Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Torque Diagrams
Enviado por
shilton1989Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Torque Diagrams
Enviado por
shilton1989Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
http://www.Drshokuhi.
com
I nternal Forces
ENGR 221
March 17, 2003
http://www.drshokuhi.com
Lecture Goals
Internal Force in Structures
Axial Load
Torque
Shear Forces
Bending Moment
What use are the I nternal Loads?
In terms of the grand scheme of things, why do we
need to find the internal loads?
Stresses are determined by the bending
moment and shear stresses are determined
by the maximum shear force and the
maximum torsional moments.
NOT ALL MAXIMUM FORCES OCCUR AT TH
SUPPORTS!
General Solution Scheme
The general scheme for finding the internal set of
forces is
a) Draw the free-body diagram
b) Determine the support reactions
c) Apply the equations of equilibrium
x y z
x y z
0 0 0
0 0 0
F F F
M M M
Simplest form Solution Scheme
Axial Forces and Torque in bars and shafts
Internal force act along the axis
Torque acts along the axis of symmetry
From the internal forces we can obtain axial
force diagram and from the torques we can
obtain a torque diagram along the axis of
symmetry.
Force Diagrams
Force diagrams show the all of the internal
forces acting in the member.
1) Axial Force Diagram
2) Torque Diagram
3) Shear Diagram
4) Moment Diagram
Axial Forces
Draw the free-body diagram and solve for the forces
acting on the body.
Take sections at each point a transition occurs and
solve for the interior forces acting at each point. A
transition is a point where a new force is applied.
Use equilibrium to solve the problem.
Draw the axial force diagram using the information
from the internal forces.
Example Axial Load Problem
Determine the axial forces transmitted by transverse
cross sections in intervals AB, BC, and CD of the bar.
Draw an axial force diagram for the bar.
Example Axial Load Problem
Determine the axial forces at point A,
x A
A
80 kips 50 kips 10 kips
20 kips
F F
F
Example Axial Load Problem
Determine the axial forces at point B,
x BC
BC
50 kips 10 kips
60 kips
F F
F
Example Axial Load Problem
Determine the axial forces at point C,
x CD
CD
10 kips
10 kips
F F
F
Example Axial Load Problem
Draw the axial force
diagram, all of the
forces are in tension.
Class Axial Load Problem
Determine the axial
forces transmitted by
transverse cross sections
at points A, B, and C of
the bar. Draw an axial
force diagram for the
bar.
Torque
Torque is a moment acting about the central axis of the
body. For a shaft
The double arrow represents the moment at a point
M
M
Torque
Solve the torque using equilibrium to find all of the
moments.
Cut a section at a transition point (torque is applied)
and solve the internal moment at the point bring the
system back to equilibrium and this is the torque at the
point.
Using this information to draw the torque diagram.
Example Torque Problem
For the steel shaft, determine the maximum torque
transmitted by any transverse cross section of the
shaft. Draw a torque diagram for the shaft.
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment T from equilibrium.
10 k-ft 17 k-ft 60 k-ft 25 k-ft 12 k-ft
54 k-ft
M T
T
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment at point moving from left to
the right at point A.
A
A
10 k-ft
10 k-ft
M M
M
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment at point B.
B
B
10 k-ft 17 k-ft
7 k-ft
M M
M
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment at point C
C
C
10 k-ft 17 k-ft 54 k-ft
47 k-ft
M M
M
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment at point D.
D
D
10 k-ft 17 k-ft 54 k-ft 60 k-ft
13 k-ft
M M
M
Example Torque Problem
Determine the moment at point E
E
E
10 k-ft 17 k-ft 54 k-ft 60 k-ft 25 k-ft
12 k-ft
M M
M
Example Torque Problem
Draw the torque diagram
Class Torque Problem
For the steel shaft, determine the maximum torque
transmitted by any transverse cross section of the
shaft. Draw a torque diagram for the shaft.
I nternal Forces and Bending
Moment
Three internal force act in members frames and beams,
axial load, F, shear force, V, and bending moment, M.
The axial load, F, is in either compression or tension and
acts along the centroid of the member.
The shear force, V, acts perpendicular to the surface of the
cut or section.
The bending moment, M, acts about the axis coming out
of the surface.
I nternal Forces and Bending
Moment
Three internal force act in members frames and beams,
axial load, F, shear force, V, and bending moment, M.
I nternal Forces and Bending
Moment
The bending moment, M.
I nternal Forces and Bending
Moment
The shear force, V.
Example I nternal Forces in a
Frame Problem
Determine the internal forces in member EFG at
point J.
Example I nternal Forces in a
Frame Problem
Draw the free body diagram
x x x
y y y
y y
D x
x
x
0
0 60 lb.
60 lb
0 2 ft. 60 lb 3 ft.
90 lb
90 lb
F D G
F D G
D G
M G
G
D
Example I nternal Forces in a
Frame Problem
Look at member EFG
x FC
FC
y y FC EA
E y
y
3
0 90 lb
5
150 lb.
4
0
5
4
0 4.5 ft. 150 lb 1.5 ft.
5
40 lb
F F
F
F G F F
M G
G
Example I nternal Forces in a
Frame Problem
Do a cut at point J and draw a free-body diagram and
use equilibrium.
x Jx
Jx
y Jy
Jy
J J
J
0 90 lb
90 lb.
0 40 lb.
40 lb.
0 40 lb 1.5 ft.
60 lb-ft
F F
F
F F
F
M M
M
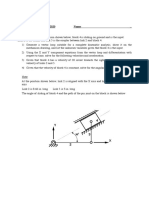
Quiz
Determine the forces exerted on the wooden
block. Points A and D are on the same plane.
Class I nternal Forces in a
Frame Problem
Determine the internal forces in member BE at
point F.
Homework (Due 3/24/03)
Problems:
8-1, 8-6, 8-10, 8-12, 8-14
Você também pode gostar
- Mechanics of Materials Lecture NotesDocumento130 páginasMechanics of Materials Lecture NotesHowl Solomon100% (2)
- 2AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES I (Review)Documento150 páginas2AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES I (Review)July Tade100% (1)
- Stress and Strain RenewDocumento65 páginasStress and Strain Renewshafarizy100% (1)
- VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 16Documento19 páginasVECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 16Yohanes Elia PAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of MeterialsDocumento142 páginasStrength of MeterialsEricJohnDeraferaAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Forces: ENGR 221 March 17, 2003Documento35 páginasInternal Forces: ENGR 221 March 17, 2003Ck MacAinda não há avaliações
- Civ100 M5Documento80 páginasCiv100 M5Anonymous WmMP8H6JGAinda não há avaliações
- Ch3 FrameDocumento51 páginasCh3 Framengkt722Ainda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Statika 3 Kesetimbangan Benda TegarDocumento37 páginasKuliah Statika 3 Kesetimbangan Benda TegarMuhammad NurdinAinda não há avaliações
- ME 101: Engineering Mechanics: Rajib Kumar BhattacharjyaDocumento55 páginasME 101: Engineering Mechanics: Rajib Kumar BhattacharjyariteshsamantrayAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Statika 3 Kesetimbangan Benda TegarDocumento37 páginasKuliah Statika 3 Kesetimbangan Benda TegarMuhammad Raihan BalfasAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials: (SI Units)Documento11 páginasStrength of Materials: (SI Units)Fitra VertikalAinda não há avaliações
- Resistencia de Materiales: Análisis de Propiedades, Esfuerzo y DeformaciónDocumento37 páginasResistencia de Materiales: Análisis de Propiedades, Esfuerzo y DeformaciónLuisAinda não há avaliações
- NotesDocumento123 páginasNotesGAURAV RATHOREAinda não há avaliações
- Practise Problems Set05Documento8 páginasPractise Problems Set05rohit kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Take Home QuizDocumento8 páginasTake Home QuizAshley SimmonsAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Set (Stress & Internal Loading) NewDocumento58 páginas1st Set (Stress & Internal Loading) NewPhyChMtAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials I: (SI Units)Documento135 páginasStrength of Materials I: (SI Units)shjahsjansha100% (3)
- Lecture 7 Plane Truss Full PageDocumento79 páginasLecture 7 Plane Truss Full Pageilhammka100% (1)
- 6 Materials Summary 2014Documento31 páginas6 Materials Summary 2014api-248740887Ainda não há avaliações
- QLM of SOMDocumento4 páginasQLM of SOMatulkumargaur26Ainda não há avaliações
- MachineFrames SplitDocumento70 páginasMachineFrames SplitRavi TilaganjiAinda não há avaliações
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocumento34 páginasStatics of Rigid BodiespesobucksAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 1 Vectors Equilibrium and Moment of A ParticleDocumento6 páginasProblem Set 1 Vectors Equilibrium and Moment of A ParticleErl GomezAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Mechanical and Structural Calculations Booklet ST PaulsDocumento43 páginas05 Mechanical and Structural Calculations Booklet ST PaulsGanesh VeluAinda não há avaliações
- Week 2 - Load and Stress AnalysisDocumento2 páginasWeek 2 - Load and Stress AnalysisAnonymous M2ZVOCfpAinda não há avaliações
- Bending of Beams SolleroDocumento34 páginasBending of Beams SolleroPedroLemosAinda não há avaliações
- Stress ConceptDocumento45 páginasStress ConceptMostafa SherifAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanic of Materials (Normal Stress)Documento44 páginasMechanic of Materials (Normal Stress)moj33Ainda não há avaliações
- Manual Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 3Documento48 páginasManual Mechanics of Deformable Bodies 3Miyamura IzumiAinda não há avaliações
- MP2001 Chapter 1Documento26 páginasMP2001 Chapter 1Jaren FooAinda não há avaliações
- BEAM Gaya Internal, Diagram Gaya Geser Dan MomenDocumento22 páginasBEAM Gaya Internal, Diagram Gaya Geser Dan Momenazamataufiq100% (1)
- Axial Deformation Problems With Solutions PDFDocumento2 páginasAxial Deformation Problems With Solutions PDFAngela ElumbaAinda não há avaliações
- Guided Tour: Chapter IntroductionDocumento3 páginasGuided Tour: Chapter IntroductionJenny PriceAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 - Tranverse ShearDocumento43 páginasChapter 7 - Tranverse Shearzamspacekl100% (1)
- Strength of Materials Objective and Conventional by S K MondalDocumento434 páginasStrength of Materials Objective and Conventional by S K Mondalpadalakirankumar33% (3)
- Theory of PlasticityDocumento10 páginasTheory of Plasticitybabu1434100% (1)
- Beam Analogy DerivationDocumento9 páginasBeam Analogy DerivationYassine Iferden TorssanovskiAinda não há avaliações
- Stress ResultantsDocumento19 páginasStress ResultantsAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 - Stress-Strain RelationshipDocumento26 páginasLecture 1 - Stress-Strain RelationshipSri JaiandranAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Stresses in BeamsDocumento32 páginas10 Stresses in BeamssephAinda não há avaliações
- Copy Slides Test 2Documento60 páginasCopy Slides Test 2fatin_musaAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Failure: Learning ObjectivesDocumento14 páginasDesign and Failure: Learning Objectivesedgar_chieyahoocomAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Mechanics - DM23801Documento41 páginasSolid Mechanics - DM23801Michael MeashoAinda não há avaliações
- MN116 - Whole-Course TutorialDocumento11 páginasMN116 - Whole-Course Tutorialjordangeorge.66jAinda não há avaliações
- StressDocumento5 páginasStressmessel2013Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 6 - Frames+Friction+FluidDocumento60 páginasWeek 6 - Frames+Friction+Fluidiwhy_Ainda não há avaliações
- Rectangular Reinforced Concrete BeamDocumento60 páginasRectangular Reinforced Concrete BeamMedianna Novita100% (1)
- Design Area Exam - Fall 2020 Name - Problem 1Documento4 páginasDesign Area Exam - Fall 2020 Name - Problem 1PriyadarshanSinghAinda não há avaliações
- Statics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisDocumento69 páginasStatics and Strength of Materials Intro Beam AnalysisSam SweeneyAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of MaterialsDocumento81 páginasStrength of MaterialsSenthil Kumar67% (3)
- Chap III - StaticsDocumento55 páginasChap III - StaticsEnas Al-khawaldehAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Stresses and Deformations Arising From Torsional LoadingDocumento31 páginas09 Stresses and Deformations Arising From Torsional LoadingMich AngelesAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 5.1 Conditions Equations of Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocumento52 páginasChap 5.1 Conditions Equations of Equilibrium of A Rigid Bodyrameshaarya99Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorials and Solution InstructionsDocumento25 páginasTutorials and Solution InstructionsDanin kimAinda não há avaliações
- Asabe Pe Review Machine DesignDocumento80 páginasAsabe Pe Review Machine DesignPradeep Kumar MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Analytic Solutions For Tapered Column Buckling PDFDocumento6 páginasAnalytic Solutions For Tapered Column Buckling PDFshilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- STEP Files - ProcedureDocumento1 páginaSTEP Files - Procedureshilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- RPM To Linear Velocity Calculator - EndMemoDocumento1 páginaRPM To Linear Velocity Calculator - EndMemoshilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- 1Documento9 páginas1shilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- Goyen HardwareDocumento3 páginasGoyen Hardwareshilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- OF Of: of P. P. 2091, An of P. On On ofDocumento5 páginasOF Of: of P. P. 2091, An of P. On On ofshilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- Preface: John Moalli Menlo Park. CaliforniaDocumento1 páginaPreface: John Moalli Menlo Park. Californiashilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- Document Change Notice DCN Number 5070: Old Revision New Revision Logistics Review (Y/N)Documento1 páginaDocument Change Notice DCN Number 5070: Old Revision New Revision Logistics Review (Y/N)shilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- T A B L E 23O.-Characterlstlcs A Number of Plastics'6Documento2 páginasT A B L E 23O.-Characterlstlcs A Number of Plastics'6shilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- Document Change Notice DCN Number 5098: Old Revision New Revision Logistics Review (Y/N)Documento1 páginaDocument Change Notice DCN Number 5098: Old Revision New Revision Logistics Review (Y/N)shilton1989Ainda não há avaliações
- PalDuct PIR Datasheet ME EN 04 15Documento2 páginasPalDuct PIR Datasheet ME EN 04 15Leonardo PimentelAinda não há avaliações
- Gaisano Express Construction Drawing - LRDocumento40 páginasGaisano Express Construction Drawing - LRJade SodosoAinda não há avaliações
- Housing Portfolio by Sapa Building System - ENDocumento39 páginasHousing Portfolio by Sapa Building System - ENSapa Building SystemAinda não há avaliações
- Livchak ASHRAE Journal Chilled Beam & DOASDocumento10 páginasLivchak ASHRAE Journal Chilled Beam & DOAS윤병택Ainda não há avaliações
- Transportation Geotechnics: Tirupan Mandal, James M. Tinjum, Tuncer B. EdilDocumento11 páginasTransportation Geotechnics: Tirupan Mandal, James M. Tinjum, Tuncer B. EdilDaniel Juan De Dios OchoaAinda não há avaliações
- EmmDocumento18 páginasEmmrajasamygopalAinda não há avaliações
- Structures Design Detail ConnectionDocumento130 páginasStructures Design Detail ConnectionTon Lee100% (1)
- Rule 16 - Plastics (Book Format)Documento3 páginasRule 16 - Plastics (Book Format)Thea AbelardoAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering GeologyDocumento19 páginasEngineering GeologyNaniAinda não há avaliações
- Mansory 1Documento5 páginasMansory 1John Isaac BanaagAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Structures: SciencedirectDocumento15 páginasEngineering Structures: SciencedirectStructural SpreadsheetsAinda não há avaliações
- Base PlateDocumento12 páginasBase PlateHSY79Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Year Project Proposal On Residential Building ProjectDocumento13 páginasFinal Year Project Proposal On Residential Building ProjectPrashant JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Diary ReportsDocumento14 páginasDaily Diary ReportsOBERT MASALILAAinda não há avaliações
- Parts-Of-The-house Worksheet (There Is - There Are - Preposition)Documento1 páginaParts-Of-The-house Worksheet (There Is - There Are - Preposition)Thanh Truc Nguyen TranAinda não há avaliações
- Design of A Rectangular ColumnDocumento4 páginasDesign of A Rectangular ColumnGnansabesan JathurschanAinda não há avaliações
- National Children's Science Centre Planning Report - Dublin City CouncilDocumento54 páginasNational Children's Science Centre Planning Report - Dublin City Councilnsheridan4190Ainda não há avaliações
- Seth Harvey Hendeve IPPPE ME QuizDocumento4 páginasSeth Harvey Hendeve IPPPE ME Quizjeams vidalAinda não há avaliações
- ProductGuideFullSet2014 7TH PDFDocumento128 páginasProductGuideFullSet2014 7TH PDFbiik0076153Ainda não há avaliações
- 10-Planning and Design of Wind FarmDocumento42 páginas10-Planning and Design of Wind FarmSein Win TunAinda não há avaliações
- Design of BearingDocumento56 páginasDesign of BearingPawan BhattaraiAinda não há avaliações
- Erw Pipe Manufacturing Process PDFDocumento2 páginasErw Pipe Manufacturing Process PDFJabulaniAinda não há avaliações
- Service ToolsDocumento29 páginasService ToolsRobert TirtaAinda não há avaliações
- ASME B16.20a-2000Documento65 páginasASME B16.20a-2000Pierre RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Quotation Letter: Yours TrulyDocumento4 páginasQuotation Letter: Yours TrulyJonathan LatawanAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Isolated & Combined FootingDocumento27 páginasDesign of Isolated & Combined Footingrraj das100% (2)
- 2x4 Half-Rack: Material List 15: 6' 2x4's 2: 8' 2x6'sDocumento2 páginas2x4 Half-Rack: Material List 15: 6' 2x4's 2: 8' 2x6'sSemhar Cédric LevasseurAinda não há avaliações
- Reebol WBDocumento2 páginasReebol WBVenkata RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Existing Vessel To Transitional VesselDocumento2 páginasExisting Vessel To Transitional VesselcarsicocnflatuoAinda não há avaliações
- Work Method Statement AgbaraDocumento28 páginasWork Method Statement Agbaravictor egharevbaAinda não há avaliações