Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP
Enviado por
Jonathan CalingTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP
Enviado por
Jonathan CalingDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
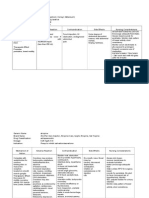
Assessment
Nursing
Diagnosis
Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
Objective:
o PR = 116
o BP =
200/150
o weak
peripheral
pulses
o Crackles
upon
auscultation
o Urine
Output =
450cc/day
Decreased
Cardiac Output
related to
Altered
myocardial
contractility
After 1 hour
of nursing
interventions,
the patient
will be able to
demonstrate
vital signs
within
acceptable
limits,
dysrhythmias
absent/contro
lled, and no
symptoms of
failure after 1
day
1. assess heart
rate
2. Palpate
peripheral
pulses.
3. Monitor BP
4. Inspect skin for
pallor
5. Monitor urine
output
6. Encourage rest,
semi recumbent
in bed or chair.
Assist with
physical care as
indicated.
7. Administer
medications as
indicated:
1. Tachycardia is usually present (even at
rest) to compensate for decreased
ventricular contractility.
2. Decreased cardiac output may be
reflected in diminished radial, popliteal,
dorsalis pedis, and posttibial pulses.
3. In early, moderate, or chronic HF, BP may
be elevated because of increased SVR.
4. Pallor is indicative of diminished
peripheral perfusion secondary to
inadequate cardiac output,
vasoconstriction, and anemia.
5. Kidneys respond to reduced cardiac
output by retaining water and sodium.
6. Physical rest should be maintained to
improve efficiency of cardiac contraction
and to decrease myocardial oxygen
demand/ consumption and workload.
7. A variety of medications may be used to
increase stroke volume, improve
contractility, and reduce congestion.
After 1 hour of nursing
interventions, the
patient demonstrated
vital signs within
acceptable limits,
dysrhythmias
absent/controlled, and
no symptoms of failure
after 1 day.
8. Diuretics-
furosemide
(Lasix)
9. ACE inhibitors-
captopril
(Capoten)
10. Digoxin
(Lanoxin)
11. Administer IV
solutions,
restricting total
amount as
indicated. Avoid
saline solutions.
12. Monitor/ replace
electrolytes.
8. Enhances excretion of sodium,
chloride,potassium by direct action at
ascending Limb of loop of Henle.
9. ACE inhibitors represent first-line therapy
to control heart failure by decreasing
venticular filling pressures and SVR while
increasing cardiac output with little or no
change in BP and heart rate.
10. Increases force of myocardial contraction
when diminished contractility is the cause
of HF, and slows heart rate by decreasing
conduction velocity and prolonging
refractory period of the atrioventricular
(AV) junction to increase cardiac
efficiency /output.
11. Because of existing elevated left
ventricular pressure, patient may not
tolerate increased fluid volume (preload).
Patients with HF also excrete less
sodium, which causes fluid retention and
increases myocardial workload.
12. Fluid shifts and use of diuretics can alter
electrolytes (especially potassium and
chloride), which affect cardiac rhythm and
contractility.
Assessment
Nursing
Diagnosis
Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
Objective:
Patient
manifested:
Edema on
extremities
Crackles,
heard on both
lung fields
RR = 30bpm
BP = 200/150
PR = 116
Weight =63kg
Urine
output=380cc
/day
Edema=
grade +1
(1mm slightly
pitting,
disappears
rapidly)
Excessive
Fluid volume r/t
sodium and
water retention
After 1 hour of nursing
interventions, the
patient will
demonstrate adequate
fluid balance as
manifested by clearing
breath sounds, and
decreasing edema
after 1 day
1. Establish rapport
2. Monitor and record VS
3. Assess patients
general condition
4. Weigh patient daily and
compare to previous
weights.
5. Follow low-sodium diet
and/or fluid restriction
6. Assess the need for an
indwelling urinary
catheter.
7. Institute/instruct patient
regarding fluid
restrictions as
appropriate.
8. Administer diuretics as
prescribed
1. To gain patients trust and
cooperation
2. To obtain baseline data
3. To determine what approach
to use in treatment
4. Body weight is a sensitive
indicator of fluid balance and
an increase indicates fluid
volume excess.
5. May include increased fluids
or sodium intake, or
compromised regulatory
mechanisms.
6. Treatment focuses on
diuresis of excess fluid.
7. This helps reduce
extracellular volume.
8. Enhances excretion of
sodium, chloride, potassium
by direct action at
ascendinglimb of loop of
Henle. Therapeutic
Effect:Produces diuresis,
lowers B/P.
Patient has
demonstrated
adequate fluid
balance: clearing
breath sounds and
decreasing edema
after 1 day
Assessment
Nursing
Diagnosis
Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective:
Objective:
Patient manifested:
presence of
crackles
upon
auscultation
RR= 30 bpm
Pallor
Impaired gas
exchange
related to
accumulation of
fluid in the
alveoli
After 30 minutes of
nursing
interventions, the
patient will be able to
demonstrate
improvement in gas
exchange as
manifested by
decrease in
respiratory rate to
normal.
1. Monitor respiratory rate
2. Elevate head of bed and
encourage frequent position
changes.
3. Promote adequate rest
periods
4. Change position q 2 hrs.
5. Administer oxygen therapy as
ordered.
1. To obtain baseline
data
2. To promote maximal
inspiration, enhance
expectoration of
secretions in order to
improve ventilation
3. Rest will prevent
weakness and
decrease oxygen
demands for
metabolic demands
4. To promote drainage
of secretions
5. O2 therapy is
indicated to increase
oxygen saturation
The patient has been
able to demonstrate
improvement in gas
exchange a decrease in
respiratory rate to normal
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Haven LinksDocumento2 páginasHaven LinksJonathan Caling100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Orif Case StudyDocumento17 páginasOrif Case Studykreny1078% (9)
- Percutaneous Interventional Cardiovascular Medicine - The PCR-EAPCI TextbookDocumento29 páginasPercutaneous Interventional Cardiovascular Medicine - The PCR-EAPCI TextbookRanda Tabbah100% (1)
- What Is The Ideal Cholesterol Level by Joel Fuhrman MDDocumento4 páginasWhat Is The Ideal Cholesterol Level by Joel Fuhrman MDDrRod SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Application LetterDocumento1 páginaApplication LetterJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Conceptual Framewor1kDocumento1 páginaConceptual Framewor1kJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Application LetterDocumento1 páginaApplication LetterJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- ResumeDocumento1 páginaResumeJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- CsDocumento1 páginaCsJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- New Case Study For Finals To Be PrintDocumento40 páginasNew Case Study For Finals To Be PrintJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs CholecystectomyDocumento5 páginasDrugs CholecystectomyJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Caling PsychDocumento17 páginasCaling PsychJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Tonsillectomy and AdenoidectomyDocumento4 páginasTonsillectomy and AdenoidectomyJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Gilbert de Vera Mamasig: Contact InformationDocumento2 páginasGilbert de Vera Mamasig: Contact InformationJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- How To Ensure The Economic Growth Also Benefit The Lower ClassesDocumento3 páginasHow To Ensure The Economic Growth Also Benefit The Lower ClassesJohn CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristic of StarsDocumento4 páginasCharacteristic of StarsJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- DM Case Study - Nursing CribDocumento6 páginasDM Case Study - Nursing CribFrancis VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Natsu Defense1Documento4 páginasNatsu Defense1Jonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Give Cold Compress On The Head. 2. Massage The Head / Neck / Arm If The Patient Can Tolerate The TouchDocumento5 páginasGive Cold Compress On The Head. 2. Massage The Head / Neck / Arm If The Patient Can Tolerate The TouchJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Panantaon, Norminah Q. Bsn3Documento1 páginaPanantaon, Norminah Q. Bsn3Jonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento2 páginasCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- AppenDocumento13 páginasAppenJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- FormatDocumento6 páginasFormatJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Rina D. Amistad Acetaminophen (Oral) (A SEET A MIN Oh Fen)Documento7 páginasRina D. Amistad Acetaminophen (Oral) (A SEET A MIN Oh Fen)Jonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Parenting A ToddlerDocumento4 páginasParenting A ToddlerJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Eva Teaching StratDocumento5 páginasEva Teaching StratJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- DigoxinDocumento3 páginasDigoxinJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- DM Case Study - Nursing CribDocumento6 páginasDM Case Study - Nursing CribFrancis VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Schizo NatDocumento3 páginasSchizo NatJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Panantaon, Norminah Q. Bsn3Documento1 páginaPanantaon, Norminah Q. Bsn3Jonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Earthquake: Different Types of FaultsDocumento16 páginasEarthquake: Different Types of FaultsJonathan CalingAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Medicine PDFDocumento76 páginasInternal Medicine PDFroxxanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pelvic ThrombophlebitisDocumento12 páginasPelvic ThrombophlebitisMicah Magallano100% (1)
- Pengaruh Senam Yoga Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada LansiaDocumento5 páginasPengaruh Senam Yoga Terhadap Penurunan Tekanan Darah Pada LansiaElvirakrtAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiology-5 DysrhythmiaDocumento16 páginasCardiology-5 DysrhythmiaMahmoud RamadanAinda não há avaliações
- Valvular Aortic Stenosis: Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocumento3 páginasValvular Aortic Stenosis: Acute Myocardial InfarctionCM NajitoAinda não há avaliações
- Adp+Pi Atp+H: Answers To Chapter 07 - 13 AssignmentDocumento6 páginasAdp+Pi Atp+H: Answers To Chapter 07 - 13 AssignmentAdetola SimeonAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Pressure by Height & AgeDocumento4 páginasBlood Pressure by Height & AgeAzmi Muliatua PanjaitanAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System - BiologyDocumento11 páginasCirculatory System - BiologyAmanda AllenAinda não há avaliações
- Phys 4.1 CV Heart Electrical NOTESDocumento5 páginasPhys 4.1 CV Heart Electrical NOTESEsther RaniAinda não há avaliações
- PericarditisDocumento3 páginasPericarditisKhalid Mahmud Arifin0% (1)
- Intercostal ArteriesDocumento3 páginasIntercostal ArteriesranshAinda não há avaliações
- 995 Bio Medicus Cannulae FamilyDocumento8 páginas995 Bio Medicus Cannulae FamilyAhmadMarshallShuaibiAinda não há avaliações
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceDocumento11 páginasIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- AHA 2017 Cardiogenic ShockDocumento37 páginasAHA 2017 Cardiogenic ShockAnastasyaLianAinda não há avaliações
- HFpEF MeDocumento28 páginasHFpEF MeRidwan YasinAinda não há avaliações
- Tachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaDocumento7 páginasTachycardia Complicated by Bradycardia Then Another Form of TachycardiaLam Sin WingAinda não há avaliações
- Congestive Heart Failure: Mulualem W.MD Dmu, Department of Internal Medicine For Ho StudentsDocumento27 páginasCongestive Heart Failure: Mulualem W.MD Dmu, Department of Internal Medicine For Ho Studentsmuluneh birhaneAinda não há avaliações
- Case 3: Aortic StenosisDocumento11 páginasCase 3: Aortic StenosisfmAinda não há avaliações
- Pengaruh Larutan Madu Terhadap Tekanan Darah Lanjut Usia HipertensiDocumento10 páginasPengaruh Larutan Madu Terhadap Tekanan Darah Lanjut Usia HipertensiNopita SariAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines Made Simple Chest PainDocumento18 páginasGuidelines Made Simple Chest PainPaul JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Life Support (BLS)Documento110 páginasBasic Life Support (BLS)daveAinda não há avaliações
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento50 páginasThe Circulatory SystemIshan Jacob PiadocheAinda não há avaliações
- Pricelist AMSDocumento1 páginaPricelist AMSMimi AnugrahAinda não há avaliações
- الباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فوراDocumento163 páginasالباطنة كلها بالتفصيل في 160 صفحة فقط لازم تحمل المذكرة فورانادين مطر0% (1)
- Arteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisDocumento22 páginasArteriosclerosis & AtherosclerosisSitty Aizah MangotaraAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Very Old Patient in ICUDocumento17 páginasManagement of Very Old Patient in ICUSuci RahmayenjAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiomiopatia Hipertrofica 2016 PDFDocumento25 páginasCardiomiopatia Hipertrofica 2016 PDFBlanca Herrera MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationDocumento6 páginas11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationKambaska Kumar BeheraAinda não há avaliações