Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
GenChem Nomenclature Updated
Enviado por
Reuben CabreraDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
GenChem Nomenclature Updated
Enviado por
Reuben CabreraDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BrO
-
hypobromite ClO
-
hypochlorite IO
-
hypoiodite
BrO
2
-
bromite ClO
2
-
chlorite IO
2
-
iodite
BrO
3
-
bromate ClO
3
-
chlorate IO
3
-
iodate
BrO
4
-
perbromate ClO
4
-
perchlorate IO
4
-
periodate
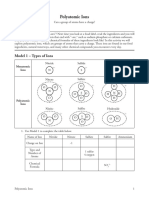
General Chemistry Nomenclature
Anions
Monoatomic Polyatomic
Cl
-
chloride OH
-
hydroxide
F
-
fluoride PO
4
-3
phosphate
Br
-
bromide CN
-
cyanide
I
-
iodide PO
3
-3
phosphite
O
-2
oxide HCO
3
-
bicarbonate
S
-2
sulfide HSO
4
-
bisulfate
H
-
hydride NO
3
-
nitrate
N
-3
nitride NO
2
-
nitrite
C
-4
carbide MnO
4
-
permanganate
C
2
H
3
O
2
-
acetate
O
2
-2
peroxide
C
2
O
4
-2
oxalate
CO
3
-2
carbonate
SO
4
-2
sulfate
SO
3
-2
sulfite
CrO
4
-2
chromate
Cr
2
O
7
-2
dichromate
Cations
+1 Cations +2 Cations +3 Cations
H
+
hydrogen Be
+2
beryllium Al
+3
aluminum
Li
+
lithium Mg
+2
magnesium
Na
+
sodium Ca
+2
calcium
K
+
potassium Sr
+2
strontium
Rb
+
rubidium Ba
+2
barium
Cs
+
cesium Zn
+2
zinc
Ag
+
silver Cd
+2
cadmium
NH
4
+
ammonium
Cations with multiple oxidation states
Fe
+2
iron (II) or ferrous Pb
+2
lead (II) or plumbous
Fe
+3
iron (III) or ferric Pb
+4
lead (IV) or plumbic
Cr
+2
chromium (II) or chromous Cu
+1
copper (I) or cuprous
Cr
+3
chromium (III) or chromic Cu
+2
copper (II) or cupric
Sn
+2
tin (II) or stannous Hg
+2
mercury (II) or mercuric
Sn
+4
tin (IV) or stannic Hg
2
+2
mercury (I) or mercurous
Acids
HF
HCl
HBr
HI
HCN
H
2
S
hydrofluoric acid
hydrochloric acid
hydrobromic acid
hydroiodic acid
hydrocyanic acid
hydrosulfuric acid
HNO
2
HNO
3
H
3
PO
4
H
2
SO
3
H
2
SO
4
HC
2
H
3
O
2
nitrous acid
nitric acid
phosphoric acid
sulfurous acid
sulfuric acid
acetic acid
H
2
CO
3
carbonic acid H
2
C
2
O
4
HClO
oxalic acid
hypochlorous acid
HClO
2
HClO
3
HClO
4
chlorous acid
chloric acid
perchloric acid
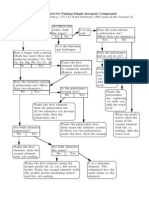
Rules for Naming Compounds
A. Binary Compounds Containing a Metal and a Nonmetal (ionic compounds)
1. Name of cation is given first (same as name of element)
2. Name of anion is given second
i. Monoatomic anions end in ide
ii. Polyatomic ion names do not change
B. Binary Compounds between Two Nonmetals (molecular compounds)
1. Prefixes are used to specify the number of each atom present
i.e. 1=mono, 2=di, 3=tri, 4=tetra, 5=penta, 6=hexa, 7=hepta, 8=octa
2. If first atom is a single atom then prefix mono is omitted
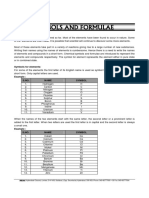
Rules for Writing Formulas
A. Ionic Compounds
1. Sum of charges of all ions must equal zero i.e. total negative charge of
all anions must cancel the total positive charge of all cations
2. Use subscripts to indicate the presence of more than one ion
3. Polyatomic ions must be in parentheses if subscripts are used.
Você também pode gostar
- 128.1 RequirementsDocumento1 página128.1 RequirementsReuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- RomDocumento1 páginaRomReuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Flip FlopDocumento1 páginaFlip FlopReuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Cheeem 14Documento1 páginaCheeem 14Reuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Answer KeyDocumento2 páginasAnswer KeyReuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Answer KeyDocumento2 páginasAnswer KeyReuben CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Common Ions: Names and FormulasDocumento2 páginasCommon Ions: Names and Formulasabdul halimAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature Worksheet Part 1Documento8 páginasNomenclature Worksheet Part 1Jocelyn MarmolAinda não há avaliações
- AP Chemistry - 03 NMSI Chemical Nomenclature STUDENTDocumento14 páginasAP Chemistry - 03 NMSI Chemical Nomenclature STUDENTAbdul SamiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Naming Compounds Flow ChartDocumento1 páginaChemistry Naming Compounds Flow ChartBob SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Reference Tables Workbook, 2nd Edition (2011) PDFDocumento241 páginasChemistry Reference Tables Workbook, 2nd Edition (2011) PDFLuis Gustavo Pacheco67% (3)
- 17 Polyatomic Ions S PDFDocumento7 páginas17 Polyatomic Ions S PDFGideon CavidaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4: Naming Ions and Compounds and Deriving Chemical FormulasDocumento13 páginasLesson 4: Naming Ions and Compounds and Deriving Chemical FormulasAljon CatibanAinda não há avaliações
- AP Chemistry Polyatomic IonsDocumento3 páginasAP Chemistry Polyatomic IonsAdam AhmatAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Compounds and Formula WritingDocumento5 páginasNaming Compounds and Formula WritingNicoleAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Problems (Chapter 2) Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds - KEYDocumento3 páginasPractice Problems (Chapter 2) Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds - KEYsarahsarfraz81Ainda não há avaliações
- (CHEM) Flowchart NamingDocumento1 página(CHEM) Flowchart Namingsodiumboyupinthishoe100% (1)
- The Three of Life: Lesson 1Documento34 páginasThe Three of Life: Lesson 1Justine Valad-onAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6Documento23 páginasLecture 6boledi angelaAinda não há avaliações
- CH1001 2010 (Language2) NotesDocumento18 páginasCH1001 2010 (Language2) Notesbav92Ainda não há avaliações
- 9th+class Symbols+and+Formulae Chemistry+MaterialDocumento12 páginas9th+class Symbols+and+Formulae Chemistry+Materialaveerareddy9Ainda não há avaliações
- Polyatomic Ions, Monatomic Ions and Elements (Honors Chemistry Nomenclature/Bonding Unit)Documento3 páginasPolyatomic Ions, Monatomic Ions and Elements (Honors Chemistry Nomenclature/Bonding Unit)JaharaAinda não há avaliações
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY I Midterms ReviewerDocumento15 páginasGENERAL CHEMISTRY I Midterms ReviewerAJ Santos100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Cont OhDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan Cont OhAnonymous viipLHxyAinda não há avaliações
- CCDocumento6 páginasCCdeckbyte865100% (1)
- Polyatomic Ions ExplainedDocumento4 páginasPolyatomic Ions ExplainedIBRAHIM ABOU EL NAAJAinda não há avaliações
- Namig Binary Compound Acids: Prepared By: Richelle Lopez InstructorDocumento14 páginasNamig Binary Compound Acids: Prepared By: Richelle Lopez InstructorIvy VillarAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocumento4 páginasNaming Ionic and Covalent CompoundsMarie GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- CH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsDocumento8 páginasCH 7 Practice Test Honor Chem Naming CompoundsBeth0% (1)
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDocumento2 páginasCommon Ions and Their ChargesSJ SuingAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Compounds FlowchartDocumento1 páginaNaming Compounds Flowchartapi-310503032Ainda não há avaliações
- Reading Essentials - Writing Formulas and Naming CompoundsDocumento8 páginasReading Essentials - Writing Formulas and Naming CompoundsMarta Cristina BarredaAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic NomenclatureDocumento28 páginasInorganic NomenclatureAbhishek SadaphulAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsDocumento5 páginas3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsKen WuAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 3 - Lecture NotesDocumento51 páginasCHAPTER 3 - Lecture NotesAlex100% (1)
- ENITV21D-Naming Compounds Summary2Documento5 páginasENITV21D-Naming Compounds Summary2Sean PimentelAinda não há avaliações