Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
SJPO 2013 Special - Round PDF
Enviado por
ziwei_from_chinaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SJPO 2013 Special - Round PDF
Enviado por
ziwei_from_chinaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SINGAPORE JUNIOR PHYSICS OLYMPIAD 2013
SPECIAL ROUND
31 August, 2013
9:15 a.m. 12:15 p.m
Time Allowed: THREE HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS
1. This paper contains 11 structural questions and 7 printed pages.
2. The mark for each part/question is indicated at the end of the part/question.
3. Answer ALL the questions in the booklet provided.
4. Scientic non-graphical calculators are allowed in this test.
5. A table of information is given in page 2. Not all information will be used in this
paper.
TABLE OF INFORMATION
Acceleration due to gravity at Earth surface, g = 9.80 m/s
2
Universal gas constant, R = 8.31 J/(mol K)
Newtons gravitational constant, G = 6.67 10
11
N m
2
/kg
2
Vacuum permittivity,
0
= 8.85 10
12
C
2
/(N m
2
)
Vacuum permeability,
0
= 4 10
7
T m/A
Speed of light in vacuum, c = 3.00 10
8
m/s
Speed of sound in air, v = 331 m/s
Charge of electron, e = 1.60 10
19
C
Plancks constant, h = 6.63 10
34
J s
Mass of electron, m
e
= 9.11 10
31
kg
Mass of proton, m
p
= 1.67 10
27
kg
Mass of neutron, m
n
= 1.67 10
27
kg
Atomic mass unit, u = 1.66 10
27
kg
Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 10
23
J/K
Avogadros number, N
A
= 6.02 10
23
mol
1
Standard atmospheric pressure = 1.01 10
5
Pa
2
1. A uniform brick of length L is laid on a smooth horizontal surface. Other equal
bricks are now piled on as shown, so that the sides form a continuous plane, but
the ends are oset at each block from the previous brick by a distance 0.15 L. How
many bricks can be stacked in this manner before the pile topples over?
[8]
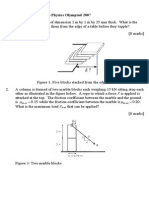
2. The trebuchet is a siege engine that was employed in the Middle Ages to smash
castle walls or to lob projectiles over them. A simplied version of a trebuchet is
shown in the following gure. A heavy weight of mass M falls under gravity, and
thereby lifts a lighter weight of mass m. The motion of the mass M is blocked
as shown in the gure, which launches the lighter mass m; the blockade forms an
angle with the vertical. The mass of the blockade is much larger than all other
masses. The shorter arm of the trebuchet is of length H, whereas the longer arm
is of length l; the whole beam (both arms) are of mass .
Calculate the angular velocity at which the projectile is launched. Express the
range R of the projectile in terms of and other quantities with respect to the
turning point. [9]
3
3. A cart of mass M has a pole on it from which a ball of mass hangs from a thin
string attached at point P. The cart and ball have initial velocity V . The cart
crashes onto another initially stationary cart of mass m and sticks to it. If the
length of the string is R, show that the smallest initial velocity for which the ball
can go round in circles around point P is of the form
1 +
M
m
(gR)
where and
are constants which you have to determine and g is the gravitational acceleration.
Neglect friction and assume M, m .
[6]
4. A 0.75-m rod has a uniform linear mass density of . A small mass m with
negligible volume is attached to one end of the rod. The rod with the attached
mass is placed in a container of unknown uid and after oscillating briey, comes to
rest at its equilibrium position. At equilibrium, the rod oats vertically with 2/3
of its length submerged and mass m in the uid. If the rod were fully submerged
it would displace 7.5 10
4
kg of uid.
(a) What is the maximum value that the mass m can have?
(b) What is the minimum value that the mass m can have?
(c) Sketch a graph that shows the values of as a function of m. [12]
5. Consider the spherically symmetric expansion of a homogeneous, self-gravitating
gas with negligible pressure. The initial conditions of expansion are unspecied;
instead, you are given that when the density is
0
, a uid element at radius R
0
from the origin has a velocity of v
0
.
By considering the motion of a unit mass at the surface of the gas, nd v(R) and
describe the ultimate fate of the gas in terms of v
0
, R
0
and
0
[6]
4
6. 1 mole of ideal gas with internal energy U =
3
2
RT, expands from initial volume
V
i
=
1
10
V
0
following the equation
p =
p
0
V
0
V +p
0
.
Find
(a) the highest temperature reached by the gas during the expansion and
(b) the maximum amount of heat taken in by the gas. [8]
7. (a) A capillary tube immersed in water (refractive index =1.33) is made of glass
with index of refraction 1.55. The outer radius of the tube is 2.5 mm. The
tube is lled with a liquid with the index of refraction 1.45. What should the
minimum internal radius of the tube be so that any ray that hits the tube
would enter the liquid in the capillary? [5]
(b) A radio receiver is set up on a mast in the middle of a calm lake to track the
radio signal from a satellite orbiting the Earth. As the satellite rises above
the horizon, the intensity of the signal varies periodically. The intensity is at
a maximum when the satellite is
1
= 3
above the horizon and then again
at
2
= 6
above the horizon. What is the wavelength of the satellite signal?
The receiver is h = 4.0 m above the lake surface. [6]
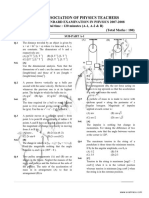
8. (a) If R
1
= R
2
= 3 in the circuit below, determine the resistance of the network
i. between points A and B and
ii. between points A and O. [5]
(b) Redo the calculations above for the case where R
1
= 3 and R
2
= 6 . [7]
5
9. In a nuclear reactor that uses U-235 as the nuclear fuel, a typical uranium nucleus
will emit 2 or 3 fast-moving neutrons during nuclear ssion after absorbing a slow
neutron having kinetic energy of 0.025 eV. Fast moving neutrons are not useful
for a sustained chain ssion reactions and the trick to produce slow neutrons is to
use graphite (carbon-12) rods as velocity reducing agents. Assume that the carbon
nucleus and the neutron are point objects undergoing elastic collisions and that a
fast neutron has initial kinetic energy of 1.75 MeV, what is the minimum number
of times that the neutron must collide with carbon nuclei before it becomes a slow
neutron? [6]
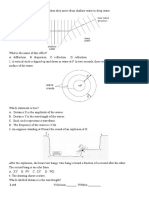
10. As indicated in the diagram below, a sphere of radius R and center O has charge
evenly distributed throughout and of electric potential at the surface as 1000 V. At
a point O
far away from the sphere lies a proton p which is red at the sphere with
kinetic energy 2000 eV in a direction parallel to OO
. The distance between the
two parallel lines denoting OO
and the direction of travel of the proton is denoted
as l.
(a) If we are to have the proton graze the surface of the sphere, what should l
be? [6]
(b) If we now have an electron in place of a proton and to have it graze the surface
of the sphere, what should l be? [4]
11. The surface temperature and radius of the Sun are approximately 5800 K and
6.96 10
8
m respectively. You may assume that the Sun behaves as a blackbody
radiator.
(a) Calculate the total energy radiated by the Sun in each second, given that the
Stefan-Boltzmann constant = 5.67 10
8
Wm
2
K
4
.
(b) What is the intensity of the solar radiation reaching the top of the Earths
atmosphere? (Distance from the Earth to the Sun = 1.50 10
11
m)
(c) If the Earth has no atmosphere, what would be the Earths equilibrium tem-
perature be so that at steady state, it radiates as much as it absorbs? (Radius
of Earth = 6.38 10
6
m)
6
(d) From measurements of the temperature at dierent parts of the Earth, the
Earths average temperature is estimated to be about 15
C. Give possible rea-
sons for the dierence between this temperature and that you have calculated
in part (c).
(e) Estimate the temperature on Mars surface, given that the distance from Mars
to the Sun = 2.28 10
11
m and radius of Mars = 3.40 10
6
m. [12]
End of Paper
7
Você também pode gostar
- SJPO Special Round 2009 Sample PDFDocumento8 páginasSJPO Special Round 2009 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Questions From Singapore Physics Olympiad 2007: M"G M"MDocumento5 páginasQuestions From Singapore Physics Olympiad 2007: M"G M"McsngAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO 2016 General Round - QuestionDocumento24 páginasSJPO 2016 General Round - QuestionZleepAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersDocumento21 páginasSJPO General Round 2009 With AnswersHaha XiAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO 2016 General Round - Answer GuideDocumento50 páginasSJPO 2016 General Round - Answer GuideZleep100% (1)
- SJPO General Round 2008Documento19 páginasSJPO General Round 2008shilgAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionDocumento23 páginasSJPO 2015 General Round - QuestionZleepAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO 2018 General Round - Answer GuideDocumento18 páginasSJPO 2018 General Round - Answer GuideDivya0% (1)
- 2018 Special Round Question PDFDocumento13 páginas2018 Special Round Question PDFmmmmmAinda não há avaliações
- 2010 Physiscs SolutionsDocumento21 páginas2010 Physiscs Solutionsjoebloggs_com100% (1)
- JC1 Math - H2 - 2019Documento347 páginasJC1 Math - H2 - 2019GQGrace TohAinda não há avaliações
- Constrained Motion Question Bank-02Documento51 páginasConstrained Motion Question Bank-02MOHAMMED ASIF86% (7)
- 2016 Australian Physics Olympiad ANSWER BOOKLETDocumento12 páginas2016 Australian Physics Olympiad ANSWER BOOKLETAlex DumortierAinda não há avaliações
- Nsea 2014 A412Documento13 páginasNsea 2014 A412Debayan BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 QualificationDocumento216 páginas2018 QualificationMOHAMED ABDUL SALAM A. AL FAHIMAinda não há avaliações
- OAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2018 OAPT Grade 11 Physics Contest ANSWER KEY PDFDocumento10 páginasOAPT - Grade 11 Physics Contest - 2018 OAPT Grade 11 Physics Contest ANSWER KEY PDFAmana Alam100% (1)
- Solutions of 8 Online Physics BrawlDocumento47 páginasSolutions of 8 Online Physics BrawlDino SelimovicAinda não há avaliações
- Pair of Lines Second Degree General EquationDocumento29 páginasPair of Lines Second Degree General Equationarjunsai100% (1)
- Solutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlDocumento45 páginasSolutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlKetul ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Mock Test - Olympiad - InPhODocumento4 páginasMock Test - Olympiad - InPhOYeswa Preetham Reddy100% (1)
- IPHO BooksDocumento3 páginasIPHO BooksRishabh Rajoria100% (1)
- Nsep Mock 1 PDFDocumento14 páginasNsep Mock 1 PDFCranxtorAinda não há avaliações
- Mcqs From Past Papers Physics All in One 2nd YearDocumento35 páginasMcqs From Past Papers Physics All in One 2nd YearIrtaza Akram50% (2)
- 2022 Mock JEE Main - 1 - PaperDocumento12 páginas2022 Mock JEE Main - 1 - Paperstudent timeAinda não há avaliações
- H2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Documento47 páginasH2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Indrik WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz On Work, Energy, and PowerDocumento2 páginasQuiz On Work, Energy, and PowerNathaniel DimaocorAinda não há avaliações
- 5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsDocumento14 páginas5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsSoya BeansAinda não há avaliações
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-23 Radioactivity PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocumento17 páginasLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-23 Radioactivity PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanAinda não há avaliações
- Answers SJPO 2009 Special Round PDFDocumento2 páginasAnswers SJPO 2009 Special Round PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section: (A) Relative Motion in One DimensionDocumento5 páginasPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section: (A) Relative Motion in One DimensionAtulAinda não há avaliações
- Adiabatic Invariants: Example 1Documento9 páginasAdiabatic Invariants: Example 1Vilakshan Gupta100% (1)
- CircularMotion PCDocumento18 páginasCircularMotion PCAaryan KeshanAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 10 Fields (HL) - IB PhysicsDocumento1 páginaTopic 10 Fields (HL) - IB PhysicsFortNite KIDAinda não há avaliações
- NSEA 2011 Q Paper With SolutionDocumento27 páginasNSEA 2011 Q Paper With SolutionSap MajumdarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Olympiad Practice TestDocumento10 páginasPhysics Olympiad Practice TestDevYShethAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 2Documento18 páginasAP Physics 1 Practice Test 2John BoswellAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational MotionDocumento39 páginasRotational MotionKhushal BhavsarAinda não há avaliações
- Nsep Solved 2007Documento10 páginasNsep Solved 2007Mahalingam NanjappanAinda não há avaliações
- IOAA 2015 Data Analysis Problems Ver 20150730 - 1851Documento22 páginasIOAA 2015 Data Analysis Problems Ver 20150730 - 1851Raja PalasaAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsDocumento19 páginasH2 Physic 2007 A Level SolutionsonnoezAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Olympiad QuestionDocumento11 páginasPhysics Olympiad QuestionIrtiza HaSanAinda não há avaliações
- Chinese Physics Olympiad 2017 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal ThamanDocumento7 páginasChinese Physics Olympiad 2017 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal Thamansmritidipa m100% (1)
- HSC Physics Sample ExamsDocumento346 páginasHSC Physics Sample Examsn100% (1)
- O Level Wave MCDocumento6 páginasO Level Wave MCDora AyeAinda não há avaliações
- ConstraitsDocumento2 páginasConstraitsVikram AdityaAinda não há avaliações
- Work and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Documento13 páginasWork and Energy Practice Problems 2011 10 12Mansoor Al TunijiAinda não há avaliações
- DYNAMICS QUESTIONS For JEEDocumento25 páginasDYNAMICS QUESTIONS For JEEAdarsh DhawanAinda não há avaliações
- Ftre 2013 Class 10 Paper 2 PDFDocumento17 páginasFtre 2013 Class 10 Paper 2 PDFvamsi2bulusu100% (6)
- Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory TestDocumento8 páginasGas Laws and Kinetic Theory Testmcdaid1888100% (1)
- Ib PhysicsDocumento10 páginasIb PhysicsAndres LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism-A Collection of Problems 20101026Documento116 páginasElectromagnetism-A Collection of Problems 20101026luddd3Ainda não há avaliações
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - WorksheetDocumento12 páginas4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - Worksheetkoelia100% (1)
- IOAA Book PDFDocumento254 páginasIOAA Book PDFEng Rit88% (8)
- SJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFDocumento10 páginasSJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Documento24 páginas11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Shivam GargAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFDocumento7 páginasSJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)Documento23 páginasCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-09 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- MRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)Documento35 páginasMRTS-3 (Paper With Solution)semofederationAinda não há avaliações
- Tong RBD3 SheetDocumento4 páginasTong RBD3 SheetAshish GiriAinda não há avaliações
- Answers For SJPO 2011 General RoundDocumento1 páginaAnswers For SJPO 2011 General Roundziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO General Round 2011 PDFDocumento21 páginasSJPO General Round 2011 PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Answers SJPO 2009 General Round PDFDocumento1 páginaAnswers SJPO 2009 General Round PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO General Round 2010 PDFDocumento19 páginasSJPO General Round 2010 PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Answers SJPO 2010 Special Round PDFDocumento3 páginasAnswers SJPO 2010 Special Round PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Answers For SJPO 2010 General Round PDFDocumento1 páginaAnswers For SJPO 2010 General Round PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Answers SJPO 2009 Special Round PDFDocumento2 páginasAnswers SJPO 2009 Special Round PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Answers For SJPO 2013 Special Round PDFDocumento1 páginaAnswers For SJPO 2013 Special Round PDFIvin LeeAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFDocumento10 páginasSJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- SJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFDocumento7 páginasSJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaAinda não há avaliações
- Torque: Course Name and Number: Student Name: Lab Number: DateDocumento6 páginasTorque: Course Name and Number: Student Name: Lab Number: Dateconstantine1106Ainda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism - Lecture 4 Dipole FieldsDocumento16 páginasElectromagnetism - Lecture 4 Dipole FieldsShlôkä JõshïAinda não há avaliações
- CJC JC1 Promo 2008 AnswersDocumento25 páginasCJC JC1 Promo 2008 AnswerscjcsucksAinda não há avaliações
- RotationDocumento47 páginasRotationilhamAinda não há avaliações
- CT 3 JEE Adv 12-05-2013 Solution EnglishDocumento12 páginasCT 3 JEE Adv 12-05-2013 Solution EnglishPrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Jan. 11 Mole Concept Grade 9Documento4 páginasLesson Plan in Jan. 11 Mole Concept Grade 9Edessa MasinasAinda não há avaliações
- Gravito ElectromagnetismDocumento15 páginasGravito Electromagnetismfevv1610Ainda não há avaliações
- DOSAGE-CALCULATION-CONVERSIONS TleDocumento1 páginaDOSAGE-CALCULATION-CONVERSIONS TleBlesie MoradaAinda não há avaliações
- Control Systems & Simulation Lab Manual Experiment - 2 Modeling of Physical Systems Using MATLABDocumento5 páginasControl Systems & Simulation Lab Manual Experiment - 2 Modeling of Physical Systems Using MATLABKrushnasamy SuramaniyanAinda não há avaliações
- Back Matter, CycloneDocumento24 páginasBack Matter, CycloneVivi Diana HariskyAinda não há avaliações
- PT Q3 Science 6Documento8 páginasPT Q3 Science 6Melchor FerreraAinda não há avaliações
- The Emergence of LightDocumento2 páginasThe Emergence of LightJuliah Elyz Alforja TanAinda não há avaliações
- Bin DesignDocumento3 páginasBin Designmahreza189Ainda não há avaliações
- IB Physics SL DefinitionsDocumento7 páginasIB Physics SL DefinitionsVaggelis KøtrønisAinda não há avaliações
- College Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test BankDocumento34 páginasCollege Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test Bankwilma100% (18)
- Chemical vs. Physical Changes: Name: Skylar Corey Grade Level: 5th Grade NGSS Performance ExpectationDocumento18 páginasChemical vs. Physical Changes: Name: Skylar Corey Grade Level: 5th Grade NGSS Performance Expectationapi-288753185Ainda não há avaliações
- University Physics With Modern Physics 12th Edition: Hugh D. Young Roger A. FreedmanDocumento65 páginasUniversity Physics With Modern Physics 12th Edition: Hugh D. Young Roger A. FreedmanEmrehan GökçayAinda não há avaliações
- Tut 1Documento2 páginasTut 1muhammadmusakhanAinda não há avaliações
- Back-Pressure Tests On. Gas-Condensate Wells: As - OndeisateDocumento9 páginasBack-Pressure Tests On. Gas-Condensate Wells: As - OndeisateAura Cristina Villafañe GeraldinoAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Homework 1 Electromagnetism IDocumento1 página10 Homework 1 Electromagnetism IKatherine Heigl MadrigalAinda não há avaliações
- Canup Moon Nature 01 PDFDocumento5 páginasCanup Moon Nature 01 PDFArcibaldMilicAinda não há avaliações
- Science Bowl PracticeDocumento13 páginasScience Bowl PracticeOsborn AgyemangAinda não há avaliações
- Johntitor TimetravelerDocumento445 páginasJohntitor Timetravelermichael100% (1)
- Sample Does Each Sample Have Mass?Documento2 páginasSample Does Each Sample Have Mass?fserhnhrAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Common Problems of Pressure - Junior PhysicsDocumento4 páginas10 Common Problems of Pressure - Junior Physicstham langAinda não há avaliações
- EC2253 Question BankDocumento7 páginasEC2253 Question BankshubhamsouravAinda não há avaliações
- Pendulum MergedDocumento78 páginasPendulum MergedEge OrhanAinda não há avaliações
- Gravitation Class 9 Science Notes - Sarthaks Econnect - Largest Online Education CommunityDocumento12 páginasGravitation Class 9 Science Notes - Sarthaks Econnect - Largest Online Education Communitysmi_santhosh100% (1)
- Lecture Planner - Physics - PW Vidyapeeth School 11th JEE (Alpha)Documento3 páginasLecture Planner - Physics - PW Vidyapeeth School 11th JEE (Alpha)Divyanshu JethwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Clases 04 Al 050919 F Is PropDocumento53 páginasClases 04 Al 050919 F Is PropMicael SorianoAinda não há avaliações
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceNo EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldNo EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNo EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNo EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNo EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNo EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (410)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNo EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyAinda não há avaliações
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNo EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNo EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (125)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldNo EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (60)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombNo EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectNo EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (20)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldNo EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (54)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldNo EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityNo EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (76)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionNo EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismNo EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (500)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeAinda não há avaliações
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxNo EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (27)