a number of issues that may cause
concern for those using radio frequencies for
network media rather than physical cables, these
include:
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Range
Interference
Security
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 15
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.43
Range
The range where wireless signals can be reliably
transmitted and received is a key parameter for a
wireless network.
In ideal conditions, a WLAN can have a range of
NCC Education Limited V1.0
300m or more.
Real world conditions are not ideal.
In an office/home, range can drop as low as 10m.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.44
Indoor Range
WLANs are normally implemented indoors and a
number of factors will affect the range of the
network:
Building design
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Construction materials
Room layout
The location and type of other electrical devices
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.45
Installation
Technically simple regarding installation and
configuration
Installation does need to take into account the
NCC Education Limited V1.0
location of:
access points
networked devices
obstacles
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 16
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.46
Interference
Radio frequency signals can be negatively affected
by other radio signals in the same frequency band.
There are two main sources of such signals:
NCC Education Limited V1.0
g
Reflected signals from the wireless network itself
Other electrical equipment
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.47
Multipath
Radio frequency signals can be affected by signals
bouncing off building surfaces and other obstacles
Signals can come from multiple directions
(multipath)
Maycancel or reduce signal strength
NCC Education Limited V1.0
May cancel or reduce signal strength
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.48
Eliminating Multipath
Most access appointments include software tools
that analyse signal strength.
These can be used to test signal strength of
networked computers.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Most networked equipment can be moved to
improve signal strength.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 17
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.49
External Interference
Radio emissions from other devices using the
same frequency band are a source of interference
There are particular industries where this is a
problem
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Hospitals use a lot of monitoring equipment that
may use the same frequency
Equipment may need to be isolated to prevent the
interference.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.50
Security Issues
Security can be compromised in different ways
from hard-wired networks.
Radio transmission cannot be limited to within the
network premises.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Therefore, the transmitted signals can be
intercepted by devices outside of a building and
this data could include sensitive business or
personal data.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.51
Driveby Hacking
Any IEEE 802.11 receiving device using the
relevant standard could pick up a transmitted
signal.
A hacker could be located near a business
NCC Education Limited V1.0
premises and pick up these signals.
As the signals are broadcast, there would be no
way of knowing that an unauthorised person had
accessed the signal.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 18
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.52
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
The first major attempt to make wireless networks
as secure as wired networks
Susceptible to eavesdropping
Has been deprecated by IEEE as it does not meet
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p y
its security goals
Still widely in use
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.53
WiFi Protected Access (WPA)
Brought in as an improvement on WEP
WPA is more secure and comes in two forms
A form using pre-shared keys for home networks
A more secure formusing an authentication server
NCC Education Limited V1.0
A more secure form using an authentication server
for business networks
WPA has also been cracked and been replaced by
WPA2 which is more secure.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.54
Bluetooth Security
There are a number of known security flaws with
Bluetooth devices and these include:
Bluejacking
Bluesnarfing
NCC Education Limited V1.0
g
Bluebugging
Bluetoothing
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 19
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.55
Bluejacking
The hacker sends a phone contact or business
card to another nearby phone.
The name' field of the contact can be misused by
replacingit with a suggestive text
NCC Education Limited V1.0
replacing it with a suggestive text.
This is equivalent to spam email since both are
unsolicited messages displayed on recipients' end
without consent.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.56
Bluesnarfing
Accesses or steals data like messages, such as a
calendar or phone book from the target device.
There have been reports of the tools that use
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p
methods such as device address guessing and
brute force in order to break-in, even when device
is configured as invisible.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.57
Bluebugging
The target device is controlled by the attacker who
sends commands as if they had physical access.
Similar to a trojan
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 20
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.58
Bluetoothing
Short range social networking
Harassment of individuals within range
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.59
Securely Using Bluetooth
Keep devices in the disabled state, enable it only
when needed
Keep the device in non-discoverable mode
Do not accept any unknown and unexpected
request for pairing your device
NCC Education Limited V1.0
request for pairing your device
Use non regular patterns as PIN keys
Keep a check of all paired devices and delete any
paired device which you are not sure about
Register your device at the manufacturer site
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Computer Networks
Topic 3 Lecture 4:
Wireless Networking Protocols
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 21
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.61
Protocol Stacks
Wireless networks have layered protocol stacks
like other networks.
We will not deal with the higher level layers.
We will examine protocol stacks and specific
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p p
technologies of:
WLAN
Bluetooth
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.62
WLAN Protocol Stack
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.63
WLAN LLC & MAC Layers
LLC designed to provide the functionality of the
High-Level Data Link Control protocol of
the standard TCP/IP protocol stack
LLC allows an 802 11 protocol stack to be grafted
NCC Education Limited V1.0
LLC allows an 802.11 protocol stack to be grafted
underneath any TCP/IP implementation with little or
no change to the upper layers
MAC provides the same functions as in other
protocol stacks
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 22
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.64
WLAN PHY Layer
Original 802.11 standard defined three specific
physical network protocols:
An infrared communications standard
A Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) RF
t l
NCC Education Limited V1.0
protocol
A Frequency-Hopping Spread Spectrum
(FHSS) RF protocol
Later versions of the 802.11 standard redefined the
physical layer to be DSSS only.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.65
Bluetooth Protocol Stack - 1
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.66
Bluetooth Protocol Stack - 2
The bottom layer of the stack is the HCI, the Host
Controller Interface
This is the interface between the host (e.g. a
computer) and the controller (e.g. a Bluetooth
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p ) ( g
device).
The layer above is L2CAP, the Logical Link
Controller Adaptation Protocol
This acts as the data multiplexer for other layers.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 23
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.67
Bluetooth Protocol Stack - 3
Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol
(BNEP)
Allows the running of other networking protocols,
such as IP, TCP, and UDP, over Bluetooth
RFCOMM is the virtual serial port protocol
NCC Education Limited V1.0
RFCOMM is the virtual serial port protocol
Allows a Bluetooth device to simulate the functions
of a serial port
Service Discovery Protocol (SDP)
Used whenever you want to find services on a
remote Bluetooth device
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.68
Bluetooth Protocol Stack - 4
The Object Exchange layer (OBEX) protocol layer
Implemented above the RFCOMM layer and is
useful when you want to transfer data as an object,
such as files
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.69
Audio/visual control transport protocol (AVCTP)
and Audio/visual data transport protocol
(AVDTP)
- Used to control and distribute audio and video over
Bluetooth Protocol Stack - 5
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Bluetooth
Used when you want to control the functions of a
media player or if you want stream audio in stereo
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 24
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.70
Wireless Technologies
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
Multiple Input Multiple Output
Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum
Adaptive FrequencyHopping
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Adaptive Frequency Hopping
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.71
FDM
Frequency division multiplexing (FDM) is a
technology that allows transmission of multiple
signals simultaneously over a single transmission
cable or wireless system.
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Each signal travels within its own unique frequency
range (carrier), which is modulated by the data
(text, voice, video, etc.).
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.72
OFDM
Orthogonal FDM is a spread spectrum technique.
Data is distributed over a large number of carriers,
spaced apart at precise frequencies.
Demodulators only pick up their own frequencies
and not other frequencies
NCC Education Limited V1.0
and not other frequencies.
The benefits of OFDM are:
high spectral efficiency
resiliency to interference
less distortion
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 25
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.73
MIMO
Multiple Input, Multiple Output OFDM
Uses multiple antennas to simultaneously
transmit/receive data
This spatial multiplexing increases data-
transmissionspeed by a factor equal to the number
NCC Education Limited V1.0
transmission speed by a factor equal to the number
of transmitting antennae
4 antennae =4 x speed
All data is transmitted in the same frequency band,
which utilises the spectrum very efficiently.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.74
FHSS
Bluetooth
Transmitter hops from frequency to frequency
hundreds of times per second
Pseudo-random number generation is used to
produce the sequence of frequencies
NCC Education Limited V1.0
produce the sequence of frequencies.
All stations use the same seed and hop to the
same frequency at the same time, thus staying
synchronised.
May use TDMA or CDMA
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.75
Time Division Multiple Access
Frequencies divided into time slots allocated to
individual users.
A user is allocated a slot on a single frequency and
then moved to another frequency
S l diff d ill b i d
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Several different data streams will be transmitted
on one frequency in short bursts with an allocated
timeslot
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 26
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.76
Code Division Multiple Access
Each transmitter may transmit over the whole
frequency spectrum all of the time.
Coding theory is used to separate all of the multiple
and simultaneous transmissions.
Comparisonof TDMA and CDMA
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Comparison of TDMA and CDMA
TDMA is like a classroom where each person takes a
turn to speak.
CDMA is like a classroom of people all speaking at the
same time but in different languages, so the messages
are only heard by people who speak that language.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.77
AFH
Adaptive frequency hopping reduces interference
between Bluetooth and other devices.
Transmission does not occur on channels that
have significant interference
NCC Education Limited V1.0
have significant interference.
Devices in the same frequency band and physical
area detect the presence of each other and adjust
their communication systems to reduce the amount
of frequency overlap.
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.78
DSSS
WLAN
Data is divided into small pieces
Each piece is allocated to a frequency channel on
the available spectrum
NCC Education Limited V1.0
p
Data is combined with a chipping code.
Chipping code helps resist interference and allows
for data recovery.
Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer Networks
V1.0 Visuals Handout Page 27
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.79
DSSS v FHSS
FHSS advantages:
Devices are usually cheaper
Uses less power
NCC Education Limited V1.0
DSSS advantages
Better performance
More reliable transmission
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.80
References
Tanenbaum, A.S. & Weatherall, D.J . (2010).
Computer Networks, 5
th
edition. Pearson
Education.
Rysavy, P. (2002). Networking Standards and
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Wireless Networks. Netmotion Wireless.
IEEE website: http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/802/
Bluetooth website: https://www.bluetooth.org
IBM website: http://www.ibm.com
Wireless Networking Standards Topic 3- 3.81
Topic 3 Wireless Networking Standards
NCC Education Limited V1.0
Any Questions?
Você também pode gostar
- Computer Networks: Topic 3: Wireless Networking StandardsDocumento81 páginasComputer Networks: Topic 3: Wireless Networking StandardsKay TunAinda não há avaliações
- WirelessNets Lect 03 WLAN Part1 SP2016Documento20 páginasWirelessNets Lect 03 WLAN Part1 SP2016PranaySingireddyAinda não há avaliações
- Scope and Coverage: Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer NetworksDocumento27 páginasScope and Coverage: Topic 3 - Wireless Networking Standards Computer NetworksFranklin DorobaAinda não há avaliações
- EC301 Chapter 5 (5.1 and 5.2)Documento46 páginasEC301 Chapter 5 (5.1 and 5.2)Ayu WafaAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Network NotesDocumento15 páginasWireless Network NotesLearn SAPAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Design Considerations in (IACS)Documento97 páginasWireless Design Considerations in (IACS)thenneberry61Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod6 - ReviewDocumento27 páginasMod6 - Reviewmichael.santiago15Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch02 Wireless Local Area NetworksDocumento57 páginasCh02 Wireless Local Area NetworksvasanthmeAinda não há avaliações
- Cwna Guide To Wireless Lans, Second Edition: Chapter OneDocumento39 páginasCwna Guide To Wireless Lans, Second Edition: Chapter Onekoppala47Ainda não há avaliações
- Understanding Network Basics: Wireless TechnologiesDocumento26 páginasUnderstanding Network Basics: Wireless Technologiesnishasaiyed2304Ainda não há avaliações
- Wireless and Mobile Communications Course OverviewDocumento45 páginasWireless and Mobile Communications Course OverviewArsalanAinda não há avaliações
- TM255 - Block 1 Part 3Documento64 páginasTM255 - Block 1 Part 3Doaa SalamaAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless and Mobile ComputingDocumento520 páginasWireless and Mobile ComputingFembiRekrisnaGrandeaPutraAinda não há avaliações
- WiFi vs Bluetooth ComparisonDocumento18 páginasWiFi vs Bluetooth Comparisonnaruto_3Ainda não há avaliações
- 3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Documento36 páginas3G vs. Wifi: Presented By:-DEEPAK GUPTA 0911HDSSD104Deepak GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- MN - Unit 2Documento50 páginasMN - Unit 212c04gokulsboaAinda não há avaliações
- CHAP 2bDocumento47 páginasCHAP 2bGANESAN AAinda não há avaliações
- WIFIDocumento24 páginasWIFIVidhila Vidhi100% (2)
- Chapter 3. Wireless Networks and Wan Technologies 1398-2-24-14-59Documento70 páginasChapter 3. Wireless Networks and Wan Technologies 1398-2-24-14-59BereketAinda não há avaliações
- Explaining operations of zigbee, WiFi, infrared and Bluetooth networksDocumento9 páginasExplaining operations of zigbee, WiFi, infrared and Bluetooth networksViJay KuMarAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Wireless TechnologyDocumento67 páginasIntroduction To Wireless TechnologyOlasupo OkunaiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Wimax Quick GuideDocumento16 páginasWimax Quick GuideramyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bluetooth and Wi-FiDocumento38 páginasBluetooth and Wi-FibudhcAinda não há avaliações
- Comparing Wired and Wireless NetworksDocumento2 páginasComparing Wired and Wireless NetworksÇoktiklananlar TiklananlarAinda não há avaliações
- Wifi Technology GuideDocumento27 páginasWifi Technology GuideAbhishek PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless LAN: Cisco Ccna BootcampDocumento28 páginasWireless LAN: Cisco Ccna BootcampRoger Embalsado100% (1)
- Lesson 5-Wireless NetworkDocumento38 páginasLesson 5-Wireless NetworkJ A Y T R O NAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 5-Wireless NetworkDocumento38 páginasLesson 5-Wireless NetworkJ A Y T R O NAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless NetworkingDocumento6 páginasWireless NetworkingPiyush SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-Ii Mobile ComputingDocumento6 páginasUnit-Ii Mobile ComputingPiyush SinghAinda não há avaliações
- L3 - Computer System - WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SET UP - WLANDocumento21 páginasL3 - Computer System - WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SET UP - WLANInnoxAinda não há avaliações
- Air FiberDocumento10 páginasAir Fibergacojoy270Ainda não há avaliações
- WPAN Chapter 4 OverviewDocumento27 páginasWPAN Chapter 4 OverviewRdsharukh DaroorAinda não há avaliações
- WCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 2Documento22 páginasWCC VTU Module 2 Additional Data 2Sushíl kanikeAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE Standard 802.16 For Global Broadband Wireless AccessDocumento33 páginasIEEE Standard 802.16 For Global Broadband Wireless Accesswork067Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter04 Latest)Documento8 páginasChapter04 Latest)Muhamad HafiziAinda não há avaliações
- Wi-Fi Hostel ReportDocumento11 páginasWi-Fi Hostel ReportMicah ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- WLANs and Wireless TechnologiesDocumento12 páginasWLANs and Wireless TechnologiesKeshan Shanuka PereraAinda não há avaliações
- Cst476 Mobile Computing 3Documento31 páginasCst476 Mobile Computing 3Ajin JosephAinda não há avaliações
- WLANDocumento26 páginasWLANAftab PopatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Networking CT043-3-1 Wireless NetworksDocumento46 páginasIntroduction To Networking CT043-3-1 Wireless Networksyoges_0695Ainda não há avaliações
- Telecommunication: The Exchange of Information in Any Form (Voice, Data, Text, Images, Audio, Video) Over NetworksDocumento40 páginasTelecommunication: The Exchange of Information in Any Form (Voice, Data, Text, Images, Audio, Video) Over NetworksLintang Panjar RinoAinda não há avaliações
- Telecommunication: The Exchange of Information Over NetworksDocumento40 páginasTelecommunication: The Exchange of Information Over NetworksNadia RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- A Paper Presentation On: The Dawn of New Technical EraDocumento17 páginasA Paper Presentation On: The Dawn of New Technical Erajyothsnas28Ainda não há avaliações
- 4G Wireless PresentationDocumento26 páginas4G Wireless PresentationArjun ShankaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesDocumento41 páginasWeek 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesAffif FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IVDocumento54 páginasUnit IVChetan SaiAinda não há avaliações
- Zigbee FinalDocumento29 páginasZigbee FinalcvmgreatAinda não há avaliações
- Recent TrendsDocumento28 páginasRecent Trendsashokyadav739Ainda não há avaliações
- Tilak Maharashtra University Technical Seminar on 4G Broadband TechnologyDocumento29 páginasTilak Maharashtra University Technical Seminar on 4G Broadband TechnologyChaitra RautAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless - Merits & DemeritsDocumento10 páginasWireless - Merits & DemeritsAnirudhan RaviAinda não há avaliações
- Wifi Vs BluetoothDocumento17 páginasWifi Vs BluetoothSIVA PRASADAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless LAN and WAN TechnologyDocumento25 páginasWireless LAN and WAN TechnologyPro NebyuAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Networks: Presented byDocumento27 páginasWireless Networks: Presented bypan_lee2Ainda não há avaliações
- WPAN Overview and TechnologiesDocumento3 páginasWPAN Overview and TechnologiesRamel PoliusAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Implementation of WIFI MAC Transmitter For Low Power ApplicationsDocumento8 páginasDesign and Implementation of WIFI MAC Transmitter For Low Power ApplicationsPadma RatnaAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Grid PresentationDocumento52 páginasSmart Grid PresentationMuhammad AfzalAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsNo EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Mobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyNo EverandMobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- YDF Guide RevisedDocumento19 páginasYDF Guide RevisedrefilwedAinda não há avaliações
- M500-20 (5-Digit Preset) PDFDocumento4 páginasM500-20 (5-Digit Preset) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Single Wall Farm Skid Tanks DrawingDocumento1 páginaSingle Wall Farm Skid Tanks DrawingSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- Removal and Disposal of Storage TanksDocumento9 páginasRemoval and Disposal of Storage TanksSrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- M100-30 (Gear Plate Selection Guide) PDFDocumento24 páginasM100-30 (Gear Plate Selection Guide) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Controls: Mechanical Temperature Volume CompensatorsDocumento8 páginasLiquid Controls: Mechanical Temperature Volume CompensatorsSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- MANUAL REPAIR SeptembetGT500Documento3 páginasMANUAL REPAIR SeptembetGT500Sarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- TNS Single Wall Horizontal Skid Tanks DrawingDocumento1 páginaTNS Single Wall Horizontal Skid Tanks DrawingSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- 0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocumento4 páginas0580 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teacherssuperbmars18Ainda não há avaliações
- M100-20 (MS Meters) PDFDocumento40 páginasM100-20 (MS Meters) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Engen Primax UnleadedDocumento1 páginaEngen Primax UnleadedSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- M400-20 (V & VS-Series Valves) PDFDocumento24 páginasM400-20 (V & VS-Series Valves) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Division P17 Procurement and Installation For Water MetersDocumento17 páginasDivision P17 Procurement and Installation For Water MetersSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- BiofuelDocumento1 páginaBiofuelSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- M100-20 (MS Meters) PDFDocumento40 páginasM100-20 (MS Meters) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M400-60 (Check Valves) PDFDocumento8 páginasM400-60 (Check Valves) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M400-20 (V & VS-Series Valves) PDFDocumento24 páginasM400-20 (V & VS-Series Valves) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M500-10 (4-Digit Preset) PDFDocumento16 páginasM500-10 (4-Digit Preset) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M-Series Meters MA - Series Meters: Installation Manual & Setup GuideDocumento28 páginasM-Series Meters MA - Series Meters: Installation Manual & Setup GuideSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- M100-11 (MA4 Meter) PDFDocumento32 páginasM100-11 (MA4 Meter) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M400-30 (K-Series Valves) PDFDocumento12 páginasM400-30 (K-Series Valves) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M400-40DK (Disass'y Kit)Documento1 páginaM400-40DK (Disass'y Kit)Sarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- M200-10 (Strainers) PDFDocumento16 páginasM200-10 (Strainers) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Controls: V-7 ValvesDocumento16 páginasLiquid Controls: V-7 ValvesSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- M300-21 (Optical Vapor Eliminator) PDFDocumento9 páginasM300-21 (Optical Vapor Eliminator) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M400-80 (500 Series Valves) PDFDocumento12 páginasM400-80 (500 Series Valves) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- M200-20 (HiCap Strainers) PDFDocumento12 páginasM200-20 (HiCap Strainers) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Controls: EP SeriesDocumento16 páginasLiquid Controls: EP SeriesSarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- LCR - Iq Wiring - Rev-J - Final - 0Documento1 páginaLCR - Iq Wiring - Rev-J - Final - 0Sarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- Lc-On The Go ™ - Setupguide - V1 - 062017Documento12 páginasLc-On The Go ™ - Setupguide - V1 - 062017Sarge ChisangaAinda não há avaliações
- PRE EmtionDocumento10 páginasPRE EmtionYahya JanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment-2: MCA204 Financial Accounting and ManagementDocumento6 páginasAssignment-2: MCA204 Financial Accounting and ManagementrashAinda não há avaliações
- Royalty-Free License AgreementDocumento4 páginasRoyalty-Free License AgreementListia TriasAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS Summary: Discover HerbicideDocumento6 páginasMSDS Summary: Discover HerbicideMishra KewalAinda não há avaliações
- Nature of ConversionDocumento18 páginasNature of ConversionKiranAinda não há avaliações
- Beams On Elastic Foundations TheoryDocumento15 páginasBeams On Elastic Foundations TheoryCharl de Reuck100% (1)
- Project The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDDocumento7 páginasProject The Ant Ranch Ponzi Scheme JDmorraz360Ainda não há avaliações
- Dairy DevelopmentDocumento39 páginasDairy DevelopmentHemanth Kumar RamachandranAinda não há avaliações
- Theme Meal ReportDocumento10 páginasTheme Meal Reportapi-434982019Ainda não há avaliações
- Bar Exam 2016 Suggested Answers in Political LawDocumento15 páginasBar Exam 2016 Suggested Answers in Political LawYlnne Cahlion KiwalanAinda não há avaliações
- Analyze Oil Wear DebrisDocumento2 páginasAnalyze Oil Wear Debristhoma111sAinda não há avaliações
- Okuma Osp5000Documento2 páginasOkuma Osp5000Zoran VujadinovicAinda não há avaliações
- CAP Regulation 20-1 - 05/29/2000Documento47 páginasCAP Regulation 20-1 - 05/29/2000CAP History LibraryAinda não há avaliações
- Inflatable Packers enDocumento51 páginasInflatable Packers enDavid LuhetoAinda não há avaliações
- CCS PDFDocumento2 páginasCCS PDFАндрей НадточийAinda não há avaliações
- AnkitDocumento24 páginasAnkitAnkit MalhotraAinda não há avaliações
- Eritrea and Ethiopia Beyond The Impasse PDFDocumento12 páginasEritrea and Ethiopia Beyond The Impasse PDFThe Ethiopian AffairAinda não há avaliações
- CFEExam Prep CourseDocumento28 páginasCFEExam Prep CourseM50% (4)
- Product Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssembliesDocumento10 páginasProduct Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssemblieslmarcheboutAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Institute of Management KozhikodeDocumento5 páginasIndian Institute of Management KozhikodepranaliAinda não há avaliações
- Oop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Documento14 páginasOop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Hashir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Group 4-Hospital Information System - His - QuizDocumento2 páginasGroup 4-Hospital Information System - His - QuizGeeyan Marlchest B NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- 13-07-01 Declaration in Support of Skyhook Motion To CompelDocumento217 páginas13-07-01 Declaration in Support of Skyhook Motion To CompelFlorian MuellerAinda não há avaliações
- 158 Oesmer Vs Paraisa DevDocumento1 página158 Oesmer Vs Paraisa DevRobelle Rizon100% (1)
- Difference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDocumento2 páginasDifference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDharma Teja TanetiAinda não há avaliações
- Gary Mole and Glacial Energy FraudDocumento18 páginasGary Mole and Glacial Energy Fraudskyy22990% (1)
- 50TS Operators Manual 1551000 Rev CDocumento184 páginas50TS Operators Manual 1551000 Rev CraymondAinda não há avaliações
- Micromaster 430: 7.5 KW - 250 KWDocumento118 páginasMicromaster 430: 7.5 KW - 250 KWAyman ElotaifyAinda não há avaliações
- Berry B Brey Part IDocumento49 páginasBerry B Brey Part Ikalpesh_chandakAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 SEED in Role ActivityDocumento2 páginasWeek 3 SEED in Role ActivityPrince DenhaagAinda não há avaliações