Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Drying Evaporation English
Enviado por
lovehope0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
24 visualizações1 páginaDrying Evaporation
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDrying Evaporation
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
24 visualizações1 páginaDrying Evaporation English
Enviado por
lovehopeDrying Evaporation
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
9
THERMAL PROCESS ENGINEERING DRYING AND EVAPORATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
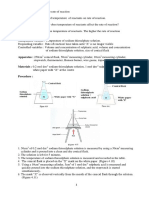
Principle of increasing the concentration of a solution by evaporating the solvent:
A solution before evaporation of solvent,
B more concentrated solution after evaporation of solvent,
Q
.
addition of heat, 1 dissolved solid, 2 solvent
In general, drying refers to the removal of moisture from solids, gases
or liquids. For drying gases and liquids, adsorption is normally used.
The food technology industry is an example of where drying solids on
a large scale is important.
Thermal drying of solids involves removing moisture from the
material by vaporisation or evaporation. The drying characteristics
depend on how the moisture is retained within the material. In the
first instance, the liquid adhering to the surface of the material to
be dried can be removed by vaporisation or evaporation. Once this
liquid has been removed, drying of the moisture contained within
the capillaries and pores of the material begins. The drying speed
reduces due to the need to overcome capillary forces and diffusion
resistance. Crystal water which is bonded into the crystal structure of
the material, can only be removed by intense heating in addition to
low drying speed.
Drying characteristics of a solid with division into drying sections (I - IV):
dX/ dt drying rate, X moisture content [kg (water) / kg (dry solid)],
t drying time;
I surface moisture, II capillary moisture, III pore moisture,
IV moisture in crystal structure
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
In the context of thermal
process engineering, evapora-
tion is understood to be the
separation of a solvent from a
solution. An example of a solu-
tion is salt water, in which salt
(the dissolved solid) is present
in the solvent, i.e. water. The
addition of heat exclusively
evaporates the pure solvent
(water in this example) from
the solution and carries it away.
The remaining solution thus
has a higher concentration
of dissolved solid than before
the addition of heat.
EVAPORATION DRYING
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Fuels and Combustion: Types, Analysis and UsesDocumento28 páginasFuels and Combustion: Types, Analysis and UsesMidhunRameshThuvasseryAinda não há avaliações
- EUV Lithography and Source TechnologyDocumento47 páginasEUV Lithography and Source TechnologyGabriel DonovanAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation and Optimization of Hydrogen Production From Autothermal Reforming of Ethane For Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocumento91 páginasSimulation and Optimization of Hydrogen Production From Autothermal Reforming of Ethane For Fuel Cell ApplicationsainmnrhAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4 - Physical Science PDFDocumento10 páginasModule 4 - Physical Science PDFDarry Blancia100% (1)
- 1st Law of Thermo WorksheetDocumento2 páginas1st Law of Thermo WorksheetAngelica Calamba CalicaAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Cooling Techniques ARCHITECUREDocumento8 páginasPassive Cooling Techniques ARCHITECURERHYME KIDSAinda não há avaliações
- 106720070205Documento8 páginas106720070205lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Uttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworkDocumento3 páginasUttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworklovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetric Nursing Sample ChapterDocumento14 páginasObstetric Nursing Sample ChapterlovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- CBSPD 2014 Pharmaceutical Price ListDocumento24 páginasCBSPD 2014 Pharmaceutical Price Listlovehope100% (1)
- J. Org. Chem., 1962, 27 (9), PP 3236-3239Documento4 páginasJ. Org. Chem., 1962, 27 (9), PP 3236-3239lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Bytes October 13-65-88 - FinalDocumento24 páginasBytes October 13-65-88 - FinallovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 - 13 - Article 5Documento4 páginas2014 - 13 - Article 5lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Developing a bio-relevant dissolution method for EfavirenzDocumento4 páginasDeveloping a bio-relevant dissolution method for EfavirenzlovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- SolutionsDocumento14 páginasSolutionsHazem DiabAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry ExpDocumento4 páginasChemistry ExplovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- A C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SDocumento5 páginasA C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SlovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of PharmacologyDocumento10 páginasIntroduction of PharmacologylovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- PeetersDocumento5 páginasPeeterslovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Attachment C454ea4cDocumento32 páginasAttachment C454ea4clovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- J Jep 2005 01 031Documento2 páginasJ Jep 2005 01 031lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 11Documento4 páginasExp 11lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of NMR - James PDFDocumento31 páginasFundamentals of NMR - James PDFSoundarya ChandramouleeswaranAinda não há avaliações
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocumento4 páginasExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- J Biomaterials 2012 03 046Documento18 páginasJ Biomaterials 2012 03 046lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- SolubilityDocumento10 páginasSolubilityOmar S. SalihAinda não há avaliações
- Exp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonateDocumento5 páginasExp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonatelovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 4Documento4 páginasExp 4lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationDocumento6 páginasExp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationlovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder PuzzlesDocumento5 páginasExp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder Puzzleslovehope0% (1)
- Exp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrieneDocumento5 páginasExp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrienelovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder PuzzlesDocumento5 páginasExp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder Puzzleslovehope0% (1)
- Exp 11Documento4 páginasExp 11lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 31Documento4 páginasExp 31lovehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Basic of ThermodynamicsDocumento12 páginasBasic of ThermodynamicsTeeranun NakyaiAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Hydronium-Ion Battery With Ultralong LifeDocumento7 páginasOrganic Hydronium-Ion Battery With Ultralong LifeNoisy RequiemAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Conversion and Management: Mohamed Lachheb, Mustapha Karkri, Fethi Albouchi, Foued Mzali, Sassi Ben NasrallahDocumento9 páginasEnergy Conversion and Management: Mohamed Lachheb, Mustapha Karkri, Fethi Albouchi, Foued Mzali, Sassi Ben NasrallahsaltyAinda não há avaliações
- Sherubtse College Faculty of Mathematics and Computer ScienceDocumento9 páginasSherubtse College Faculty of Mathematics and Computer ScienceSampa Nima YoezerAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Saving Research of Natural Gas Liquefaction Plant Based On Waste Heat Utilization of Gas Turbine ExhaustDocumento11 páginasEnergy Saving Research of Natural Gas Liquefaction Plant Based On Waste Heat Utilization of Gas Turbine ExhaustAbelardo Nardo Guzmán LavadoAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE 2013 Chemistry Question Paper DownloadDocumento5 páginasCBSE 2013 Chemistry Question Paper DownloadKhushi ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Primary Hydrocarbon Recovery Exam KeyDocumento7 páginasFundamentals of Primary Hydrocarbon Recovery Exam KeyEdward ZhouAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Fluid Chillers: Design for Reliable OperationDocumento7 páginasPrinciples of Fluid Chillers: Design for Reliable OperationAzim AdamAinda não há avaliações
- Session 6 - Analytical Chem - Complexation and Precipitation Part 2Documento22 páginasSession 6 - Analytical Chem - Complexation and Precipitation Part 2MehdiAinda não há avaliações
- 10 - Chapter5Documento50 páginas10 - Chapter5Mahdi AL-oqilyAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Ceramics Chapter 1Documento38 páginasFundamentals of Ceramics Chapter 1Tamiru MisikirAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Gas Laws with Kinetic Molecular Theory SimulationsDocumento5 páginasUnderstanding Gas Laws with Kinetic Molecular Theory SimulationsAdam CrabbAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Methacrylate Co-Agents On Peroxide Cured PP Epdm Thermoplastic VulcanizatesDocumento17 páginasEffect of Methacrylate Co-Agents On Peroxide Cured PP Epdm Thermoplastic VulcanizatesFairmont Ind Quality DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- !doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Documento4 páginas!doctype H P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)jenisatrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Di (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexDocumento5 páginasDi (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexGoutam BissoyiAinda não há avaliações
- Cutting Methods and Perspectives of Carbon NanotubesDocumento25 páginasCutting Methods and Perspectives of Carbon NanotubesHanee Farzana HizaddinAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5Documento3 páginasExperiment 5Andrea KingAinda não há avaliações
- BMITablePropertiesofSaturatedRefrigerant22inSIUnitsDocumento17 páginasBMITablePropertiesofSaturatedRefrigerant22inSIUnitsStar GlacierAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Documento70 páginasSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)NOREEN KAYE ROYOAinda não há avaliações
- Wave OpticsDocumento33 páginasWave OpticsmisspayujiAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledDocumento11 páginasAn Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledCicero LimaAinda não há avaliações
- 12U Chem Final June 05bDocumento14 páginas12U Chem Final June 05bedeceAinda não há avaliações
- Class 11 Annual ExamDocumento9 páginasClass 11 Annual ExamAshraf KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Chemistry A Molecular Approach 4th Edition by Tro ISBN 0134112830 9780134112831Documento36 páginasTest Bank For Chemistry A Molecular Approach 4th Edition by Tro ISBN 0134112830 9780134112831shawnramirez06042001jzc100% (23)