Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Radioactive Decay Questions
Enviado por
Cikita IsmailDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Radioactive Decay Questions
Enviado por
Cikita IsmailDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
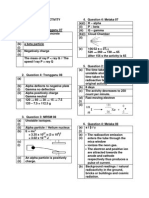
QUESTION 1: TRIAL SELANGOR 2009
2(a) alpha 1
(b) Background emission // alpha has a short range in air 1
(c) 1. Correct axis
2. Correct curve
1
1
(d) Any value from 20-40 minutes // shown on graph 1
QUESTION 2: TRIAL KEDAH 2009
6(a) State the meaning correctly
- Time for the activity of the radioactive substance to become half of the original
activity // Time taken for half of the mass of radioactive substance to decay
1
(b) (i) State the half life correctly
- X : 10 minutes
- Y : 5 minutes
1
1
(b) (ii) State the answer correctly
- X : 50 %
- Y : 25 %
1
1
(c) State the comparison correctly
- The decay rates for substance X is slower//vice versa
State the relationship correctly
- The shorter the half life, the higher the decay rate
1
1
(d) Give the reason correctly
Background radiation
1
QUESTION 3: TRIAL PAHANG 2009
(a) Unstable isotope 1
(b)) D : Reading of rate meter increase 2
(c)(i) 226 Ra 222Rn = 4He
88 86 2
2
(c)(ii)
Sodium: 45/3=15 hrs
Cobalt 60: 15.9/3 = 5.3 yrs
Radium : 4860/3 = 1620 yrs
4
(d) Sodium 24 :
short half life
Emit beta, can penetrate soil
3
QUESTION 4: TRIAL PERAK 2009
8 (a) i
8 (a) ii
8 (a) iii
8 (b) i
8 hours
Shorter time taken
Strong
Gamma ray
Liquid
Easier to dissolved
8 (b) ii
8 (c) i
8 (c) ii
Geiger Muller Tube/ Spark counter/ Diffusion cloud Chamber/ Gold leaf
electroscope/ Photographic detector
To detect leakage in underground pipe/ Thickness control in paper and metal
sheet production/ Examine contamination in canned food/ In medical
treatment/ In archaeology/ In agriculture
QUESTION 5: TRIAL SBP 2008
2. (a)
(b)
(c) (i)
(ii)
(d)
Fast moving electron
GM tube
Decrease//low
The beta particle is block by the juice
Low penetrating power
1
1
1
1
1
QUESTION 6: TRIAL SBP 2009
12 (a) Radioisotopes are isotopes which have unstable nuclei. 1
(b)
Characteristics Explanation
Has a long half-
life
Can be used for a long time hence save cost
Emits beta Can penetrate box and liquid and is less
dangerous than gamma
Solid form Easy to handle and contain.
Low ionising
power
Does not change the state and taste of juice.
Radioisotope T It has long half life, emits beta, in solid form and
has low ionising power.
2
2
2
2
2
(c) (i) Geiger Muller Tube 1
(ii) 1. Bottle E
2. Rate meter reading is the highest
3. Most radiation can reach the detector without being block by
juice
1
1
1
(d)
1. Correctly stated that as He
4
2
2. Correctly stated that as e
0
1
3. Working is shown
4. X = 3
5. Y = 2
1
1
1
1
1
Total 20
QUESTION 7: TRIAL TERENGGANU 2008
Section Marks Answer Note
(a) 1 Unstable nucleus
(b)(i) 1
1
Exponential graph
The time taken for the activity to become half of its
initial value is constant
(ii) 1
1
The time taken for the activity of P to be half its initial
value is constant //5 hrs
The time taken for the activity of Q to be half its
initial value is constant //100 s
(iii) 1 Half-life
(c) 1
1
1
1
1
Put the radioactive source opposite the detector
Detector is connected to the thickness indicator
Detector detect the reading of the changes in counts
Thickness is measured with the thickness indicator
If the reading of the detector is less than the specified
value, the thickness of the paper is too tick/ vice versa
Max 4
(d) 1,2
3,4
5,6
7,8
9,10
Uses thick lead box
Radioactive rays cannot pass through
Packed into concrete drum and buried underground
Prevent the radioactive waste discharged to the
environment
Use forceps/ robotic hand
Avoid direct touching
Use siren
Faster warning when leakage
Wearing photographic films
Detect the exposure radiations
Accept other ways and
reasons
Total 20
QUESTION 8: TRIAL KELANTAN 2008
12(a) (i) The time taken for half of nucleus radioactive material to decay. 1
12(a) (ii) Fast moving electron / electron 1
12(a) (iii) Geiger-Muller tube 1
12 (b) 800 ---------> 400 ---------> 200 ----------> 100----------> 50 // 1
14 days 14 days 14 days 14 days
No. of T 1/2 = 4
4 x 14 days // 64 days 1
12 (c) - The state of matter of radioisotope is solid.
- Easier to handled.
- Emits gamma-ray.
- Penetrating power is high.
- Long half-life.
- Last longer.
- The most suitable radioisotope is Cobalt-60.
- Because the state of matter is solid, emits gamma-ray and long half-life
12(d)(i) The process of breaking up of on heavy nucleus into lighter nucleus.
12(d)(ii) - Neutron bombarded a uranium nucleus //Diagram
- Three neutrons produced // Diagram
- The new neutron bombarded a new uranium nucleus // Diagram
- For every reaction, the neutrons produced will
12(d)(iii)
QUESTION 9: TRIAL SBP 2013
12 (a) Cosmic ray// radiation from surrounding //radioactive materials from earth//
leakage of radioactive from nuclear power plant
(b)(i) Alpha
(b)(ii) 1. The ray ionises the air molecule
2. Negative ions attracted to the plate
3. Neutralised the electroscope
(c) Characteristics Reasoning
Liquid Easy to flow with blood
Short half life Not long in the body // less harmful
Gamma Ray Cannot ionised the living cell // high penetrating power
GM tube detector Can detect ray effectively// portable
K is chosen Because it is in liquid state , has short half life, emits gamma ray and
can be detected easily detected by GM tube detector.
(d) (i) m = [235.04392 + 1.00867] [140.91963 + 92.92157 + 2(1.00867)]
= [236.05259] [ 235.85854]
= 0.19405u
m = 0.19405 x 1.66 x 10
-27
= 0.0322 x 10
-27
= 3.22123 x 10
-28
kg
(ii) E = mc
2
= (3.22123 x 10
-29
) (3.0 x 10
8
)
2
= 28.99x10
7
x 10
-12
= 2.899x10
7
x 10
-11
J
QUESTION 10: TRIAL SBP 2012
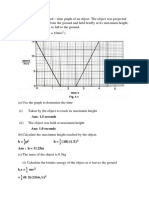
12 (a) (i)
State the meaning of radioisotope
Unstable isotope
(ii)
State the explanation
1. Beta particles penetrates through the paper and
2. detected by the detector
3.If the detector detect lower reading the paper is too thick // If the detector detect higher reading
the paper is thin
4. The roller has to compress harder if the paper is thick // Vice versa
(b)(i)
Aspects Reasoning
Graphite to slow down the fast neutrons produced by the fission.
Boron / Cadmium to absorb some of the neutrons // reduce the rate of the fission
reaction.
Heavy water To absorb heat from the nuclear reaction.
// have high specific heat capacity
Thick To prevent leakage of radiation from the reactor core
R is chosen Graphite,Boron, heavy water and thick wall
(b)(ii)
Você também pode gostar
- Paper 2 Jun 2000 PhysicsDocumento4 páginasPaper 2 Jun 2000 Physicssolarixe100% (3)
- Simulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExpDocumento4 páginasSimulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExppixelhoboAinda não há avaliações
- SAXS PresentationDocumento27 páginasSAXS PresentationkikujimojiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Chapter 10 AnswerDocumento8 páginasPhysics Chapter 10 AnswerXin HuiAinda não há avaliações
- SPM 2015 MODULE ENHANCEMENT EXAM ANSWERS FOR CHAPTER 4: HEATDocumento10 páginasSPM 2015 MODULE ENHANCEMENT EXAM ANSWERS FOR CHAPTER 4: HEATIr Fik TAinda não há avaliações
- Buddy: Chapter 5: PAPER 2 (Section A) 1. KedahDocumento8 páginasBuddy: Chapter 5: PAPER 2 (Section A) 1. KedahAriffin AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- 6 RadioactiveDocumento9 páginas6 RadioactiveAnna Latifah CammryAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactivity QuestionDocumento16 páginasRadioactivity QuestionVanusha AzzrielAinda não há avaliações
- 4531 FIZ - Skema Kertas 2Documento7 páginas4531 FIZ - Skema Kertas 2Yeow Pow Choo33% (3)
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1Documento14 páginasPeperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1nik mohamad solehinAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Documento8 páginasSkema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Chin Shee YanAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Jawapan SOLAF 3 Sains SPM 2011F PDFDocumento9 páginasSkema Jawapan SOLAF 3 Sains SPM 2011F PDFRoxus ThamAinda não há avaliações
- PERLIS-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Documento14 páginasPERLIS-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmoza0% (2)
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisDocumento9 páginasSkema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial Perlisenasizuka100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 2: Answer With The Correct UnitDocumento9 páginasSkema Jawapan Kertas 2: Answer With The Correct UnitNg Yew MengAinda não há avaliações
- Namibia University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Physics B Exam PaperDocumento7 páginasNamibia University Faculty of Engineering Introduction to Physics B Exam PaperNyashah FelixAinda não há avaliações
- FORM 3 CHEMISTRY END TERM MARKINGDocumento5 páginasFORM 3 CHEMISTRY END TERM MARKINGBenjamin mwanikiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDocumento9 páginasPhysics P2 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Documento9 páginasAnswer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Cikgu FaizalAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Sonication Time On The Production of Graphene by Electrochemical Exfoliation MethodDocumento6 páginasEffect of Sonication Time On The Production of Graphene by Electrochemical Exfoliation MethodYe Zar Ni HtweAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10: RadioactivityDocumento6 páginasChapter 10: RadioactivitychorianAinda não há avaliações
- FT/SCAK/1019A Answer Key and Exam PaperDocumento6 páginasFT/SCAK/1019A Answer Key and Exam PaperA BLESTAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactive Paper 1 Chapter 10Documento16 páginasRadioactive Paper 1 Chapter 10Eng BahanzaAinda não há avaliações
- Markscheme HL Paper3Documento60 páginasMarkscheme HL Paper3dilemAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactivity QuestionDocumento16 páginasRadioactivity Questionjesunathan44@yahoo.comAinda não há avaliações
- Skema K2 Set A JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMDocumento7 páginasSkema K2 Set A JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMCikgu FaizalAinda não há avaliações
- Part Test-6: Allindiatest SeriesDocumento12 páginasPart Test-6: Allindiatest SeriesafasdfasdAinda não há avaliações
- Skema, Trial 1 ChemistryDocumento6 páginasSkema, Trial 1 Chemistryhuda186Ainda não há avaliações
- 15 Kelantan SkemaDocumento16 páginas15 Kelantan SkemaNadia SaidonAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Sai Bharath College of Arts and Science: Optics Spectroscopy and Modern PhysicsDocumento1 páginaSri Sai Bharath College of Arts and Science: Optics Spectroscopy and Modern PhysicsAllen Judis RozarioAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear Chem 2010Documento7 páginasNuclear Chem 2010neil-lakdawala-8738Ainda não há avaliações
- X-Science-Ms (Set-3)Documento5 páginasX-Science-Ms (Set-3)ruhiagarwal2916Ainda não há avaliações
- 4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Documento22 páginas4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Robert HicksAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Kinetics and Equilibrium SQPDocumento7 páginasChemical Kinetics and Equilibrium SQPPrashanth 070Ainda não há avaliações
- Science & Technology (Part 1) : Solution: Practice Activity Sheet 5Documento4 páginasScience & Technology (Part 1) : Solution: Practice Activity Sheet 5nikhilverhani0Ainda não há avaliações
- The MCQDocumento8 páginasThe MCQAboahmed Ali100% (1)
- Aakash NBTS - 02 (2022) (@TEAMFLOOD)Documento21 páginasAakash NBTS - 02 (2022) (@TEAMFLOOD)Vahida KadiwalAinda não há avaliações
- Bgcse Double Award 2018 SolutionsDocumento16 páginasBgcse Double Award 2018 SolutionsCrystal Machipisa100% (1)
- 4541-1&2&3 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Documento22 páginas4541-1&2&3 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Yeow Pow ChooAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear Chemistry: Na NaDocumento4 páginasNuclear Chemistry: Na Nanagendra_rdAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Section B and C and Paper 3Documento21 páginasAnswer Section B and C and Paper 3Adnan ShamsudinAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 FS PhySci GR 10 Jun Exam EngDocumento15 páginas2018 FS PhySci GR 10 Jun Exam EngkatlehoweymersAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Science and Engineering BDocumento6 páginasMaterials Science and Engineering BAdi Primanto ShevaAinda não há avaliações
- Science and Technology Part 1Documento5 páginasScience and Technology Part 1cttrpk134Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 13 - Week 12Documento4 páginasUnit 13 - Week 12Neha MohamadAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Modul 6Documento14 páginasSkema Modul 6nik mohamad solehinAinda não há avaliações
- Skemapraktisbestari - Juj 2010Documento22 páginasSkemapraktisbestari - Juj 2010azharsarahAinda não há avaliações
- C04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kDocumento46 páginasC04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kMThana Balan0% (1)
- Group - IDocumento13 páginasGroup - ISudharm KeertiAinda não há avaliações
- Model Test Paper - (VIII Studying) - Foundation PDFDocumento14 páginasModel Test Paper - (VIII Studying) - Foundation PDFayushAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper - VII - SA1 - SCIENCE - 13-14 - SET-1Documento3 páginasQuestion Paper - VII - SA1 - SCIENCE - 13-14 - SET-1Amrita SenAinda não há avaliações
- CAPE Physics 2004 U1 P2Documento18 páginasCAPE Physics 2004 U1 P2ashleighAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 19: The Nucleus: A Chemist's ViewDocumento13 páginasChapter 19: The Nucleus: A Chemist's ViewIron ManAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsDocumento2 páginasRadioactivity and Nuclear Reactionsdulalsushant3Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Solved-Sample-Paper-Class-7-SA1-Set-1Documento5 páginasScience Solved-Sample-Paper-Class-7-SA1-Set-1SushilAinda não há avaliações
- IR Spectroscopy Determines CO2 in WaterDocumento4 páginasIR Spectroscopy Determines CO2 in Watersm_carvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of EnviromagneticsNo EverandEnvironmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of EnviromagneticsAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Plasmon Enhanced, Coupled and Controlled FluorescenceNo EverandSurface Plasmon Enhanced, Coupled and Controlled FluorescenceAinda não há avaliações
- Compendium of Atomic Alkali Resistant Optical Thin Films, Diffusion and Electrical Mobility in Diode Pumped Alkali Lasers (DPALs)No EverandCompendium of Atomic Alkali Resistant Optical Thin Films, Diffusion and Electrical Mobility in Diode Pumped Alkali Lasers (DPALs)Ainda não há avaliações
- Industrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsNo EverandIndustrial Chemistry of Oxides for Emerging ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Skor A+ Fizik JPNS 2014 - Elektromagnet - SkemaDocumento6 páginasModul Skor A+ Fizik JPNS 2014 - Elektromagnet - SkemaCikita IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Modul Skor A+ Fizik ELEKTRONIKDocumento8 páginasSkema Modul Skor A+ Fizik ELEKTRONIKCikita IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- SMKMM Phy p1Documento7 páginasSMKMM Phy p1Amaliana OthmanAinda não há avaliações
- @ SM Teknik Dungun, TerengganuDocumento26 páginas@ SM Teknik Dungun, TerengganuCikita IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Modul Skor A+ Fizik ELEKTRONIKDocumento8 páginasSkema Modul Skor A+ Fizik ELEKTRONIKCikita IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- SC PMRDocumento10 páginasSC PMRSiti Mas Aida MesrahAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz TemplateDocumento22 páginasQuiz TemplateantisocialimperialAinda não há avaliações
- SC PMRDocumento10 páginasSC PMRSiti Mas Aida MesrahAinda não há avaliações
- Question - Set 1, Paper 1Documento11 páginasQuestion - Set 1, Paper 1Puteri NurfatinAinda não há avaliações
- Perkembangan Teori CahayaDocumento6 páginasPerkembangan Teori Cahayakojo_87Ainda não há avaliações
- Mark Scheme Paper 3 June 99Documento3 páginasMark Scheme Paper 3 June 99Abdo AbdalatifAinda não há avaliações
- 3235Documento4 páginas3235fotickAinda não há avaliações
- SoundDocumento45 páginasSoundAli AbdallahAinda não há avaliações
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocumento31 páginasSpeed Velocity and AccelerationJoric MagusaraAinda não há avaliações
- How to solve calculus problems in physicsDocumento3 páginasHow to solve calculus problems in physicsAparAinda não há avaliações
- Kundt's TubeDocumento4 páginasKundt's Tubevijendra maurya100% (1)
- C18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsDocumento106 páginasC18-Radioactivity and Nuclear ReactionsAbhishek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Hong Kong Physics Olympiad Lesson 15Documento31 páginasHong Kong Physics Olympiad Lesson 15Sumihar SimangunsongAinda não há avaliações
- Radiation HazardsDocumento40 páginasRadiation HazardsMunish Dogra100% (1)
- Doppler EffectDocumento5 páginasDoppler EffectMohamed Jameel100% (1)
- Practice Quiz Diffraction 1Documento2 páginasPractice Quiz Diffraction 1pauljkt1Ainda não há avaliações
- C2 FiberOpticsBasics-L6Documento17 páginasC2 FiberOpticsBasics-L6sid011Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 22Documento43 páginasChapter 22Mohamed Saied FrahatAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 Nuclear ChemistryDocumento35 páginasChapter 10 Nuclear Chemistryapi-30718309100% (1)
- 4 1 MotionDocumento21 páginas4 1 Motionapi-261462856Ainda não há avaliações
- P6311 Basic Flourescent ScreenDocumento4 páginasP6311 Basic Flourescent ScreenSarah BowersAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 QuestionsDocumento6 páginasChapter 14 QuestionsJovic LiwagAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer: Physical Origins and Rate Equations: Chapter One Sections 1.1 and 1.2Documento11 páginasHeat Transfer: Physical Origins and Rate Equations: Chapter One Sections 1.1 and 1.2Rokib HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter11-Nuclear ChemistryDocumento52 páginasChapter11-Nuclear ChemistryfranantapurbaAinda não há avaliações
- IAEA Chapter 05 Teletherapy MachinesDocumento126 páginasIAEA Chapter 05 Teletherapy Machineslnader19Ainda não há avaliações
- UFO Propulsion SystemsDocumento3 páginasUFO Propulsion SystemsSamuel TrevinoAinda não há avaliações
- Inverse Square LawDocumento70 páginasInverse Square LawEngr Rab Nawaz ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Radioactive Decay - WikipediaDocumento22 páginasRadioactive Decay - WikipediaSaksham100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodyDocumento22 páginasChapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodylozzzzzAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - AHLDocumento41 páginasTopic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - AHLPaul Amezquita100% (1)
- E M WavesDocumento11 páginasE M WavesEleena GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Structure (L3) - StudentDocumento28 páginasAtomic Structure (L3) - StudentdzikranAinda não há avaliações