Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
D 3159 - 98 Rdmxntktotg - PDF
Enviado por
alfgraga60430 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
35 visualizações5 páginasThis specification covers melt processible molding and extrusion materials of modified ETFE-fluoropolymer. The ETFE resin is a copolymer of ethylene containing approximately 75 mass % of tetrafluoroethylene. This specification does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use.
Descrição original:
Título original
D 3159 – 98 ;RDMXNTKTOTG_.pdf
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis specification covers melt processible molding and extrusion materials of modified ETFE-fluoropolymer. The ETFE resin is a copolymer of ethylene containing approximately 75 mass % of tetrafluoroethylene. This specification does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
35 visualizações5 páginasD 3159 - 98 Rdmxntktotg - PDF
Enviado por
alfgraga6043This specification covers melt processible molding and extrusion materials of modified ETFE-fluoropolymer. The ETFE resin is a copolymer of ethylene containing approximately 75 mass % of tetrafluoroethylene. This specification does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
Designation: D 3159 98
Standard Specication for
Modied ETFE-Fluoropolymer Molding and Extrusion
Materials
1
This standard is issued under the xed designation D 3159; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
1.1 This specication covers melt processible molding and
extrusion materials of modied ETFE-uoropolymer. The
ETFE resin is a copolymer of ethylene containing approxi-
mately 75 mass % of tetrauoroethylene.
1.2 The values stated in SI units as detailed in IEEE/ASTM
SI-10 are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in
parentheses are for information only.
NOTE 1Although this specication and ISO 12086-1 (1994) and ISO
12086-2 (1994) differ in approach or detail, data obtained using either are
technically equivalent.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test method portion, Section 11, of this specication. This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
tions prior to use.
1.4 Recycled material is not appropriate for this specica-
tion because performance requirements cannot be met with
recycled material. Therefore, this specication is for virgin
material only.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 150 Test Methods for A-C Loss Characteristics and
Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insu-
lating Materials
2
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
Insulating Materials for Testing
3
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
3
D 792 Test Methods for Specic Gravity (Relative Density)
and Density of Plastics by Displacement
3
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
3
D 1238 Test Method for Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by
Extrusion Plastometer
3
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
Plastics
3
D 3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Poly-
mers by Thermal Analysis
4
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
4
E 177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods
5
SI 10 Use of the International System of Units (SI): The
Modem Metric System
5
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 12086-1 (1994) PlasticsFluoropolymer Dispersions
and Moulding and Extrusion MaterialsPart 1
ISO 12086-2 (1994) PlasticsFluoropolymer Dispersions
and Moulding and Extrusion MaterialsPart 2
3. Terminology
3.1 Denitions:
3.1.1 GeneralThe terminology given in Terminology
D 883 is applicable to this specication.
3.1.2 lot, none production run or a uniform blend of two
or more production runs.
3.1.3 Abbreviated Terms:
3.1.4 GeneralThe abbreviated terms given in Terminol-
ogy D 1600 are applicable to this specication.
4. Classication
4.1 This specication covers three types of modied ETFE-
uoropolymer supplied in pellet form classied according to
their specic gravity. The resins of each type are divided into
two grades according to their melt ow rate.
4.2 An one-line system may be used to specify materials
covered by this specication. The system uses predened cells
to refer to specic aspects of this specication, as illustrated as
follows:
1
This specication is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials (Section D20.15.12).
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1998. Published February 1999. Originally
published as D 3159 73. Last previous edition D 3159 95a.
This edition was modied in 1.1.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
1
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Specication
Standard Number : Type : Grade : Special
Block : : : Notes
: : : , :
Example: Specication D 3159 95, I 2
For this example, the line callout would be, Specication D
3159 95,I2 and would specify a modied ETFE-
uoropolymer that has all of the properties listed for that type
and grade in the appropriate specied properties, or tables, or
both, in the specication identied. A comma is used as the
separator between the standard number and the type. Separa-
tors are not needed between the type and grade.
6
Provision for
special notes is included so that other information can be
provided when required. An example would be in Specication
D 3295 where dimensions and tolerances are specied for each
AWG size within the type and class. When special notes are
used, they should be preceded by a comma.
5. General Requirements
5.1 The material shall be of uniform composition and so
prepared as to conform to the requirements of this specica-
tion.
5.2 The material described in this specication shall be free
of foreign matter to such a contamination level as may be
agreed upon between the purchaser and the seller.
6. Performance Requirements
6.1 The average test result of the lot shall conform to the
requirements prescribed in Tables 1 and 2 when tested by the
procedures specied herein. Table 2 lists those tests requiring
a specimen molded as described in Section 8.
7. Sampling
7.1 The materials shall be sampled in accordance with an
adequate statistical sampling program.
8. Specimen Preparation
8.1 Prepare a molded sheet 1.5 6 0.3 mm (0.06 6 0.01 in.)
thick. Use a picture-frame-type chase having a suitable
blanked-out section and thickness to produce the desired sheet.
Use clean aluminum foil, 0.13 to 0.18 mm (0.005 to 0.007 in.)
thick, in contact with the resin. A high-temperature mold
release agent may be sprayed on the aluminum foil to help
prevent the foil from sticking to the sheet. Use steel molding
plates at least 1.0 mm (0.040 in.) thick and of an area adequate
to cover the chase.
8.2 Lay down and smoothly cover one plate with a sheet of
aluminum foil. Place the mold chase on top of this assembly.
Place within the mold chase sufficient molding material to
produce the required sheet in such manner that the polymer
charge is a mound in the middle of the chase. Place a second
sheet of aluminum foil on top of the granules and add the top
mold plate. Place the assembly in a compression molding press
having platens that have been heated to 300 6 5C
(572 6 10F).
8.3 Bring the press platens to incipient contact with the
mold assembly. Hold for 2 to 4 min without pressure. Apply
approximately 1 MPa (145 psi) and hold for 1 to 1.5 min. Then
apply 2 to 4 MPa (290 to 580 psi) and hold for 1 to 1.5 min.
Maintain the press at 300 6 5C (572 6 10F) during these
steps. Remove the assembly from the press and place between
two 20 6 7-mm (0.75 6 0.25-in.) steel plates whose tempera-
ture is less than 40C (104F).
8.4 When the sheet is cool enough to touch (about 50 to
60C (122 to 140F)), remove aluminum foil from the sheet. (If
the sheet is allowed to cool to room temperature, the aluminum
foil cannot be pulled free.)
9. Conditioning
9.1 For tests of specic gravity, tensile properties, and
electrical properties, condition the molded test specimen in
accordance with Practice D 618, Condition 4/23/50. The other
tests require no conditioning.
9.2 Conduct tests at the standard laboratory temperature of
23 6 2C (73.4 6 3.6F) for determination of specic gravity,
tensile properties, and electrical properties only. Since the resin
does not absorb water, the maintenance of constant humidity
6
See the ASTM Form and Style Manual, available from ASTM Headquarters.
TABLE 1 Specic Gravity, Melting Point, and Flow Rate
Requirements
Type Grade
I II III
1
A
2
B
1 2 1 2
Specic gravity,
min: 1.69 1.69 1.75 1.75 1.83 1.83
max: 1.76 1.76 1.84 1.84 1.88 1.88
Melting point, C,
min: 255 255 220 220 220 220
max: 280 280 255 255 230 230
Flow rate, g/10 min,
min: 2.0 8.0
C
2.0 10.1 9.0 25.0
max: 16.0 28.0
C
10.0 19.0 18.0 35.0
A
Formerly Types I and II.
B
Formerly Type III.
C
Measured with 1.588-mm (0.0625-in.) orice; other values measured with
2.095-mm (0.0825-in.) orice.
TABLE 2 Detail Requirements for Molded Test Specimens for All
Resins in This Specication
Type Grade
I II III
1 2 1 2 1 2
Tensile strength, min, psi: 5500 4400 4500 4500 4000 4000
Elongation, min, %: 275 200 300 300 350 350
Dielectric constant,
10
3
Hz, max: 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6 2.6
10
6
Hz, max: 2.7 2.7 2.7 2.7 2.7 2.7
Dissipation factor,
10
3
Hz, max: 0.0008 0.0008 0.003 0.003 0.0008 0.0008
10
6
Hz, max: 0.009 0.009 0.009 0.009 0.009 0.009
D 3159
2
during testing is not necessary. Conduct tests for ow rate and
melting endotherm under ordinary laboratory conditions.
10. Packaging and Marking
10.1 PackagingThe material shall be packaged in stan-
dard commercial containers so constructed as to ensure accep-
tance by common or other carriers for safe transportation to the
point of delivery unless otherwise specied in the contract or
order.
10.2 MarkingShipping containers shall be marked with
the name of the material, type, and quantity therein.
10.3 All packing, packaging, and marking provisions of
Practice D 3892 shall apply to this specication.
11. Test Methods
11.1 Melt Flow Rate:
11.1.1 Principle of Test MethodDetermine the ow rate at
297 6 1C using Procedure A or B or Test Method D 1238.
Use the extrusion plastometer described in Test Method
D 1238 and modied in accordance with 11.1.2. The sample
may be pellets or pieces of approximately the same suitable
size cut from molded or extruded forms. Strips about 6 mm
wide by 76 mm long (0.25 by 3 in.) may be conveniently
handled. See Table 2 or 3 of Test Method D 1238 for the
amount of charge that should be adjusted accordingly with the
melt density of ETFE being used. Usually the charge amount is
5 to 15 g. Measure the ow rate using a load of 49 N for Types
I, II, and III. Collect four successive cuts for the manual
method.
11.1.2 ApparatusThe apparatus shall consist of an extru-
sion plastometer, described in Test Method D 1238, modied
by use of corrosion-resistant
7
alloy for the barrel lining, orice,
piston tip, and orice securing device.
8
The orice diameter is
2.095 by 8.000 mm long (0.0825 by 0.315 in.) for all types
except 1.588 by 6.070 mm (0.0625 by 0.239 in.) for Type I,
Grade 2.
11.1.3 Procedure:
11.1.3.1 Temperature CalibrationThe specied melt tem-
perature of 297 6 1C is the temperature measured in the melt
13 mm (0.5 in.) above the orice. This temperature may be
obtained by controlling the temperature measured in the
thermometer well at approximately 305C. Prior to making a
test, set the plastometer temperature as follows: With the
orice in place, insert a standardized thermocouple (Note 2)
through the orice from the bottom of the plastometer to a
point 13 mm (0.5 in.) above the top of the orice. Charge 5 g
of resin granules to the plastometer, compact with the piston,
and wait 10 6 0.5 min for the melt temperature to reach
equilibrium. Make the necessary adjustment in the temperature
controller to bring the melt temperature to 297 6 1C. Repeat
this calibration procedure and record the temperature versus
time at 1-min intervals for the rst 10 min. The polymer should
reach the 297C temperature within 5 min. With polymer in the
plastometer for an elapsed time of 10 min for each point
measured, determine the melt temperature at 6.4-mm (0.25-in.)
intervals from 6.4 mm to 51 mm (2 in.) above the orice. The
entire temperature prole should be within a range of 2C. This
precision is readily obtained by proper insulation of the sides,
bottom, and top of the plastometer.
NOTE 2Suitable standards for thermocouple calibration are: lead,
m.p. 327.5C, potassium dichromate, m.p. 398.0C, and zinc, m.p.
419.4C.
11.1.4 Precision and BiasPrecision and bias for this test
method are to be determined by round-robin testing.
11.2 Specic Gravity Determine the specic gravity of a
specimen approximately 25 by 38 mm (1 by 1.5 in.) blanked or
cut from the molded plaque (see Section 8) in accordance with
the procedures described in Test Methods D 792. Add 2 drops
of a wetting agent to the water in order to reduce the surface
tension and ensure complete wetting of the specimen.
11.3 Melting Endotherm Peak Temperature:
11.3.1 Determine the endotherm melting peak with a differ-
ential thermal analyzer (DTA) or with a differential scanning
calorimeter (DSC) operated in a DTA mode at 10C/min
(18F/min).
11.3.1.1 If DTA equipment is used, refer to Test Method
D 3418 except that the DTA shall be run at 10C/min to 325C
(617F).
11.3.1.2 With either the DTA or DSC, extend the straight
lines tangent to both sides of the endotherm melting tempera-
ture. Take the temperature at which the lines intersect as the
endotherm melting peak temperature.
11.3.2 PrecisionThe single instrument precision of the
differential thermal analysis applied to this test method is
61.2C (2S) as dened in Practice E 177.
11.3.3 Other thermal techniques capable of measuring the
melting endotherm giving equivalent results may be used.
11.4 Tensile Properties:
11.4.1 Cut ve specimens with the microtensile die shown
in Fig. 1. The die shall be of the steel-rule or solid metal type
of curvature of 5 6 0.5-mm (0.2 6 0.02-in.) type. Determine
the tensile properties in accordance with the procedures de-
scribed in Test Method D 638 except that the specimens used
shall be as detailed above, the initial jaw separation shall be
22.0 6 0.13 mm (0.875 6 0.005 in.), and the speed of testing
shall be 50 6 5 mm/min (2 6 0.2 in./min). Clamp the speci-
mens with essentially equal lengths in each jaw. Determine the
elongation from the chart, expressing it as a percentage of the
initial jaw separation.
11.4.2 PrecisionFor tensile strength, the within-
laboratory precision is 65 % of the average (2S), and the
between-laboratory precision is 67 % of the average (2S). For
elongation, the within-laboratory precision is 610 % (2S), and
the between-laboratory precision is 12 % (2S).
9
7
Stellite Grade No. 19, Haynes-Stellite Co., Kokomo, IN, and Duranickel
No. 301, International Nickel Co., 67 Wall St., New York, NY 10005, have been
found resistant to uorocarbon resins.
8
Suitable instruments are available commercially from the F. F. Slocomb Corp.,
1400 Poplar St., Wilmington, DE 19899; Tinius Olsen Testing Machine Co., 2020
Easton Rd., Willow Grove, PA 19090; and D & R Plastic Welders, Inc., Box J,
Hazardville, CT 06036.
9
Supporting data are available from ASTM Headquarters, Request RR:D20-
1067.
D 3159
3
NOTEAll dimensions are in millimetres.
FIG. 1 Microtensile Die
D 3159
4
11.4.3 BiasNo statement of bias can be prepared for this
test method, since there is no absolute method for use as a
comparison basis.
11.5 Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor
Determine dielectric constant and dissipation factor in accor-
dance with Test Methods D 150. Testing shall be done at 10
3
Hz and 10
6
Hz.
12. Number of Tests
12.1 One set of test specimens as prescribed in Section 11
shall be considered sufficient for testing each sample. The
average result of the samples tested shall conform to the
requirements of this specication.
13. Certication and Inspection
13.1 Inspection and certication of the material supplied
with reference to this specication shall be for conformance to
the requirements specied herein.
13.2 Lot-acceptance inspection shall be the basis on which
acceptance or rejection of the lot is made. The lot-acceptance
inspection shall consist of the following:
13.2.1 Melt ow rate, and
13.2.2 Melting point.
13.3 Periodic-check inspection with reference to a speci-
cation shall consist of the tests for all requirements of the
material under the specication. Inspection frequency shall be
adequate to ensure the material is certiable in accordance with
13.4.
13.4 Certication shall be that the material was manufac-
tured by a process in statistical control, sampled, tested and that
the average values for the lot meet the requirements of the
specication.
13.5 ReportsWhen specied in the purchase order or
contract, a report of the test results shall be furnished. The
report shall consist of results of the lot-acceptance inspection
for the shipment.
14. Keywords
14.1 ETFE uoropolymer; extrusion material; uoropoly-
mers; melt-processible uoropolymer; molding material; re-
cycled; tetrauoroethylene copolymers; tetrauoroethylene-
ethylene copolymers
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
This section identies the location of selected changes to this specication. For the convenience of the user,
Committee D-20 has highlighted those changes that may impact the use of this specication. This section may
also include descriptions of the changes, or reasons for the changes, or both.
D 315998:
(1) Added IEEE/ASTM SI 10 in 1.2.
(2) Added statement for recycled products in 1.4.
(3) Deleted reference to Practice D 1898.
(4) Added IEEE/ASTM SI-10 in 2.1.
(5) Added lot denition in 3.1.2.
(6) Replaced Practice D 1898 with an adequate statistical
sampling program in 7.1 to be consistent with Guide D 5740.
(7) In Section 13, replaced with wording from Guide D 5740
for clarity.
ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned
in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk
of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every ve years and
if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards
and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should
make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below.
This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,
United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above
address or at 610-832-9585 (phone), 610-832-9555 (fax), or service@astm.org (e-mail); or through the ASTM website
(www.astm.org).
D 3159
5
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Funeral HandbookDocumento13 páginasFuneral Handbookalfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Ultrasonic CleaningDocumento129 páginasUltrasonic Cleaningalfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
- Module Gen Chem 1 Week 1Documento34 páginasModule Gen Chem 1 Week 1Won YudingzAinda não há avaliações
- GRCA 2015 Congress - The International Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete Association (GRCA) For All Your GRC - GFRC InformationDocumento2 páginasGRCA 2015 Congress - The International Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete Association (GRCA) For All Your GRC - GFRC InformationselcuksivaciAinda não há avaliações
- Tetric+N Bond+Universal 2Documento30 páginasTetric+N Bond+Universal 2alexAinda não há avaliações
- EDM Calibration Handbook Dec 2017Documento25 páginasEDM Calibration Handbook Dec 2017alfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
- TV Emerson Et-13p2Documento26 páginasTV Emerson Et-13p2alfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
- Laser ExtensometroDocumento26 páginasLaser Extensometroalfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
- FDA Guia IndustryDocumento11 páginasFDA Guia Industryalfgraga6043Ainda não há avaliações
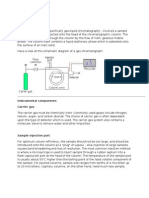
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento5 páginasGas ChromatographyasjawolverineAinda não há avaliações
- Mineralogy 100A Syllabus 2016-EditDocumento4 páginasMineralogy 100A Syllabus 2016-Editnot realAinda não há avaliações
- 430 SSDocumento2 páginas430 SStranngocthuan200Ainda não há avaliações
- Tech AlloyDocumento2 páginasTech AlloyDave MulvihillAinda não há avaliações
- Metamorphic Rocks PracticalDocumento27 páginasMetamorphic Rocks PracticalMr Gk meenaAinda não há avaliações
- Astm Material HardnessDocumento7 páginasAstm Material Hardnessdramilt100% (1)
- Verification Examples EN PDFDocumento143 páginasVerification Examples EN PDFSAMRIDDHI SAHUAinda não há avaliações
- First Floor PlanDocumento1 páginaFirst Floor PlanHEET MEWADAAinda não há avaliações
- Drill Compund Kopr Kote Oilfield MsdsDocumento1 páginaDrill Compund Kopr Kote Oilfield MsdsDumitru MoldovanAinda não há avaliações
- Method Statement For Stone Finish GRC Fabrication and ErectionDocumento5 páginasMethod Statement For Stone Finish GRC Fabrication and ErectionAnjo MolinaAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper Relation Between Workability and Compressive Strength of Self-Compacting ConcreteDocumento4 páginasResearch Paper Relation Between Workability and Compressive Strength of Self-Compacting ConcreteArockia Berlin SoniaAinda não há avaliações
- Two Bedroom Apartment 2Documento1 páginaTwo Bedroom Apartment 2RUTH ELIZABETH NAMUTEBIAinda não há avaliações
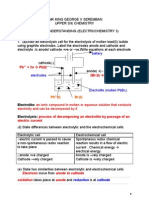
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocumento11 páginasElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshAinda não há avaliações
- 1 PDFDocumento8 páginas1 PDFAke BenAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Information Technical Information: General Information R2 R15Documento42 páginasTechnical Information Technical Information: General Information R2 R15safat parAinda não há avaliações
- PREP FOR Fire Water Line PDFDocumento154 páginasPREP FOR Fire Water Line PDFDusngi MoAinda não há avaliações
- F2 Chem Et2 QNDocumento11 páginasF2 Chem Et2 QNJOSEPH MWANGIAinda não há avaliações
- Science 5 q3 Module 3Documento7 páginasScience 5 q3 Module 3Alli SinaAinda não há avaliações
- Hedenquist 2018 - Epithermal Features at Shallow DepthDocumento26 páginasHedenquist 2018 - Epithermal Features at Shallow Depthcarlos arroyo huaracaAinda não há avaliações
- CastMaterials E00510Documento6 páginasCastMaterials E00510samir basuniAinda não há avaliações
- (English) Translating Chemistry Word Problems (DownSub - Com)Documento4 páginas(English) Translating Chemistry Word Problems (DownSub - Com)ikhsania utamiAinda não há avaliações
- InDocumento135 páginasInNAVNEET BAGGAAinda não há avaliações
- 15 - Mangla Joshi PDFDocumento22 páginas15 - Mangla Joshi PDFSHIKHA SINGHAinda não há avaliações
- Supramolecular Polymers: Alberto CiferriDocumento10 páginasSupramolecular Polymers: Alberto CiferrisnitintAinda não há avaliações
- CUI - Work Instruction - Piping List IdentificationDocumento17 páginasCUI - Work Instruction - Piping List Identificationrty2Ainda não há avaliações
- Cement BoardDocumento5 páginasCement BoardYsabella May Sarthou CervantesAinda não há avaliações
- Indrakanty Surya ShashankDocumento10 páginasIndrakanty Surya ShashankINDRAKANTY SURYA SHASHANKAinda não há avaliações