Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
A Study of Factor Pattern in Order To Discuss The Cluster in Which The Different Aspects of Chemistry Fall.
Enviado por
Anonymous CwJeBCAXp0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
17 visualizações5 páginasThe present study was concerned with the investigation of factor pattern in order to discuss the
clusters in which the different aspects of achievement in Chemistry fall at senior secondary level.
Researcher constructed 18 achievement tests in Chemistry. Authentic scores obtained from
reliable and valid objective type tests were taken into items and distributed over the whole
course to get factors which were obtained after first reiteration. Orthogonal rotation had to be
carried out and Turnstone’s method of Extended Vectors was used, as it leads to the simple
structure. Only the first five factors were taken for rotation. The obtained results indicate that
the fundamental abilities essential for learning Chemistry are: (a) Conceptual and Visual
Perception (b) Deductive Reasoning (c) Mechanism and nomenclature (d) Numerical (e)
Inference.
Keywords: Factors, Learning, Chemistry, Senior Secondary.
Título original
A STUDY OF FACTOR PATTERN IN ORDER TO DISCUSS THE CLUSTER IN WHICH THE DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF CHEMISTRY FALL.
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe present study was concerned with the investigation of factor pattern in order to discuss the
clusters in which the different aspects of achievement in Chemistry fall at senior secondary level.
Researcher constructed 18 achievement tests in Chemistry. Authentic scores obtained from
reliable and valid objective type tests were taken into items and distributed over the whole
course to get factors which were obtained after first reiteration. Orthogonal rotation had to be
carried out and Turnstone’s method of Extended Vectors was used, as it leads to the simple
structure. Only the first five factors were taken for rotation. The obtained results indicate that
the fundamental abilities essential for learning Chemistry are: (a) Conceptual and Visual
Perception (b) Deductive Reasoning (c) Mechanism and nomenclature (d) Numerical (e)
Inference.
Keywords: Factors, Learning, Chemistry, Senior Secondary.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
17 visualizações5 páginasA Study of Factor Pattern in Order To Discuss The Cluster in Which The Different Aspects of Chemistry Fall.
Enviado por
Anonymous CwJeBCAXpThe present study was concerned with the investigation of factor pattern in order to discuss the
clusters in which the different aspects of achievement in Chemistry fall at senior secondary level.
Researcher constructed 18 achievement tests in Chemistry. Authentic scores obtained from
reliable and valid objective type tests were taken into items and distributed over the whole
course to get factors which were obtained after first reiteration. Orthogonal rotation had to be
carried out and Turnstone’s method of Extended Vectors was used, as it leads to the simple
structure. Only the first five factors were taken for rotation. The obtained results indicate that
the fundamental abilities essential for learning Chemistry are: (a) Conceptual and Visual
Perception (b) Deductive Reasoning (c) Mechanism and nomenclature (d) Numerical (e)
Inference.
Keywords: Factors, Learning, Chemistry, Senior Secondary.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
JULY-AUG, 2014. VOL-II/XIII www.srjis.
com Page 1768
A STUDY OF FACTOR PATTERN IN ORDER TO DISCUSS THE CLUSTER IN
WHICH THE DIFFERENT ASPECTS OF CHEMISTRY FALL.
B.P.Singh, Ph D*Associate Professor,MLRS PG College of Education,Charkhi Dadri(Bhiwani)
Haryana
The present study was concerned with the investigation of factor pattern in order to discuss the
clusters in which the different aspects of achievement in Chemistry fall at senior secondary level.
Researcher constructed 18 achievement tests in Chemistry. Authentic scores obtained from
reliable and valid objective type tests were taken into items and distributed over the whole
course to get factors which were obtained after first reiteration. Orthogonal rotation had to be
carried out and Turnstones method of Extended Vectors was used, as it leads to the simple
structure. Only the first five factors were taken for rotation. The obtained results indicate that
the fundamental abilities essential for learning Chemistry are: (a) Conceptual and Visual
Perception (b) Deductive Reasoning (c) Mechanism and nomenclature (d) Numerical (e)
Inference.
Keywords: Factors, Learning, Chemistry, Senior Secondary.
INTRODUCTION: There is a need to show balance between the aspirations of parents and
abilities of their wards. Every parent is interested to enroll the ward in science stream to make
him a good doctor, engineer or technocrat. His ward can be a good student only when he/she
possesses requisite mental abilities required for the success of science courses. There are some
specific cognitive abilities essential for each subject of science and technology. Some structure
of intellect abilities have found related with Physics (Ignatz 1982, Spero 1974), Mathematics
(Peterson 1965,Chauhan 1984), Biology (Chhikara 1984). Ptrich, PaulR(1990) found that self
efficacy and intrinsic value were positively related to cognitive engagement and performance.
Kember, David(2003) found that a student adopting a surface approach does not seek
understanding and, therefore, relies upon memorization. GWO-Hshiang Tzen (2007) carried out
Scholarly Research Journal's is licensed Based on a work at www.srjis.com 4.194, 2013 SJIF
SRJIS 2014
Abstract
SRJIS/BIMONTHLY/ B.P. SINGH (1768-1772)
JULY-AUG, 2014. VOL-II/XIII www.srjis.com Page 1769
a research on evaluating intertwined effect in e-learning programs. A novel hybrid MCDM
Model based on factor analysis. Hilde Brand H.P (2011) conducted a research on a factorial
study of introversion- extroversion and it was found that previous research suggested that Jungs
theory of psychological types could be best examined by factorial method.
A review of studies carried out in the field of factor analysis reveals that no systematic attempt
has been made to assess the cognitive abilities in Chemistry. Since there is paucity of such
studies, it is appropriate to investigate factor pattern in order to discuss the clusters in which the
different aspects of achievement in Chemistry fall.
OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
1. To construct 18 objective type achievement tests for assessing the achievement in different
aspects of Chemistry at Senior Secondary level.
2. To find out the correlations between the achievements in different aspects and to apply factor
analysis in order to extract common factor.
3. To interpret the factors and study the factor-pattern in order to discuss the clusters in which the
different aspects of achievements in Chemistry fall.
METHOD OF STUDY AND PROCEDURE
Researcher constructed 18 achievement tests covering entire curriculum of senior secondary.
These tests were standardized; correlation matrix among them was obtained from reliable, valid
objective items. Factors were found out by Centric Method. Orthogonal simple structure was not
possible. Oblique rotation had to carried out and Thurstons method of extended vector was used.
SAMPLE: Sampling was done on two occasions. Try out test was administered to about 75
students out of theses 69 were selected at random to get data about each individual item. Sample
of 250 students was taken finally.
INSTRUMENTATION: The researcher constructed 18 achievement tests for assessing
achievements in different aspects of Chemistry. The purpose was to find out the inter
correlations of the scores in different aspects for the factor analysis.
ANALYSIS OF DATA
Investigator decided to use the Centric method for factor analysis of the correlation matrix.
Factor analysis was stopped after fifth factor after first reiteration as the loading of the sixth
factor fell short of Guilford and Laceys Criterion. To give meaning and fixity to factor pattern
for interpretation, Turnstone concept of simple structure was applied but orthogonal simple
SRJIS/BIMONTHLY/ B.P. SINGH (1768-1772)
JULY-AUG, 2014. VOL-II/XIII www.srjis.com Page 1770
structure was not possible. Oblique rotation had to be carried out and Turnstones method of
extended vectors was used, as it leads to simple structure.
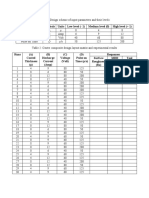
Table 01: Rotated Factor Matrix with Unexpended Vectors (V) V = Eaj or C
Test A B C D E
1. 0.114 -0.015 0.149 0.396 0.094
2. 0.166 0.010 0.205 -0.323 -0.114
3. -0.184 -0.249 0.000 0.451 0.147
4. -0.152 -0.157 0.237 0.443 0.313
5. 0.146 0.053 0.415 -0.047 0.137
6. 0.727 0.793 0.286 0.238 0.142
7. 0.346 0.279 0.210 0.089 0.028
8. 0.613 0.424 -0.116 0.168 -0.285
9. 0.710 0.500 -0.108 0.079 -0.339
10. 0.713 0.649 0.310 0.037 -0.004
11. 0.501 0.376 0.047 -0.010 -0.173
12. 0.084 0.081 0.143 0.122 0.125
13. 0.060 -0.073 -0.008 0.038 -0.095
14. 0.176 0.059 0.270 -0.088 0.012
15. 0.353 -0.053 -0.183 -0.007 -0.478
16. 0.005 0.003 -0.004 0.013 0.018
17. 0.137 0.367 0.541 -0.040 0.459
18. -0.014 0.020 0.209 0.054 0.176
Table 02: The Matrix of correlation between oblique factors () = D C D
A B C D E
A 1.000 -0.929 -0. -0.664 0.948
B -0.929 1.000 0.916 0.669 -0.962
C -0.907 0.916 1.000 0.754 -0.980
D -0.664 0.669 0.754 1.000 -1.02
E -0.948 -0.962 -0.980 -1.02 1.000
CONCLUSIONS
From the table 01, it is clear that test no 6, 10,9,8,11,15 and 7 are of conceptual nature. These
seven tests relate to fundamental nature of Chemistry. This factor has highest loading on test no
6 (0.727), 10(0.713) and 9(0.710). These three tests require achievement in Chemistry; only then
the students can differentiate between the related terms, facts, laws, principles, constitution of
various compounds, properties, structures and figures. We may call Factor A a Conceptual
and Visual Perception Factor. This factor has high correlation with factor E as discrimination
requires a lot of judicious bent of mind.
It is evident from table 01 that seven tests have appreciable loading in Factor B. Four tests out of
7 have more than 0.4 loading in test no 6,10,9 and 8 which involve the complete and critical
understanding of facts taught in Chemistry. These tests indicate that one has to draw conclusions
from the derived formula or have to solve the problem on the basis 0f established fact. A lot of
SRJIS/BIMONTHLY/ B.P. SINGH (1768-1772)
JULY-AUG, 2014. VOL-II/XIII www.srjis.com Page 1771
reasoning is required to understand Chemistry. Similarly from table 02 Factor B has high
correlation with factor C (Mechanism and Nomenclature) and D (Numerical Factor). Keeping in
mind the above observations, Factor B is called Deductive Reasoning as it involves the
application of established facts and principle already learnt to apply in new situations.
Factor C has 0.541 loading on test no 17 (Mechanism aspect) as per table 01. This test measures
the ability to know various steps involved in completing a reaction. This factor has 0.415 loading
on test no 5 (Nomenclature aspect). This test is purported to measure the abilities to see whether
the examinee is able to express the symbolic formula into word. Organic and inorganic chemistry
can be understood only when a student is well aware with the IUPAC nomenclature as well as
trivial name. This factor has appreciable correlations with Factor B (Deductive Reasoning) and D
(Numerical Factor). Mechanism of a reaction depends upon deductive reasoning as well as it
involves mathematical calculations. Hence, this Factor C may be called as Mechanism and
Nomenclature factor.
It is evident from table 01 that loading on test no 3(0.451), 4(0.443) and 1(0.396) for factor D
shows mathematical manipulation for balancing of equations, writing of electronic configuration
and in solving numerical. Factor D has appreciable correlation with factor B (Deductive
Reasoning) and Factor C (Mechanism and Nomenclature) as per table 02. These factors B and C
involve mathematical calculation. Hence, in light of above studies, it is reasonable to regard
Factor D as a Numerical Factor.
From table 01, it is clear that factor E has 0.459 loading for test no 17(Mechanism Aspect) and
0.313 loading for test no 4 (Configuration Aspect). If a student knows about the electronic
configuration of the element, he can easily interpret its valency, oxidation state, reactivity and
stability. Similarly the mechanism of reaction also determines its reactivity. Factor E has
correlation with Factor A (Conceptual and Visual Perception)as per table 02. It is reasonable to
call Factor E as an Inference Factor.
REFERENCES
Anastasi, Anne: Differential Psychology (3
rd
.ed) New York; Macmilan, 1958.
Anastasi, A: Psychological Testing, New York; Macmillan, 1968.
Bloom, B.S. et. al, : Taxonomy of educational objectives hand book:Cognitive domain, New
York; Mckey, 1956.
SRJIS/BIMONTHLY/ B.P. SINGH (1768-1772)
JULY-AUG, 2014. VOL-II/XIII www.srjis.com Page 1772
Comrey, Andrew, L: A first course in factor anaylsis, New York and London: Academic Press,
Inc. 1973.
Fruchter, B: Introduction to factor anaylsis, New York: Van Reinhold, 1954.
Guilford, J.P. : Psycholmetric Method (2
nd
. ed) Bombay and New Delhi: Tata Mc Graw-Hi11,
Co. Ltd., 1954.
Garret, Henry E: Statistics in psychology and education, Bombay; Vakil Peffer and Simons Pvt.
Ltd., 1969.
Guildford J.P.: Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and education (4
th
. Ed.) New York: Mc
Graw- Hill Book Co., 1965.
GWO-Hshiung Tzeng (2007). Evaluating intertwined effects in e-learning programs. A novel
hyprid MCDM model based on factor analysis and DEMATEL; Science Direct; volume
32, Issue 4, May 2007.
H.P. HILDERBRAND (2011). A Factorial study of introversion- extraversion. British Journal of
Psychology, Volume 49, Issue 1.
John, Mcleod (1968). Dyslexia in young children. A Factorial study with special reference to the
Illinois test of psycholinguistic abilities, IREC, University of Illinois.
New York: Mc Graw-Hill Book Co., 1965.
Indian Educational Review, NCERT, Oct. 1982.
Thorndike, R.L., and Egen, E; Measurement and evaluation in psychology and education
(3
rd
.ed), New Delhi, Wiley Eastern Pvt. Ltd.
Você também pode gostar
- A Study To Interpret Common Factors Found in Learning Chemistry at Senior Secondary LevelDocumento6 páginasA Study To Interpret Common Factors Found in Learning Chemistry at Senior Secondary LevelAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Approaches To Data Analysis of Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento17 páginasApproaches To Data Analysis of Multiple-Choice QuestionsNina KhadjiAinda não há avaliações
- Richard R. Hake: Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana 47405Documento11 páginasRichard R. Hake: Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana 47405Ardhi PrayadhaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S1877042812014930 MainDocumento5 páginas1 s2.0 S1877042812014930 MainAshley OfracioAinda não há avaliações
- IonisasiDocumento7 páginasIonisasiNunu LuthuAinda não há avaliações
- Uji Gain HakeDocumento26 páginasUji Gain HakeDyah Lukito SariAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Students' Achievement in TIMSSDocumento11 páginasMathematics Students' Achievement in TIMSSNethan SanduetaAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring of Student Learning Performance Based OnDocumento8 páginasMeasuring of Student Learning Performance Based OnVusale İsrafilzadeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3-SuggestionsDocumento14 páginasChapter 3-SuggestionsVanito SwabeAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Analysis of Multiple Choice TestDocumento7 páginasQuality Analysis of Multiple Choice Testrmm0415Ainda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Statistical Learning From A Reg PDFDocumento25 páginasAn Introduction To Statistical Learning From A Reg PDFJawadAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE Education Society Papers-04589061Documento8 páginasIEEE Education Society Papers-04589061Anoop MathewAinda não há avaliações
- 5118 Combined ScienceDocumento45 páginas5118 Combined ScienceLin Emancipation0% (1)
- Compulsory Schooling and Returns To Education: A Re-ExaminationDocumento20 páginasCompulsory Schooling and Returns To Education: A Re-ExaminationMichelleAinda não há avaliações
- Exploratory Factor AnalysisDocumento12 páginasExploratory Factor AnalysisAtiqah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Action Research JelaiDocumento11 páginasAction Research JelaichicpareAinda não há avaliações
- Thornton Etal FMCEvsFCIDocumento8 páginasThornton Etal FMCEvsFCIArjun Singh GambhirAinda não há avaliações
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNo EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Analysis of Level Practice Satisfaction On Basic Chemical Laboratory Performance Faculty of Mipa Jenderal Soedirman UniversityDocumento11 páginasAnalysis of Level Practice Satisfaction On Basic Chemical Laboratory Performance Faculty of Mipa Jenderal Soedirman UniversityDiah Ratna AnggraeniAinda não há avaliações
- Construction of Parallel Forms of Grade 10Documento24 páginasConstruction of Parallel Forms of Grade 10Lets LearnAinda não há avaliações
- Ma FLD011 PT Appendix PDFDocumento103 páginasMa FLD011 PT Appendix PDFabu aAinda não há avaliações
- Physics and ChemistryDocumento25 páginasPhysics and ChemistryPlimmos PlimalAinda não há avaliações
- Item Response Theory and Confirmatory Factor Analysis: Complementary Approaches For Scale DevelopmentDocumento23 páginasItem Response Theory and Confirmatory Factor Analysis: Complementary Approaches For Scale Developmentlengers poworAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 Final Examination - FinalDocumento7 páginas2021 Final Examination - Finalndt280504Ainda não há avaliações
- Mid-Term of Scientific WritingDocumento44 páginasMid-Term of Scientific WritingNguyễn UyênAinda não há avaliações
- The Hierarchy Consistency Index: Evaluating Person Fit For Cognitive Diagnostic AssessmentDocumento33 páginasThe Hierarchy Consistency Index: Evaluating Person Fit For Cognitive Diagnostic AssessmentianchongAinda não há avaliações
- AnalyzingChange Gain HakeDocumento4 páginasAnalyzingChange Gain HakeDeborah StewartAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On Organizational Climate in Technical Educational Institutions in Telangana.Documento14 páginasA Study On Organizational Climate in Technical Educational Institutions in Telangana.మోహన్ కృష్ణAinda não há avaliações
- ScienceDocumento44 páginasSciencenonoAinda não há avaliações
- An Analysis of Student Kinematics Concept Knowledge: Andreas Lichtenberger, Andreas Vaterlaus and Clemens WagnerDocumento15 páginasAn Analysis of Student Kinematics Concept Knowledge: Andreas Lichtenberger, Andreas Vaterlaus and Clemens WagnerKristian I. H.Ainda não há avaliações
- Substantive Theory and Constructive Measures: A Collection of Chapters and Measurement Commentary on Causal ScienceNo EverandSubstantive Theory and Constructive Measures: A Collection of Chapters and Measurement Commentary on Causal ScienceAinda não há avaliações
- UG Syllabus (GE) STAT W.E.F 2020-21 - 15.09.2021-Pages-49-57-1Documento9 páginasUG Syllabus (GE) STAT W.E.F 2020-21 - 15.09.2021-Pages-49-57-1Pallavi TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Research Example - Integrative StemDocumento18 páginasResearch Example - Integrative StemsiawAinda não há avaliações
- An Item Response Curves Analysis of The Force Concept InventoryDocumento9 páginasAn Item Response Curves Analysis of The Force Concept InventoryMark EichenlaubAinda não há avaliações
- REFERENCIA 3 Safety Climate Model BrownDocumento16 páginasREFERENCIA 3 Safety Climate Model Brownvap96.14Ainda não há avaliações
- Structural Equation Modeling Analysis Student Satisfaction and LoyaltyDocumento7 páginasStructural Equation Modeling Analysis Student Satisfaction and LoyaltyIJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento6 páginasChapter 3EllenMaeMalikStylesAinda não há avaliações
- Students' Developing Knowledge in A Subject Discipline: Insights From Combining Quantitative and Qualitative MethodsDocumento15 páginasStudents' Developing Knowledge in A Subject Discipline: Insights From Combining Quantitative and Qualitative MethodsMBRAinda não há avaliações
- 2634-Article Text-5113-1-10-20201212Documento8 páginas2634-Article Text-5113-1-10-20201212QURTUNISA IRDINAAinda não há avaliações
- PHD Thesis On Job PerformanceDocumento4 páginasPHD Thesis On Job PerformanceBuyAPhilosophyPaperUK100% (2)
- Stevens' Handbook of Experimental Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience, MethodologyNo EverandStevens' Handbook of Experimental Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience, MethodologyAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research 2Documento14 páginasPractical Research 2Vince Darwin Gabona100% (1)
- Anderson and Gerbing 1988Documento13 páginasAnderson and Gerbing 1988Minh NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryNo EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillAinda não há avaliações
- Fraenkel6 Im Ch15Documento10 páginasFraenkel6 Im Ch15Ameer BakhshAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento6 páginasChapter 2Jhosfer Khent Padilla Pam-otAinda não há avaliações
- External Variables That Impact Mobile Learning (M-Learning) Acceptance - A Meta-AnalysisDocumento15 páginasExternal Variables That Impact Mobile Learning (M-Learning) Acceptance - A Meta-AnalysisMarisol de DiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding and Conducting Research in the Health SciencesNo EverandUnderstanding and Conducting Research in the Health SciencesAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2 StatisticsDocumento7 páginasAssignment 2 StatisticsSam AbdulAinda não há avaliações
- Mohd Haikal Bin Mohd Zain 2016330745 (Mae712)Documento5 páginasMohd Haikal Bin Mohd Zain 2016330745 (Mae712)Mohd HaikalAinda não há avaliações
- Econometrics LecturesDocumento22 páginasEconometrics LecturesFarhan ShariarAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Data Analysis and Modelling in Chemical EngineeringNo EverandAdvanced Data Analysis and Modelling in Chemical EngineeringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Why Some Schools Do BetterDocumento21 páginasWhy Some Schools Do BettermatthewgeraldfrenchAinda não há avaliações
- Beichner (1994)Documento7 páginasBeichner (1994)Pessoa_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Revision, Research MethodologyDocumento6 páginasFinal Revision, Research MethodologySahar Al-Jobury80% (5)
- What Is Quantitative ResearchDocumento3 páginasWhat Is Quantitative ResearchGynzelle OpallaAinda não há avaliações
- 25.suresh ChenuDocumento9 páginas25.suresh ChenuAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 19.Dr Ibrahim Aliyu ShehuDocumento29 páginas19.Dr Ibrahim Aliyu ShehuAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 4.Dr Gagandeep KaurDocumento13 páginas4.Dr Gagandeep KaurAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Homesh RaniDocumento7 páginasHomesh RaniAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 29.yuvraj SutarDocumento4 páginas29.yuvraj SutarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 13.nasir RasheedDocumento9 páginas13.nasir RasheedAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Customers' Consciousness About Financial Cyber Frauds in Electronic Banking: An Indian Perspective With Special Reference To Mumbai CityDocumento13 páginasCustomers' Consciousness About Financial Cyber Frauds in Electronic Banking: An Indian Perspective With Special Reference To Mumbai CityAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Aggression Among Senior Secondary School Students in Relation To Their Residential BackgroundDocumento8 páginasAggression Among Senior Secondary School Students in Relation To Their Residential BackgroundAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Life Skill Training On Mental Health Among B.ed. Interns in Relation To Their Impulsive BehaviourDocumento9 páginasEffect of Life Skill Training On Mental Health Among B.ed. Interns in Relation To Their Impulsive BehaviourAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of Effect of Age and Gender On Stress of AdolescentsDocumento5 páginasA Study of Effect of Age and Gender On Stress of AdolescentsAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 25 AshaDocumento5 páginas25 AshaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 1.prof. Ajay Kumar AttriDocumento8 páginas1.prof. Ajay Kumar AttriAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Technostress, Computer Self-Efficacy and Perceived Organizational Support Among Secondary School Teachers: Difference in Type of School, Gender and AgeDocumento13 páginasTechnostress, Computer Self-Efficacy and Perceived Organizational Support Among Secondary School Teachers: Difference in Type of School, Gender and AgeAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- The Need of Remote Voting Machine in Indian Voting SystemDocumento7 páginasThe Need of Remote Voting Machine in Indian Voting SystemAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Historical Development of Play Schools in IndiaDocumento11 páginasHistorical Development of Play Schools in IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 29 Balwinder SinghDocumento8 páginas29 Balwinder SinghAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 31 Dr. Suman Kumari, Prof. Sudarshana Rana & Ms. Anita VermaDocumento9 páginas31 Dr. Suman Kumari, Prof. Sudarshana Rana & Ms. Anita VermaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- A Lookout at Traditional Games Played by Tribes in IndiaDocumento4 páginasA Lookout at Traditional Games Played by Tribes in IndiaAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- The Use of English Language During PandemicDocumento7 páginasThe Use of English Language During PandemicAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 28 Shailaja KanwarDocumento12 páginas28 Shailaja KanwarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 30 Trishala BhaskarDocumento7 páginas30 Trishala BhaskarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Women Empowerment and Religion's Role in Gender Relations in KargilDocumento10 páginasWomen Empowerment and Religion's Role in Gender Relations in KargilAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Deepa AnwarDocumento17 páginasDeepa AnwarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Adv Raj KumarDocumento5 páginas24 Adv Raj KumarAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 26 Dr. Reni Francis Mr. Rajendra DeshmukhDocumento5 páginas26 Dr. Reni Francis Mr. Rajendra DeshmukhAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 23 JayalakshmiDocumento9 páginas23 JayalakshmiAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Payal BhatiDocumento10 páginasPayal BhatiAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 21 DR ReniDocumento6 páginas21 DR ReniAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- 22 Pavithra.g ArticleDocumento8 páginas22 Pavithra.g ArticleAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- Suyambukani VDocumento6 páginasSuyambukani VAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAinda não há avaliações
- University of Tehran Faculty of New Science & Technology Master's Thesis Proposal DefenseDocumento46 páginasUniversity of Tehran Faculty of New Science & Technology Master's Thesis Proposal DefenseSoheilDarvishMotavalliAinda não há avaliações
- TOS 8 Household ServicesDocumento2 páginasTOS 8 Household ServicesGalvez ChaChaAinda não há avaliações
- Entire Environmental Quality - DesignDocumento374 páginasEntire Environmental Quality - DesignLTE002Ainda não há avaliações
- Cpu 2000 App ListDocumento11 páginasCpu 2000 App ListKaiser IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Outline: Introduction To LeadershipDocumento2 páginasLesson Outline: Introduction To LeadershipAmritpal SinghAinda não há avaliações
- The Psychometrician Licensure Examinations (Pmle) : Impact To The Behavioral Science CurriculumDocumento21 páginasThe Psychometrician Licensure Examinations (Pmle) : Impact To The Behavioral Science CurriculumghAinda não há avaliações
- Design MatrixDocumento1 páginaDesign MatrixThakur Kali DassAinda não há avaliações
- CDI1Documento40 páginasCDI1Leonino Angelica Aiko S.Ainda não há avaliações
- 30 Contoh Soal Passive Voice Pilihan Ganda Dan JawabannyaDocumento13 páginas30 Contoh Soal Passive Voice Pilihan Ganda Dan Jawabannyafutrika saragi100% (1)
- AWS Certified Developer - AssociateDocumento2 páginasAWS Certified Developer - AssociateKS ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- HPC Module 1Documento48 páginasHPC Module 1firebazzAinda não há avaliações
- Research ProposalDocumento3 páginasResearch Proposaljan ray aribuaboAinda não há avaliações
- E-Rpms Portfolio (Design 3) - Depedclick-1Documento42 páginasE-Rpms Portfolio (Design 3) - Depedclick-1angeliAinda não há avaliações
- Eaton Industrial Special Process List (SPL)Documento5 páginasEaton Industrial Special Process List (SPL)amirkhakzad498Ainda não há avaliações
- Xpert R410a Onoff Ar Na 230613Documento62 páginasXpert R410a Onoff Ar Na 230613Wilson Segovia CarrascoAinda não há avaliações
- BARAKA Modelling ProposalDocumento9 páginasBARAKA Modelling Proposalmurali.5482Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Differential Equations (PDF)Documento88 páginasFinal Differential Equations (PDF)Tina ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)Documento3 páginasAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)HANIFAH50% (2)
- Contribucion de Las FE A La AutorregulacionDocumento24 páginasContribucion de Las FE A La AutorregulacionAmanda Riedemann CarrilloAinda não há avaliações
- Nasution 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1235 012115Documento8 páginasNasution 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1235 012115RiswanHariantoAinda não há avaliações
- 193-Cable Tray QtyDocumento4 páginas193-Cable Tray QtyprkshshrAinda não há avaliações
- A Comparative Study of Indian and Western Music FormsDocumento6 páginasA Comparative Study of Indian and Western Music FormsSophieAinda não há avaliações
- How To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentDocumento19 páginasHow To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentClaudiu Stefan HaiduAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Manual: Buildings and Infrastructure Protection SeriesDocumento514 páginasReference Manual: Buildings and Infrastructure Protection SeriesmydearteacherAinda não há avaliações
- Business Ethics PDFDocumento16 páginasBusiness Ethics PDFRitika DiwakarAinda não há avaliações
- Public Servants and Government ServantsDocumento10 páginasPublic Servants and Government Servantsalexandra angelinaAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Parametric TestsDocumento1 páginaNon-Parametric TestssdvdsvAinda não há avaliações
- 4UIE - AB - Nov 23Documento2 páginas4UIE - AB - Nov 23aaaAinda não há avaliações
- SPHE8281DDocumento35 páginasSPHE8281Ddiego-tAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Ijcms-V3i2-2012-02Documento6 páginas5 Ijcms-V3i2-2012-02saiAinda não há avaliações