Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Material Reference
Enviado por
Roshin99Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Material Reference
Enviado por
Roshin99Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Material Reference
The chart below is intended to help in the material selection stage of designing rubber parts / products. Rubber compounding is a very broad and
technical field, since basic rubbers or elastomers are mixed with various chemicals and ingredients (and even with each other) to obtain desired
physical properties.
A wide variety of basic polymers (rubbers) are available, and a literally infinite array of compounds exhibiting unique physical properties as well as
chemical, fluid, and temperature resistances are possible. This chart, therefore, deals only with very general features of the most common basic rubber
or elastomer compounds, but more specific information is available upon request.
Common
Name(s)
Designation
(2)
Composition Min/Max Temp
Operating
Range (F) (5)
General
Properties(1)
General Chemical Resistance (3)
Resistant to: Attacked by:
Neoprene CR Chloroprene -30 F / 212 F Good Weathering
Resistance. Flame
retarding.
Moderate
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Moderate
chemicals and
acids, ozone, oils,
fats, greases,
many oils, and
solvents.
Strong oxidizing
acids, esters,
ketones,
chlorinated,
aromatic and nitro
hydrocarbons.
EPDM EPDM,
EPM
Ethylene-propylene-
diene; Ethylene-
propylene
-40 F / 300 F Excellent ozone,
chemical, and
aging resistance.
Poor resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Animal and
vegetable oils,
ozone, strong and
oxidizing
chemicals.
Mineral oils and
solvents, aromatic
hydrocarbons.
Buna-N NBR Nitrile-butadiene -30 F / 250 F Excellent
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids. Good
physical properties.
Many
hydrocarbons,
fats, oils, greases,
hydraulic fluids,
chemicals.
Ozone (except
PVC blends),
ketones, esters,
aldehydes,
chlorinated and
nitro hydrocarbons.
Silicone Q, Si Polysiloxane -80 F / 420 F Excellent high and
low temperature
properties. Fair
physical properties.
Moderate or
oxidizing
chemicals, ozone,
concentrated
sodium hydroxide.
Many solvents,
oils, concentrated
acids, dilute
sodium hydroxide.
SBR SBR Styrene-butadiene -20 F / 212F Good physical
properties and
abrasion
resistance. Poor
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Most moderate
chemicals, wet or
dry, organic acids,
alcohols, ketones,
aldehydes.
Ozone, strong
acids, fats, oils,
greases, most
hydrocarbons.
Butyl IIR Isobutene-isoprene -60 F / 250 F Very good
weathering
resistance.
Excellent dielectric
properties. Low
permeability to air.
Good physical
properties. Poor
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Animal and
vegetable fats,
oils, greases,
ozone, strong and
oxidizing
chemicals.
Petroleum,
solvents, coal tar
solvents, aromatic
hydrocarbons.
Natural, Gum
Rubber
NR Isoprene, natural -60 F / 220 F Excellent physical
properties
including abrasion
and low
temperature
resistance. Poor
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Most moderate
chemicals, wet or
dry, organic acids,
alcohols, ketones,
aldehydes.
Ozone, strong
acids, fats, oils,
greases, most
hydrocarbons.
Hypalon (4) CSM Chloro-sulfonyl-
polyethylene
-40 F / 320 F Excellent ozone,
weathering, and
acid resistance.
Good and abrasion
and heat
resistance. Fair
resistance to
petroleum-based
fluids.
Similar to
Neoprene with
improved acid
resistance.
Concentrated
oxidizing acids,
esters, ketones,
chlorinated,
aromatic, and nitro
hydrocarbons.
Urethane AU, EU Polyethylene-apdate,
Poly (oxy-1, 4,
butylene) ether
-40 F / 175 F Good aging and
excellent abrasion,
tear, and solvent
resistance. Poor
high temperature
properties.
Ozone,
hydrocarbons,
moderate
chemicals, fats,
oils, greases.
Concentrated
acids, ketones,
esters, chlorinated
and nitro
hydrocarbons.
Viton (4),
Fluoro-
elastomer
FPM Hexaflouropropylene-
vinylidene fluoride
- 10 F / 400 F Excellent oil and
air resistance both
at low and high
temperatures. Very
good chemical
resistance.
All aliphatic,
aromatic and
halogenated
hydrocarbons,
acids, animal and
vegetable oils.
Ketones, low
molecular weight
esters and nitro
containing
compounds.
Fluoro-silicone FSi Fluorocarbon -60 F / 350 F Offers superior
heat resistance.
resistant to cold,
oils and solvents of
fluorinated rubber.
Good for special
applications where
general resistance
to oxidizing
chemicals,
aromatic and
chlorinated solvent
bases are required.
Narrower Temp
range than silicone
but better fluid
resistance
Moderate or
oxidizing
chemicals, ozone,
aromatic
chlorinated
solvents, bases.
Brake fluids,
hydrazine,
ketones.
Hydrogenated
Nitrile
HNBR Hydrogenated
Acrylonitrile-
butadiene rubber
-22 F / 300 F Excellent heat and
oil resistance,
improved fuel and
ozone resistance
(approximately 5X)
over Nitrile Good
abrasion
resistance.
Decreased
elasticity at low
temperatures with
hydrogenation over
standard nitrile.
Many
hydrocarbons,
transmission
fluids,
refrigerants,
diluted acids,
hydraulic fluids,
silicone oils,
vegetable and
animal fats and
oils, water and
steam.
Chlorated
hydrocarbons,
keytones, strong
acids.
Carboxylated
Nitrile
XNBR Carboxylated Nitrile -20 F / 250 F Excellent Abrasion
and Tear
Resistance, Fair
Ozone and Steam
Resistance. Poor
to Fair Sunlight
and Outdoors.
Good to Excellent
Oil Resistance.
Many
hydrocarbons,
fats, oils, greases,
hydraulic fluids,
chemicals.
Ozone (except
PVC blends),
ketones, esters,
aldehydes,
chlorinated and
nitro hydrocarbons.
Footnotes
1. From the "Sheet Rubber Handbook - Gasket and Packing Materials" publication #IP-40 of the Rubber Manufacturers Association (RMA).
2. ASTM D 1418-79
3. 1979 Yearbook of the Los Angeles Rubber Group, Inc.
4. "Viton" and "Kalrez" are registered trademarks of E.I. Dupont, Inc.
5. The temperature range is determined by the base elastomer used. This chart depicts the maximum temperature range for each elastomer.
The temperature range for a specific compound may not reach these maximum limits. Higher temperatures may be considered if exposure
is short or intermittent.
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Isolated Foundation Calculation SheetDocumento5 páginasIsolated Foundation Calculation SheetMohammad Tawfiq Wara100% (4)
- Site Engineering Query (SEQ)Documento1 páginaSite Engineering Query (SEQ)Roshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Diff-Limit State & Working StressDocumento2 páginasDiff-Limit State & Working StressRoshin99100% (1)
- Tank Test CertificatesDocumento1 páginaTank Test CertificatesRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Design of Purlins per IS800 and SP38Documento2 páginasDesign of Purlins per IS800 and SP38MM93% (29)
- Concrete Placement Record ReportDocumento1 páginaConcrete Placement Record ReportRoshin99100% (1)
- PulpDocumento382 páginasPulpBeerBie100% (1)
- Process Design for Coal Liquefaction and Exergy AnalysisDocumento46 páginasProcess Design for Coal Liquefaction and Exergy AnalysisSukaran SinghAinda não há avaliações
- ABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueDocumento56 páginasABS Fire Extinguisher CatalogueqwertyAinda não há avaliações
- Inspection Report For Field WeldDocumento1 páginaInspection Report For Field WeldRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Inspection Record For Switch HousesDocumento1 páginaInspection Record For Switch HousesRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Inspection Record For Cabinets - ConsolesDocumento2 páginasInspection Record For Cabinets - ConsolesRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Insp Record For Install Accept Safeguarding SystemDocumento1 páginaInsp Record For Install Accept Safeguarding SystemRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Test Record For Overcurrent - Earth Fault - Prot Relay-Induction TypeDocumento1 páginaTest Record For Overcurrent - Earth Fault - Prot Relay-Induction TypeRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Foundation Force TransmissionDocumento8 páginasFoundation Force Transmissiondeepakram04Ainda não há avaliações
- WeldingDocumento1 páginaWeldingVinothAinda não há avaliações
- IR For Cable Tray & LaddersDocumento1 páginaIR For Cable Tray & LaddersSchwihdi ZakAinda não há avaliações
- Inspection Record for Gates SEODocumento1 páginaInspection Record for Gates SEORoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Inspection Record For Air Ducting System: Items To InspectDocumento1 páginaInspection Record For Air Ducting System: Items To InspectSchwihdi ZakAinda não há avaliações
- Insp Record For Block WorkDocumento1 páginaInsp Record For Block WorkRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Instion Test Record-PaintingDocumento1 páginaInstion Test Record-PaintingkeronsAinda não há avaliações
- Insp Record For Block WorkDocumento1 páginaInsp Record For Block WorkRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Record of Vessel TestsDocumento1 páginaRecord of Vessel TestsRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Certificate For Mech Completion - Ready For Start UpDocumento1 páginaCertificate For Mech Completion - Ready For Start UpRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Inspection & Test Record Control Valve Pre-InstallationDocumento1 páginaInspection & Test Record Control Valve Pre-InstallationRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Report For Quality Audit PDFDocumento1 páginaReport For Quality Audit PDFRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Incoming Equipment Inspection RecordDocumento1 páginaIncoming Equipment Inspection RecordRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Insp & Test Recds For Outgoing Units-LV SwitchgearDocumento2 páginasInsp & Test Recds For Outgoing Units-LV SwitchgearRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Insp & Test Record Underground Piping PDFDocumento1 páginaInsp & Test Record Underground Piping PDFRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Continuity Test Record For Earthing Conductor For EquipmentDocumento1 páginaContinuity Test Record For Earthing Conductor For EquipmentRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Inspection-Record-AHUDocumento2 páginasInspection-Record-AHUSchwihdi ZakAinda não há avaliações
- Project Site Engineering Query LogDocumento1 páginaProject Site Engineering Query LogRoshin99Ainda não há avaliações
- Insp & Test Records of Switching Units-HV - SwitchgearDocumento3 páginasInsp & Test Records of Switching Units-HV - SwitchgearRoshin99100% (2)
- Synthesis and Charn of in Situ Cross-Linked Hydrogel Based On Self-Assembly of Thiol-Modified Chitosan With PEG DiacrylateDocumento8 páginasSynthesis and Charn of in Situ Cross-Linked Hydrogel Based On Self-Assembly of Thiol-Modified Chitosan With PEG Diacrylatealchemik1515Ainda não há avaliações
- Atoms, Elements & Compounds 1 QP PDFDocumento10 páginasAtoms, Elements & Compounds 1 QP PDFClinton ChikengezhaAinda não há avaliações
- AP Chemistry Unit 6 worksheet key conceptsDocumento5 páginasAP Chemistry Unit 6 worksheet key conceptsburcak gecAinda não há avaliações
- KTM Valve General CatalogDocumento20 páginasKTM Valve General Catalogferdy110276Ainda não há avaliações
- P Block Elements DPP 07 Extra DPP Yakeen 20 2023 PW StarDocumento3 páginasP Block Elements DPP 07 Extra DPP Yakeen 20 2023 PW StarAgnibha MaitiAinda não há avaliações
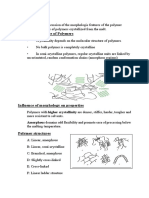
- Morphology of PolymersDocumento7 páginasMorphology of PolymersYounis Muhsin100% (1)
- Aroso 2015Documento7 páginasAroso 2015H Louis AcuñaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Astm D 6928Documento7 páginas12 Astm D 6928Joel BecerraAinda não há avaliações
- Ec Clean - SdsDocumento5 páginasEc Clean - SdsMary JosephineAinda não há avaliações
- X. S. Ling Et Al - Superheating and Supercooling of Vortex Matter in A NB Single Crystal: Direct Evidence For A Phase Transition at The Peak Effect From Neutron DiffractionDocumento4 páginasX. S. Ling Et Al - Superheating and Supercooling of Vortex Matter in A NB Single Crystal: Direct Evidence For A Phase Transition at The Peak Effect From Neutron DiffractionKolddeAinda não há avaliações
- Festo OD TubingDocumento40 páginasFesto OD TubingyogitatanavadeAinda não há avaliações
- Advancesin Bricksand Blocksfor Building ConstructionDocumento14 páginasAdvancesin Bricksand Blocksfor Building ConstructionBharath GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Furadur Kittloesung 20120416 en SD 91070119 PDFDocumento9 páginasFuradur Kittloesung 20120416 en SD 91070119 PDFBarbara Andreina Sanchez AmayaAinda não há avaliações
- Stability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectDocumento13 páginasStability Analysis of Geocell Reinforced Slopes by Considering Bending EffectRakesh KapoorAinda não há avaliações
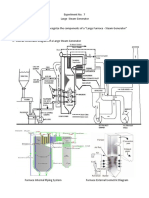
- Large Steam GeneratorDocumento12 páginasLarge Steam GeneratorChe AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Unistrut Uniper Pipe Support SystemsDocumento24 páginasUnistrut Uniper Pipe Support SystemsmolinachAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Characterization of Al-Cu Thermal Contact ResistanceDocumento20 páginasExperimental Characterization of Al-Cu Thermal Contact Resistancenozue.tatsuhiro nozueAinda não há avaliações
- LPSR Based Paper - Optik JournalDocumento12 páginasLPSR Based Paper - Optik JournalSK ChaulyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Funtional Group PropertiesDocumento38 páginasChapter 2 Funtional Group Properties伟铭100% (1)
- Waste management in Israel - background, policy, projects & opportunitiesDocumento15 páginasWaste management in Israel - background, policy, projects & opportunitiesLuan NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- PETRONAS Distributor Price List - W.E.F 10-10-23Documento2 páginasPETRONAS Distributor Price List - W.E.F 10-10-23Mujeeb SiddiqueAinda não há avaliações
- Part1 High Voltage Engineering PDFDocumento67 páginasPart1 High Voltage Engineering PDFQais Alsafasfeh0% (1)
- Basic Type Heat ExchangerDocumento25 páginasBasic Type Heat ExchangerTaifurAinda não há avaliações
- DOWSIL™ 795 Structural Glazing Sealant Technical Data SheetDocumento5 páginasDOWSIL™ 795 Structural Glazing Sealant Technical Data SheetTrung Nguyễn NgọcAinda não há avaliações
- MDtrm questions on art elements, principles and mediumsDocumento28 páginasMDtrm questions on art elements, principles and mediumsNicole Dang BallaretAinda não há avaliações
- WPS - 008Documento11 páginasWPS - 008MAT-LIONAinda não há avaliações