Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chemistry Final
Enviado por
At TanwiDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chemistry Final
Enviado por
At TanwiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
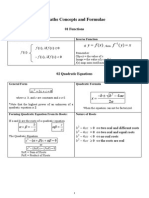
Short Notes Chemistry
Chemical Formulae and Equation
Calculation Calculation
Summary Summary
molar volume
molar volume
molar mass
Avogadro Constant
Number of
particles
Mole of
particles
Mass of particle
(in gram)
Avogadro Constant molar mass
Volume of
Gas
For Solid, liquid or gas
mass of subtance
number of mole =
molar mass
Molar mass =RAM/RMM/RFM in gram
For gas (only)
volume of gas
number of mole =
molar volme
Molar volume =24dm
3
at room temperature
Molar volume =22.4dm
3
at s.t.p.
For Solution
MV
number of mole =
1000
M =molarity
V =Volume of solution in cm
3
For quantity of particle(atom,molecule,ion)
23
quantity of particle
number of mole =
6.02 10
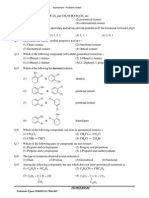
Chemical Formula
Cation (Positive Ions)
Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Ion Symbol
Potassium K
+
Calcium Ca
2+
Aluminium Al
3+
Sodium Na
+
Magnesium
Mg
2+
Iron (III) Fe
3+
Lithium Li
+
Zinc
Zn
2+
Chromium(III) Cr
3+
Hydrogen H
+
Barium
Ba
2+
Argentums(I) Ag
+
Iron (II)
Fe
2+
Mercury(I) Hg
+
Tin (II)
Sn
2+
Ammonium NH
4
+
Lead(II)
Pb
2+
Copper(II)
Cu
2+
Manganese(II)
Mn
2+
Anion (Negative Ions)
Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Ion Symbol
Oxide
O
2-
Hydroxide
OH
-
Ethanoate
CH
3
COO
-
Fluoride
F
-
Sulphate
SO
4
2-
Manganate(VII)
MnO
4
-
Chloride
Cl
-
Nitrate
NO
3
-
Dichromate(VI)
Cr
2
O
7
2-
Bromide
Br
-
Carbonate
CO
3
2-
Phosphate
PO
4
3-
Iodide
I
-
Thiosulphate
S
2
O
3
2-
Formulae for Certain Molecule
Karbon monoxide CO Ammonia NH
3
Carbon dioxide CO
2
water H
2
O
Nitrogen monoxide NO Hydrogen chloride HCl
Nitrogen dioxide NO
2
Tetrachloromethane CCl
4
Sulphur dioxide SO
2
Glucose C
6
H
12
O
6
Sulphur trioxide SO
3
Hydrogen bromide HBr
Fluorine F
2
Hydrogen iodide HI
Bromine Br
2
Hydrogen sulphide H
2
S
Chlorine Cl
2
Ethanol C
2
H
5
OH
Iodine I
2
Ethanoic Acid CH
3
COOH
Periodic Table
Reaction of Group 1 Elements
1. Reaction with Oxygen
The entire group 1 metal can react with oxygen to form metal oxide.
4Li +O
2
2Li
2
O
4Na +O
2
2Na
2
O
4K +O
2
2K
2
O
The metal oxide of group 1 elements can dissolve in water to form alkali (hydroxide) solution
Li
2
O +H
2
O 2LiOH
Na
2
O +H
2
O 2NaOH
K
2
O +H
2
O 2KOH
2. Reaction with halogen (Chlorine)
2Li +Cl
2
2LiCl
2Na +Cl
2
2NaCl
2K +Cl
2
2KCl
3. Reaction with water
The entire group 1 metal can react with water to produce alkali (hydroxide) solution and hydrogen gas.
2Li +2H
2
O 2LiOH +H
2
2Na +2H
2
O 2NaOH +H
2
2K +2H
2
O 2KOH +H
2
Reaction of Group 17 Elements
1. React with water
Cl
2
+H
2
O HCl +HOCl
Br
2
+H
2
O HBr +HOBr
I
2
+H
2
O HI +HOI
2. React with Sodium Hydroxide
Cl
2
+ 2NaOH NaCl + NaOCl + H
2
O
Br
2
+ 2NaOH NaBr + NaOBr + H
2
O
I
2
+ 2NaOH NaI + NaOI + H
2
O
3. React with Iron
3Cl
2
+2Fe 2FeCl
3
3Br
2
+2Fe 2FeBr
3
3I
2
+2Fe 2FeI
3
Preparation of Chlorine Gas
2KMnO
4
+16HCl 2KCl +2MnCl
2
+5Cl
2
+8H
2
O
Electrochemistry
Electrolyte
Ionisation of Electrolyte
Ionisation of Molten Compound
PbBr
2
Pb
2+
+Br
-
NaCl Na
+
+Cl
-
Al
2
O
3
2Al
3+
+3O
2-
Ionisation of Aqueous Solution
NaCl Na
+
+Cl
-
H
2
O H
+
+OH
-
HCl H
+
+Cl
-
H
2
O H
+
+OH
-
CuSO
4
Cu
2+
+SO
4
2-
H
2
O H
+
+OH
-
Discharge of Positive Ion Discharge of Negative Ion
Na
+
+e Na
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
Al
3+
+3e Al
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
Pb
2+
+2e Pb
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
Cu
2+
+2e Cu
Observation:
Brown deposit is formed.
Ag
+
+e Ag
Observation:
Silver deposit is formed.
2H
+
+2e H
2
Observation:
Gas bubble is formed. A pop sound is produced
when a lighted splinter is placed near the mouth of
the test tube.
2Cl
-
Cl
2
+2e
Observation:
Bubbles of pungent yellowish green gas are
produced. The gas turns moist litmus paper to red
and then bleaches it.
2Br
-
Br
2
+2e
Observation:
Molten electrolyte:
Brown colour gas is produced.
Aqueous solution:
Light brown solution is formed.
2I
-
I
2
+2e
Observation:
Molten electrolyte:
Brown colour gas is produced.
Aqueous solution:
Light brown solution is formed. The solution turns
blue when a few drops of starch solution is added in.
4OH
-
O
2
+2H
2
O +4e
Observation:
Gas bubble is formed. Gas produces light up a
wooden splinter.
Acid and Base
Ionisation of Acid
Hydrochloric Acid
HCl H
+
+Cl
-
HCl +H
2
O H
3
O
+
+Cl
-
Nitric Acid
HNO
3
H
+
+NO
3
-
HNO
3
+H
2
O H
3
O
+
+NO
3
-
Sulphuric Acid
H
2
SO
4
H
+
+SO
4
2-
H
2
SO
4
+2H
2
O 2H
3
O
+
+SO
4
2-
Ethanoic Acid
CH
3
COOH H
+
+CH
3
COO
-
CH
3
COOH +H
2
O H
3
O
+
+CH
3
COO
-
Chemical Properties of Acid
Acid + Reactive Metal Salt + H
2
Example:
2HCl +Zn ZnCl
2
+H
2
6HNO
3
+2Fe 2Fe(NO
3
)
3
+3H
2
H
2
SO
4
+Pb PbSO
4
+H
2
6CH
3
COOH +2Al 2Al(CH
3
COO)
3
+3H
2
Acid + Metal Oxide Salt + H
2
O
Example:
2HCl +ZnO ZnCl
2
+H
2
O
2HNO
3
+MgO Mg(NO
3
)
2
+H
2
O
H
2
SO
4
+CuO CuSO
4
+H
2
O
2CH
3
COOH +Na
2
O 2CH
3
COO
-
Na
+
+H
2
O
Acid + Metal Hydroxide Salt + H
2
O
Example:
2HCl +Ca(OH)
2
CaCl
2
+2H
2
O
HNO
3
+NaOH NaNO
3
+H
2
O
H
2
SO
4
+2NH
4
OH (NH
4
)
2
SO
4
+2H
2
O or H
2
SO
4
+2NH
3
(NH
4
)
2
SO
4
CH
3
COOH +KOH CH
3
COO
-
K
+
+H
2
O
Acid + Metal Carbonate Salt + CO
2
+ H
2
O
Example:
2HCl +ZnCO
3
ZnCl
2
+CO
2
+H
2
O
2HNO
3
+CaCO
3
Ca(NO
3
)
2
+CO
2
+H
2
O
H
2
SO
4
+Na
2
CO
3
Na
2
SO
4
+CO
2
+H
2
O
2CH
3
COOH +MgCO
3
Mg(CH
3
COO)
2
+CO
2
+H
2
O
Salt
Solubility of Salt
Salt Solubility
Salt of potassium, sodium and ammonium All are soluble in water
Salt of nitrate All are soluble in water
Salt of sulphate Mostly soluble in water except:
(Pb) Lead sulphate
(Ba) Barium sulphate
(Ca) Calcium sulphate
Salt of chloride Mostly soluble in water except:
(Pb) Lead chloride
(Ag) silver chloride
(Hg) mercury chloride
Salt of carbonate Mostly insoluble in water except:
Potassium carbonate
Sodium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate
Oxide and Hydroxide Solubility
Oxide Mostly insoluble in water except: K
2
O and Na
2
O.
Hydroxide Mostly insoluble in water except: NH
4
OH, KOH and NaOH
Preparation of Salt
Preparation of Soluble Salt
Salt of Potassium, Sodium and Ammonium
Acid +Alkali Salt +Water
Example: Preparation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
HCl +NaOH NaCl +H
2
O
Salt of non-Potassium, Sodium and Ammonium
Acid +Reactive metal Salt +Hydrogen Gas
Acid +Metal Oxide Salt +Water
Acid +Metal Carbonate Salt +Water +Carbon Dioxide
Example: Preparation of Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO
4
)
H
2
SO
4
+Zn ZnSO
4
+H
2
H
2
SO
4
+ZnO ZnSO
4
+H
2
O
H
2
SO
4
+ZnCO
3
ZnSO
4
+H
2
O +CO
2
6
Preparation of Insoluble Salt
Ionic Precipitation
Insoluble salts can be made by double decomposition. This involves mixing a solution that contains its
positive ions with another solution that contains its negative ions.
Example: Preparation of Silver Nitrate
AgNO
3
(aq)
+NaCl
(aq)
AgCl
(s)
+NaNO
3
(aq)
Ag
+
(aq)
+C1
-
(aq)
AgCl
(s)
(ionic equation)
Colour of Salt
Salt or metal oxide Solid Aqueous solution
Salt of:
Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminium, zinc,
Lead, ammonium
Chloride, sulphate, nitrate, carbonate
White Colourless
Salt of Copper(II).-
Copper(II) Carbonate Green Insoluble
Copper(II) sulphate, Copper(II) nitrate, Copper(II)
chloride
Blue Blue
Copper(II) oxide Black Insoluble
Salt of Iron (II)
Iron(II) sulphate; Iron(II) nitrate; Iron(ID chloride
Green Green
Salt of Iron (III).
Iron(III) sulphate; Iron(III) nitrate; Iron(III)
chloride
Brown Brown
Lead Iodide
Yellow Insoluble
Lead Chloride
White Insoluble
Zink oxide Yellow when it is hot and
white when it is cold.
Insoluble
Lead(II) oxide- Brown when it is hot and
yellow when it is cold.
Insoluble
Magnesium oxide, Aluminium oxide White Insoluble
Potassium oxide, Sodium oxide, Calcium oxide White Colourless
7
Heating effect on Salt
Heating
Effect
CO
3
2-
NO
3
-
SO
4
2-
Cl
-
Most Probably
Release CO2
Most Probably
Release NO2
Most Probably
Release SO3
Most Probably
No effect
Heating Effect on Carbonate Salt
Carbonate Salt Equation of The Reaction
Potassium carbonate
Sodium carbonate
Not decomposible
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate
Aluminium carbonate
Zinc carbonate
Iron (III) carbonate
Lead(II) carbonate
Copper(II) carbonate
CaCO
3
CaO +CO
2
MgCO
3
MgO +CO
2
Al
2
(CO
3
)
3
Al
2
O
3
+3CO
2
ZnCO
3
ZnO +CO
2
Fe
2
(CO
3
)
3
Fe
2
O
3
+3CO
2
PbCO
3
PbO +CO
2
CuCO
3
CuO +CO
2
Mercury(II) carbonate
Silver(I) carbonate
2HgCO
3
2Hg +2CO
2
+O
2
2Ag
2
CO
3
4Ag +2CO
2
+O
2
Ammonium carbonate
(NH
4
)
2
CO
3
NH
3
+CO
2
+H
2
O
Heating Effect on Nitrate Salt
Nitrate Salt Equation of The Reaction
Potassium nitrate
Sodium nitrate
2KNO
3
2KNO
2
+O
2
2NaNO
3
2NaNO
2
+O
2
Calcium nitrate
Magnesium nitrate
Aluminium nitrate
Zink nitrate
Iron (III) nitrate
Lead(II) nitrate
Copper(II) nitrate
2Ca(NO
3
)
2
2CaO +4NO
2
+O
2
Mg(NO
3
)
2
2MgO +4NO
2
+O
2
4Al(NO
3
)
3
2Al
2
O
3
+12NO
2
+3O
2
Zn(NO
3
)
2
2ZnO +4NO
2
+O
2
4Fe(NO
3
)
3
2Fe
2
O
3
+12NO
2
+3O
2
Pb(NO
3
)
2
2PbO +4NO
2
+O
2
Cu(NO
3
)
2
2CuO +4NO
2
+O
2
Mercury(II) nitrate
Silver(I) nitrate
Hg(NO
3
)
2
Hg +2NO
2
+O
2
2AgNO
3
2Ag +2NO
2
+O
2
Ammonium nitrate
NH
4
NO
3
N
2
O +2H
2
O
[NOTES: Nitrogen dioxide, NO
2
is acidic gas and is brown in colour.]
8
Heating effect on sulphate salt The heating effect on chloride salts
Most sulphate salts do not decompose by heat. Only
certain sulphate salts are decomposed by heat when
heated strongly.
Zinc sulphate, Copper (II) sulphate, Iron (III)
sulphate
ZnSO
4
ZnO +SO
3
CuSO
4
CuO +SO
3
2Fe
2
(SO
4
)
3
Fe
2
O
3
+SO
2
+SO
3
Ammonium sulphate
(NH
4
)
2
SO
4
2NH
3
+H
2
SO
4
All chloride salts are not decomposable by heat
except ammonium chloride.
Example:
NH
4
Cl NH
3
+HCl
Identification of Gases
Gasses Characteristics
Oxygen Rekindle glowing splinter.
Hydrogen Explode with a pop sound when brought close to a lighted splinter.
Carbon Dioxide Turns lime water chalky.
Chlorine Bleach moist litmus paper.
Ammonia Pungent smell.
Turn moist red litmus paper to blue.
Produces white fume when reacts with concentrated hydrochloric Acid.
Sulphur Dioxide Pungent smell.
Bleach the purple colour of potassium manganate(VII).
Turn moist blue litmus paper to red.
Nitrogen Dioxide Pungent smell.
Brown in colour.
Turn moist blue litmus paper to red.
Qualitative analysis
Identification of Anions (Negative ions)
Diluted HCl or
diluted HNO
3
or
diluted H
2
SO
4
BaCl (aq) or Ba(NO
3
)
2
(aq) follow by diluted
HCl/HNO
3
AgNO
3
follow by
diluted HNO
3
.
Brown Ring Test
( + FeSO
4
(aq ) +
concentratedH
2
SO
4
CO
3
2-
Carbon Dioxide is
released.
White precipitate is
formed. It is soluble in
diluted HCl/HNO
3
White precipitate is
formed. It is soluble in
diluted HNO
3
-
SO
4
2-
-
White precipitate is
formed. It is NOT soluble
in diluted HCl/HNO
3
- -
Cl
-
- -
White precipitate is
formed. It is NOT
soluble in diluted
HNO
3
-
NO
3
-
- - -
Formation of Brown
Ring
9
Idendification of cation
NaOH(ak) NH
3
(ak) HCl or NaCl
H
2
SO
4
or
Na
2
SO
4
Na
2
CO
3
KI
Na
+
Ca
2+
White
precipitate.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Mg
2+
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Al
3+
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Zn
2+
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NH
3
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Pb
2+
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in hot
water
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Yellow
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in hot
water
Fe
2+
Dirty green
precipitate is
produced.
Dirty green
precipitate is
produced.
Green
precipitate is
produced.
Fe
3+
Red brown
precipitate is
produced.
Red brown
precipitate is
produced.
Brown
precipitate is
produced.
A red brown
solution formed.
Cu
2+
Blue precipitate
is produced.
Blue precipitate
is produced.
Dissolve in
excess NH
3
solution and
form a blue
solution.
Blue precipitate
is produced.
White
precipitate form
in brown
solution
NH
4
+
=No changes is observed
10
Distibguish Iron(II) and Iron(III)
Reagent Observation Ion presents
Light blue precipitate Fe
2+
Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(II)
Dark Blue precipitate Fe
3+
Dark blue precipitate Fe
2+
Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(III)
Greenish brown solution Fe
3+
Pinkish solution Fe
2+
Solution of potassium Thiocyanate(II)
Blood red solution Fe
3+
Manufactured Substances in Industry
Contact Process (Making Sulphuric Acid)
Stage 1: Formation of SO
2
Combustion of Sulphur
S
(s)
+O
2
(g) SO
2
(g)
or
Heating of metal sulphide such as lead(II) sulphide
2PbS
(s)
+3O
2(g)
2PbO
(s)
+2SO
2(g)
or
Combustion of hiydrogen sulphide
2H
2
S
(g)
+3O
2(g)
2SO
2(g)
+2H
2
O
(ce)
Stage 2: Formation of SO
3
2SO
2
(g)
+O
2
(g)
2SO
3
(g)
Catalyst: vanadium(V) oxide
Temperature: 450C
Pressure: 2-3 atmospheres
Stage 3 Formation of oleum H
2
S
2
O
7
SO
3(g)
+H
2
SO
4(aq)
H
2
S
2
O
7(l)
Stage 4:Formation of Sulphuric acid
H
2
S
2
0
7
(1)
+H
2
O
(1)
2H
2
SO
4(aq)
11
Haber Process (Making Ammonia)
Sources of the raw material
Hydrogen 1. Reaction between steam and heated coke
H
2
O +C CO +H
2
2. Reaction between steam and natural gas.
2H
2
O + CH
4
CO
2
+4H
2
Nitrogen From distillation of liquid air.
The reaction
1. Ammonia is made by the Haber process from nitrogen and hydrogen:
N
2
(g) +3H
2
(g) 2NH
3
(g); H =-92 kJ mo1
-1
Catalyst: Iron
Promoter: Aluminium oxide
Temperature: 450 C
Pressure: 200-1000 atm
12
1
Rate or Reaction
Calculation
Rate of Reaction (Average Rate)
Quantity change of reactants/products
Rates of reaction =
Total time for the reaction
If the quantity change is immeasurable
1
Rates of reaction =
Total time for the reaction
Find the Rate From a Graph
Average Rate Rates At an Instant
The rate of reaction is equal to the slope of the graph
of quantity against time.
(Product)
Rate of Reaction =
(Time)
The rate of reaction at an instant, t, is equal to the
slope of tangent at that instant.
(Product)
Rate of Reaction =
(Time)
2
Chemical Reaction
Precipitation of Sulphur
2HCl
(aq)
+ Na
2
S
2
O
3(aq)
2NaCl
(aq)
+ S
(s)
+ SO
2(g)
+ H
2
O
(l)
Notes:
1. Yellow precipitate (sulphur) is formed.
2. The reaction is slow.
Na
2
S
2
O
3
: Sodium thiosulphate
Potassium Dichromate (VI) with Ethanedioic Acid
Cr
2
O
7
2-
+ 14H
+
+ 3C
2
O
4
2-
6CO
2
+ 7H
2
O + 2Cr
3+
Notes:
1. In the reaction, the orange colour of the solution
turns into green.
Cr
2
O
7
2-
: dichromate(VI) ion (Orange)
C
2
O
4
2-
: ethanedioate ion (Colourless)
Cr
3+
: Chromium(III) ion (green)
Potassium Manganate(VII) with Ethanedioic Acid
2MnO
4
-
+ 16H
+
+ 5C
2
O
4
2-
10CO
2
+ 8H
2
O + 2Mn
2+
Notes:
1. Mn
2+
is colourless
2. In the reaction, the purple colour of the solution
turns into colourless.
MnO
4
-
: Manganate(VII) ion (Purple)
Mn
2+
: Manganese(II) ion colourless
Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
2H
2
O
2
-
2H
2
O + O
2
Catalyst: manganese(IV) oxide(MnO
2
), Iron(III) oxide (Fe
2
O
3
), silver (Ag)
Haber Process (Manufacture Ammonia)
N
2
+ 3H
2
2NH
3
(More detail in Form 4 Chapter 9)
Contact Process(Manufacture Sulphuric Acid)
2SO
2
+ O
2
2SO
3
3
Ostwald Process (Manufacture Nitric Acid)
Stage 1
4NH
3(g)
+ 5O
2(g)
4NO
(g)
+ 6H
2
O
(g)
Notes:
1. Temperature = 900oC
2. Pressure = 4-10 atm
3. Catalyse = Platinum (Pt)
Stage 2
2NO
(g)
+ O
2(g)
2NO
2(g)
Dissolve in water
3NO
2(g)
+ H
2
O
(l)
2HNO
3(aq)
+ NO
(g)
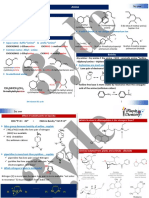
Carbon Compound
Alkane
Alkane
Combustion
Complete
Combustion
Incomplete
Combustion
Substitution
Reaction
(Halogenation)
Combustion
Complete combustion
C
2
H
6
+
7
2
O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
Incomplete combustion
C
2
H
6
+
5
2
O
2
2CO + 3H
2
O
C
2
H
6
+
3
2
O
2
2C + 3H
2
O
4
Substitution Reaction
Alkene
Alkene
Combustion
Complete
Combustion
Incomplete
Combustion
Addition Reaction
+Bromine/Chlorine
+Potassium
Manganate(VII)
+Hydrogen
+Hydrogen Halide
+Steam
Polymerization
Alkane Alcohol
Craking Dehydration
Preparation of Alkene
Cracking of Alkane
2C
4
H
10
CH
4
+ C
2
H
4
+ C
2
H
6
+ C
3
H
6
Dehydration of Alchohol
C
2
H
5
OH + C
2
H
4
+ H
2
O
5
Combustion:
Complete combustion:
C
2
H
4
+ 3O
2
2CO
2
+ 2H
2
O
Incomplete combustion
C
2
H
4
+ 2O
2
2CO + 2H
2
O
C
2
H
4
+ O
2
2C + 2H
2
O
Addition Reaction:
+ Bromine:
+ Potassium Manganate(VII):
+ Hydrohen:
(Catalyst: platinum/nickel)
+ Hydrogen Halide:
+ Steam (H
2
O):
(Catalyst: phosphoric acid; Temperature: 300
o
C; Pressure: 60atm)
Polymerization
(Catalyst: oxygen; Temperature: 200
o
C; Pressure: 1200atm)
6
Alcohol
Alkene Carbohydrate
Alcohol fermentation Addition
+Sodium dehydration Combustion
Oxidation
(+K
2
CrO
7
/KMnO
4
)
Preparation of alchohol
Fermentation of Carbohydrate (Glucose)
C
6
H
12
O
6
2C
2
H
5
OH + 2CO
2
Addition of Alkene
C
2
H
4
+ H
2
O C
2
H
5
OH
[Catalyst:Phosphoric acid; Temperature:300
o
C; Pressure: 60atm ]
or
C
2
H
4
+ H
2
SO
4
CH
3
CH
2
OSO
3
H
CH
3
CH
2
OSO
3
H + H
2
O CH
3
CH
2
OH + H
2
SO
4
Combustion of Alcohol
C
2
H
5
OH + 3O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
Dehydration of Alcohol
C
2
H
5
OH + C
2
H
4
+ H
2
O
Alcohol + Sodium
2C
2
H
5
OH + 2Na 2C
2
H
5
ONa + H
2
Oxidation of Alcohol
C
2
H
5
OH + 2[O] CH
3
COOH + H
2
O
7
Carboxylic Acid
Aldehydes Alchohol
Carboxylic acid Oxidation Oxidation
+Metal +oxide base +alkali +Metal carbonate +Alchohol
Salt +H
2
O Salt +H
2
O Salt +H
2
Salt +CO
2
+H
2
O
Esther
Preparation of Carboxylic acid
Oxidation of Alcohol
C
2
H
5
OH + 2[O] CH
3
COOH + H
2
O
Oxidation of Aldehyde
C
2
H
6
O + [O] CH
3
COOH
Reaction
Carboxylic Acid + Alkali
CH
3
COOH + NaOH CH
3
COONa + H
2
O
Carboxylic Acid + Metal Oxide
2CH
3
COOH + MgO Mg(CH
3
COO)
2
+ H
2
O
Carboxylic Acid + Metal
2CH
3
COOH + Mg Mg(CH
3
COO)
2
+ H
2
Carboxylic Acid + Metal Carbonate
2CH
3
COOH + CaCO
3
Ca(CH
3
COO)
2
+ CO
2
+H
2
O
Carboxylic Acid + Alchohol
CH
3
COOH + C
2
H
5
OH CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
+ H
2
O
8
Summary of The Reaction
9
Oxidation and Reduction
Iron(II) to Iron(III)
Oxidising agent: Chlorine or Bromine
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
Cl
2
+ 2e 2Cl
2Fe
2+
+ Cl
2
2Fe
3+
+ 2Cl
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
Br
2
+ 2e 2Br
2Fe
2+
+ Br
2
2Fe
3+
+ 2Cl
Observation:
1. The green colour of Fe
2+
solution turns brown
Observation:
1. The green colour of Fe
2+
solution turn brown
2. The brown colour of bromine water turns into
colourless.
Oxidising agent: Potassium Permanganate(VII)
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
MnO
4
+ 8H
+
+ 5e Mn
2+
+ 4H
2
O
5Fe
2+
+ MnO
4
+ 8H
+
5Fe
3+
+ Mn
2+
+ 4H
2
O
Observation:
1. The green colour of solution Fe
2+
turns brown
2. The purple colour of the MnO
4
solution turns into colourless
Oxidising agent: Potassium Dichromate(VI)
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
Cr
2
O
7
2-
+ 14 H
+
+ 6e 2Cr
3+
+ 7H
2
O
6Fe
2+
+ MnO
4
+ 8H
+
6Fe
3+
+ Mn
2+
+ 4H
2
O
Observation:
1. The green colour of solution Fe
2+
turns brown.
2. The orange colour of the Cr
2
O
7
2-
solution turns green.
Oxidising agent: Hidrogen Peroxide
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
H
2
O
2
+ 2H
+
+ 2e 2H
2
O
2Fe
2+
+ H
2
O
2
+ 2H
+
2Fe
3+
+ 2H
2
O
Observation:
1. The green colour of solution Fe
2+
turns brown
Oxidising agent: Concentrated Nitric Acid
+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
NO
3
-
+ 4H
+
+ 3e NO + 2H
2
O
3Fe
2+
+ NO
3
-
+ 4H
+
3Fe
3+
+ NO + 2H
2
O
Observation:
1. The green colour of solution Fe
2+
turns brown
10
Iron(III) to Iron(II)
Reducing Agent: More reactive Metal
+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
Zn Zn
2+
+ 2e
2Fe
3+
+ Zn 2Fe
2+
+ Zn
2+
Observation:
1. The brown colour of the iron(III) solution turn green.
2. Zinc powder dissolve in the solution.
Reducing Agent: Sulphur Dioxide
+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
SO
2
+ 2H
2
O SO
4
2-
+ 4H
+
+ 2e
2Fe
3+
+ SO
2
+ 2H
2
O 2Fe
2+
+ SO
4
2-
+ 4H
+
Observation:
1. The brown colour of the iron(III) solution turn green.
Reducing Agent: Hydrogen Sulphide
+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
H
2
S 2H
+
+ S + 2e
2Fe
3+
+ H
2
S 2Fe
2+
+ 2H
+
+ S
Observation:
1. The brown colour of the iron(III) solution turn green.
2. Yellow precipitate forms in the solution.
Reducing Agent: Sodium Sulphite
+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
SO
3
2-
+ H
2
O SO
4
2-
+ 2H
+
+ 2e
2Fe
3+
+ SO
3
2-
+ H
2
O 2Fe
2+
+ SO
4
2-
+ 2H
+
Observation:
1. The brown colour of the iron(III) solution turn green.
Reducing Agent: Tin(II) Chloride
+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
Sn
2+
Sn
4+
+ 2e
2Fe
3+
+ Sn
2+
2Fe
2+
+ Sn
4+
Observation:
1. The brown colour of the iron(III) solution turn green.
11
Displacement of Metal
[A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive ion of metal from its compound.]
Example:
Mg + PbCl
2
MgCl
2
+ Pb
3Zn + Fe
2
O
3
3ZnO + 2Fe
Al + CuSO
4
Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
+ Cu
Electrochemical Series
Reactivity Series
Displacement of Halogen
[A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halide from its compound.]
Example:
Cl
2
+ KBr KCl + Br
2
Br
2
+ NaI NaBr + I
2
F
2
+ KI KF + I
2
Reactivity of Halogen
Colour of Halogen and Halide
Halogen Colour in
water
Colour in
CCl
4
Chlorine (Cl
2
) Pale Yellow Pale Yellow
Bromine (Br
2
) Brown/Orange/
Yellow
Brown/Orange/
Yellow
Iodine (I
2
) Brown/Orange/
Yellow
Purple
Halogen Colour in
water
Colour in
CCl
4
Chloride (Cl
-
) Colourless Colourless
Bromide (Br
-
) Colourless Colourless
Iodide (I
-
) Colourless Colourless
More reactive
F
2
> Cl
2
> Br
2
> I
2
> At
2
More reactive
K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, C, Zn, H, Fe, Sn, Pb, Cu, Ag
More electropositive
K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Sn, Pb, H, Cu, Ag
Kalau Nak Cari Makanan Ada Zat Ferum Seperti Papaya Harus Cari di Argentina
12
The Oxidising Agent and Reducing Agent
Oxidising Agent (Reduction) Redusing Agent (Oxidation)
Halogen
Cl
2
+ 2e 2Cl
Br
2
+ 2e 2Br
I
2
+ 2e 2I
Metal
Mg Mg
2+
+ 2e
Zn Zn
2+
+ 2e
Al Al
3+
+ 2e
Metal Ion
Mg
2+
+ 2e Mg
Pb
2+
+ 2e Pb
Sn
2+
+ 2e Sn
Halide Ion
2Cl
Cl
2
+ 2e
2Br
Br
2
+ 2e
2I
I
2
+ 2e
Fe
3+
Fe
3+
+ e Fe
2+
Fe
2+
Fe
2+
Fe
3+
+ e
Potassium Manganate(VII)
MnO
4
+ 8H
+
+ 5e Mn
2+
+ 4H
2
O
Sulphur Dioxide
SO
2
+ 2H
2
O SO
4
2-
+ 4H
+
+ 2e
Potassium Dicromate(VI)
Cr
2
O
7
2-
+ 14 H
+
+ 6e 2Cr
3+
+ 7H
2
O
Hydrogen Sulphide
H
2
S 2H
+
+ S + 2e
Hydrogen Peroxide
H
2
O
2
+ 2H
+
+ 2e 2H
2
O
Sodium Sulphite Aqueous
SO
3
2-
+ H
2
O SO
4
2-
+ 2H
+
+ 2e
Concentrated Nitric Acid
NO
3
-
+ 4H
+
+ 3e NO + 2H
2
O
Tin(II) Chloride Aqueous
Sn
2+
Sn
4+
+ 2e
Rusting
Step 1: Formation pf Ion
Anode:
Fe Fe
2+
+ 2e
Cathode:
O
2
+ H
2
O 4OH
-
+ 4e
Step 2: Corrosion of Iron
Fe
2+
+ 2OH
-
Fe(OH)
2
Step 3: Formation of iron(III) hydroxide
4Fe(OH)
2
+ H
2
O + O
2
4Fe(OH)
3
Step 4: Formation of Hydrated Iron(III) Oxide
Fe(OH)
3
Fe
2
O
3
xH
2
O
General Equation
4Fe + 3O
2
+ xH
2
O 2Fe
2
O
3
xH
2
O
13
Preparation of Oxygen Gas
Decomposition of Potassium Manganate (VII)
2KMnO
4
K
2
MnO
4
+ MnO
2
+ O
2
Decomposition of Potassium Chlorate (V)
2KClO
3
2KCl + 3O
2
[Manganese(IV) Oxide as catalyst]
Decomposition of Potassium Nitrate
2KNO
3
2KNO
2
+ O
2
Extraction of Iron From Its Ore
Production of Carbon Dioxide
C + O
2
CO
2
Production of Carbon Monoxide
CaCO
3
CaO + CO
Reduction of Iron Ore to Iron
Upper Section of the Ballast Furnace
Fe
2
O
3
+ 3CO 2Fe + 3CO
2
Fe
3
O
4
+ 4 CO 3Fe + 4CO
2
Lower Section of the Ballast Furnace
Fe
2
O
3
+ 3C 2Fe + 3CO
Fe
3
O
4
+ 4 C 3Fe + 4CO
2
Removal of Impurities
CaO + SiO
2
CaSiO
3
14
Thermochemistry
Calculation
Heat of Reaction
Thermal Energy Change
Number of Mole
H =
Thermal Energy Change
Q = mc
m = mass of solution = volume of solution
c = specific heat capacity of solution
Number of Mole
For solution
1000
MV
n =
For gas (When volume is given)
3 3
Volume of gas
Molar volume of gas (22.4dm at stp / 24dm at rtp)
n =
For solid, liquid or gas ( When mass is given )
mass
Molar mass (RAM/RMM)
n =
Chemical Reaction
Exothermic Reaction
Dissolving Alkali or Acid
-
2
NaOH Na OH
H O +
+
2
2
2 4 4
H SO H SO
H O
+
+
Dissolving of Anhydrous Salt
2 2
2
4 4
CuSO Cu SO
H O
+
+
2
2
2 3 3
Na CO 2Na CO
H O
+
+
15
Combustion of Fuel
Example:
Combustion of Carbon
C + O
2
CO
2
Combustion of Hydrogen
2H
2
+ O
2
2H
2
O
Combustion of Ethane
C
2
H
6
+
7
2
O
2
2CO
2
+ 3H
2
O
Reaction of Acid
Neutralisation
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H
2
O
2HNO
3
+ CaO Ca(NO
3
)
2
+ H
2
O
Acid + Reactive Metal
H
2
SO
4
+ Zn ZnSO
4
+ H
2
Acid + Carbonate Acid
HCl + CaCO
3
CaCl
2
+ CO
2
+ HCl
Displacement Reaction
Zn + CuSO
4
ZnSO
4
+ Cu
Endothermic Reaction
Dissolving of Ammonium Chloride, Ammonium Nitrate and Ammonium Sulphate
-
2
4 4
NH Cl NH Cl
H O
+
+
2
4 3 4 3
NH NO NH NO
H O
+
+
2
2
4 4 4 4
(NH )SO 2NH SO
H O
+
+
Dissolving of Hydrated Salt
CuSO
4
xH
2
O Cu
2+
+ SO
4
2-
+ xH
2
O
Na
2
CO
3
xH
2
O 2Na+ + CO
3
2-
+ xH
2
O
Thermal Decomposition of salts
CaCO
3
CaO + CO
2
2Ca(NO
3
)
2
2CaO + 4NO
2
+ O
2
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Parāśara Jyoti A: Devaguru B Haspati CenterDocumento6 páginasParāśara Jyoti A: Devaguru B Haspati CenterGovardhan PanatiAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Optics Part IDocumento62 páginasWave Optics Part IAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Divine Teachings of Kriya Yoga Master Paramahamsa Hariharananda GiriDocumento4 páginasDivine Teachings of Kriya Yoga Master Paramahamsa Hariharananda GiriAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Key Points and FormulaeDocumento35 páginasPhysics Key Points and FormulaeAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapters 0 and 1Documento29 páginasChapters 0 and 1Tulus PramujiAinda não há avaliações
- 27 Nakshatra PadasDocumento13 páginas27 Nakshatra PadasAstrologer in Dubai Call 0586846501Ainda não há avaliações
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDocumento16 páginasMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Review Test II: Course Name: QUARKDocumento1 páginaReview Test II: Course Name: QUARKAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Problems For 9Documento1 páginaProblems For 9At TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Intercepted Signs in Horoscopes A New Concept B WDocumento15 páginasIntercepted Signs in Horoscopes A New Concept B WAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Shiv MahapuranaDocumento43 páginasShiv MahapuranaAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Problems in IsomerismDocumento5 páginasProblems in IsomerismAt Tanwi100% (1)
- Physics Class Test 27 July 2013-Quark: Non-Zero Angle Between Velocity and Change in Velocity..............Documento1 páginaPhysics Class Test 27 July 2013-Quark: Non-Zero Angle Between Velocity and Change in Velocity..............At TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Jee MainDocumento15 páginasChemistry Jee MainAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- ChemLab - Chemistry 6 - Spectrum of The Hydrogen Atom - Chemistry & BackgroundDocumento13 páginasChemLab - Chemistry 6 - Spectrum of The Hydrogen Atom - Chemistry & BackgroundAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Students Must ReadDocumento1 páginaStudents Must ReadAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Test KinemeticsDocumento2 páginasPhysics Test KinemeticsAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Test Paper Class XIDocumento4 páginasTest Paper Class XIAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Question PaperDocumento1 páginaChemistry Question PaperAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocumento3 páginasMolecular Orbital TheoryAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- Fridge Autodef EffDocumento3 páginasFridge Autodef EffAt TanwiAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- One Pot (Shake & Bake) Methamphetamine Labs: PresentationDocumento0 páginaOne Pot (Shake & Bake) Methamphetamine Labs: PresentationAbdullah S. Abdullah63% (8)
- Precipitation ReactionDocumento1 páginaPrecipitation ReactionMaiden Joy UtaydeAinda não há avaliações
- Iq Sensornet Calibration & Troubleshooting GuideDocumento92 páginasIq Sensornet Calibration & Troubleshooting GuideFélix Alexander Gallegos ServigónAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 3L Group 4 Cation 1Documento6 páginasCHEM 3L Group 4 Cation 1Beatrice AlejeAinda não há avaliações
- 12 AcidifiersDocumento25 páginas12 AcidifiersUmar Ilyasu JibrilAinda não há avaliações
- PDF Document 3Documento14 páginasPDF Document 3Akshat GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Oct 25, 2021Documento7 páginasAdobe Scan Oct 25, 2021Srushti ChouguleAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Acids and BasesDocumento25 páginasNotes Acids and BasesHuda 1521Ainda não há avaliações
- Thesis ReportDocumento106 páginasThesis ReportMuhammad HaseebAinda não há avaliações
- Amine 1Documento2 páginasAmine 1haAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Hand Dishwashing Detergent CompositionDocumento38 páginasLiquid Hand Dishwashing Detergent CompositionEdgardo Ed RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Chemsheets A2 009 (Acids & Bases)Documento21 páginasChemsheets A2 009 (Acids & Bases)ilias197380% (5)
- Formula Writing and Naming of CompoundsDocumento1 páginaFormula Writing and Naming of CompoundsMon ColinaAinda não há avaliações
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowDocumento0 páginaHazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowAbhishek VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Sigma Chemical Resistance ChartDocumento7 páginasSigma Chemical Resistance Chartshahbaz1979Ainda não há avaliações
- Salt AnalysisDocumento8 páginasSalt AnalysisSyed Mohdammad AliAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento13 páginasUntitledUpagya AwasthiAinda não há avaliações
- 100L Lecture 4 SaltsDocumento6 páginas100L Lecture 4 SaltsMichael EhondorAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Compounds - Ammonia A. State One Observation For The FollowingDocumento6 páginasStudy of Compounds - Ammonia A. State One Observation For The FollowingVishal SAinda não há avaliações
- TtyDocumento81 páginasTtyOrlando Diaz M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Lech204 PDFDocumento22 páginasLech204 PDFPaula ManolacheAinda não há avaliações
- Surfactant Titration MonographDocumento233 páginasSurfactant Titration MonographGustavo Sánchez100% (2)
- Ammonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestDocumento2 páginasAmmonium Chloride Salt Analysis TestSantosh Kumar Sahu100% (1)
- The Photometric Determination of Quaternary Ammomum Salts and of Certain Amines by Compound Formation With IndicatorsDocumento15 páginasThe Photometric Determination of Quaternary Ammomum Salts and of Certain Amines by Compound Formation With IndicatorsKilsys AlvaradoAinda não há avaliações
- PreLab Report 5Documento9 páginasPreLab Report 5Jacques TuckerAinda não há avaliações
- Ammonia, Sulfur, Air N Water - 2Documento2 páginasAmmonia, Sulfur, Air N Water - 2bilalAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 Orion Catalog - ISE ElectrodesDocumento11 páginas2012 Orion Catalog - ISE ElectrodesmorphelyaAinda não há avaliações
- Salt Analysis - Xii PDFDocumento9 páginasSalt Analysis - Xii PDFहर्ष सैनी. कक्षा::बारहवीं 'द'Ainda não há avaliações
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocumento16 páginasShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationSHARIN HANUM AB RAHMANAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesDocumento8 páginasCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-13: Amines AminesAryan MeenaAinda não há avaliações