Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Indo
Enviado por
krupamayekarDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Indo
Enviado por
krupamayekarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Indo-German Economic Relations
Enlarge imageChancellor
Merkel and Prime Minister Singh at the Hanover
Fair in 2006( dpa)With trade history that spans
more than 500 years, India and Germany share
a strategic partnership that has its basis in
strong business and economic links. Over the
years, not only has the bilateral trade
increased, but German firms have discovered
new investment opportunities in India and so
have the Indian firms in Germany.
Indo-German economic relations have an
interesting history. The first economic links
between India and Germany date as far back as
the 16th century. Jakob Fugger, a merchant
and banker from Augsburg, financed the
voyage of the first German ships to Goa, thus
opening up the trade route between Germany
and India. Between the 16th and the 18th
centuries, a number of German companies
were established with the aim of trading with
Indian and other East Asian countries. In the
19th century it was the German company
Siemens who built the first telegraph
connection between Kolkata and London, via
Berlin.
India & Germany as Trading Partners
For the year 2010, Indo-German trade
relations achieved a new
high, with trade volume
crossing the 15 billion
mark. According to figures
released by the German
Federal Statistics Office, between January to
December 2010, the total volume of bilateral
trade increased by 17.9 per cent compared to a
negative percentage in 2009. First 5 months of
this year has shown an outstanding growth of
28% in total volumes.
Enlarge imageThe Volkswagen plant in Pune,
western India( picture alliance)Germany and
India have set a bilateral annual trade target of
20 billion by 2012.
The bilateral trade picked up tremendous
momentum in the post-liberalisation era. The
trade volume has increased nearly six times
since 1991 -- with exports to Germany
increasing five times and imports from
Germany to India almost seven times.
The new century led to even stronger growth
indicators in bilateral trade, which has grown
by an average of 29 per cent per annum since
2003. A new milestone was reached in 2006,
when the total volume of trade crossed the 10
billion threshold, three years earlier than
expected. The bilateral trade numbers
continued on an upward swing in 2007 and
2008, with volume of trade reaching 12.07
billion and 13.41 billion respectively. The
recession affected the bilateral trade in 2009,
but only marginally, with the figures declining
to 13.10 billion.
Indian economy
The economy of India is the tenth-largest in the
world by nominal GDP and the third-
largest bypurchasing power parity (PPP).
[3]
The
country is one of the G-20 major economies, a
member ofBRICS and a developing economy
that is among the top 20 global traders
according to the WTO.
[28]
India was the 19th-
largest merchandise and the 6th largest
services exporter in the world in 2013; it
imported a total of $616.7 billion worth of
merchandise and services in 2013, as the 12th-
largest merchandise and 7th largest services
importer.
[29]
India's economic growth slowed to
4.7% for the 201314 fiscal year, in contrast to
higher economic growth rates in 2000s.
[30]
IMF
projects India's GDP to grow at 5.4% over 2014-
15.
[31]
Agriculture sector is the largest employer
in India's economy but contributes a declining
share of its GDP (13.7% in 2012-13).
[5]
Its
manufacturing industry has held a constant
share of its economic contribution, while the
fastest-growing part of the economy has been
its services sector - which includes construction,
telecom, software and information technologies,
infrastructure, tourism, education, health care,
travel
, trade, banking and others components of its economy.
[6]
The post independence-era Indian economy
(from 1947 to 1991) was a mixed economy with
an inward-looking, centrally
planned, interventionist policies and import-
substituting economic model that failed to take
advantage of the post-war expansion of trade
and that nationalized many sectors of its
economy.
[32]
India's share of global trade fell
from 1.3% in 1953 to 0.5% in 1983.
[33]
This
model contributed to widespread inefficiencies
and corruption, and it was poorly
implemented.
[34]
After a fiscal crisis in 1991, India has
increasingly adopted free-market principles and
liberalised its economy to international trade.
These reforms were started by former Finance
minister Manmohan Singh under the Prime
Ministership of P.V.Narasimha Rao. They
eliminated much of Licence Raj, a pre- and
post-British era mechanism of strict government
controls on setting up new industry. Following
these economic reforms, and a strong focus on
developing national infrastructure such as
the Golden Quadrilateral project by former
Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the
country's economic growth progressed at a
rapid pace, with relatively large increases in per-
capita incomes.
[35]
The south western state
of Maharashtra contributes the highest towards
India's GDP among all states, while Bihar is
among its poorest states in terms of GNI per
capita. Mumbai is known as the trade and
financial capital of India.
Global trade relations
Until the liberalisation of 1991, India was largely
and intentionally isolated from the world
markets, to protect its economy and to achieve
self-reliance. Foreign trade was subject to
import tariffs, export taxes and quantitative
restrictions, while foreign direct investment (FDI)
was restricted by upper-limit equity participation,
restrictions on technology transfer, export
obligations and government approvals; these
approvals were needed for nearly 60% of new
FDI in the industrial sector. The restrictions
ensured that FDI averaged only around
$200 million annually between 1985 and 1991; a
large percentage of the capital flows consisted
of foreign aid, commercial borrowing and
deposits of non-resident Indians.
[196]
India's
exports were stagnant for the first 15 years after
independence, due to general neglect of trade
policy by the government of that period. Imports
in the same period, due to industrialisation being
nascent, consisted predominantly of machinery,
raw materials and consumer goods.
India is a founding-member of General
Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) since
1947 and its successor, the WTO. While
participating actively in its general council
meetings, India has been crucial in voicing the
concerns of the developing world. For instance,
India has continued its opposition to the
inclusion of such matters as labour and
environment issues and other non-tariff barriers
to trade into the WTO policies.
economy
of Germany
Germany is the largest national economy
in Europe, the fourth-largest by nominal GDP in
the world, and fifth by GDP (PPP). Since the
age of industrialisation and beyond, the country
has been a driver, innovator, and beneficiary of
an ever more globalised economy. Germany's
economic policy is based on the concept of
thesocial market economy. The country is a
founding member of the European Union and
the Eurozone.
[15][16]
Germany is the third largest
exporter in the world with $1.516 trillion
exported in 2012.
[17][dated info]
Exports account for
more than one-third of national output.
[18][dated
info]
[19]
In 2013, Germany recorded the highest
trade surplus in the world worth $270
billion,
[20]
making it the biggest capital exporter
globally.
[21]
Germany is the largest producer of lignite in the
world. Germany is also rich in timber, iron
ore, potash, salt, uranium, nickel, copper and
natural gas. Energy in Germany is sourced
predominantly by fossil fuels, followed by
nuclear power, and by renewable energy like
biomass (wood and biofuels), wind, hydro and
solar.
The service sector contributes around 70% of
the total GDP, industry 29.1%, and agriculture
0.9%. Most of the country's products are in
engineering, especially in automobiles,
machinery, metals, and chemical
goods.
[22]
Germany is the leading producer of
wind turbines and solar power technology in the
world.
[23]
Combination of service-oriented
manufacturing,
[24]
R&D spending, links between
industry and academia, international
cooperation and the Mittelstand contribute to the
overall competitiveness of the economy of
Germany.
[25][26]
Germany is the world's top location for trade
fairs.
[27]
Around two thirds of the world's leading
trade fairs take place in Germany.
[28]
The largest
annual international trade fairs and congresses
are held in several German cities such
as Hanover, Munich, Frankfurt and Berlin.
Germany as a federation is a polycentric country
and does not have a single economic center.
The stock exchange is located in Frankfurt am
Main, the largest Media company (Bertelsmann
AG) is headquartered in Gtersloh; the largest
car manufacturers are
in Wolfsburg, Stuttgart and Mnchen.
[68]
Germany is an advocate of closer European
economic and political integration. Its
commercial policies are increasingly determined
by agreements among European Union (EU)
members and EU single market legislation.
Germany introduced the common European
currency, the euro on 1 January 1999. Its
monetary policy is set by theEuropean Central
Bank in Frankfurt.
The southern states ("Bundeslnder"),
especially Bayern, Baden-Wrttemberg and
Hessen, are economically stronger than the
northern states. One of Germany's traditionally
strongest (and at the same time oldest)
economic regions is the Ruhr area in the west,
between Bonn and Dortmund. 27 of the
country's 100 largest companies are located
there. In recent years, however, the area, whose
economy is based on natural resources and
heavy industry, has seen a substantial rise in
unemployment (2010: 8.7%).
[68]
The economy of Bayern and Baden-
Wrttemberg, the states with the lowest number
of unemployed people (2010: 4.5%, 4.9%), on
the other hand, is based on high-value products.
Important sectors are automobiles, electronics,
aerospace and biomedicine, among others.
Baden-Wrttemberg is an industrial center
especially for automobile and machine building
industry and the home of brands like Mercedes-
Benz (Daimler), Porsche and Bosch.
[68]
India Trade Relations
India being an emerging economy of the world
has a strong economic policy which stresses on
developing and strengthening bilateral trade
relations with different nations across the world.
Top Ten Trading Partners of India
As of 2008-09, Indias top ten trading partners
and the trade carried out with them has been
summarised as
Country Trade 2008-
09
(Rs. In
crores)
Trade
Balance
CHINA 1,63,202 -92,676
USA 1,55,353 12,254
UAE 1,52,668 -1,934
SAUDI
ARABIA
1,05,602 -64,303
GERMANY 67,602 -19,497
SINGAPORE 63,280 2,934
U K 50,144 524
HONG KONG 50,129 1,772
BELGIUM 41,552 -5,294
NETHERLAND 33,099 19,049
Bilateral Trade, Germany and India
Economic Relations between India and
Germany
Indo- German Chamber of Commerce
(IGCC) has eventually expanded into the
largest foreign chamber of commerce and
trade in India and also as the biggest
German bi-national Chamber globally. In
2006 the IGGC celebrated its 50th year of
trade and commerce relations. India also
partnered with the Germans in the 2006
Hannover Fair, which is recognised as the
worlds largest technology fair. The IGGC
have set up a goal to achieve trade up to
20 billion Euros by 2012.
Figures of Indo-German Export Market
Overall the export industry is growing day
by day and the figures indicate a rise in
the trade between the two countries. The
textile industry accounts for the highest
trade with figures of export touching Euro
1.5 Billion. The second position is
occupied by the chemical products which
are worth about Euro 585 million. Data
processing, electronic and optical
equipment with 579 million come next to
it. The fourth and fifth spots are taken by
machinery with 418 million and leather
products with 396 million.
German Exports to India
Germany, which is one of the worlds
leading exporters stands on the fifth
position globally as Indias trade
associate. It is also the largest trading
partner within the European Union.
Germany shares a notable 11 per cent of
the total business dealings between EU
and India. German exports to India grew
to 8.2 billion, advancing at a rate of over
12 per cent in 2008. In 2009, this figure
reduced by 1.2 percent to arrive at 8.1
billion.
India Germany Trade
Relations
Many years of collaboration and mutual
understanding has been the bench mark of India
Germany trade relations. Political relations date
back to the 1950s.
ECONOMIC RELATIONS BETWEEN INDIA
AND GERMANY
Indo- German Chamber of Commerce (IGCC)
has eventually expanded into the largest foreign
chamber of commerce and trade in India and
has also become the largest German bi-national
Chamber globally. In 2006 the IGGC celebrated
its 50th year of trade and commerce relations.
India also partnered with the Germans in the
2006 Hannover Fair, which is recognised as the
worlds largest technology fair. The IGGC have
set up a goal to achieve trade up to 20 billion
Euros by 2012.
INDIAS OVERALL EXPORTS TO GERMANY
The bilateral trade relations between India and
Germany have remarkably increased over the
years and both Indian and German firms have
had their share of investment. Post recession
period Indian exports to Germany have seen an
incredible growth in 2010, recording a total
increase of 21.5%. The figures of total exports
have touched to Euro 6.2 billion.
Indian textile Exports to Germany
The Indian Textile industry generally
comprises of manufacturers, wholesalers,
suppliers, and exporters of cotton textiles,
handloom, woollen textiles etc. Germany
is one of t he foremost importers of
handmade fibre textile of India. Indian
textile export to Germany resulted for the
highest share and it amounted to Euro 1.5
billion in 2010.
Indian IT Exports to Germany
CeBIT 2011, Hannover Germany
One of Indias prime trade facilitation
organizations, Electronics and Computer
Software Export Promotion Council (ESC)
having more than 2,300 members took
part in a grand way at the CeBIT held
from March 1-5th 2011at Hannover,
Germany.
CeBIT is one of the best known
international trade fair showcasing the
technological process used all across the
world. The main objective of the trade
show was to help out the associate
exporters to expand their business base
globally. Users from industry, skilled
trades, banks, services sector,
government agencies, science and all
passionate about technology were the
key target groups.
Roughly 20 Indian ICT companies
participated at CeBIT under ESC banner.
The mass participation of the Indian
companies clearly indicated their
increasing interests of investment in the
EU region, with Germany being a prime
target. ICT products as ERP, business
process management, business
intelligence, vertical market solutions,
managed services, internet solutions, web
content management, ecommerce, web
design and technologies and many others
were on display at the CeBIT. ESC has
been a regular participant at the CeBIT
since last many years. The Indian
companies under ESC have expressed
their interests in setting up joint ventures,
having further marketing associations with
the EU. The ESC has reportedly
mentioned that there has been a
remarkable rise in ICT exports from India
to Germany.
INDIASOFT 2011
The ESC also hosted a large delegation
from EU which participated at
INDIASOFT 2011 on March 25-26.
INDIASOFT is one of the biggest IT
networking events as per global
standards and this years venue for the
event was Pune. It resulted in further
strengthening the IT relations between
India and EU and particularly with
Germany.
India has requested to Germany to
remove technology trade restrictions
For better trade relations, especially high-
end technology trade with Germany, India
has urged the European nation to ease
trade restrictions and thus provide a
suitable platform for both the countries to
work on and gain mutual benefit.
Indian Leather Export to Germany
The Indian leather export industry eyes
Germany as a prime target for exporting
its leather items. 80 per cent of the
country's total leather exports are mainly
to the US and Europe with Germany
accounting to 14 percent, to UK around
13 percent, the US about 9 percent.
Indian Agro Exports to Germany
Agricultural sector is the backbone of the
rural Indian economy. Agro Exports to
Germany from India has been a
significant part of the total export of Indian
agricultural items. The major Indian
agricultural products exported to
Germany are floricultural products,
walnuts, dried and preserved vegetables,
poultry products, processed meat, natural
honey etc. Among the floricultural
products, the chief share is of cut flowers.
Cut flowers, flowering and ornamental
plants, bulbs, tubers, rhizomes, chicory,
orchids, mosses etc are the, main
floricultural items exported from India.
Germany holds a percentage of 5.41% in
the floriculture export market of India.
Indian Glass Industry Trade with
Germany
Kolkata based Hindustan National Glass
& Industries (HNG), has bought a
German company, Agenda Glass, (AG)
for an un-revealed amount. HNG is
Indias largest maker of glass containers
and has a total share of 55% in the
market. The new company has been
renamed as HNG Global GmbH. The deal
was signed this May11, 2011. Saxony
Anhalt will continue to be the main centre
for glass production in Germany, as
ensured by HNG. HNG can benefit from
the "excellent conditions" available as
high quality raw materials and modern
infrastructure.
Figures of Indo-German Export Market
Overall the export industry is growing day
by day and the figures indicate a rise in
the trade between the two countries. The
textile industry accounts for the highest
trade with figures of export touching Euro
1.5 Billion. The second position is
occupied by the chemical products which
are worth about Euro 585 million. Data
processing, electronic and optical
equipment with 579 million come next to
it. The fourth and fifth spots are taken by
machinery with 418 million and leather
products with 396 million.
German Exports to India
Germany, which is one of the worlds leading
exporters stands on the fifth position globally as
Indias trade associate. It is also the largest
trading partner within the European Union.
Germany shares a notable 11 per cent of the
total business dealings between
EU
and India. German exports to India grew to 8.2
billion, advancing at a rate of over 12 per cent in
2008. In 2009, this figure reduced by 1.2
percent to arrive at 8.1 billion.
India Germany Tourism
German Tourism Board has launched
shops in IndiaGerman National Tourist
Board launched more tourism operators
and travel agencies and special schemes
for the Indian tourists willing to travel to
Germany.
Indo German Friendship Society Goa
(IGSG) to organise fourth German
Cultural week in Goa: The success of the
third German Cultural Week held from
December 8-12, 2010 has further inspired
the organisers of the festival to come up
with more lively events in December
2011. The festival will be celebrated from
December7-11, 2011.
INDIAN EXPORTS TO
GERMANY
Indian exports to Germany have shown a
considerable growth since the last two decades
with the export items ranging from textiles to
leather goods to IT solutions etc.
OVERVIEW INDIAN EXPORTS TO GERMANY
Trade relations
(http://business.mapsofindia.com/trade-
relations/) between the two nations have
increased to a remarkable extent and have
recorded a positive growth over the last couple
of years. Figures as of 2009, show that India is
on 28th position on the list of sourcing countries
for Germany and is ranked 27th among the
main destinations for German exports. Post to
the global recession, there has been an
increase in the exports from India to Germany
with the figures touching to 21.5% and the total
exports amounting to Euro 6.2 billion.
FIGURES OF INDO-GERMAN EXPORT
MARKET
There is a growing trend in the bilateral trade
between the two nations and the export industry
has registered an incredible growth. Figures of
export for the textile industry
(http://business.mapsofindia.com/india-industry/)
touched Euro 1.5 billion. Export of chemicals
occupied the second position with statistics
showing export worth about Euro 585 million.
The next spot is taken by data processing,
electronic and optical equipment where export
reached Euro 579 million. Machinery and
leather exports occupied the fourth and fifth
positions with export figures worth Euro 418
million and Euro 396 million respectively.
Products exported to Germany
Indian exports to Germany from textiles, to IT
solutions, leather, agricultural produce, glass
materials etc.
Leather Exports to Germany
Leather accessories occupy an important part of
the Leather Industry in India and the Germany is
one of the prime destinations for export of
leather goods from India. Germany accounts to
about 14% of the export market of the items of
leather from India.
Textile Exports to Germany
The Indian textile industry has shown a
remarkable growth over the years and has more
than four million handlooms. The sector is
responsible for 14% of the over all industrial
output and is on the rise in the global textile
sector. It generally consists of suppliers,
manufacturers, exporters of textiles of cotton,
handloom, woollen goods etc. Germany is one
of the front runners when it comes to import of
handmade Indian fibre textile. Germany resulted
for the highest share of the Indian textile export
market as indicated by the figures which
reached to Euro 1.5 billion as of 2010.
Agricultural Exports to Germany
The agro products exported to Germany
from India are listed below:
Floriculture
Walnuts
Dried and Preserved vegetables
Poultry products
Processed meat
Guar Gum
Natural Honey
IT Exports to Germany
Indian companies
(http://business.mapsofindia.com/india-
company/) are prime outsourcing firms and
display a huge potential in the IT export market.
Germany is a prime destination in the export
market for India providing technology solutions.
India is a powerful center for research and
development and also gives computer software
service export, network infrastructure
management, IT consulting.
Indian Glass Trade with Germany
Agenda Glass AG, a German based glass
manufacturing industry was bought recently by
Kolkata based Hindusthan
National
Glass (http://business.mapsofindia.com/india-
company/h/hindustan-national-glass.html) &
Industries (HNG), for an undisclosed amount.
HNG Global GmbH is the name of the new
venture.
GERMAN EXPORTS TO
INDIA
German Exports to India is an integral part of
the bilateral economic relations between the
two nations, India and Germany. There exists
an intensive co-operation in the field of economy
and the year 2005 witnessed the celebration of
the 500 years of the establishment ofIndo-
German trade relations. After US, UK and
Japan, Germany is India's fourth largest trading
partner with about 5% of Indian international
trade accounting to 4.94 billion Euro in total.
German Exports to India: overview
The Indo-German trade volume has increased
by 180% from 2,7 Billion EUR in 1990 to 7,6
Billion EUR in 2005, with the German Exports
to India have been recorded to have increased
by almost 135%. The total volume of the Indo-
German tradeincreased by 22% in 2005 with
the amount of German Exports to
Indiaincreasing by 28% to record 4,2 Billion
EUR. In the year 2006, the Indo-German trade
increased by 39% with the German Exports to
Indiaincreasing by 52% to record 6,3 Billion
EUR.
Factors facilitating German Exports to India-
The German Exports to India is facilitated due
to the liberalization policies of India along with
her democratic form of government, a well
defined political system and legal framework,
efficient entrepreneurs, talented engineers and
world class scientists, all of these ensuring
lasting business opportunities for the foreign
countries. German Exports to India has been
encouraged with India sourcing less raw
materials, semi-finished goods, and primary
products and on the other hand it had been
importing finished goods from Germany.
Items of German Exports to India:
Important items of German Exports to
India are like machinery, electro technology as
well as plants and metal products followed by
aircraft, measurement and control equipment,
plastics and plastic products, chemicals and
pharmaceuticals and automobile products and
components. Of these machinery exports to
India comprises one third share of totalGerman
Exports to India.
German Foreign investments Exports to
India:
India is a lucrative center for foreign investors
and in terms of foreign investments, German
Exports to India in total from 1991 to
December 2005 has been less than one and a
half billion dollars. At present there are more
than 600 German companies operating in India
and a robust German export of investments
to India have been in practice.
German exports to India is not only important
in terms of goods exported by Germany, but its
significance lies in the high exports
accompanied by large flows of investment and
technology to India. The best example is the
Germany's first and biggest aid project, the steel
plant at Rourkela, in India. Since the post
liberalization era in India the German exports
to India has been boosted for an increase in the
new investment and technical cooperation
projects.
Centers regulating the German Exports to
India:
The Indo German Chamber of Commerce
and Industry is the major instrument in the
promotion of Indo-German trade relations .
Another significant center is the German Office
for Foreign Trade with regular market studies
on important economic developments in India. It
assists the German investors in researching the
investment opportunities in India.
However, still German Exports to India have
not yet reached any significant level as even as
per recorded in 2006, less than one percent
of German foreign trade is exchanged with
India while Germany in terms of her worldwide
export volume ranks as the first exporter of the
world.
INDIAN IT EXPORTS TO
GERMANY
ndian IT Exports to Germany is the upcoming
profitable venture between the two countries,
India and Germany. There exists active
cooperation in the field of economy with the
celebration of the 500 years of the
establishment of Indo-German trade
relations in the year 2005.
Indian IT Exports to Germany: Overview
In the year 2000-01, Indian IT Exports to
Germany registered a growth of 48 per cent
amounting to $235 million. In the previous
year,India's computer software and services
export to Germanyamounted to $160 million. In
terms ofIndian IT Exports to Germany, the
latter nation is the third largest destination.
An Electronics and Computer Software
Export Promotion Council in order to increase
the scope for Indian software exports in
Germany, sent a delegation in the Cebit 2002
show that took place in Hannover in 2002. Since
then the Indian IT Exports to Germany gained
further impetus.
The Indian IT Exports to Germany has started
after exporting to the US market, with
theGerman IT services market worth as 26.5
billion Euros. The Indian software and
services firms have started looking beyond
their domestic boundaries to the European
countries for further growth. There exists huge
opportunity for them in Germany as this
European country accounts for only 2.8 percent
of Indias software exports. One of the
software companies such as Hexaware have
been quick to grab this opportunity. In the first
half of 2004, of the 25 percent revenues from
the European market 15 to 20 percent was
contributed by the German unit of the
Hexaware. At present, the clients of Hexaware
are like Citibank, Lufthansa Systems and
Deutsche Leasing in Germany.
Products under Indian IT Exports to
Germany: India got a platform to display its
huge potential in the German market as one of
the highly competitive onsite provider and
supplier of technology. Moreover India is also an
outsourcing destination and a powerful center
for research and development. Not only in terms
of providing computer software and
services
export to the foreign countries, India is also
gaining importance in newer
services
like packaged software implementation,
systems integration, network infrastructure
management, and IT consulting.
Factors facilitating the growth of Indian IT
Exports to Germany: The factors facilitating
the growth of Indian IT Exports to
Germany are like the increased specialization,
availability of a large section of low cost, but
highly skilled, educated and fluent English-
speaking workers for the development of the IT
sectors in India. However, on the other hand,
the rise in demand from foreign consumers
interested in India's service exports and due to
those foreign countries looking to outsource
their operations the Indian software firms
flourished.
The recent rise in the Indian IT Exports to
Germany is due to some benefits as these
exports do not require the purchase of hardware
or software by the Indian company or the
provision of any significant technology
infrastructure within the country. Moreover,
since the onsite exports are based on links with
foreign collaborators, they do not require that
standard of marketing and financing as
competition within the open market would.
INDO- GERMAN CHAMBER
OF COMMERCE AND
INDUSTRY
ndo- German Chamber of Commerce and
Industry is the most important regulatory body
controlling the Indo-German trade relations.
The companies of both the countries interested
in business with each other are required to first
contact the Indo-German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry.
History of the Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry:
Indo- German Chamber of Commerce and
Industry, established under the Indian
Companies' Act VII of 1913 with its
incorporation in the year 1956 is the
largest German Bilateral Chamber abroad
comprising of more than 6500 Indian and
German members. Moreover there are 80
professionals facilitating Indo-German
Business in both the countries. TheIndo-
German Chamber of Commerce and
Industry is absolutely indispensable and
necessary for the benefits of small and medium-
sized enterprises. The head office is in Mumbai,
with the branch offices in different parts of India
like Delhi, Bangalore, Kolkata and Chennai, and
a liaison office in Duesseldorf in Germany.
Management of the Indo- German Chamber
of Commerce and Industry:
The Management of the Indo- German
Chamber of Commerce and
Industry comprise of 20 elected Indian and
German members, who are acting industrialists
and CEOs of German and Indo-German
companies. The main portfolio holders of the
Chamber are the President, Vice-President,
Treasurer and Director General.
Activities of the Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry:
The Activities of the Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry are classified in two
broad divisions like the standard
services
and specialized
services
. Other noteworthy
services
offered by the Chamber are-
Business Partner Search
Legal Information
Debt Collection
Investment Opportunities
HR Recruitment Services
Market Intelligence Services
Event Management
Credit Rating
The Indo- German Chamber of Commerce
and Industry offers another worldwide new
service, DEinternational which is flexible
enough to suit the needs of the various clients of
different countries.
Current upcoming events of the Indo-
German Chamber of Commerce and
Industry: TheIndo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry in the present year
2007, has laid down certain lofty plans for the
further benefit of the Indo German trade
relations. They are like-
From 24th to 28th September 2007 there
will be a delegation from important
sectors like automotive, machinery,
engineering from South Hesse to different
parts of India.
The Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry will organize
the world's largest international textile
machinery exhibition or ITMA 2007 in
Munich, which will be a rewarding
platform for buyers and sellers from all
over the world.
From 6th to 11th January 2008 under
the Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry a Bavarian
Delegation of Automotive Suppliers will
visit different cities of India.
From 13th to 23rd September 2007
the Indo- German Chamber of
Commerce and Industry will organize
Indian participation, catalog show &
delegation to the 62nd International Motor
Show Cars, in Frankfurt.
The Indo-German Chamber of
Commerce is organizing a business
delegation to Germany in September
2007, for the benefit of Indian enterprises
from the Auto Components Aerospace
& Mechanical Engineering Industry.
TOP TEN EXPORTERS TO INDIA, BY VALUE OF TRADE IN US$M AND SHARE OF TOTAL
Click headings to sort table. Download the data for all countries worldwide
Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep)
CHINA 28025.57 11.92
UAE 19622.81 8.35
SAUDI ARABIA 16094.83 6.85
USA 12208.05 5.19
SWITZERLAND 10779.45 4.59
IRAQ 9803.79 4.17
TOP TEN EXPORTERS TO INDIA, BY VALUE OF TRADE IN US$M AND SHARE OF TOTAL
Click headings to sort table. Download the data for all countries worldwide
Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep)
QATAR 8144.45 3.47
KUWAIT 8134.73 3.46
GERMANY 7154.41 3.04
INDONESIA 6944.86 2.95
TOP TEN IMPORTERS FROM INDIA, BY VALUE OF TRADE IN US$M AND SHARE OF TOTAL
Click headings to sort table. Download the data for all countries worldwide
Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep)
USA 19704.05 13.87
TOP TEN IMPORTERS FROM INDIA, BY VALUE OF TRADE IN US$M AND SHARE OF TOTAL
Click headings to sort table. Download the data for all countries worldwide
Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep)
UAE 18601.71 13.09
SINGAPORE 6652.77 4.68
CHINA 6417.32 4.52
HONG KONG 6137.9 4.32
SAUDI ARAB 4636.29 3.26
NETHERLANDS 4458.24 3.14
U K 4112.26 2.89
GERMANY 3491.77 2.46
TOP TEN IMPORTERS FROM INDIA, BY VALUE OF TRADE IN US$M AND SHARE OF TOTAL
Click headings to sort table. Download the data for all countries worldwide
Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep)
BRAZIL 3042.64 2.14
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
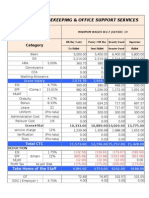
- Breakup: Housekeeping & Office Support Services Site:: CategoryDocumento2 páginasBreakup: Housekeeping & Office Support Services Site:: CategorykrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Shahnaz HusainDocumento2 páginasShahnaz HusainrpdesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Breakup - Jul'14 To Dec'14 For WaitersDocumento2 páginasBreakup - Jul'14 To Dec'14 For WaiterskrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On Women EntrepreneurshipDocumento10 páginasCase Study On Women EntrepreneurshipkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- (446995147) 14.vol - 01 - Issue - 05 MEENU GOYAL Women PaperDocumento20 páginas(446995147) 14.vol - 01 - Issue - 05 MEENU GOYAL Women PaperkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Ngo AarambhDocumento23 páginasNgo AarambhkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- NestleDocumento31 páginasNestlekrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Questionnaire On ParleDocumento3 páginasQuestionnaire On Parlekrupamayekar92% (13)
- Full Project On SunsilkDocumento28 páginasFull Project On Sunsilkkrupamayekar40% (5)
- Ngo AarambhDocumento23 páginasNgo AarambhkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Drverghese Kurien, Former Chairman of Thegcmmf, Is Recognized As A Key Person Behind The SuccessDocumento14 páginasDrverghese Kurien, Former Chairman of Thegcmmf, Is Recognized As A Key Person Behind The Successkrupamayekar75% (4)
- Research Methodology On DmartDocumento33 páginasResearch Methodology On Dmartkrupamayekar57% (7)
- Lux SoapDocumento6 páginasLux SoapkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Index: NO. Particulars Page NoDocumento3 páginasIndex: NO. Particulars Page NokrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Downsizing in Axis BankDocumento10 páginasDownsizing in Axis BankkrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- HRM in TcsDocumento42 páginasHRM in TcskrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10Documento22 páginasChapter 10krupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- NisanDocumento8 páginasNisankrupamayekarAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)