Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
B862 PDF
Enviado por
Prasetyo Adi0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
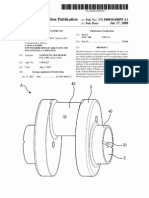
31 visualizações2 páginasMotorcycle chassis design is the art and science of motorcycle handling and chassis design. A bike's chassis is a combination of its frame, forks, sprockets, shock absorbers, springs, struts, spring rate and weight distribution. The bike's suspension consists of a number of components including springs, dampers, spring rates, tyres, calipers, pads and brake calipers.
Descrição original:
Título original
B862.pdf
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoMotorcycle chassis design is the art and science of motorcycle handling and chassis design. A bike's chassis is a combination of its frame, forks, sprockets, shock absorbers, springs, struts, spring rate and weight distribution. The bike's suspension consists of a number of components including springs, dampers, spring rates, tyres, calipers, pads and brake calipers.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
31 visualizações2 páginasB862 PDF
Enviado por
Prasetyo AdiMotorcycle chassis design is the art and science of motorcycle handling and chassis design. A bike's chassis is a combination of its frame, forks, sprockets, shock absorbers, springs, struts, spring rate and weight distribution. The bike's suspension consists of a number of components including springs, dampers, spring rates, tyres, calipers, pads and brake calipers.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
1 Function and history
Some basic denitions
Function
History
Front suspension
Rear suspension
Spring types
Load Compensation
2 Tyres
Weight support
Suspension action
Tyre stiffness or spring rate
Contact area
Area when cornering
Friction (grip)
Braking & driving
Cornering
Mechanisms of grip
Under- and over-steer
Construction
Materials
Summary
3 Geometric considerations
Basic motorcycle geometry
Trail
Rake or castor angle (steering axis
inclination)
Wheelbase
Wheel diameter
Other considerations
Angular motions
4 Balance and steering
Balance
Steering
Gyroscopic effects only
Gyroscopic with tyre camber force only
Gyroscopic with tyre camber and steer
forces
Tyre forces only - no gyroscopic effects
Body lean only - no steering
Conclusions
5 Aerodynamics
Drag
Evolution of the racing fairing
Internal air ow
Lift
Airow evaluation
Side wind stability (traditional view)
Steady state directional stability
Dynamic directional stability
Summary
6 Suspension principles
Springs
Damping
Sprung and unsprung mass
Basic suspension principles
Other factors
Lateral suspension
Summary
7 Front suspension
Head stock mounted forks
Alternatives to the head stock
mounted fork
Hub centre steered
Double link
McPhearson strut based
Virtual steering axis
8 Rear suspension
Effective spring rate
Chain effects
Wheel trajectory
Structural
Single or dual sided
Summary
9 Squat and dive
Load transfer
Squat and dive
Shaft drive
Chain drive
Aerodynamic squat
Braking reaction (rear)
Dive (front)
Dynamic effects
Summary
10 Structural considerations
Fatigue
Structural efciency
Triangulation
MOTORCYCLE HANDLING AND
CHASSIS DESIGN
the art and science
List of Chapters:
Beam frames
Triangulated frames
Tubular backbone
Structural comparison
Fabricated backbone
Monocoque
Structural engine
Conventional multi-tubular
Twin-spar
Other types
Summary
11 Engine Mounting
12 Braking
The basics
Effects of CoG height
Generation of torque
Hardware
Discs
Calipers
Pads
Linked brakes
ABS
13 Materials and properties
Typical properties of some common
materials
Frame
Wheels
Fuel tank
Brake discs
Bodywork
14 Stability & control
Under-/over-steer
High-siding
Stability under braking
Instabilities
Damping
15 Performance measurement
Track side
Laboratory
Strength analysis
Measurement and simulation
Future development
16 Practical frame building
Welding
Distortion
Gussets
Jigging
Tube proling
Tube types
Tube sizes
Frame nishes
Design layout
17 Case study
Measurement
Main frame
Engine mounting
Results
Material
Swing arm
Forks
Caution
Tuning
18 Future developments
The status quo
Future possibilities
Active suspension
Rheological Fluids
Two wheel drive (2WD)
Two wheel steering (2WS)
Feet-Forward motorcycles. (FF)
Appendices
A1 Experiments with rake and trail
Rake
TraiI
Conclusions
Post script
A2 Glossary of terms
A3 Units conversion
A4 Gyroscopic effects
A5 Basic physics of motorcycles
Basic Trigonometry
Units of angle
Velocity
Acceleration
Mass
Momentum
Newtons laws
Force and weight
Moments, couples and torque
Centripetal & centrifugal force
Addition and resolution of velocities and
forces
Work, energy and power
Nomenclature and sign conventions
Normalization
A6 Analysis of mechanisms
A7 CoG and mass distribution of rider
A8 Typical data
Notes
MOTORCYCLE HANDLING AND CHASSIS DESIGN
the art and science
Você também pode gostar
- Moto3 - Honda Nsf250rDocumento2 páginasMoto3 - Honda Nsf250rPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Super Mastercam + Rra BRT 2017Documento1 páginaSuper Mastercam + Rra BRT 2017Prasetyo Adi85% (26)
- Affects of Alignment, Chain Tension and Tire PressureDocumento2 páginasAffects of Alignment, Chain Tension and Tire PressurePrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Miniature InductiveDocumento5 páginasMiniature InductivePrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Tech110 PDFDocumento4 páginasTech110 PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Us20080168859a1 PDFDocumento7 páginasUs20080168859a1 PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Cylinder Head Design and Modification - Getting StartedDocumento4 páginasCylinder Head Design and Modification - Getting StartedBruno BambinetiAinda não há avaliações
- Us20080168859a1 PDFDocumento7 páginasUs20080168859a1 PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Suspension Setup PDFDocumento11 páginasSuspension Setup PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Gts Dyno Form PDFDocumento4 páginasGts Dyno Form PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- E Catalogue of MIKUNI INDONESIA PT PDFDocumento1 páginaE Catalogue of MIKUNI INDONESIA PT PDFPrasetyo AdiAinda não há avaliações
- Motorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFDocumento3 páginasMotorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFPrasetyo Adi40% (5)
- Motorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFDocumento3 páginasMotorcycle Chassis Design and Dynamics PDFPrasetyo Adi40% (5)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- BIR Form 2307Documento20 páginasBIR Form 2307Lean Isidro0% (1)
- BA5411 ProjectGuidelines - 2020 PDFDocumento46 páginasBA5411 ProjectGuidelines - 2020 PDFMonisha ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Graphene/Metal Organic Framework Composites As Adsorbents For Adsorption Chiller ApplicationsDocumento88 páginasGraphene/Metal Organic Framework Composites As Adsorbents For Adsorption Chiller ApplicationsNajam Ul QadirAinda não há avaliações
- GMDS - Course - FinalDocumento282 páginasGMDS - Course - FinalLuisPazPerdomo100% (1)
- Manual TP5000Documento206 páginasManual TP5000u177427100% (4)
- Overview 6T40-45 TransmissionDocumento14 páginasOverview 6T40-45 TransmissionLeigh100% (1)
- Funny AcronymsDocumento6 páginasFunny AcronymsSachinvirAinda não há avaliações
- NHS FPX 5004 Assessment 4 Self-Assessment of Leadership, Collaboration, and EthicsDocumento4 páginasNHS FPX 5004 Assessment 4 Self-Assessment of Leadership, Collaboration, and EthicsEmma WatsonAinda não há avaliações
- 2UEB000133 ACS2000 4kV Motor Temp Supervision Rev BDocumento3 páginas2UEB000133 ACS2000 4kV Motor Temp Supervision Rev BSherifAinda não há avaliações
- Unix Training ContentDocumento5 páginasUnix Training ContentsathishkumarAinda não há avaliações
- Archer AX53 (EU) 1.0 - DatasheetDocumento7 páginasArcher AX53 (EU) 1.0 - DatasheetLucAinda não há avaliações
- Executive Order No. 786, S. 1982Documento5 páginasExecutive Order No. 786, S. 1982Angela Igoy-Inac MoboAinda não há avaliações
- MN502 Lecture 3 Basic CryptographyDocumento45 páginasMN502 Lecture 3 Basic CryptographySajan JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Venezuela's Gold Heist - Ebus & MartinelliDocumento18 páginasVenezuela's Gold Heist - Ebus & MartinelliBram EbusAinda não há avaliações
- Nammcesa 000010 PDFDocumento1.543 páginasNammcesa 000010 PDFBasel Osama RaafatAinda não há avaliações
- Geometric Driver Components Serial Copy: Topsolid'WoodDocumento22 páginasGeometric Driver Components Serial Copy: Topsolid'Wooddrine100% (1)
- The Man Who Knew Too Much: The JFK Assassination TheoriesDocumento4 páginasThe Man Who Knew Too Much: The JFK Assassination TheoriesedepsteinAinda não há avaliações
- Landini Tractor 7000 Special Parts Catalog 1820423m1Documento22 páginasLandini Tractor 7000 Special Parts Catalog 1820423m1katrinaflowers160489rde100% (122)
- Service Manual JLG 1055 S-N01600727600Documento566 páginasService Manual JLG 1055 S-N01600727600RAPID EQUIPMENT RENTAL67% (6)
- To. Whom It May Concern: Available Mentioned Position in IndonesiaDocumento8 páginasTo. Whom It May Concern: Available Mentioned Position in IndonesiaGreen Sustain EnergyAinda não há avaliações
- 8 e Daft Chapter 01Documento29 páginas8 e Daft Chapter 01GabAinda não há avaliações
- Unit I Lesson Ii Roles of A TeacherDocumento7 páginasUnit I Lesson Ii Roles of A TeacherEvergreens SalongaAinda não há avaliações
- WFP Situation Report On Fire in The Rohingya Refugee Camp (23.03.2021)Documento2 páginasWFP Situation Report On Fire in The Rohingya Refugee Camp (23.03.2021)Wahyu RamdhanAinda não há avaliações
- Translation and Distribution Agreement PDFDocumento7 páginasTranslation and Distribution Agreement PDFClaudio Valerio Gaetani80% (5)
- Test P1 Chapter 10Documento10 páginasTest P1 Chapter 10Prince PersiaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1 - 2017 EETDocumento10 páginasPaper 1 - 2017 EETRayAinda não há avaliações
- Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Indonesian HospitalsDocumento12 páginasSurveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Indonesian HospitalsRidha MardiyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Bidding Process in Infrastructure ProjectsDocumento44 páginasBidding Process in Infrastructure ProjectsRajesh Chowdary Chintamaneni100% (2)
- Part - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No. Questions Bloom's Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocumento11 páginasPart - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No. Questions Bloom's Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDevendra BhavsarAinda não há avaliações
- 1000.01 Good Documentation PracticesDocumento13 páginas1000.01 Good Documentation PracticescipopacinoAinda não há avaliações