Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
12 Isometric Drawing
Enviado por
Lorenzo TorresDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
12 Isometric Drawing
Enviado por
Lorenzo TorresDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Isometric Drawing
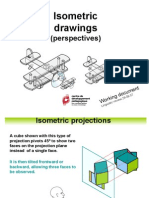
Axonometric Projection
A
B
C
D
Parallel & normal
to picture plane
Line
of
sight
A
B
C
D
Axonometric Projection
Type of axonometric drawing
a
b
c 2. Dimetric
Two angles are equal.
b
a
c 3. Trimetric
None of angles are
equal.
a
b c
1. Isometric All angles are equal.
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
Axonometric axis
Axonometric axis
Axonometric axis
Isometric Drawing
Isometric drawing is a drawing drawn on an
isometric axes using full scale.
Isometric projection
(True projection)
Isometric drawing
(Full scale)
Forshorten
Full scale
Positions of Isometric Axes
Isometric axes can be arbitrarily positioned to create
different views of a single object.
Regular
isometric
Reverse axis
isometric
Long axis
isometric
View point is looking
down from the top of
the object.
View point is looking
up from the bottom of
the object.
View point is looking
from the right (or left)
of the object.
Distance in Isometric Drawing
Isometric line is the line that run parallel to
any of the isometric axes.
Isometric axes
True-length distances are shown along
isometric lines.
Nonisometric lines
Isometric
Sketching
2. Define an isometric axis.
3. Sketching the enclosing box.
4. Estimate the size an and relationship of each
details.
5. Darken all visible lines.
1. Place the object in the position which its shape
and features are clearly seen.
Sketch from an actual object
STEPS
1. Positioning object.
2. Select isometric axis.
3. Sketch enclosing box.
4. Add details.
5. Darken visible lines.
Sketch from an actual object
1. Positioning object.
2. Select isometric axis.
3. Sketch enclosing
box.
4. Add details.
Note In isometric sketch/drawing), hidden lines are omitted
unless they are absolutely necessary to completely
describe the object.
Sketch from an actual object
STEPS
5. Darken visible lines.
1. Interpret the meaning of lines/areas in
multiview drawing.
2. Locate the lines or surfaces relative to
isometric axis.
Sketch from multiview drawing
Front View
Top View
Side View
Example 1 : Object has only normal surfaces
Bottom View
Bottom
Front
Side
Side
Front
Top
Regular
Reverse
W
D
H
H
D W
Example 2 : Object has inclined surfaces
W
H
D
y
x
Front View
y
x
Nonisometric line
Nonisometric line
A
A
x
y
x
x
B
B
A B
C
C
C
x
y
Example 3 : Object has inclined surfaces
A
A
B
B
C
D
E
D
E F
F
x
y
Front View
Regular
C
Example 4
Reverse
Circle & Arc in Isometric
In isometric drawing, a circle appears as an ellipse.
2. Construct an isometric square.
3. Sketch arcs that connect the
tangent points.
Sketching Steps
1. Locate the centre of an ellipse.
Circle & Arc in Isometric
3. Construct a perpendicular
bisector from each tangent point.
4. Locate the four centres.
5. Draw the arcs with these centres
and tangent to isometric square.
Sketching Steps
Four-centre method is usually used when drawn an
isometric ellipse with drawing instrument.
2. Construct an isometric square.
1. Locate the centre of an ellipse.
Example 5
Irregular Curve in Isometric
1. Construct points along the
curve in multiview drawing.
2. Locate these points in the
isometric view.
3. Sketch the connecting lines.
Steps
References
CfBT Lincolnshire School Improvement
Service.ppt
Você também pode gostar
- Mechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsNo EverandMechanical Drawing - Projection Drawing, Isometric and Oblique Drawing, Working DrawingsAinda não há avaliações
- Isometric ProjectionsDocumento26 páginasIsometric ProjectionsSuneel Kumar MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Freehand SketchingDocumento45 páginasFreehand Sketchingamsubra8874100% (1)
- Isometric Projections: Hareesha N G Dept of Aeronautical Engg Dayananda Sagar College of Engg Bangalore-78Documento39 páginasIsometric Projections: Hareesha N G Dept of Aeronautical Engg Dayananda Sagar College of Engg Bangalore-78Hareesha N G100% (5)
- ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF SECTIONING AND DEVELOPMENT OF SOLIDSDocumento26 páginasENGINEERING APPLICATIONS OF SECTIONING AND DEVELOPMENT OF SOLIDShotnili100% (2)
- Drafting ExercisesDocumento12 páginasDrafting ExercisesJaime Andres Velez100% (3)
- ISOMETRIC PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDSDocumento20 páginasISOMETRIC PROJECTIONS OF SOLIDSRamesh KomiriAinda não há avaliações
- Section of SolidsDocumento25 páginasSection of SolidsSuneel Kumar MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing Form 4 (Circles)Documento12 páginasEngineering Drawing Form 4 (Circles)farah sakinahAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing: Mechanical Engineering Department L.J. PolytechnicDocumento40 páginasEngineering Drawing: Mechanical Engineering Department L.J. PolytechnicTufel NooraniAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering DrawingDocumento136 páginasEngineering DrawingVijay Pal Singh85% (13)
- Sectional Drawing ViewsDocumento17 páginasSectional Drawing Viewsapi-25981522100% (1)
- 3 - Orthographic ProjectionDocumento61 páginas3 - Orthographic ProjectionaliffAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics Chapter 6Documento63 páginasEngineering Graphics Chapter 6aemychangminAinda não há avaliações
- Technical DrawingDocumento191 páginasTechnical DrawingAbdulrazzak Aman100% (8)
- Orthographic Projections: Engineering Drawing BasicsDocumento62 páginasOrthographic Projections: Engineering Drawing BasicsHareesha N G100% (1)
- Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Bridge CourseDocumento45 páginasIntroduction to Mechanical Engineering Bridge Coursekrunal07786Ainda não há avaliações
- Sectionofsolids 131212040444 Phpapp01Documento22 páginasSectionofsolids 131212040444 Phpapp01api-264299618Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 PT M PerspectiveDocumento4 páginas2 PT M PerspectiveCristianJiménezAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Engineering DrawingDocumento213 páginasPrinciples of Engineering DrawingSarthak Bhargava80% (20)
- Abbott TechnicalDrawing TextDocumento210 páginasAbbott TechnicalDrawing Textmrafiq9002Ainda não há avaliações
- Exercises On Engineering DrawingDocumento42 páginasExercises On Engineering Drawingdradell86% (7)
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocumento47 páginasEngineering Graphics Question Bankswapnil kale86% (7)
- Engineering Graphics For DiplomaDocumento326 páginasEngineering Graphics For DiplomaCvaldivia00186% (7)
- Engineering Drawing Orthographic Proj Lect 3Documento121 páginasEngineering Drawing Orthographic Proj Lect 3Abdulrahman Mohammed100% (1)
- Orthographic ProjectionDocumento51 páginasOrthographic ProjectionAjit ParwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing BASICSDocumento111 páginasEngineering Drawing BASICSajscad89% (18)
- Importance of Engineering DrawingDocumento24 páginasImportance of Engineering DrawingDhanis Paramaguru69% (13)
- Chapter 3 - Development DrawingDocumento30 páginasChapter 3 - Development Drawingsuriakuma75% (8)
- Chapter One Introduction To Graphic Communication 1.1 DrawingDocumento24 páginasChapter One Introduction To Graphic Communication 1.1 DrawingVanessa CadsawanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Perspective DrawingDocumento23 páginasChapter 1 - Perspective DrawingryanAinda não há avaliações
- Axonometric and Isometric Drawings: Sabine Pauli Spauli@cityu - Edu.hkDocumento6 páginasAxonometric and Isometric Drawings: Sabine Pauli Spauli@cityu - Edu.hkAliaa Ahmed Shemari0% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Form 4 (Tangents)Documento21 páginasEngineering Drawing Form 4 (Tangents)farah sakinah100% (3)
- Engineering Drawing WorkbookDocumento322 páginasEngineering Drawing WorkbookRosalie Vasquez100% (3)
- Chapter 1 - Perspective DrawingDocumento23 páginasChapter 1 - Perspective Drawingsuriakuma100% (9)
- Isometric Drawing Guide with 13 Block ExamplesDocumento14 páginasIsometric Drawing Guide with 13 Block ExamplesCik Sue100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing.1Documento231 páginasEngineering Drawing.1Sateesh Saati100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsDocumento9 páginasEngineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsJithesh.k.sAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Technical DrawingDocumento46 páginasChapter 11 Technical DrawingEF E RoysAinda não há avaliações
- Orthographic ProjectionDocumento26 páginasOrthographic Projectionpresario_nyioq75% (12)
- Learn How To Draw GoodDocumento133 páginasLearn How To Draw GoodTaggedOnlineAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 05 Pictorial SketchingDocumento36 páginasChapter 05 Pictorial SketchingManvendra Pratap Singh BishtAinda não há avaliações
- Axonometric & Oblique Projection GuideDocumento37 páginasAxonometric & Oblique Projection GuideBahar Aktuna100% (1)
- Chapter 05 Pictorial SketchingDocumento36 páginasChapter 05 Pictorial SketchingAlexShearAinda não há avaliações
- Lincolnshire School Improvement Service provides guidance on technical drawing techniquesDocumento38 páginasLincolnshire School Improvement Service provides guidance on technical drawing techniquesSanthan SalaiAinda não há avaliações
- IsometricDocumento51 páginasIsometricSindhuja Ramachandra100% (1)
- Isometric Projections EGDocumento24 páginasIsometric Projections EGThulasi RamAinda não há avaliações
- Isometrics - CcoryDocumento27 páginasIsometrics - Ccorynaik4u2002Ainda não há avaliações
- Isometric and Oblique Drawing TechniquesDocumento28 páginasIsometric and Oblique Drawing Techniqueshisham_eyesAinda não há avaliações
- Mech 102 Lecture 4 - Systems of Projection - Isometric DrawingDocumento31 páginasMech 102 Lecture 4 - Systems of Projection - Isometric DrawingJoyfulAinda não há avaliações
- Session 3: Projection MethodDocumento33 páginasSession 3: Projection MethodetaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing=IsometricDocumento16 páginasEngineering Drawing=Isometricpanashezhou321Ainda não há avaliações
- Draftec1 Lo 2.7 Pictorial DrawingsDocumento5 páginasDraftec1 Lo 2.7 Pictorial DrawingsVon AsiaAinda não há avaliações
- Isometric Projections NMD PDFDocumento48 páginasIsometric Projections NMD PDFNaman Dave100% (5)
- Lecture 4-Pictorial DrawingDocumento46 páginasLecture 4-Pictorial DrawingLayike AlemayehuAinda não há avaliações
- Isometric Drawing GuideDocumento18 páginasIsometric Drawing GuideFacking Layf JobenAinda não há avaliações
- Isometric DrawingsDocumento27 páginasIsometric DrawingsMichael Martinez100% (1)
- Making An Isometric Drawing.1Documento23 páginasMaking An Isometric Drawing.1kurt wellsAinda não há avaliações
- 03 BODY, FAITH AND CULTURE by Felipe JocanoDocumento11 páginas03 BODY, FAITH AND CULTURE by Felipe JocanoLorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- References Time and Motion StudyDocumento14 páginasReferences Time and Motion StudyLorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 - Geometric Construction 1Documento16 páginasLecture 1 - Geometric Construction 1Lorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Analysis of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesDocumento3 páginasStatistical Analysis of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesLorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical KineticsDocumento4 páginasChemical KineticsLorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Analysis of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesDocumento3 páginasStatistical Analysis of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesLorenzo TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Panasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Documento39 páginasPanasonic 2012 PDP Troubleshooting Guide ST50 ST Series (TM)Gordon Elder100% (5)
- Motor GraderDocumento24 páginasMotor GraderRafael OtuboguatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Rotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRDocumento20 páginasRotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRNguyễn Hữu DũngAinda não há avaliações
- Organizing Small Items with Glass Bottle OrganizersDocumento70 páginasOrganizing Small Items with Glass Bottle OrganizersDy SaiAinda não há avaliações
- 1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDDocumento81 páginas1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDJerome Samuel100% (1)
- 1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFDocumento4 páginas1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFIan WoodsAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Note Taker Saves Time With Air WritingDocumento17 páginasSmart Note Taker Saves Time With Air WritingNagarjuna LokkuAinda não há avaliações
- Railway Airport Docks and HarbourDocumento21 páginasRailway Airport Docks and HarbourvalarmathibalanAinda não há avaliações
- Stability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelDocumento7 páginasStability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelSamwailAinda não há avaliações
- CG Module 1 NotesDocumento64 páginasCG Module 1 Notesmanjot singhAinda não há avaliações
- FP-XH PGRG eDocumento936 páginasFP-XH PGRG ebvladimirov85Ainda não há avaliações
- Flood FillDocumento1 páginaFlood FillshubhamAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis and Calculations of The Ground Plane Inductance Associated With A Printed Circuit BoardDocumento46 páginasAnalysis and Calculations of The Ground Plane Inductance Associated With A Printed Circuit BoardAbdel-Rahman SaifedinAinda não há avaliações
- Maintenance Handbook On Compressors (Of Under Slung AC Coaches) PDFDocumento39 páginasMaintenance Handbook On Compressors (Of Under Slung AC Coaches) PDFSandeepAinda não há avaliações
- BMW Motronic CodesDocumento6 páginasBMW Motronic CodesxLibelle100% (3)
- Conjoint Analysis Basic PrincipleDocumento16 páginasConjoint Analysis Basic PrinciplePAglu JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Nikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Documento12 páginasNikola Tesla Was Murdered by Otto Skorzeny.Jason Lamb50% (2)
- Internship ReportDocumento18 páginasInternship ReportRathan Kumar SMAinda não há avaliações
- Basic First AidDocumento31 páginasBasic First AidMark Anthony MaquilingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry of FormazanDocumento36 páginasChemistry of FormazanEsteban ArayaAinda não há avaliações
- Detection and Attribution Methodologies Overview: Appendix CDocumento9 páginasDetection and Attribution Methodologies Overview: Appendix CDinesh GaikwadAinda não há avaliações
- Elevator Traction Machine CatalogDocumento24 páginasElevator Traction Machine CatalogRafif100% (1)
- Canon imageFORMULA DR-X10CDocumento208 páginasCanon imageFORMULA DR-X10CYury KobzarAinda não há avaliações
- SOIL ASSESSMENT AND PLANT PROPAGATION OF BELL PEPPERS (Capsicum Annuum)Documento35 páginasSOIL ASSESSMENT AND PLANT PROPAGATION OF BELL PEPPERS (Capsicum Annuum)Audrey Desiderio100% (1)
- GLOBAL Hydro Turbine Folder enDocumento4 páginasGLOBAL Hydro Turbine Folder enGogyAinda não há avaliações
- Private Schools Provide Better EducationDocumento2 páginasPrivate Schools Provide Better EducationcitraAinda não há avaliações
- Plate-Load TestDocumento20 páginasPlate-Load TestSalman LakhoAinda não há avaliações
- JY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsDocumento1 páginaJY Series Single-Phase Capacitor Induction MotorsAditya PrasetyoAinda não há avaliações
- Ro-Buh-Qpl: Express WorldwideDocumento3 páginasRo-Buh-Qpl: Express WorldwideverschelderAinda não há avaliações
- European GMP Annex 1 - 2008 Edition - 'Pmeasuring'Documento3 páginasEuropean GMP Annex 1 - 2008 Edition - 'Pmeasuring'Khairul AnwarAinda não há avaliações