Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anemia DiagnosticTree PDF
Enviado por
guadialvarezDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anemia DiagnosticTree PDF
Enviado por
guadialvarezDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
56...............................................................................................................................................................................
NAVC Clinicians Brief / July 2010 / Diagnostic Tree
Di agnost i c Tr ee / INTERNAL MEDICINE
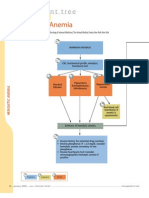
Anemia
Aggregate reticulocyte count > 60,000/mcL (cats)
or > 80,000/mcL (dogs)?
Evidence of increased MCV, MCHC, or RDW?
Regenerative anemia
Peer Reviewed
Caroline M. Kiss, DVM, &
Bess J. Pierce, DVM, Diplomate ABVP & ACVIM
Virginia-Maryland Regional College of
Veterinary Medicine
ANEMIA
Do history and physical examination
identify a cause of blood loss?
No Yes
Low to low-normal total
solids or albumin and
globulin?
Yes
Blood smear evaluation
No
Spherocytes or
autoagglutination
Heinz bodies or
eccentrocytes
Blood parasites
Unremarkable
RBC morphology
Primary or
secondary
IMHA
Rule out underlying
infectious, neoplastic,
drug, or toxic process
Anemia/
oxidative
damage
Rule out onions, garlic,
zinc,
acetaminophen,
propylene glycol
Rule out
Mycoplasma, Babesia,
or Ehrlichia
Rule out occult
hemorrhage, IMHA,
enzymopathies,
hereditary anemias,
hemophagocytic
syndromes, and
hypophosphatemia
Microangiopathic
anemia*
Rule out hemangio-
sarcoma, DIC, vasculitis,
splenic torsion, heat
stroke, dirofilariasis
Nonregenerative anemia
Significant
acanthocytes, schistocytes
DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation; FeLV = feline leukemia virus; FIV = feline immunodeficiency virus; IMHA = immune-mediated
hemolytic anemia; MCHC = mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; MCV = mean cell volume; NRBC = nucleated red blood cell;
RBC = red blood cell; RDW = red cell distribution width
* Microangiopathic anemia occasionally presents as nonregenerative anemia
Spherocyte-like RBC morphology may be noted in zinc toxicity; however, Heinz bodies are usually more prevalent
Yes No
Blood loss
(23 days post acute or
chronic without iron
deficiency)
Rule out gastrointestinal parasites
or ulceration, coagulopathy, throm-
bocytopenia, neoplasia, or trauma
Diagnostic Tree / NAVC Clinicians Brief / July 2010...............................................................................................................................................................................57
Infectious
cause
Ehrlichia
Anaplasma
Parvovirus
FeLV
FIV
Depression
by disease
1
Anemia of inflam-
matory disease
Cancer-associated
anemia
Chronic liver &
kidney disease
Critical illness
Hypothyroidism
Hypoadrenocorticism
Nonregenerative Anemia
Is animal presenting with acute clinical
signs of anemia (eg, weakness, pallor,
tachypnea, tachycardia, etc)?
Preregenerative anemia
Low to low-normal
total solids or albumin
and globulin levels?
No
Yes
Acute
blood loss
Rule out
neoplasia, trauma,
coagulopathy,
thrombocytopenia,
or gastrointestinal
ulceration
Acute
hemolytic
disease
Rule out primary
or secondary
IMHA, blood para-
sites, Heinz body
anemia, microan-
giopathic anemia
True nonregenerative anemia
Do history, physical examination, and diagnostic
tests indicate that another disease process is occurring?
Bone marrow aspirate
or core biopsy
Bone marrow
neoplasia
Aplastic anemia
Pure red cell aplasia
Myelonecrosis
Myelophthisis
Myelodysplastic
syndrome
Presence of NRBCs with or
without basophilic stippling?
Lead poisoning
Low to low-normal total
serum iron and high to high-
normal transferrin levels?
Yes No
Iron deficiency
anemia
Rule out chronic
blood loss
Rule out anemia
due to inflammatory
disease, chronic liver
disease, or folate or
cobalamin deficiency
See Aids & Resources, back page, for references and suggested reading.
Yes Yes
Yes No
Presence of microcytosis
or hypochromasia?
Yes No
Yes No No
Diagnosis Result Investigation
Você também pode gostar
- Radiographic Signs of Pulmonar DiseaseDocumento10 páginasRadiographic Signs of Pulmonar DiseaseMarleeng CáceresAinda não há avaliações
- ASK - Vertebral Heart Scale-1Documento5 páginasASK - Vertebral Heart Scale-1Francisco Rivera AvelarAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg in DogsDocumento107 páginasEcg in DogsPLABITA GOSWAMI100% (2)
- Surgery of The Bovine Large IntestineDocumento18 páginasSurgery of The Bovine Large IntestineJhon Bustamante CanoAinda não há avaliações
- Accd e BookDocumento154 páginasAccd e BookAchmad Nur MmadAinda não há avaliações
- Corrective Shoeing of Equine DenoixDocumento9 páginasCorrective Shoeing of Equine DenoixEduardo JaraAinda não há avaliações
- Manejo Falla Cardiaca Aguda en Gatos PDFDocumento17 páginasManejo Falla Cardiaca Aguda en Gatos PDFFelipeAinda não há avaliações
- Amputation of Tail in AnimalsDocumento8 páginasAmputation of Tail in AnimalsSabreen khattakAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Book of Veterinary Internal Medicine (VetBooks - Ir)Documento88 páginasHand Book of Veterinary Internal Medicine (VetBooks - Ir)Shakil MahmodAinda não há avaliações
- Suspensory Ligament Rupture Tech During Small Animal OH PDFDocumento8 páginasSuspensory Ligament Rupture Tech During Small Animal OH PDFRiesky NudialestariAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Atlas of Canine and Feline Ophthalmic DiseaseNo EverandClinical Atlas of Canine and Feline Ophthalmic DiseaseAinda não há avaliações
- Feline Urologic Syndrome enDocumento2 páginasFeline Urologic Syndrome enSitiNurjannahAinda não há avaliações
- FELINE-Clinical Forms of Acquired Myasthenia Gravis in CatsDocumento7 páginasFELINE-Clinical Forms of Acquired Myasthenia Gravis in Catstaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- Media Analysis For SoundDocumento32 páginasMedia Analysis For SoundJerralynDavisAinda não há avaliações
- Current Diagnostic Techniques in Veterinary Surgery PDFDocumento2 páginasCurrent Diagnostic Techniques in Veterinary Surgery PDFKirti JamwalAinda não há avaliações
- Small Animal/ExoticsDocumento3 páginasSmall Animal/Exoticstaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- Ovariectomia Vs OvariohisterectomiaDocumento5 páginasOvariectomia Vs OvariohisterectomiaRicardo CaveroAinda não há avaliações
- How To Anaesthetize A GiraffeDocumento4 páginasHow To Anaesthetize A Giraffeltrathie3087100% (2)
- Diagnostic Tree - Hemolytic AnemiaDocumento2 páginasDiagnostic Tree - Hemolytic AnemiaЂорђеAinda não há avaliações
- Colic in HorsesDocumento2 páginasColic in HorsesRamos SHAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Surgical InstrumentsDocumento93 páginasVeterinary Surgical InstrumentsEster ToledanoAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Cytology by Leslie C. Sharkey, M. Judith Radin, Davis SeeligDocumento994 páginasVeterinary Cytology by Leslie C. Sharkey, M. Judith Radin, Davis SeeligBê LagoAinda não há avaliações
- Harvard Tools For Small Animal SurgeryDocumento7 páginasHarvard Tools For Small Animal SurgeryJoel GoodmanAinda não há avaliações
- Hints On Veterinary Ophthalmology: By/Sara Ahmed Hassouna BVSC, MSC Surgery Dept. Vet. Med. Alex. UniDocumento39 páginasHints On Veterinary Ophthalmology: By/Sara Ahmed Hassouna BVSC, MSC Surgery Dept. Vet. Med. Alex. UniBibek SutradharAinda não há avaliações
- Dystocia in Mare: - By: Dr. Dhiren BhoiDocumento50 páginasDystocia in Mare: - By: Dr. Dhiren BhoidrdhirenvetAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 Proceeding - Management of The Patient With Canine Parvovirus EnteritisDocumento7 páginas2015 Proceeding - Management of The Patient With Canine Parvovirus EnteritisJHack2Ainda não há avaliações
- LPM-UNIT-III-16 Breeding Ram BuckDocumento16 páginasLPM-UNIT-III-16 Breeding Ram BuckSachin PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Sutures عبد الرحمن الزميليDocumento54 páginasSutures عبد الرحمن الزميليعبد الرحمن خالد الزميليAinda não há avaliações
- Toxin Mechanism of Action Sign of Toxicity Diagnosis Treatment Anticholinesterase InsecticidesDocumento2 páginasToxin Mechanism of Action Sign of Toxicity Diagnosis Treatment Anticholinesterase Insecticidesrayrrn00100% (1)
- 9 A31 Ad 01Documento302 páginas9 A31 Ad 01bhoopendrabisht100% (3)
- Companion September 2014 Low ResDocumento32 páginasCompanion September 2014 Low ReslybrakissAinda não há avaliações
- Fluidtherapy GuidelinesDocumento11 páginasFluidtherapy Guidelineshamida fillahAinda não há avaliações
- Wobblers SyndromeDocumento37 páginasWobblers SyndromeSazzle CakeAinda não há avaliações
- Immunolocalization of Aquaporin-5 Expression in Sweat Gland Cells From Normal and Anhidrotic Horses (Pages 17-23)Documento7 páginasImmunolocalization of Aquaporin-5 Expression in Sweat Gland Cells From Normal and Anhidrotic Horses (Pages 17-23)jenAinda não há avaliações
- Horse HerniaDocumento2 páginasHorse HerniaHadi Putra RihansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy Animals, Healthy CanadaDocumento276 páginasHealthy Animals, Healthy CanadaThe Council of Canadian AcademiesAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Cat Spaying or Dog Spaying?Documento6 páginasWhat Is Cat Spaying or Dog Spaying?Dutchnesia SibaraniAinda não há avaliações
- Canine InsulinomaDocumento5 páginasCanine Insulinomasoff4ikaAinda não há avaliações
- Rinderpest and Peste des Petits Ruminants: Virus Plagues of Large and Small RuminantsNo EverandRinderpest and Peste des Petits Ruminants: Virus Plagues of Large and Small RuminantsAinda não há avaliações
- Canine Ehrlichiosis With Uveitis in A Pug Breed Dog: Case StudDocumento2 páginasCanine Ehrlichiosis With Uveitis in A Pug Breed Dog: Case StudDR HAMESH RATREAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals 3rd EditionDocumento646 páginasVeterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals 3rd Editionmaria da matosAinda não há avaliações
- (Michael Schaer D.V.M) Clinical Signs in Small AnimalDocumento506 páginas(Michael Schaer D.V.M) Clinical Signs in Small AnimalJunior SantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Small Animal Spinal Disorders Diagnosis and Surgery, 2nd Edition (Vetbooks - Ir)Documento369 páginasSmall Animal Spinal Disorders Diagnosis and Surgery, 2nd Edition (Vetbooks - Ir)ghimboasaAinda não há avaliações
- Companion May 2014 Low ResDocumento36 páginasCompanion May 2014 Low ReslybrakissAinda não há avaliações
- Swine EuthanasiaDocumento20 páginasSwine Euthanasia18ovejasAinda não há avaliações
- 1-Equine Digestion PowerPointDocumento15 páginas1-Equine Digestion PowerPointMazhar FaridAinda não há avaliações
- Special Veterinary Pathology: The Canadian Veterinary Journal. La Revue Veterinaire Canadienne February 1990Documento2 páginasSpecial Veterinary Pathology: The Canadian Veterinary Journal. La Revue Veterinaire Canadienne February 1990Alonso Guardado100% (1)
- Birds and Exotics - MCannon PDFDocumento42 páginasBirds and Exotics - MCannon PDFAl OyAinda não há avaliações
- Lumpy Skin DiseaseDocumento28 páginasLumpy Skin DiseaseShivaputraAinda não há avaliações
- Outcomes of Dogs Undergoing Limb Amputation, Owner Satisfaction With Limb Amputation Procedures, and Owner Perceptions Regarding Postsurgical Adaptation: 64 Cases (2005-2012)Documento7 páginasOutcomes of Dogs Undergoing Limb Amputation, Owner Satisfaction With Limb Amputation Procedures, and Owner Perceptions Regarding Postsurgical Adaptation: 64 Cases (2005-2012)William ChandlerAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudiesDocumento56 páginasCase StudiesMayra F. MontielAinda não há avaliações
- Equine Castration AU Vet JournalDocumento7 páginasEquine Castration AU Vet JournalYolandi Lewis StoltzAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Canine and Feline Reproduction: Evidence-Based AnswersNo EverandClinical Canine and Feline Reproduction: Evidence-Based AnswersAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Post Mortem TechnicDocumento263 páginasVeterinary Post Mortem TechnicEdgar EndressAinda não há avaliações
- Companion March2013Documento36 páginasCompanion March2013lybrakissAinda não há avaliações
- Canine CastrationDocumento6 páginasCanine CastrationAnonymous c215Fq6Ainda não há avaliações
- Joints and Ligaments of Hind Limbs in Bison and Its Posnatal DevelopmentDocumento67 páginasJoints and Ligaments of Hind Limbs in Bison and Its Posnatal DevelopmentguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Cushing's Disease in DogsDocumento2 páginasCushing's Disease in DogsguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- In Practice - 2008 - Bradbury - Field Anaesthesia in CamelidsDocumento4 páginasIn Practice - 2008 - Bradbury - Field Anaesthesia in CamelidsguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of The Equine Foot Medical Pain Management For Laminitis 2021Documento13 páginasPharmacology of The Equine Foot Medical Pain Management For Laminitis 2021guadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Cranial Morphology in The Brachygnathic SheepDocumento9 páginasCranial Morphology in The Brachygnathic SheepguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- AnesthesiaDocumento5 páginasAnesthesiaguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnóstico Clínico de Alotrofagia en Bovinos Del Departamento deDocumento6 páginasDiagnóstico Clínico de Alotrofagia en Bovinos Del Departamento deguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Cliquer Box - Anesthesiology - Issue 2 - FinalDocumento45 páginasCliquer Box - Anesthesiology - Issue 2 - FinalguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Lameness Examination in CattleDocumento13 páginasLameness Examination in CattleguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Bat-Standards July 2013 HADocumento67 páginasBat-Standards July 2013 HAguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Listeriosis in Sheep and Goats - Sheep & GoatsDocumento3 páginasListeriosis in Sheep and Goats - Sheep & GoatsguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Essentials of Avian Medicine A Guide For PractitionersDocumento369 páginasEssentials of Avian Medicine A Guide For Practitionersguadialvarez100% (9)
- Polioencephalomalacia - Sheep & GoatsDocumento5 páginasPolioencephalomalacia - Sheep & GoatsguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Practioner Guide Working DogDocumento8 páginasPractioner Guide Working DogguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Construction and Validation of A Decision Tree For Treating Metabolic Acidosis in Calves With Neonatal DiarrheaDocumento17 páginasConstruction and Validation of A Decision Tree For Treating Metabolic Acidosis in Calves With Neonatal DiarrheaguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Umbilical Surgery CalvesDocumento8 páginasUmbilical Surgery CalvesguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- A Review of The Relationship Between Hoof Trimming and Dairy Cattle WelfareDocumento11 páginasA Review of The Relationship Between Hoof Trimming and Dairy Cattle WelfareguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Calf CareDocumento72 páginasCalf CareigorgaloppAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenteric Disease in CalfDocumento5 páginasGastroenteric Disease in CalfguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Comparing The Effect of Three Different Disbudding Methods On Behaviour and Plasma Cortisol of Calves.Documento9 páginasComparing The Effect of Three Different Disbudding Methods On Behaviour and Plasma Cortisol of Calves.guadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison Between The Hanging-Drop Technique and The Running-Drip Method For Identification of The Epidural Space in Dogs.Documento2 páginasComparison Between The Hanging-Drop Technique and The Running-Drip Method For Identification of The Epidural Space in Dogs.guadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Analgesic Efficacy of Sodium Salicylate in An Amphotericin B-Induced Bovine Synovitisarthritis ModelDocumento70 páginasAnalgesic Efficacy of Sodium Salicylate in An Amphotericin B-Induced Bovine Synovitisarthritis ModelguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Calf CareDocumento72 páginasCalf CareigorgaloppAinda não há avaliações
- Umbilical Surgery in CalvesDocumento11 páginasUmbilical Surgery in CalvesguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Abdi Least Squares 06 PrettyDocumento7 páginasAbdi Least Squares 06 PrettyMohd Faiz Mohd ZinAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Phase Proteins As Early Non-Specific Biomarkers of Human and Veterinary DiseasesDocumento420 páginasAcute Phase Proteins As Early Non-Specific Biomarkers of Human and Veterinary DiseasesguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Hell Remedies Veterinary GuideDocumento93 páginasHell Remedies Veterinary GuideNick Max100% (2)
- Paratuberculosis Organism, Disease, Control 2010Documento388 páginasParatuberculosis Organism, Disease, Control 2010guadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Metabolism - Cell Homeostasis and Stress ResponseDocumento218 páginasCell Metabolism - Cell Homeostasis and Stress ResponseguadialvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Information Form For Passengers Requiring Medical Clearance - MEDIF / Part 1Documento2 páginasInformation Form For Passengers Requiring Medical Clearance - MEDIF / Part 1MOHAMEDAinda não há avaliações
- CAseDocumento3 páginasCAseabdihakemAinda não há avaliações
- The Efficacy of Medicinal Leeches in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - A Systematic Review of 277 Reported Clinical Cases-2Documento11 páginasThe Efficacy of Medicinal Leeches in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - A Systematic Review of 277 Reported Clinical Cases-2Wara Samsarga GedeAinda não há avaliações
- First Aid and CPR Training Providing Company ProfileDocumento11 páginasFirst Aid and CPR Training Providing Company ProfilemedicalserviceAinda não há avaliações
- ANGIOLOGYDocumento32 páginasANGIOLOGYFaisal IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Technician or Instrument Room TechDocumento2 páginasSurgical Technician or Instrument Room Techapi-78323882Ainda não há avaliações
- CV 2017 VirginiaDocumento4 páginasCV 2017 Virginiaapi-353693776Ainda não há avaliações
- RE6210 66b2ef9052fullabstract PDFDocumento110 páginasRE6210 66b2ef9052fullabstract PDFmariamonaAinda não há avaliações
- Epistaxis and TumorDocumento20 páginasEpistaxis and TumorTri Ayu WdAinda não há avaliações
- Nur Assess BSN Nursing Care PlanDocumento12 páginasNur Assess BSN Nursing Care PlanWen SilverAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Physiotherapist in Neuro-RehabilitationDocumento3 páginasRole of Physiotherapist in Neuro-RehabilitationMohammad AkheelAinda não há avaliações
- Pain Management in Dentistry: Jeff Burgess, DDS, MSD (Retired) Clinical Assistant Professor, Department ofDocumento14 páginasPain Management in Dentistry: Jeff Burgess, DDS, MSD (Retired) Clinical Assistant Professor, Department ofStefanus TabboAinda não há avaliações
- Referralsystem 161202080450Documento21 páginasReferralsystem 161202080450DRx Sonali Tarei100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento11 páginasAnnotated Bibliographyapi-321537874100% (1)
- Teaching Plan Assignment Template Assessment (These Are Possible Assessment Elements)Documento4 páginasTeaching Plan Assignment Template Assessment (These Are Possible Assessment Elements)api-402048659Ainda não há avaliações
- Pre-Participation Screening: The Use of Fundamental Movements As An Assessment of Function - Part 2Documento8 páginasPre-Participation Screening: The Use of Fundamental Movements As An Assessment of Function - Part 2gogo36Ainda não há avaliações
- Referat CA KolonDocumento48 páginasReferat CA KolonRenata CilestrinaAinda não há avaliações
- All Ic AppendDocumento73 páginasAll Ic AppendSlaviša KovačevićAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 TabletsDocumento84 páginasChapter 8 Tabletsashrutsumi86100% (1)
- SEMINARDocumento28 páginasSEMINARRajvir Pandher Mudahar0% (1)
- Safety in Hospitals: A Computer - Based Learning Program For StudentsDocumento15 páginasSafety in Hospitals: A Computer - Based Learning Program For Studentsmonir61Ainda não há avaliações
- BKA ProsthesisDocumento3 páginasBKA ProsthesisAditi Lakhwara KohliAinda não há avaliações
- Parkway Group HotelsDocumento11 páginasParkway Group HotelsAryan GargAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Best Nursing Action of Nurse Patricia in Line With The Environmental Theory?Documento2 páginasWhat Is The Best Nursing Action of Nurse Patricia in Line With The Environmental Theory?CHELSEA MAE SAULOAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership and Management For NursesDocumento18 páginasLeadership and Management For NursesmerAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Discharge SummaryDocumento4 páginasSample Discharge SummaryPatient Safety My100% (2)
- The Art and Science of Cytology and Cytopathology Has Been Implemented and Recognized As Early As The 18thDocumento3 páginasThe Art and Science of Cytology and Cytopathology Has Been Implemented and Recognized As Early As The 18thphysiosyedAinda não há avaliações
- Inflammatory Lesions of The JawsDocumento54 páginasInflammatory Lesions of The JawsAi Rafikah Nurpratiwi100% (1)
- Transtracheal Wash and Bronchoalveolar Lavage: Maureen D. Finke, DVM, DACVIMDocumento4 páginasTranstracheal Wash and Bronchoalveolar Lavage: Maureen D. Finke, DVM, DACVIMSandra Putri DewiAinda não há avaliações
- Immortally YoursDocumento13 páginasImmortally YoursMacmillan Publishers80% (5)