Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nutritions: What Is Nutrition?
Enviado por
Naavenesh RaoTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nutritions: What Is Nutrition?
Enviado por
Naavenesh RaoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
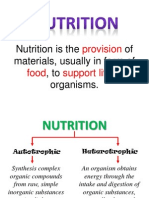
NUTRITIONs
WHAT IS NUTRITION?
The process that organisms obtain energy from food, for growth, maintenance and repair of
damage tissue
TYPES OF NUTRITION
1) Autotrophs (self, feed)
* Photosynthesis (Green plants)
* Chemosynthesis (Bacteria synthesis organic compounds by oxidising inorganic compounds -
ammonia)
2) Heterotrophs (cannot synthesise their own food)
* Holozoic (Herbivours, Carnivours & Omnivours)
* Saprophytic (Organisms fed on dead / decaying matter
* Parasitic (Organisms obtains nutrient by living on/ in the body of other living organisms
BALANCE DIET
* Balance diet: a diet which contains the right amounts of carbohydrate, proteins, fat,
vitamins, mineral, water and fibers.
* Healthy diet: should provide the body with all the substances necessary to maintain growth,
to keep good health and repair damage tissue.
WHAT ARE THE FACTORS THAT EFFECTING THE DAILY ENERGY REQUIREMENT?
Climate!
Colder place need more energy to maintain body temp.
because of the lost of energy to the surrounding.
FACTORS EFFECTING DAILY ENERGY REQUIREMENT
* Body size - The smaller person have a larger surface per unit volume compare to a larger
person, the rate of heat loss is higher, they need more energy.
* Gender - Male need more energy because they are more active & the metabolic rate is
higher then female.
* Growing children have higher metabolic rate than older people. They need more energy.
* Occupation - Person does heavy work needs more energy than a person who is only
moderately active.
NUTRIENTS IN FOOD
* Carbohydrates: (rice, noodles, potatoes)
o Source of energy for motion and growth
o Used to form supporting structures in plants (cell wall)
o Effective methods for food storage (starch/glycogen)
o Part of nucleus (DNA)
o Lack of it : become very weak
* Proteins : (meat, fish, cheese, eggs)
o Make new cells for growing
o Repair & Replace damaged cells/tissues
o Make enzymes, antibodies & hormones
o Lack of it: kwashiorkor, very weak, muscle are poorly developed
* Fat : ( oils, butter, milk, nuts)
o Supply energy
o Part of cell membrane
o Help absorb certain vitamins (ADEK)
o Too much: excess fat stored under the skin (obese)
o Too little: vitamins wont be absorbed, cell membrane wont be formed normally
* Vitamins:
o To protect health.
o Biological catalyst for chemical reaction in
the body.
o 2 categories:
i) Fat soluble vitamins
+ A,D,E,K
+ Stored in the body fat
+ No need to consume everyday (stored in
the body)
ii) Water soluble vitamins
+ C and B (8 types)
+ Dissolved easily in water, easily lost
+ Cannot be stored in the body, need to be
consumed everyday.
Vitamin Source Functions Defiency
Vitamin
A
Milk, green leaf, butter,
tomatoes, cod liver, egg
Normal growth,
healthy eyes &
skin.
Night blindness
Vitamin
B1
Milk, peas, cereals, green
leaf.
Growth &
development
Beriberi (disease
affects the nervous
system).
Vitamin
B2
Peas, yeast, egg, meat Healthy skin
growth
Skin disease,
retarded growth
Vitamin
B4
Whole cereals, potatoes,
tomatoes, meat, fish
Healthy skin,
digestive &
nervous system
Pellagra (disease
affect the skin,
alimentary canal &
nervous system).
Vitamn c Tomatoes, green leaf,
vegetables, fruits.
Healthy growth,
strong blood
vessels
Scurvy (gums easily
bleed).
Vitamin
D
Sunlight, milk, butter Strong bones &
teeth
Rickets ( Soft
bones & deformed
on children)
Vitamin
E
Vegetables, oils, milk, butter. : Protect the cell
membrane.
Affect fertility.
Vitamin
K
Green vegetables, Soya bean
oils
Help in clotting the
blood
Help in clotting the
blood
* Mineral salts:
o Major trace mineral- required in large amount
o Minor trace mineral- required in small amount
* Iron - Formation of heamoglobin
* Calcium - Strong bones & teeth, muscle contractions, clotting blood
* Phosphorus - Strong bones
* Potassium - Growth & osmotic balance
* Sodium - Osmotic balance, proper functioning of nervous system
* Iodine - Body metabolism, development of brain
* Roughage/ fiber
o Higher water holding capacity
o Help peristalsis / bowel movement
o Prevent from constipation
o Lower the cholesterol
o Reduce the risk of heart disease
* Water:
o Medium for biochemical reactions
o Medium for transportation of respiratory gases
o Regulates body temp.
o Removes excretory waste
o Maintain osmotic pressure
o Aids peristaltic movement
o Hydrolyse some food substances
o Dissolve most chemical substances
SPECIAL DIET
* Pregnant lady
Need more nutrient to provide more energy to meet the need of my growing fetus
o Folate brain development
o Iron prevent from anemic
o Calcium - growth of babys bone & teeth
* Baby
Need mothers milk to provide me with energy & nutrient.
* Children
They are active & love to play. They need carbohydrates to give us energy and protein to
develop new tissue.
* Vegetarian
They need supplement in order to complete their need.
* Diabetic
Low sugar.
* Teenagers
o Carbohydrates provides energy (theyre active)
o Protein still growing
o Iron menstruation (girl)
* Athletes
Carbohydrates they need more energy.
MALNUTRITION
* Starvation insufficient amount of food
* Eating disorder:
o Anorexia Nervosa Girls believe themselves to be fat (theyre extremely thin), dont want to
eat.
Bulimia Over concern with body weight, eat a lot and then force themselves to vomit.
* Overweight/ Obesity - high risk of diabetes, hypertension, heart attack
* Over consumption of cholesterol & saturated fat:
o Can cause arthrosclerosis (build up fatty deposits in the coronary arteries/ blood vessels.
* Constipation: lack of dietary fiber.
Class Of Chemicals
Cells need various types of organic and inorganic compounds to enable them to carry out their
functions, as well as build their cellular components. While organic compounds contain the
element carbon, inorganic compounds do not.
Below is the classified descriptions of chemical compound.
Carbohydrate
* Starch made up of long chain of glucose
* The ratio of C:H:O in it is 1:2:1
* Cellulose that strengthens the cell walls of plants
* Maltose can be converted into glucose by hydrolysis
* Its glucose molecules can be converted into glycogen
Lipid
* Cholesterol is an example of it
* Fats have the triglyceride molecules in them
* Fatty acids can be saturated and unsaturated
* The hormone testosterone is an example of it
Nucleic Acid
* An example is the DNA found in the nucleus of a cell
* Genetic material that directs protein synthesis
* Contain pentose sugars and phosphate groups
Protein
* Amino acids are its building blocks
* Nearly all enzymes are examples of it
* The haemoglobin molecules in the red blood cells
* Builds muscles and aids growth
Water
* An inorganic compound with no carbon in it
* A polar molecule with two H atoms and one O atom
* A universal solvent
* Acts as a medium for reactions in one's body
Você também pode gostar
- Diet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Documento52 páginasDiet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Ina100% (1)
- Emily Ness - The Testosterone ChefDocumento210 páginasEmily Ness - The Testosterone ChefJake Masters100% (2)
- Macronutrients and MicronutrientsDocumento49 páginasMacronutrients and MicronutrientsrahmarosyidahAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition 101 Presentation PDFDocumento20 páginasNutrition 101 Presentation PDFViktória MolnárAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurvedic Concept of Food and NutritionDocumento8 páginasAyurvedic Concept of Food and NutritionsatishAinda não há avaliações
- Year 10 BiologyDocumento38 páginasYear 10 BiologyChyrsella VerenaAinda não há avaliações
- Components of FoodDocumento37 páginasComponents of Foodrathee1966Ainda não há avaliações
- Vitamins MCQs PDFDocumento5 páginasVitamins MCQs PDFBijay Kumar MahatoAinda não há avaliações
- NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDocumento11 páginasNUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDon Maur ValeteAinda não há avaliações
- Food Nutrients and NutritionDocumento10 páginasFood Nutrients and NutritionAceAinda não há avaliações
- Iodometric Analysis For Vitamin C Lab ReportDocumento9 páginasIodometric Analysis For Vitamin C Lab ReportAlleia Mae Urbano Mazo78% (9)
- Nutrient Depletion GuideDocumento2 páginasNutrient Depletion GuideMichael CabarlesAinda não há avaliações
- Personalities of MineralsDocumento125 páginasPersonalities of MineralsManuel DíazAinda não há avaliações
- Food and Nutrition Revision NotesDocumento9 páginasFood and Nutrition Revision NotesNiamh Marie McCarville100% (3)
- Public Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationDocumento36 páginasPublic Health Nutrition: Its Importance For Health Promotion & Health PreservationSumaia Rahman100% (1)
- The Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterDocumento21 páginasThe Different Sources and Function of Nutrients: Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, Carbohydrates, Fats, WaterCharity Faith EnriquezAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6. Human EnergyDocumento8 páginasLesson 6. Human EnergyLoveyysolonAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionDocumento5 páginasBiology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionzaedmohdAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Nutrition?Documento7 páginasWhat Is Nutrition?hema lathaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Animal Nutrition B5.01 DietDocumento4 páginasGrade 8 Animal Nutrition B5.01 DietAmy BeacherAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 NuritionDocumento54 páginasChapter 2 NuritionteacherYatie82Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit - 2A Nutritional Elements:: Carbohydrate, Protein, Fats and MineralsDocumento34 páginasUnit - 2A Nutritional Elements:: Carbohydrate, Protein, Fats and MineralsEvet VaxbmAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Vitamins & NutrientsDocumento8 páginasEssential Vitamins & NutrientsPritamveer SirviAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition: How The Body Uses FoodDocumento5 páginasNutrition: How The Body Uses FoodMuda MuditaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Six Essential Nutrients (Macro & Micronutrients)Documento127 páginasChapter 1 Six Essential Nutrients (Macro & Micronutrients)Dolly Jane JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Components of FoodDocumento23 páginasComponents of FoodMigi Moncy JacobAinda não há avaliações
- Folio Form 2 Nutrition IIDocumento11 páginasFolio Form 2 Nutrition IIEncik Amir Kamal100% (1)
- Balance Diet 321Documento5 páginasBalance Diet 321Aroob YaseenAinda não há avaliações
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocumento24 páginasStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanAinda não há avaliações
- Stage I. Health ProblemsDocumento24 páginasStage I. Health ProblemsBalajinagarajan AlagappanAinda não há avaliações
- THesisDocumento21 páginasTHesismahoojhaaseAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition BasicsDocumento15 páginasNutrition BasicsMandeep DalorAinda não há avaliações
- NUTRITIONDocumento5 páginasNUTRITIONDesy Ayu SukmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Grade-12Documento5 páginasChapter 5 Grade-12umamahfarooq75Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Food ManagementDocumento11 páginasAdvanced Food ManagementRenDenverL.DequiñaIIAinda não há avaliações
- Green White Illustration Vegetables Healthy Balanced Diet PresentationDocumento31 páginasGreen White Illustration Vegetables Healthy Balanced Diet PresentationEvangeline De OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of HoustonDocumento20 páginasNutrition 101: Brought To You by The University of Houstonriki187Ainda não há avaliações
- The Body's Need For Food (Autosaved)Documento33 páginasThe Body's Need For Food (Autosaved)nina lykka calaraAinda não há avaliações
- L-7 Public Health Nutrition (PHN)Documento50 páginasL-7 Public Health Nutrition (PHN)Asta BlackAinda não há avaliações
- Summarizing The Text (Nutrition)Documento5 páginasSummarizing The Text (Nutrition)Shobibur rohmah maulidiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 NutritionDocumento24 páginasUnit 5 Nutritionyarutewelde5.yaredteweldeAinda não há avaliações
- Formerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of Midwifery: 2. Identify and Discuss The Function of Macro and Micro NutrientsDocumento20 páginasFormerly: Notre Dame Hospital and School of Midwifery: 2. Identify and Discuss The Function of Macro and Micro NutrientsMhianne SarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)Documento26 páginasChapter 7 Section 1 (Nutrients)lolyvwuAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 105 Prelims NotesDocumento24 páginasNCM 105 Prelims NotesJustine FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Food & Nutrition: Indian Hills Middle SchoolDocumento15 páginasFood & Nutrition: Indian Hills Middle SchoolAlfie DilagAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Basic NutDocumento5 páginas6 Basic Nutshellym127Ainda não há avaliações
- Nutrition: How The Body Uses FoodDocumento3 páginasNutrition: How The Body Uses FoodEmanuela CosaccoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Human NutritionDocumento45 páginasChapter 7 Human Nutritionjzdf2d9nnvAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONDocumento31 páginasUnit 7-HUMAN NUTRITIONfreefortnie75Ainda não há avaliações
- Itsmejarong PE 01 NutritionDocumento21 páginasItsmejarong PE 01 Nutritiondave lucasAinda não há avaliações
- Provision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsDocumento37 páginasProvision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsSanthiya MadhavanAinda não há avaliações
- 26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Documento6 páginas26 July 2018: Geology 101 Report Page ! of ! 1 2Anshu MovvaAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Finding Sindi NurhayatiDocumento5 páginasTugas Finding Sindi NurhayatiSindi NurhayatiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Nutrition - 0Documento23 páginasIntroduction To Nutrition - 0Nezlyn Cressida D'SouzaAinda não há avaliações
- #1 Nutrients Group: PrelimDocumento18 páginas#1 Nutrients Group: PrelimEster Libunao DollagaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6: Health Eating Habits Lesson ObjectivesDocumento13 páginasLesson 6: Health Eating Habits Lesson ObjectivesJewel BerbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Proteins: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSC Fundamentals of Human NutritionDocumento32 páginasProteins: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSC Fundamentals of Human NutritionYouness Abou SalehAinda não há avaliações
- Ch10 NutritionDocumento38 páginasCh10 NutritionMs RoxannaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3Documento33 páginasModule 3Saalif RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Sports &nutrition 12thDocumento4 páginasSports &nutrition 12thPavitra Kumar JainAinda não há avaliações
- Muhamad Nazrul Bin Zainol Abidin 2011834644 Ahmad Zulkhairi Bin Mohamad 2011664074 Mohd Khairul Darimi Bin Abdu Rani 2011870072 Mohd Hairy Bin RamliDocumento63 páginasMuhamad Nazrul Bin Zainol Abidin 2011834644 Ahmad Zulkhairi Bin Mohamad 2011664074 Mohd Khairul Darimi Bin Abdu Rani 2011870072 Mohd Hairy Bin RamliMuhamad Nazrul BoyoteenAinda não há avaliações
- Macronutrien TS: Alexander John Apuang Allessandria Daphne Bagacina Alyssa Kristine RealuyoDocumento49 páginasMacronutrien TS: Alexander John Apuang Allessandria Daphne Bagacina Alyssa Kristine RealuyoAllessandria Daphne Sac BagacinaAinda não há avaliações
- Let Us Study Things That Are No More.: It Is Necessary To Understand Them, If Only To Avoid Them.Documento9 páginasLet Us Study Things That Are No More.: It Is Necessary To Understand Them, If Only To Avoid Them.Naavenesh RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Pt3 (English)Documento6 páginasPt3 (English)Naavenesh RaoAinda não há avaliações
- HUNAROBO Workbook SampleDocumento10 páginasHUNAROBO Workbook SampleNaavenesh RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Pt3 (English)Documento6 páginasPt3 (English)Naavenesh RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of VitaminsDocumento6 páginasIntroduction of VitaminsBenny HermawanAinda não há avaliações
- Chat GPTDocumento4 páginasChat GPTnewtihstishAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin A Deficiency QuestionnaireDocumento6 páginasVitamin A Deficiency QuestionnaireBagus Ananta50% (2)
- Q&A Plant PhysiologyDocumento202 páginasQ&A Plant PhysiologyLhu CerdonAinda não há avaliações
- Composition of Vernoniaamygdalina and Its Potential Health BenefitsDocumento13 páginasComposition of Vernoniaamygdalina and Its Potential Health BenefitsIJEAB JournalAinda não há avaliações
- 2MS File 3 Lesson PlansDocumento17 páginas2MS File 3 Lesson PlansPearla WawaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional Comparison Between Brown Rice and White RiceDocumento2 páginasNutritional Comparison Between Brown Rice and White RiceSouvik TewariAinda não há avaliações
- CHM151 Experiment 1Documento2 páginasCHM151 Experiment 1Foo Zhi YuanAinda não há avaliações
- EWG's 2010 Sunscreen GuideDocumento54 páginasEWG's 2010 Sunscreen GuideEnvironmental Working GroupAinda não há avaliações
- Eto Gawa KoDocumento14 páginasEto Gawa KoBarangay San PabloAinda não há avaliações
- c18 Enzymes Vitamins HormonesDocumento3 páginasc18 Enzymes Vitamins HormonesShashank KukretiAinda não há avaliações
- VitaminsDocumento3 páginasVitaminsJayaprabhu PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- RicketsDocumento5 páginasRicketsNader SmadiAinda não há avaliações
- Imani-Lara Lansiquot Masterclass: Half Marathon Guide Shakes For DaysDocumento70 páginasImani-Lara Lansiquot Masterclass: Half Marathon Guide Shakes For DaysArnav GautamAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional Requirements of Animal Cells in Culture-SerumDocumento51 páginasNutritional Requirements of Animal Cells in Culture-SerumMahesh Aithal0% (1)
- Nutrition of Adolescent Girls in Low and Middle Income CountriesDocumento12 páginasNutrition of Adolescent Girls in Low and Middle Income CountriesmanalAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of BiochemDocumento19 páginasImportance of BiochemAmal100% (1)
- IodatometricDocumento4 páginasIodatometricTYAAinda não há avaliações
- Bernard English EczDocumento50 páginasBernard English EczKeen SqúìshAinda não há avaliações
- MushroomsDocumento3 páginasMushroomsjunver100% (1)
- Whitening Injection Informed ConsentDocumento3 páginasWhitening Injection Informed ConsentCalix Jr Rambuyon0% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Environmetal and Nutritional DiseasesDocumento12 páginasChapter 9 - Environmetal and Nutritional DiseasesAgnieszka WisniewskaAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Gizi Ibu HamilDocumento11 páginasJurnal Gizi Ibu Hamilrina astutiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento17 páginasChapter 3Geoana Jane BadenasAinda não há avaliações