Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Diabetes Mellitus Drug Chart
Enviado por
lui.stephanie1751100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
271 visualizações3 páginasdrug chart for dm
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentodrug chart for dm
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
271 visualizações3 páginasDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chart
Enviado por
lui.stephanie1751drug chart for dm
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
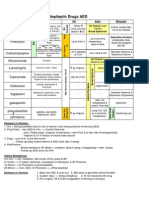
DIABETES MELLITUS PHARMACOLOGICAL ALTERNATIVES
DRUG MOA EFFICACY/
PLACE IN DM MANAGEMENT
USUAL
DOSING/DAY
Onset/PK CONTRAINDICATIONS S/E DI CONVENIENCE/
COST
BIGUANIDE
Metformin 500mg,
850mg
(Glucophage,
generic)
500mg bid or tid
ac. Titration
required (start at
500mg qd)
24hours
Duration: 8-12hr
Excretion: 100%
renally
$9 (ODB covered)
Extended release
500mg (Glumetza)
Decrease hepatic glucose output.
Improved insulin action (less insulin
resistance) w/ enhanced glucose
uptake into muscle.
Beneficial effects on body weight
(stable/reduced).
Lower fasting glycemia.
! A1C by ~1.5-2% (similar to sulfonylureas).
1
st
line tx in all patients w/ type II DM.
Can be used in patients w/ stable and non-severe
heart failures since it exerts no adverse cardiac
effects.
Does not cause hypoglycemia when used as
monotherapy.
Triglyceride/LDL reduction by 15%
! FPG to 60-80mg/dL
Modest weight lost.
1500mg qd in 1
dose with meal.
Titration required.
Duration: 24hr
Renal insufficiency; CrCL<30mL/min
(caution if <50mL/min) and may
increase risk of lactic acidosis.
Infertile women w/ polycystic ovary
syndrome may experience resumptive
ovulation (may have to start BC)
Caution in patients w/ RF for lactic
acidosis
Well tolerated.
GI s/e (anorexia, nausea, ab
discomfort, diarrhea) but minimized
when taken w/ meals and titrated
Metallic taste.
Rarely can cause lactic acidosis (esp.
in renal failure).
! Vit B12 and folate
absorption, but
clinical anemia is
rare.
Cimetidine competes
No CYP interactions
$52 (ODB
covered)
SULFONYLUREAS
Gliclazide 80mg 80 qd/bid w/ food Duration: 16-24hr $11 (ODB
covered)
Gliclazide 30mg
Modified Release
60mg qd w/ meals. Duration: 24hr
Suitable for renal insufficiency
(completely metabolized to inactive
compounds) $23 (ODB)
Glimepiride 1mg,
2mg, 4mg
2-4mg qd w/ meals. Duration: 24hr Suitable for renal insufficiency $16
Glyburide 2.5mg,
5mg
Insulin secretagogues.
Lower glycemia by enhancing
insulin secretion (both basal and
prandial).
! A1C by ~1.5-2% (similar to metformin).
Onset of effects are relatively rapid, glycemic
targets over time are not as good as monotherapy
w/ a TZD or metformin.
2
nd
line
Fully effects usually realized at ! max. doses and
higher doses should be avoided. Initial doses
should start at 50%
10mg qd/bid w/
food. Titrate ALL
Duration: 16-24hr Caution in CrCL<30mL/min; dose
adjustment
Hypoglycemia (more frequent in the
elderly, poor eaters, renal/hepatic
impairment) with risk as follows
glyburide>glimepiride>gliclazide,
weight gain (2-3kg), rash, gi
disturbances.
Beta-blockers mask
hypoglycemia
symptoms
$4 (ODB covered)
MEGLITINIDES
Repaglinide
0.5mg, 1mg, 2mg
(Gluconorm)
1-2mg tid ac
(30mins ac). (Max.
4mg qid)
$28
Nateglinide 60mg,
120mg, 180mg
(Starlix)
Insulin secretagogues.
Stimulate insulin secretion, although
they bind to a different site w/in the
sulfonylurea receptor.
Primarily stimulate prandial insulin
secretion (rather than basal insulin
secretion).
! A1C by ~1-1.5% in repaglinide (similar to
sulfonylureas)
! A1C by only 0.5-1% in nateglinide (similar to
acarbose).
For monotherapy of T2DM or for use in combo w/
metformin in patients not adequately controlled on
either agent alone. Dont use w/ sulfonylureas
Better control of postprandial glucose than
sulfonylureas
120mg tid ac
(30mins ac). (Dose
can be as low as
60mg or as high as
180mg tid ac).
Onset: 15-30min
w/ peak levels at
1 hr
Duration: 4hr
Caution in missed meals"dose should
be skipped or delayed.
Caution in hepatic insufficiency (may
cause elevation of drug levels and
increase risk of hypoglycemia).
Suitable for renal insufficiency and in
heart failure.
Hypoglycemia risk is significantly
lower than w/ sulfonylurea, but risk of
weight gain is similar
Gemfibrozil (lipid
lowering agent)
inhibits 2C9 and
results in increase
concn of repaglinide.
Inhibitors or inducers
of CYP 2C8, 2C9,
3A4
$42
GLITAZONES (THIAZOLIDINEDIONES/TZDs)
Pioglitazone 15mg,
30mg, 45mg
(Actos, generic)
! A1C by 1-1.5% (similar to metformin)
More durable effect on glycemic control
Approved for monotherapy or w/ metformin or
sulfonylurea, but not use as triple tx.
Preferred over rosi due to CVD concerns.
15-45mg in 1 dose
w/out regard to
food
$34-71 (EAP
covered)
Rosiglitazone 2mg,
4mg, 8mg
(Avandia)
PPAR ! modulator. Increase
sensitivity of muscle, fat, and liver
to endogenous and exogenous
insulin.
Does not cause hypoglycemia when
used alone.
Pioglitazone modestly improves
lipids and possibly decrease CV
events.
! A1C by 1-1.5% (similar to metformin)
More durable effect on glycemic control esp. when
compared to sulfonylureas.
Approve in combo w/ metformin
4-8mg in 1-2 doses
w/out regard to
food
Onset: 2-4 weeks
Duration: 1-2
weeks
Max response: 6-
12 weeks
Metabolism: 2C8
(pioglitazone also
metabolized by
3A4)
Hepatic insufficiency may lead to
accumulation (okay to use in renal
insufficiency).
Unstable or severe heart failure
Infertile women w/ polycystic ovary
syndrome
Caution in postmenopausal women at
risk of osteoporosis due to an
increased risk of bone fractures
Weight gain (4-6kg), fluid retention,
increase plasma volume, Increase risk
of CV events (MI) w/ rosiglitazone
(30-40% increase).
Increased fracture risk, bladder cancer
risk (rosiglitazone)
All patients should be monitored for
s&sx of fluid retention, heart failure
(edema, rapid weight gain, fatigue,
SOB)
Use w/ insulin not
approved unless there
is close monitoring
for heart failure
Rosiglitazone: 2C8
inhibitors
(gemfibrozil) and 2C8
inducers (rifampin)
$61-86 (EAP
covered)
ALPHA-GLUCOSIDE INHIBITOR
Acarbose 50mg,
100mg (Glucobay)
Prandial glucose regulator.
Inhibits alpha-glucosidase, which
normally hydrolyzes starches and
sugars in the intestine to liberate
glucose.
Reduce the rate of digestion of
polysaccharides in the proximal
small intestines.
! A1C by 0.5-0.8%. Fasting blood glucose and
overall glycemic control are only modestly
improved.
Lowers postprandial glucose levels (by 2-
3mmol/L) w/out causing hypoglycemia.
In patients w/ prediabetes (IGT, IFG), reduced
progression to DM by 25%.
No systemic toxicity.
50mg in tid taken
with first bite of
meal. Titrate to
decrease GI sx
(start at 25mg qd to
tid and increase by
25mg/day q3-
7days).
Duration: 4hr
Absorption:
minimal
Caution in IBD, intestinal obstruction,
colonic ulceration, large hernias.
Increased gas production and GI sx
(e.g. diarrhea, abdominal pain)
GI sx are dose dependent and abate w/
time and proper titration.
High sucrose diet leads to increase
flatulence and diarrhea.
Hypoglycemic rxns must be treated w/
monosaccharide (such as dextrose)
Digestive pancreatic
enzyme supplements
may decrease
efficacy.
$23 (LU)
DPP-4 INHIBITOR
Sitagliptin 100mg
(Januvia)
Inhibits DPP-4, which rapidly
degrades GLP-1 and GIP, incretins
that increase glucose-mediated
insulin secretion and suppress
glucagon secretion.
Hypoglycemia is avoided
Neutral effect on body weight.
! A1C by 0.6-1%. Improvements in overall
glycemic control are relatively modest.
Use only as add-on therapy for patients who are
inadequately controlled by metformin tx.
Postprandial BG values are reduced to a greater
degree than fasting BG values.
100mg qd Onset: 4 weeks,
max effect in 18
weeks
Duration: 24hr
Excretion: 80%
renally
CrCL<50mL/min since drug
accumulation can occur; dose adjusted
for renal insufficiency
Relatively well tolerated. Headaches
and infections (nasopharyngitis,
urinary tract) possibly due to immune
impairment, anemia, decreased
lympocytes
Metabolic drug
interactions unlikely
since hepatic
metabolism is
minimal (Cyp3A4)
Can cause increase
diogoxin
$87 (ODB
covered)
GLUCAGON-LIKE PEPTIDE-1 (GLP-1) AGONISTS
Exenatide BID SC Not recommended in renal
insufficiency (<50mL/min);
<30mmol/min for exenatide
High frequency of GI disturbances
(N/V/D), which tend to abate w/ time,
pancreatitis (rare)
Chance of thyroid cancer
Liraglutide
Binds avidly to GLP-1 receptor on
the pancreatic beta-cell and
increases glucose-mediated insulin
secretion. Suppresses glucagons
secretion and slows gastric motility.
(stimulate insulin release in the
presence of glucose & induce
feeling of satiety)
! A1C by 0.5-1% mainly by lowering
postprandial blood glucose levels.
Weight loss 2-3kg over 6 mos.
Use in combo w/ metformin, sulfonylurea, and/or
TZD.
No hypoglycemia
Liraglutide more effective than exenatide
Once daily SC Not approved in
Canada
AMYLIN AGONISTS
Pramlintide Synthetic analogue of beta-cell
hormone amylin. Slows gastric
emptying, inhibits glucagons
production
! A1C by 0.5-0.7%.
Weight loss 1-1.5kg over 6 mos.
As adjunctive tx w/ regular insulin or rapid-acting
insulin analogues.
SC AC GI s/e, which tend to abate w/ time
0.6mg/day to 1.8 ml/day
linagliptin (DPP4 inhibitor) - 5 mg QD
ANTI-OBESITY AGENTS
Orlistat 120mg
(Xenical)
360mg in 3 doses Duration: 4hr $140 (not covered)
Sibutramine
10mg, 15mg
(Meridia)
reversible inhibitor of lipases that
form covalent bonds with the active
serine site of gastric & pancreatic
lipases and thus unavailable to
hydrolyze dietary fat in the form of
triglycerides into FFA and
monoglycerides
can be used in combo with anti-diabetic agents) to
improve blood glucose control in overweight
T2DM patients who are inadequately controlled on
diet, exercise, and one or more of a sulphonylurea,
metformin, insulin
10mg in 1 dose Duration: 24hr
Monitor for anti-coagulants GI side effects Inhibit fat soluble
vitamins (A,D,E,K)
$120 (not covered)
Colesevelam Binds to bile acid inintestinal
lumen, decreasing the bile acid pool
for reabsorption. Precise MOA for "
plasma glucose is unknown
A1C reductions ~0.4% when added to stable
metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin.
" FPG ~5-10mmol/DL
" LDL cholesterol ~12-16%
No effect on weight
625mg tablets six
times daily (two
tablets three times
daily)
Constipation, dyspepsia 4 hours space
between this and
other drugs. Take
with meals and lots of
water
Expensive and not
covered
INSULIN PRODUCTS AVAILABLE IN CANADA
FORMULATION PHARMACOLOGY PLACE IN THERAPY DOSING PCK DOSAGE FORMS CONVIENENCE
RAPID ACTING ANALOGUES
Aspart (NovoRapid) Vial 10mL, cartridge
3mL
LU
$25/vial, $50/5
cartridges
Lispro (Humalog) Vial 10mL, cartridge
3mL, pen 3mL (prefilled)
ODB: Yes
Cost: $25/vial,
$50/5 cartridges
Glulisine (Apidra)
Differentiated from human insulin by location of a.a. in the
B-chain and results in monomeric insulin (decreased
tendency to form hexamers) that enters blood more
quickly.
Human insulin: proline and lysine positioned on B28 and
B29, respectively, on B-chain
Aspart: proline on B28 is replaced w/ aspartate
Lispro: proline and lysine on B29 and B28, respectively
Glulisine: asparagines on B3 is replaced by lysine and
lysine on B29 replaced by glutamate
Possess the same metabolic effects as
regular insulin and thus have the same
indications. Should be administered w/
longer-acting (NPH, glargine, detemir)
insulin to maintain overall BG control. Can
be used alone if used in a continuous
infusion device.
Rapid onset, better control of post-prandial
hyperglycemia, shorter duration of action,
and potentially reduced incidence of late
postprandial hypoglycemia. May prove to
be more convenient for management of DM
since regular insulin must be injected 30min
prior to eating and requires additional
planning around mealtime.
Same dosing as regular insulin can be used
(although w/ more BG lowering effect).
Inject ~10-15min prior to meal (although
can be used as late as start of the meal or end
of the meal to determine dose of insulin via
amount of food consumed).
Glulisine: Can be mixed w/ NPH insulin if
administered immediately after mixing.
Onset: 10-15min (more rapidly absorbed)
Maximal effect: 1-1.5h (50% higher peaks)
Duration of action: 3-5h (shorter duration of
action)
Cartridge 3mL, pen 3mL
(prefilled)
ODB: No
Cost: $50/5
cartridges
SHORT ACTING ANALOGUES
Regular (Humulin R,
Novolin ge Toronto, Hypurin
Regular Pork)
Onset: 30-60min
Maximal effect: 2-3h
Duration of action: 6.5h
Vial 10mL, cartridge
3mL. Hypurin only
available in vials.
ODB: Yes (not
Hypurin)
INTERMEDIATE ACTING INSULIN
NPH (Humulin N, Novolin ge
NPH, Hypurin NPH Pork)
Used as basal insulin via intermittent
injections.
Inferior to long-acting analogues b/c
duration is <24h and b/c of maximal effects
peaks b/w 5-8h.
Weight gain (0.5-1.5kg).
Require bid dosing (duration of action
<18h).
Inject before breakfast and then before
supper to bedtime. Bedtime dosing is better
to address the dawn effects and to prevent
nocturnal hypoglycemia.
Onset: 1-3h
Maximal effect: 5-8h (undesirable for basal
insulin)
Duration of action: up to 18h
Humulin: vial 10mL,
cartridge 3mL, and pen
3mL (prefilled)
Novolin: vial 10mL,
cartridge 3mL
Hypurin: vial 10mL
Cloudy suspension.
ODB: Yes (not
Hypurin)
LONG ACTING ANALOGUES
Detemir (Levemir) Slow absorption and prolonged action due to 1) molecules
exist in tight association (bound together) at site of
injection in SC tissue and have affinity for tissue albumin,
2) reversibly bound to circulating serum albumin from
which it is slowly released.
50% of total insulin requirement.
QD or BID dosing (may patients require
BID). QD dosing at bedtime. BID dosing
qam and qpm.
Do not mix w/ other insulin products.
Onset: 1.5h
Maximal effect: Modest peak effect, must
less than NPH, but more than glargine, in a
dose-dependent manner
Duration of action: 16-24h, dependent on
dose
Cartridge 3mL
Clear soln and does not
require resuspension.
ODB: No
Cost: $115/5
cartridges
Glargine (Lantus) Modified human insulin to make it acidic and less soluble
at physiological pH of SC site. Formation of
microprecipitate in tissue.
Mainly used for T2DM
Used as basal insulin for widely fluctuating
FPG.
! AIC 3%
Lower incidence of hypoglycemia compared
w/ NPH insulin, particularly nocturnal
hypoglycemia in patients injected at
nighttime.
Avoids insulin stackin (when peak of NPH
coincides w/ prandial insulins).
Detemir is weight neutral.
50% of total insulin requirement. When
switching from NPH, consider decreasing
dose by 20%.
QD dosing, usually qhs, but administration
at any time of the day is appropriate as long
as injection time is consistent.
Do not mix w/ other insulin products
(precipitation may occur).
Onset: 1.5h
Maximal effect: No peak. Relatively
insoluble in tissue and absorbed very slowly
for up to 24 hours.
Duration of action: 24h
Vial 10mL, cartridge
3mL, and pen 3mL (pre-
fill). Clear soln and does
not require resuspension.
ODB: Yes
Cost: $60/vial,
$115/5 cartridges
PREMIXED BIPHASIC INSULIN
Aspart + Protamine Aspart
(PA) (Novomix 30)
Rapid + Intermediate mixture.
Contains 30% soluble aspart and 70% basal aspart insulin
(similar action to NPH). Basal component is aspart
protamine crystals suspension where aspart is co-
crystallized w/ protamine to produced SR prep w/ also
rapid effect.
Given bid and results in significantly lower
BG concn after breakfast, before lunch,
after dinner, and at bedtime when compared
to insulin 30/70, w/out risk of hypoglycemia.
BID
Do not mix w/ other insulin products.
Cartridge 3mL ODB: Yes
Cost: $55/5
cartridges
Lispro + Protamine Lispro
(PL) (Humalog Mix25,
Mix50)
Rapid + Intermediate mixture.
Containing ratio of soluble lispro to basal lispro insulin
(similar action to NPH) of 25:75 and 50:50. Basal
component is lispro protamine suspension where lispro is
co-crystallized w/ protamine to produce sustained-release
prep w/ also rapid action.
Mix25 is given bid and results in lower
postprandial BG concn after morning and
evening meals. Similar to insulin 30/70.
Mix50 is similar to insulin 50/50, but
provides a higher dose of rapid-acting
insulin for greater prandial glucose lowering
effect
BID
Do not mix w/ other insulin products.
Onset: 10-15min
Maximal effect: 1-8h
Duration of action: up to 18h
Cartridge 3mL and pen
3mL (pre-filled)
ODB: Yes
Cost: $55/5
cartridges
Regular + NPH (Humulin
30/70, Novolin ge 30/70,
Novolin ge 40/60, 50/50)
Short + Intermediate mixture Do not mix w/ other insulin products. Onset: 30-60min
Maximal effect: 2-8h
Duration of action: up to 18h
Vial 10mL, cartridge
3mL. Novolin 40/60 and
50/50 only in 3mL
ODB: Yes
SE: Hypoglycemia, weight gain
ODB covered and cheap (some newer ones can be expensive)
Efficacy: rapid-acting insulin analogues allow for more flexibility to control postprandial glucose b/c faster onset vs. short-acting insulins. Long-acting insulin analogues produce more predictable effects than intermediate-
acting human insuli n(NPH) and may be associated with less nocturnal hypoglycemia but are more expensive and not as much safety/efficacy data, and thus some clinicians reserve this for 2
nd
line
Adverse effects:
1. Hypoglycemia (most common): usually due to missed meal or unusual amount of exercise; frequent hypoglycemia may lead to hypoglycemia unawareness
" Mild hypoglycemia by autonomic symptoms: sweating, tremor, tachycardia, hunger, nausea, and a general sensation of weakness. Easily treated with a oral source of sugar (15g of glucose will raise the
levels to approximately 2mmol/L within 20minutes
" Severe hypoglycemia: neuroglycopenic symptoms (ie. confusion, altered behavior, difficulty speaking, disorientation can progress to seizures, coma)
2. Localized fat hypertrophy: from frequent use of same injection site resulting in low or unpredictable adsorption of insulin from that site
3. Allergic reactions (uticaria, angioedema, rash, local erythema [rare with human insulin]
4. Immune-mediated insulin resistance b/c production of antibody is also rare wit human insulin
5. Increased cancer rates have been reported in retrospective, observational studies of the long-acting insulin analogue glargine compared to human insulins evidence of weak and inconclusive
Drug interactions:
!requirement for insulin: Antipsychotics: chloropromazine, corticosteroids, diazoxide, diuretics: thiazide diuretics or loop diuretics, sympathomimetic agents, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, smoking may also antagonise
the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin.
" requirement for insulin: ACE inhibitors. Episodic heavy drinking (binge drinking) carries a particularly high risk of hypoglycaemic episodes. Anabolic steroids, Analgesics: NSAIDS, or salicylates, particularly large doses of
aspirin, Androgens: testosterone, Anti-arrhythmics: disopyramide, Anti-depressants: monoamine oxidase inhibitors or fluoxetine. Concomitant use of amitriptyline with insulin may lead to hypoglycaemia, Antihypertensives:
guanethidine, Antimalarials, Fenfluramine, Hormone antagonists: octreotide, Lipid-regulating drugs: fibrates, Mebendazole, Pentoxifylline, Tetracyclines
Alcohol: moderate or large amounts of alcohol (more than 2 units per day for women and more than 3 units per day for men) can decrease the requirements for insulin and may lead to hypoglycaemic attacks.
! or " requirement for insulin: Antihypertensives: clonidine, Beta blockers, Calcium channel blockers: nifedipine may occasionally impair glucose tolerance, Cyclophosphamide, Isoniazid, Lipid-regulating drugs: gemfibrozil,
Oral contraceptives
Você também pode gostar
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocumento18 páginasPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Documento8 páginas100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocumento12 páginasCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes MedicationDocumento3 páginasDiabetes MedicationRuben Gutierrez-ArizacaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Values Chart GuideDocumento5 páginasLab Values Chart GuideVanessaMUeller100% (3)
- Antibiotics ChartDocumento10 páginasAntibiotics Chartadom09Ainda não há avaliações
- AntimicrobialsDocumento1 páginaAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocumento3 páginasCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryAinda não há avaliações
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Documento1 páginaBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testAinda não há avaliações
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocumento4 páginasLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testAinda não há avaliações
- Labs Electrolyte ChartDocumento1 páginaLabs Electrolyte ChartmdcmepAinda não há avaliações
- Common MedicationsDocumento4 páginasCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoAinda não há avaliações
- Test InformationDocumento5 páginasTest InformationCatalina BorquezAinda não há avaliações
- Common Medications UsedDocumento3 páginasCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananAinda não há avaliações
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFDocumento6 páginasNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocumento3 páginasCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- Antibiotics Chart 1Documento7 páginasAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendAinda não há avaliações
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocumento3 páginasSphere: These Diarrheamed testAinda não há avaliações
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocumento8 páginasApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryDocumento5 páginasDrug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryMarcel YoungAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotics Chart 2Documento10 páginasAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocumento2 páginasUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocumento2 páginasNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Medications Chart PDFDocumento1 páginaDiabetes Medications Chart PDFRachel Lalaine Marie SialanaAinda não há avaliações
- Git Drugs TablesDocumento3 páginasGit Drugs TablesSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr Lohani100% (1)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento21 páginasRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocumento3 páginasPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotic TableDocumento7 páginasAntibiotic TablenkuligowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes DrugsDocumento1 páginaDiabetes Drugsmed testAinda não há avaliações
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyDocumento18 páginasMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- Drug CardDocumento1 páginaDrug CardPaul AlfonsoAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Rhythms S SDocumento3 páginasHeart Rhythms S SGloryJane100% (1)
- Drug of ChoiceDocumento2 páginasDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- Medications and assessmentsDocumento225 páginasMedications and assessmentsJessica 'Baker' IsaacsAinda não há avaliações
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFDocumento1 página0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeAinda não há avaliações
- GI Drugs PDFDocumento6 páginasGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Anemia ChartDocumento1 páginaAnemia ChartBetsy Brown ByersmithAinda não há avaliações
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocumento4 páginasPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Comprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFDocumento97 páginasComprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFKenia GeorgesAinda não há avaliações
- NCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNDocumento43 páginasNCLEX Review: Pharmacology Charlene Natale, BSN, RNMenly Susada100% (1)
- Common Cardiac Related MedicationsDocumento18 páginasCommon Cardiac Related MedicationsTracy100% (2)
- Blood Test Reference GuideDocumento3 páginasBlood Test Reference GuideHAinda não há avaliações
- Lang 10 EditionDocumento235 páginasLang 10 Editionraju niraulaAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs WorksheetDocumento16 páginasDrugs Worksheetninja-2001Ainda não há avaliações
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocumento1 páginaAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction to commonly used antibioticsDocumento2 páginasIntroduction to commonly used antibioticsAmir AmirulAinda não há avaliações
- Med Geeks Clinical Lab GuideDocumento17 páginasMed Geeks Clinical Lab GuideHuy Hoang100% (1)
- Antiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Documento2 páginasAntiarrhythmic Medication Chart - EBM Consult v3Linlin100% (1)
- Anti Infective Drug ChartDocumento1 páginaAnti Infective Drug ChartJessica100% (1)
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Documento48 páginasNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs of ChoiceDocumento3 páginasDrugs of ChoiceReeti R. Bhat100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocumento3 páginasCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120Ainda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Values: An Easy Guide to Learn Everything You Need to Know About Laboratory Medicine and Its Relevance in Diagnosing DiseaseNo EverandLab Values: An Easy Guide to Learn Everything You Need to Know About Laboratory Medicine and Its Relevance in Diagnosing DiseaseNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Literature ReviewDocumento4 páginasLiterature Reviewapi-549241187Ainda não há avaliações
- Librarianship and Professional Ethics: Understanding Standards for Library ProfessionalsDocumento12 páginasLibrarianship and Professional Ethics: Understanding Standards for Library ProfessionalsHALLAinda não há avaliações
- Think Like An EconomistDocumento34 páginasThink Like An EconomistDiv-yuh BothraAinda não há avaliações
- Are Moral Principles Determined by SocietyDocumento2 páginasAre Moral Principles Determined by SocietyKeye HiterozaAinda não há avaliações
- Bible Study RisksDocumento6 páginasBible Study RisksVincentAinda não há avaliações
- Why Research Is Important in The BusinessDocumento2 páginasWhy Research Is Important in The BusinessBricx BalerosAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Documento3 páginasAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosAinda não há avaliações
- ADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2Documento10 páginasADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2domingohAinda não há avaliações
- St. Louis ChemicalDocumento8 páginasSt. Louis ChemicalNaomi Alberg-BlijdAinda não há avaliações
- ARCH1350 Solutions 6705Documento16 páginasARCH1350 Solutions 6705Glecy AdrianoAinda não há avaliações
- We Don't Eat Our: ClassmatesDocumento35 páginasWe Don't Eat Our: ClassmatesChelle Denise Gumban Huyaban85% (20)
- The Republic of LOMAR Sovereignty and International LawDocumento13 páginasThe Republic of LOMAR Sovereignty and International LawRoyalHouseofRA UruguayAinda não há avaliações
- Culture of BMWDocumento6 páginasCulture of BMWhk246100% (1)
- Kurukshetra English August '17Documento60 páginasKurukshetra English August '17amit2688Ainda não há avaliações
- Ashe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Documento25 páginasAshe v. Swenson, 397 U.S. 436 (1970)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Hitachi Datasheet Thin Image SnapshotDocumento2 páginasHitachi Datasheet Thin Image Snapshotemail7urangAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Quiz Corrections ADocumento4 páginasChapter 5 Quiz Corrections Aapi-244140508Ainda não há avaliações
- Javier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyDocumento290 páginasJavier Couso, Alexandra Huneeus, Rachel Sieder Cultures of Legality Judicialization and Political Activism in Latin America Cambridge Studies in Law and SocietyLívia de SouzaAinda não há avaliações
- Debt Recovery Management of SBIDocumento128 páginasDebt Recovery Management of SBIpranjalamishra100% (6)
- Ernst & Young: Public Sector Compensation ReviewDocumento88 páginasErnst & Young: Public Sector Compensation ReviewThe Vancouver SunAinda não há avaliações
- Marwar Steel Tubes Pipes StudyDocumento39 páginasMarwar Steel Tubes Pipes Studydeepak kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Self PDFDocumento23 páginasSexual Self PDFEden Faith Aggalao100% (1)
- Comparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsDocumento31 páginasComparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsJuan ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Dwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&5Documento4 páginasDwi Athaya Salsabila - Task 4&521Dwi Athaya SalsabilaAinda não há avaliações
- The Art of Woodworking Shaker FurnitureDocumento147 páginasThe Art of Woodworking Shaker Furnituremalefikus100% (2)
- S The Big Five Personality TestDocumento4 páginasS The Big Five Personality TestXiaomi MIX 3Ainda não há avaliações
- Benchmarking The Formation Damage of Drilling FluidsDocumento11 páginasBenchmarking The Formation Damage of Drilling Fluidsmohamadi42Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 1 Amanda CeresaDocumento2 páginasWeek 1 Amanda CeresaAmanda CeresaAinda não há avaliações
- Intrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Documento12 páginasIntrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Roy MontoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Christian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Documento78 páginasChristian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremAinda não há avaliações