Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
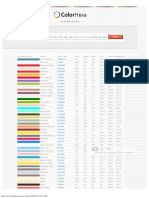
RGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)
Enviado por
Mera KaramDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
RGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)
Enviado por
Mera KaramDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A color space is a mathematical representation of a set of colors
.
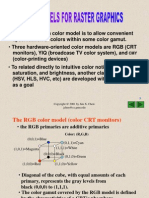
The three most popular color models are
RGB (used in computer graphics);
YIQ , YUV or YCbCr (used in video systems);
and CMYK (used in color printing).
However , none of these color spaces are directly related to the
intuitive notions of hue , saturation , and brightness .
This resulted in the temporary pursuit of other models , such as
HSI and HSV , to simplify programming , processing , and end-
user manipulation .
All of the color spaces can be derived from the RGB information
supplied by devices such as cameras and scanners .
The color systems used by scientists and artists are entirely
different. An artist will mix blue and yellow paint to get a shade
of green; a scientist will mix green and red light to create
yellow.
The printed page in a magazine is yet another system.
It's important to define the two different kinds of color that we
see in the world as the first step in understanding color systems.
First, there's the color you can touch, such as the skin of an
apple or a painted wall. These colors are part of the surface of
an object. Next, there's the color you can't touch, such as a
beam of red light and the colors produced by your computer
monitor.
Colors generated by light are part of one color system. The
tangible colors which are on the surface of objects or on the
printed page are another color system.
There are five major models, that sub-divide into others, which
are: CIE, RGB, YUV, HSL/HSV, and CMYK.
CIE
CIE 1931 XYZ
The first attempt to produce a color space based on
measurements of human color perception and it is the basis for
almost all other color spaces.
CIELUV
A modification of "CIE 1931 XYZ" to display color differences
more conveniently. The CIELUV space is especially useful for
additive mixtures of lights, due to its linear addition properties
CIELAB
The intention of CIELAB (or L*a*b* or Lab) is to produce a color
space that is more perceptually linear than other color spaces.
Perceptually linear means that a change of the same amount in
a color value should produce a change of about the same visual
importance. CIELAB has almost entirely replaced an alternative
related Lab color space "Hunter Lab". This space is commonly
used for surface colors, but not for mixtures of (transmitted)
light.
CIEUVW
Measurements over a larger field of view than the "CIE 1931
XYZ" color space which produces slightly different results.
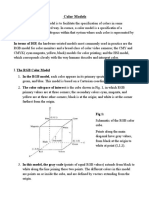
Additive Color System
Red - Green - Blue (RGB)
Scientists recognize the light primaries of red, green and blue.
When combined, red and green light rays produce yellow, blue
and green produce cyan, red and blue produce magenta. Red,
green and blue mix to create white (light).
This color model is used in computer monitors, television sets,
and theater.
Red, green and blue dots of light are creating the image. Where
red and green overlap, you'll see yellow.
This system applies only to devices employing light, such as
computer monitors and television sets.
RGBA with an additional channel, alpha, to indicate RGB is
transparency.
Subtractive Color System
Red - Yellow - Blue
Most artists recognize red, yellow and blue as the 3 basic
primary colors. These primaries are the pure colors which cannot
be created by mixing any other colors. Secondary hues are the
result of mixing any of the two primaries. Tertiary colors result
from mixing the secondary hues.
In subtractive color theory, all colors mix to yield black.
Luma plus chroma / chrominance
YIQ, YUV, YDbDr
chroma or value with two luma tem stores a This sys
values, corresponding approximately to the chrominance
amounts of blue and red in the color.
YPbPr, YCbCr
YPbPr is a scaled version of YUV. It is most commonly seen in
, used widely YCbCr its digital form,
compression schemes such image and video in
. JPEG and MPEG as
xvYCC
xvYCC is an extension of YCbCr that extends the color gamut
beyond the R/G/B primaries specified by BT.709.
Hue and saturation
HSV
(hue, saturation, value), also known as HSB (hue,
saturation, brightness), is often used by artists because it is
often more natural to think about a color in terms of hue and
saturation than in terms of additive or subtractive color
components. HSV is a transformation of an RGB color space,
and its components and colorimetry are relative to the RGB
color space from which it was derived.
HSL
(hue, saturation, lightness/luminance), also known as HSL, HSI
(hue, saturation, intensity) or HSD (hue, saturation, darkness), is
quite similar to HSV, with "lightness" replacing "brightness". The
difference is that the brightness of a pure color is equal to the
brightness of white, while the lightness of a pure color is equal
to the lightness of a medium gray.
CMYK (Cyan - Magenta - Yellow - Black)
CMYK is used in the printing process, because it describes what
kind of inks need to be applied so the light reflected from the
substrate and through the inks produces a given color. One
starts with a white substrate (canvas, page, etc.), and uses ink to
subtract color from white to create an image. CMYK stores ink
values for cyan, magenta, yellow and black. There are many
CMYK color spaces for different sets of inks, substrates, and
press characteristics (which change the dot gain or transfer
function for each ink and thus change the appearance).
In the print industry, cyan, magenta, yellow and black are used
as the primary colors. When you mix all the colors, the result is
gray.
RESOURCES :
http://www.colormatters.com/color-and-design/color-systems-rgb-and-cmyk
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_color_spaces_and_their_uses
http://www.compression.ru/download/articles/color_space/ch03.p
df
Você também pode gostar
- Scholastic K Skills (Color & Numbers)Documento49 páginasScholastic K Skills (Color & Numbers)amysore2908100% (17)
- Watercolour Cheat SheetsDocumento16 páginasWatercolour Cheat SheetsMouli Thirumalasetty100% (17)
- List of Colors - A-F - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento26 páginasList of Colors - A-F - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediadialauchennaAinda não há avaliações
- Colour Theory PowerpointDocumento10 páginasColour Theory Powerpointapi-335210893Ainda não há avaliações
- A GlassDocumento67 páginasA GlassJulio Mauricio GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- List of ColorsDocumento14 páginasList of ColorsVenkatesh RajaAinda não há avaliações
- Color Image ProcessingDocumento189 páginasColor Image ProcessingruikarsachinAinda não há avaliações
- Pantone CoatedDocumento1 páginaPantone CoatedAscenderBSPAinda não há avaliações
- Hsi - HSL - HSVDocumento27 páginasHsi - HSL - HSVspahicdaniloAinda não há avaliações
- Source Book SwatchesDocumento6 páginasSource Book SwatchesDu Thủy TiênAinda não há avaliações
- Color SpaceDocumento6 páginasColor SpaceMoji Piyapong0% (1)
- Color Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDocumento20 páginasColor Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDinesh ScorpAinda não há avaliações
- Colour (Compatibility Mode)Documento30 páginasColour (Compatibility Mode)PradeepvenugopalAinda não há avaliações
- CG - Chapter 6 Color ModelsDocumento19 páginasCG - Chapter 6 Color Modelstyv89783Ainda não há avaliações
- DipDocumento4 páginasDipLekshmi Devi RanjithAinda não há avaliações
- Sistemi Boja U Rcunarskoj GraficiDocumento12 páginasSistemi Boja U Rcunarskoj GraficiNefertitiladyAinda não há avaliações
- Sistemi Boja U Racunarskoj GraficiDocumento12 páginasSistemi Boja U Racunarskoj GraficiNefertitiladyAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Initial Display and Scientific VisualizationDocumento32 páginas05 Initial Display and Scientific VisualizationNurFadhilah Husna Bt AzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Computer Vision: CIE Chromaticity Diagram and Color GamutDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To Computer Vision: CIE Chromaticity Diagram and Color GamutDiego AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment of Digital Image Processing: Bachelor of Science (Computer Science) Session (2020-2024) Submitted byDocumento5 páginasAssignment of Digital Image Processing: Bachelor of Science (Computer Science) Session (2020-2024) Submitted bysumanafzal1212Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap1 2 3Documento27 páginasChap1 2 3Hàng Không Mẫu HạmAinda não há avaliações
- Color Model 1Documento20 páginasColor Model 1sharmilaAinda não há avaliações
- Color NewDocumento19 páginasColor NewZacardious DhanrajAinda não há avaliações
- What Is ColorDocumento9 páginasWhat Is ColorPankon TharlayAinda não há avaliações
- oRGB: A Practical Opponent Color Space For Computer GraphicsDocumento14 páginasoRGB: A Practical Opponent Color Space For Computer GraphicsLuis Martínez RamírezAinda não há avaliações
- RGB Color ModelDocumento11 páginasRGB Color ModelspahicdaniloAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Documento6 páginasMachine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Om BhamareAinda não há avaliações
- Q1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanDocumento4 páginasQ1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanahsAinda não há avaliações
- RGB Color ModelDocumento15 páginasRGB Color ModelPopescu Tiberius NectarAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 8 Color SystemDocumento28 páginasLecture 8 Color SystemAbdelRahman MahmoudAinda não há avaliações
- Hue Is One of The Main Properties (Called: Color Appearance Parameters ColorDocumento5 páginasHue Is One of The Main Properties (Called: Color Appearance Parameters ColorRobert Kite ClementeAinda não há avaliações
- Gamuts: A Typical CRT GamutDocumento5 páginasGamuts: A Typical CRT GamutlokeshnannuAinda não há avaliações
- CV 3Documento10 páginasCV 3Bilal KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Color Image ProcessingDocumento15 páginasColor Image ProcessingRaviteja UdumudiAinda não há avaliações
- Various Colour Spaces and Colour Space Conversion Algorithms 44 48Documento5 páginasVarious Colour Spaces and Colour Space Conversion Algorithms 44 48Ali Musilim TemamAinda não há avaliações
- Color ModelsDocumento33 páginasColor ModelsAditya PugaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Color Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduDocumento60 páginasColor Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduRavi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Map SymbolsDocumento15 páginasMap Symbolsgreyproperties88Ainda não há avaliações
- CGMM 3Documento3 páginasCGMM 3nishita patidarAinda não há avaliações
- RGB Color ModelDocumento15 páginasRGB Color ModelkavitaAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz DIPDocumento7 páginasQuiz DIPayesha bashirAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento25 páginasChapter 7MuhdFikriAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Image Processing, Color ModelsDocumento40 páginasDigital Image Processing, Color Modelsk_kunarajAinda não há avaliações
- Colour ModelsDocumento5 páginasColour ModelsKrishanu Modak100% (1)
- Color: CSC361/661 - Digital Media Burg/WongDocumento30 páginasColor: CSC361/661 - Digital Media Burg/WongRevathy KalimuthuAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No.5Documento4 páginasExperiment No.5Tejas PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Color Image Processing 26-7-2012 PDFDocumento27 páginasColor Image Processing 26-7-2012 PDFU.Ida PerciaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Image Processing (EE 4235) Lecture: Color (Part 1)Documento23 páginasDigital Image Processing (EE 4235) Lecture: Color (Part 1)Andrew WilcoxAinda não há avaliações
- © UW CSE Vision FacultyDocumento62 páginas© UW CSE Vision FacultyDuong TheAinda não há avaliações
- Color Lecture Part 1Documento61 páginasColor Lecture Part 1api-270388254Ainda não há avaliações
- 03 Color Space Lecture NoteDocumento65 páginas03 Color Space Lecture Notethuandvt97Ainda não há avaliações
- U2T1. - Practice Report - UP170496Documento4 páginasU2T1. - Practice Report - UP170496Sergio Alejandro MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Lec-11 - RGB and CMY Color ModelDocumento22 páginasLec-11 - RGB and CMY Color Modelbijoystudent481Ainda não há avaliações
- HSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..Documento15 páginasHSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..ramu.paturi7712Ainda não há avaliações
- Cvdip AssignmentDocumento12 páginasCvdip AssignmentJagadeesh NarendraAinda não há avaliações
- Art Color Systems HandbookDocumento9 páginasArt Color Systems HandbookAli HosenAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT-4 Color Image ProcessingDocumento17 páginasUNIT-4 Color Image ProcessingShravani ChettineniAinda não há avaliações
- Color Feature ExtractionDocumento2 páginasColor Feature ExtractionodelacruzfAinda não há avaliações
- Segmentation 2Documento8 páginasSegmentation 2Sufian SarinAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Graphics: Color ModelsDocumento35 páginasComputer Graphics: Color Modelsمروة عبدالله محمد علي حبيبانAinda não há avaliações
- Color ModelsDocumento15 páginasColor Modelss_paraisoAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Color Physics 03 SlideDocumento55 páginasTheory of Color Physics 03 SlideRikta IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Color Models in Computer GraphicsDocumento6 páginasColor Models in Computer GraphicsKellie LewisAinda não há avaliações
- RgbcmyDocumento12 páginasRgbcmybhariprasad_mscAinda não há avaliações
- Paint Inspired Color Mixing and Compositing For VisualizationDocumento5 páginasPaint Inspired Color Mixing and Compositing For VisualizationDarkangelcaliAinda não há avaliações
- Colors Tutorial: CSS Color ValuesDocumento16 páginasColors Tutorial: CSS Color ValuesKashif KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Colour Image ProcessingDocumento60 páginasColour Image ProcessingkondurukarthikAinda não há avaliações
- Color Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionNo EverandColor Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionAinda não há avaliações
- SecAppDev2013 - SDLC Session Bart de Win v1.0Documento57 páginasSecAppDev2013 - SDLC Session Bart de Win v1.0Mera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- An Automated Framework For Testing Source Code Static Analysis ToolsDocumento5 páginasAn Automated Framework For Testing Source Code Static Analysis ToolsMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- Methodological Framework For Analysis and Synthesis of A Set of Secure Software Development ControlsDocumento12 páginasMethodological Framework For Analysis and Synthesis of A Set of Secure Software Development ControlsMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- TSWJ2014 805856 PDFDocumento12 páginasTSWJ2014 805856 PDFMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- MyVAC 3 GUI 2 SSDLC v1Documento59 páginasMyVAC 3 GUI 2 SSDLC v1Mera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Secure and Traceable Requirement Engineering Process For Security-Sensitive ProjectsDocumento11 páginasDesign of Secure and Traceable Requirement Engineering Process For Security-Sensitive ProjectsMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- SDLC Security Framework For Software Startups: S. Jeyapriya, C. RekhaDocumento4 páginasSDLC Security Framework For Software Startups: S. Jeyapriya, C. RekhaMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- List of Important TermsDocumento1 páginaList of Important TermsMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- RH124Documento2 páginasRH124Mera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- Progress Test 2 (Units 4-6)Documento8 páginasProgress Test 2 (Units 4-6)Mera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Finish The Following Dialogue:: A Test On Units 11: 15Documento3 páginas1) Finish The Following Dialogue:: A Test On Units 11: 15Mera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- Student HandOut QuestionsDocumento4 páginasStudent HandOut QuestionsMera KaramAinda não há avaliações
- Eci BVDM Graycon Doc Eng v2Documento17 páginasEci BVDM Graycon Doc Eng v2Donato PaceAinda não há avaliações
- Color WorksheetDocumento2 páginasColor Worksheetapi-315608861100% (2)
- Bs2660 C1olour ChartDocumento1 páginaBs2660 C1olour ChartNavneethAinda não há avaliações
- MCI Colours StandardDocumento4 páginasMCI Colours StandardrujanacAinda não há avaliações
- Color SchemesDocumento32 páginasColor SchemesAndreas Budi SantosaAinda não há avaliações
- RGB Color Codes ChartDocumento7 páginasRGB Color Codes ChartSai Ram PallaAinda não há avaliações
- CIE Lab Color SpaceDocumento6 páginasCIE Lab Color SpaceOswaldo Cortés Vázquez0% (1)
- List of Descriptive WordsDocumento7 páginasList of Descriptive Wordsreinaldo guerraAinda não há avaliações
- Triumph FarbcodesDocumento13 páginasTriumph FarbcodesbmcaustriaAinda não há avaliações
- Pantone PDFDocumento53 páginasPantone PDF2dlmediaAinda não há avaliações
- New Beetle Paint ColorsDocumento7 páginasNew Beetle Paint ColorsAlejandro Noe NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Tabla de Colores CMYKDocumento1 páginaTabla de Colores CMYKibnmlrAinda não há avaliações
- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Colours. What Is Colour?Documento4 páginasPrimary, Secondary and Tertiary Colours. What Is Colour?orionsalinasAinda não há avaliações
- Threadart Conversion Chart PDFDocumento5 páginasThreadart Conversion Chart PDFangelaAinda não há avaliações
- Mixing Coloured LightDocumento2 páginasMixing Coloured LightPowerhouse MuseumAinda não há avaliações
- Cie Xyz 29082000Documento30 páginasCie Xyz 29082000chiuhereAinda não há avaliações
- RgbcmyDocumento12 páginasRgbcmybhariprasad_mscAinda não há avaliações
- DyStar Product Selection - CA RSL - Version Apr 2013 - 3sep13 - Final PDFDocumento39 páginasDyStar Product Selection - CA RSL - Version Apr 2013 - 3sep13 - Final PDFAzizAinda não há avaliações
- Ral Colour ChartDocumento2 páginasRal Colour ChartSheraz FarukiAinda não há avaliações
- CIE Color SpaceDocumento8 páginasCIE Color SpaceJuan Felipe Gutierrez GomezAinda não há avaliações