Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
DLD&CO
Enviado por
sj8190 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
48 visualizações8 páginasThis document discusses various types of combinational logic circuits including half adders, full adders, multiplexers, demultiplexers, and decoders. It provides block diagrams, truth tables, and logic circuit diagrams to explain how each circuit functions. Specifically, it explains that a half adder can add two single bit binary numbers, a full adder can add two bits and a carry, a multiplexer selects one of several data inputs to output based on a code, and a decoder converts a binary code to activate one of multiple outputs.
Descrição original:
Combinational logic circuits
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document discusses various types of combinational logic circuits including half adders, full adders, multiplexers, demultiplexers, and decoders. It provides block diagrams, truth tables, and logic circuit diagrams to explain how each circuit functions. Specifically, it explains that a half adder can add two single bit binary numbers, a full adder can add two bits and a carry, a multiplexer selects one of several data inputs to output based on a code, and a decoder converts a binary code to activate one of multiple outputs.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
48 visualizações8 páginasDLD&CO
Enviado por
sj819This document discusses various types of combinational logic circuits including half adders, full adders, multiplexers, demultiplexers, and decoders. It provides block diagrams, truth tables, and logic circuit diagrams to explain how each circuit functions. Specifically, it explains that a half adder can add two single bit binary numbers, a full adder can add two bits and a carry, a multiplexer selects one of several data inputs to output based on a code, and a decoder converts a binary code to activate one of multiple outputs.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 8
Competency 3: Lecture Hour 1:
Combinational Logic Circuits
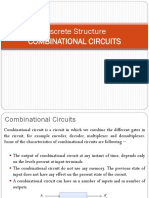
Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different gates in the
circuit for example encoder, decoder, multiplexer and de-multiplexer. Some of the
characteristics of combinational circuits are following.
The output of combinational circuit at any instant of time depends only on the levels
present at input terminals.
The combinational circuit do not use any memory. The previous state of input does
not have any effect on the present state of the circuit.
A combinational circuit can have n number of inputs and m number of outputs.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
We're going to elaborate few important combinational circuits as follows.
Half Adder
Half adder is a combinational logic circuit with two inputs and two outputs. The half
adder circuit is designed to add two single bit binary numbers A and B. It is the basic
building block for addition of two single bit numbers. This circuit has two
outputs carry and sum.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TRUTH TABLE
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Full Adder
Full adder is developed to overcome the drawback of Half Adder circuit. It can add
two one-bit numbers A and B, and carry c. The full adder is a three input and two
output combinational circuit.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TRUTH TABLE
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Competency 4: Lecture Hour 2
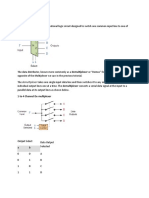
Multiplexers
Multiplexer is a special type of combinational circuit. There are n-data inputs, one
output and m select inputs with 2m = n. It is a digital circuit which selects one of the n
data inputs and routes it to the output. The selection of one of the n inputs is done by
the selected inputs. Depending on the digital code applied at the selected inputs, one
out of n data sources is selected and transmitted to the single output Y. E is called the
strobe or enable input which is useful for the cascading. It is generally an active low
terminal that means it will perform the required operation when it is low.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Multiplexers come in multiple variations
2 : 1 multiplexer
4 : 1 multiplexer
16 : 1 multiplexer
32 : 1 multiplexer
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TRUTH TABLE
Competency 4: Lecture Hour 3
De-multiplexers
A de-multiplexer performs the reverse operation of a multiplexer i.e. it receives one
input and distributes it over several outputs. It has only one input, n outputs, m select
input. At a time only one output line is selected by the select lines and the input is
transmitted to the selected output line. A de-multiplexer is equivalent to a single pole
multiple way switch as shown in fig.
De-multiplexers come in multiple variations
1 : 2 de-multiplexer
1 : 4 de-multiplexer
1 : 16 de-multiplexer
1 : 32 de-multiplexer
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TRUTH TABLE
Competency 4: Lecture Hour 4
Decoder
A decoder is a combinational circuit. It has n input and to a maximum m = 2n outputs.
Decoder is identical to a de-multiplexer without any data input. It performs operations
which are exactly opposite to those of an encoder.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Examples of Decoders are following.
Code converters
BCD to seven segment decoders
Nixie tube decoders
Relay actuator
2 to 4 Line Decoder
The block diagram of 2 to 4 line decoder is shown in the fig. A and B are the two
inputs where D through D are the four outputs. Truth table explains the operations of
a decoder. It shows that each output is 1 for only a specific combination of inputs.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TRUTH TABLE
LOGIC CIRCUIT
Você também pode gostar
- Combinational Circuit Adder, Subtractor and MultiplexerDocumento24 páginasCombinational Circuit Adder, Subtractor and Multiplexerram5nath-3100% (1)
- A. Multiplexers: Combinational Circuit Is A Circuit in Which Different Gates Are CombinedDocumento4 páginasA. Multiplexers: Combinational Circuit Is A Circuit in Which Different Gates Are CombinedhaiqalAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational Logic CircuitsDocumento17 páginasCombinational Logic CircuitsAdarsha Bhattarai100% (1)
- Gates Half Adder Full Adder Combinational Circuits Decoder Encoder Multiplexer De-Multiplexer Stored Program Concept Flynn's ClassificationDocumento17 páginasGates Half Adder Full Adder Combinational Circuits Decoder Encoder Multiplexer De-Multiplexer Stored Program Concept Flynn's ClassificationRitika SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitDocumento15 páginasCombinational CircuitTanmay HazraAinda não há avaliações
- CombinationalcircuitDocumento23 páginasCombinationalcircuitMuhammad uzairAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento11 páginasCombinational CircuitsBruce LambAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational Circuits: UNIT-2Documento11 páginasCombinational Circuits: UNIT-2Kuldeep SainiAinda não há avaliações
- 3.unit III updatEDDocumento66 páginas3.unit III updatEDPrashant SarrafAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational Circuit Is A Circuit in Which We Combine The Different Gates in The CircuitDocumento13 páginasCombinational Circuit Is A Circuit in Which We Combine The Different Gates in The Circuitalvin castroAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3Documento58 páginasUnit 3Anji ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento18 páginasCombinational CircuitsSalil TimalsinaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics-6 PDFDocumento8 páginasDigital Electronics-6 PDFTapas BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics 4Documento8 páginasDigital Electronics 4Tapas BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- CS33CS1301CS1301 (SM5) PDFDocumento42 páginasCS33CS1301CS1301 (SM5) PDFMohitrajAinda não há avaliações
- Course Code: CS 281 Course Title: Digital Logic Design (DLD)Documento15 páginasCourse Code: CS 281 Course Title: Digital Logic Design (DLD)Niaz Ahmed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento44 páginasCombinational CircuitsWisdom tabuloAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignDocumento37 páginasChapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignSruthy SasiAinda não há avaliações
- L3: Multiplexer & Demultiplexer, Encoder & Decoder: Dr. Koushik BarmanDocumento19 páginasL3: Multiplexer & Demultiplexer, Encoder & Decoder: Dr. Koushik BarmanShiv shankar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento5 páginasCombinational CircuitsRafena17Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 - Combinational Logic CircuitsDocumento56 páginas2 - Combinational Logic CircuitsSiegrique Ceasar A. JalwinAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No:: Subject: Name: Rollno.Documento25 páginasAssignment No:: Subject: Name: Rollno.Sharad Patil DholeAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational Circuits: 4 To 2 EncoderDocumento5 páginasCombinational Circuits: 4 To 2 EncoderRafena MustaphaAinda não há avaliações
- Cpe101 HW 3Documento9 páginasCpe101 HW 3Fred UniraAinda não há avaliações
- DLLec7c NotesDocumento4 páginasDLLec7c NotesChintan MandalAinda não há avaliações
- DigitalDocumento85 páginasDigitalRaghavan23100% (2)
- Dec Lab QuestionsDocumento25 páginasDec Lab QuestionsPrathiksha Harish Medical Electronics EngineeringAinda não há avaliações
- MultiplexerDocumento22 páginasMultiplexerMa. Patricia PalibinoAinda não há avaliações
- Fallsem2019-20 Ece2003 Eth Vl2019201000898 Reference Material I 10-Sep-2019 Cat 2 Digital Note Book Without AnswerDocumento34 páginasFallsem2019-20 Ece2003 Eth Vl2019201000898 Reference Material I 10-Sep-2019 Cat 2 Digital Note Book Without AnswermrjAinda não há avaliações
- Msi Logic CircuitDocumento17 páginasMsi Logic CircuitAnonymous AyCl4LAinda não há avaliações
- Decoder and Encoder With ApplicationDocumento38 páginasDecoder and Encoder With ApplicationParth KapadiaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5 MUX DEMUXDocumento4 páginasExperiment 5 MUX DEMUXMD Sadique AnsariAinda não há avaliações
- Mult and DemultDocumento8 páginasMult and Demultkarim mohamedAinda não há avaliações
- DecoderDocumento9 páginasDecoderYves AbalosAinda não há avaliações
- Combinational CircuitsDocumento19 páginasCombinational CircuitsjayaprabasAinda não há avaliações
- Dpco Book1Documento4 páginasDpco Book1SELVAM SAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplex Er 1Documento19 páginasMultiplex Er 1pkrk123456789100% (1)
- DD and COmodule 2Documento97 páginasDD and COmodule 2Madhura N KAinda não há avaliações
- UnityDocumento31 páginasUnitySiva GethuAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Logic Design: Subject - SemDocumento58 páginasDigital Logic Design: Subject - Semavi yadavAinda não há avaliações
- DSD Lab Manual AitdDocumento31 páginasDSD Lab Manual Aitdprathameshbhat88Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Combinational Functions1Documento106 páginasUnit 3 Combinational Functions1sharvarictamaneAinda não há avaliações
- 4 (Lec 9)Documento23 páginas4 (Lec 9)A HahaAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplexer/Decoder: 41.what Is Mux, Demux, and Decoder?Documento4 páginasMultiplexer/Decoder: 41.what Is Mux, Demux, and Decoder?ayushAinda não há avaliações
- 4-Cominational Circuit Design With Decoders, Multiplexers, and EncodersDocumento14 páginas4-Cominational Circuit Design With Decoders, Multiplexers, and EncodersHadeer GamalAinda não há avaliações
- BARUN KUMAR SINGH - ESC-301 - ReportDocumento14 páginasBARUN KUMAR SINGH - ESC-301 - ReportBARUN SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- DDL 06Documento8 páginasDDL 06Anonymous KLGejaVAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplex ErsDocumento22 páginasMultiplex ErsfjburgosfAinda não há avaliações
- The Demultiplexer Lecture NotesDocumento4 páginasThe Demultiplexer Lecture Notesraul gironella100% (1)
- Multiplexer and DemultiplexerDocumento18 páginasMultiplexer and DemultiplexerTara SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Encoder, DecoderDocumento39 páginasChapter 3 - Encoder, Decodernizar_ayub95Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture #8 - Combinational CircuitsDocumento13 páginasLecture #8 - Combinational CircuitsAhmadnur JulAinda não há avaliações
- Digital PracticalDocumento32 páginasDigital PracticalSaif Ali KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Practice4 (Adder & SustractorDocumento7 páginasPractice4 (Adder & SustractorManolo-Hues Diaz SAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento88 páginasUnit 2Navjot Kaur MahiAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Electronics PDFDocumento20 páginasDigital Electronics PDFVenkataKartheek NuneAinda não há avaliações
- DP - 26 DocumentationDocumento64 páginasDP - 26 DocumentationViplav SangvaiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Investigatory Project: Topic: To Construct AnDocumento24 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project: Topic: To Construct Anpradhumna dixitAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity From WalkingDocumento8 páginasElectricity From WalkingSanthosh100% (6)
- Digital Indicating Controller Sdc30: DigitronikDocumento12 páginasDigital Indicating Controller Sdc30: DigitronikAkurato Tunas MandiriAinda não há avaliações
- COMEM Cataloge - Spare-Parts - 12-05-2021Documento22 páginasCOMEM Cataloge - Spare-Parts - 12-05-2021VanaAinda não há avaliações
- Form 1 - General System Data: A) Basic System InformationDocumento15 páginasForm 1 - General System Data: A) Basic System InformationVenkataramanan S75% (4)
- ConvertersDocumento3 páginasConvertersnoddy10265Ainda não há avaliações
- Berchtold Chromophare D-530,540,650,660 - Preinstallation InformationDocumento14 páginasBerchtold Chromophare D-530,540,650,660 - Preinstallation InformationMahnaz BakhshiAinda não há avaliações
- Simatic Net Profibus Network Manual System ManualDocumento350 páginasSimatic Net Profibus Network Manual System ManualAlejandro Fernández SalasAinda não há avaliações
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) (Theory and Implementation)Documento54 páginasFast Fourier Transform (FFT) (Theory and Implementation)dshyam1991Ainda não há avaliações
- Tma SolutionDocumento2 páginasTma SolutionMinh NamAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank Module 1Documento6 páginasQuestion Bank Module 1Varshetha AAinda não há avaliações
- Mux Demux Encoder DecoderDocumento18 páginasMux Demux Encoder Decoderaryan.bhosale002Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet 1Documento3 páginasSheet 1Mohammad AmmarAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: Compact Component SystemDocumento93 páginasService Manual: Compact Component Systemsaputra ekaAinda não há avaliações
- Remotely Monitor and Control Multiple Transfer Switches: Hmi Remote Annunciator ControllerDocumento4 páginasRemotely Monitor and Control Multiple Transfer Switches: Hmi Remote Annunciator ControllerRajSekhar VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- UF4001 UF4007: 1.0 Amp High Efficiency RectifiersDocumento2 páginasUF4001 UF4007: 1.0 Amp High Efficiency RectifiersYonathan LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Synopsis RailwayDocumento8 páginasSynopsis RailwaySathwik HvAinda não há avaliações
- 630 FTIR Site Prep G8043-90020Documento4 páginas630 FTIR Site Prep G8043-90020abasakAinda não há avaliações
- Ecad Lab ManualDocumento83 páginasEcad Lab ManualJacklyn Untalan100% (1)
- Star-Star Connection of TransformerDocumento7 páginasStar-Star Connection of TransformerNavneet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Moving Head Mini Wash 555-12630Documento8 páginasMoving Head Mini Wash 555-12630ledaggettAinda não há avaliações
- Pipeline Locator VLoc Series 2 BrochureDocumento6 páginasPipeline Locator VLoc Series 2 Brochuresashikant31Ainda não há avaliações
- 43.1 Description of Flash Code 43: Ddec Iii/Iv Single Ecm Troubleshooting GuideDocumento4 páginas43.1 Description of Flash Code 43: Ddec Iii/Iv Single Ecm Troubleshooting GuideMarco Antonio Rubiano GómezAinda não há avaliações
- Sirit ID 6204 User GuideDocumento104 páginasSirit ID 6204 User GuidedavidbarrozoAinda não há avaliações
- Question: Yes, Consider The Half Wave Recti Er Circuit of G 4.21 A.) Above WDocumento1 páginaQuestion: Yes, Consider The Half Wave Recti Er Circuit of G 4.21 A.) Above WSsebass PozzoAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Control Systems A Textbook For Engineering StudentsDocumento695 páginasLinear Control Systems A Textbook For Engineering Studentsعزت عادل عزت محمد100% (2)
- Finite and Infinite Response Design FilterDocumento16 páginasFinite and Infinite Response Design FilterLUIS ROBERTO PONTILLAS. SOLIMANAinda não há avaliações
- Semiconductor MaterialsDocumento12 páginasSemiconductor MaterialsVaibhavAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4 - ElectrostaticsDocumento73 páginasModule 4 - ElectrostaticsIntilegienceAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: Food Processor HR7620 HR7625Documento3 páginasService Manual: Food Processor HR7620 HR7625Sorin OlteanuAinda não há avaliações