Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Guided Reading - Chapter 11 and 45
Enviado por
Katara Hokaida0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
287 visualizações5 páginasThis document contains a guided reading assignment on cell signaling pathways and the endocrine system. It includes 31 questions about signal transduction pathways, hormone function, the endocrine and nervous systems, feedback loops, stress responses, and sex hormones. Students are asked to define key terms, label diagrams of signaling pathways and endocrine glands, explain concepts like amplification and feedback, and analyze diagrams of hormone regulation and calcium homeostasis. The assignment covers topics in chapters 11 and 45 and is intended to help students learn about intercellular communication and the endocrine system.
Descrição original:
Campbell 10th edition
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document contains a guided reading assignment on cell signaling pathways and the endocrine system. It includes 31 questions about signal transduction pathways, hormone function, the endocrine and nervous systems, feedback loops, stress responses, and sex hormones. Students are asked to define key terms, label diagrams of signaling pathways and endocrine glands, explain concepts like amplification and feedback, and analyze diagrams of hormone regulation and calcium homeostasis. The assignment covers topics in chapters 11 and 45 and is intended to help students learn about intercellular communication and the endocrine system.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
287 visualizações5 páginasGuided Reading - Chapter 11 and 45
Enviado por
Katara HokaidaThis document contains a guided reading assignment on cell signaling pathways and the endocrine system. It includes 31 questions about signal transduction pathways, hormone function, the endocrine and nervous systems, feedback loops, stress responses, and sex hormones. Students are asked to define key terms, label diagrams of signaling pathways and endocrine glands, explain concepts like amplification and feedback, and analyze diagrams of hormone regulation and calcium homeostasis. The assignment covers topics in chapters 11 and 45 and is intended to help students learn about intercellular communication and the endocrine system.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________
Guided Reading Chapter 11 and 45
Page 1 of 5 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp
Chapter 11
1. What is a signal transduction pathway?
2. Define the following:
a. Local regulator
b. Hormone
c. Pheromones (remember them?)
d. Paracrine signaling
e. Synaptic signaling
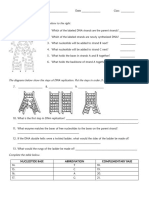
3. Using the relevant terms from Question 2 and Figure 11.5, label the following diagram:
4. List and explain the three stages of signaling.
a.
b.
c.
5. How do cell junctions affect the signaling systems? Use the
diagram to the right if you prefer.
Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________
Guided Reading Chapter 11 and 45
Page 2 of 5 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp
6. Label the following diagram with the
stages of signaling.
7. Define ligand.
8. What is a G protein-linked receptor?
9. Label the image below: 10. Label the diagram below of a G protein-linked receptor:
11. What is a kinase?
12. Label the diagram of the receptor tyrosine kinase below:
Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________
Guided Reading Chapter 11 and 45
Page 3 of 5 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp
13. Label and title the diagram below: 14. Label the diagram below:
15. The signal transduction pathway is important because of amplification. Explain what is meant by
amplification.
16. What is the significance of the diagram below and label it?
Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________
Guided Reading Chapter 11 and 45
Page 4 of 5 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp
Chapter 45
17. What is a hormone?
18. What is the endocrine system and what are its functions?
19. What are endocrine glands?
20. How does synaptic signaling demonstrate the overlap between the endocrine and nervous system?
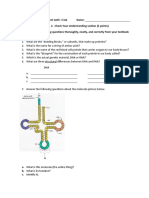
21. The diagram to the right represents the basic
patterns of hormonal control. Part (c) shows a
combination of neuroendocrine and endocrine
mechanisms. Label Parts A and B as either endocrine
or neuroendocrine, using Figures 45.10 and 45.11 as
guides:
22. What are the three major classes of molecules
that function as hormones in vertebrates?
a.
b.
c.
23. How can one chemical signal cause different effects?
24. How does the hypothalamus integrate information?
25. What is the importance of tropic hormones?
Name: _____________________________________ Date: __________________
Guided Reading Chapter 11 and 45
Page 5 of 5 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp
26. What is the main function of the parathyroid hormone and, in your own words, why is it important?
27. Complete the diagram to the right of the feedback loops
concerning calcium regulation (fill in the six open shapes).
The bottom half corresponds to PTH feedback as in Figure
45.19; the upper half is not in your book but represents
the calcitonins opposite effect. This is very important and
you will need to think on your own to complete this
problem.
28. Consider Figure 45.20. How does the body respond differently to long-term and short-term stressors?
Why is this an advantage?
29. How could chronic short-term stress responses be a disadvantage to the organism?
30. What are the gonadal sex hormones?
31. What is the pineal gland and why is it important?
Você também pode gostar
- Biochemical Correlates of Brain Structure and FunctionNo EverandBiochemical Correlates of Brain Structure and FunctionA.N. DavisonAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology - CH 45 Guided ReadingDocumento6 páginasAP Biology - CH 45 Guided ReadingrenubalAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine System Notes 1314Documento9 páginasEndocrine System Notes 1314Adrianna LjubiAinda não há avaliações
- AP Bio Midterm ReviewDocumento38 páginasAP Bio Midterm ReviewCandice LongAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Chapter 17 Reading GuideDocumento15 páginasAP Biology Chapter 17 Reading GuideSam BAinda não há avaliações
- Ssabsa: 2004 BIOLOGYDocumento30 páginasSsabsa: 2004 BIOLOGYJennifer StanleyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17: From Gene To ProteinDocumento17 páginasChapter 17: From Gene To ProteinBen LucasAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 17 Guided Reading AssignmentDocumento8 páginasAP Biology Name - Chapter 17 Guided Reading AssignmentSkylerFragozco0% (3)
- CH 45 Guided ReadingDocumento6 páginasCH 45 Guided ReadingSteven BrownAinda não há avaliações
- SBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistryDocumento6 páginasSBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistrySukhvir AujlaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5 Guided Reading AP BiologyDocumento5 páginasCH 5 Guided Reading AP BiologyAlex SuAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Energy SEDocumento7 páginasCell Energy SEFakunle TimileyinAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17 AnswersDocumento15 páginasChapter 17 AnswersBen LucasAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous System WorksheetDocumento6 páginasNervous System WorksheetSteve MacarioAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet - DNA Replication Worksheet2Documento2 páginasWorksheet - DNA Replication Worksheet2MairaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Energy SEDocumento6 páginasCell Energy SEArt LoversAinda não há avaliações
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center College of Medicine SY 2018-2019 Department of BiochemistryDocumento20 páginasUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center College of Medicine SY 2018-2019 Department of BiochemistryManila MedAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Biology Six WeeklyDocumento6 páginasGrade 11 Biology Six WeeklyNicketa AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- Don Bosco College: Basic Education Department Junior High School Level Canlubang, Calamba City S.Y. 2021-2022Documento12 páginasDon Bosco College: Basic Education Department Junior High School Level Canlubang, Calamba City S.Y. 2021-2022Anton Joaquin PatulotAinda não há avaliações
- Control & Cooridnation Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocumento3 páginasControl & Cooridnation Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Sciencepdthedon007Ainda não há avaliações
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocumento2 páginasThe Cell Cycle WorksheetPol Marasigan BanzonAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Lymphatic SystemDocumento4 páginasManual Lymphatic Systemrayverjohnlayam073Ainda não há avaliações
- Control & Cooridnation Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocumento3 páginasControl & Cooridnation Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 Scienceclashhunting123123Ainda não há avaliações
- STF Science SPMDocumento190 páginasSTF Science SPMnursyidhassan100% (1)
- UST Bio Exam Part ReviewerDocumento6 páginasUST Bio Exam Part ReviewerAmanda PoetirayAinda não há avaliações
- SMJK Pei Yuan Kampar Monthly Test March 2011 Science Form 4 1 HourDocumento10 páginasSMJK Pei Yuan Kampar Monthly Test March 2011 Science Form 4 1 HourAlan WongAinda não há avaliações
- BCMB 415 Exam 3, Fall 2016 KeyDocumento9 páginasBCMB 415 Exam 3, Fall 2016 KeyzzmasterAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 222 Assignment 2Documento49 páginasChem 222 Assignment 2Jay TrebleyAinda não há avaliações
- hssb0400s StudygdbDocumento12 páginashssb0400s StudygdbMohamed HassaneinAinda não há avaliações
- Folder No:: WRITTEN EXAM: Pharmacology With Toxicology Pharmacology: Questions 1-10 Toxicology: Questions 11-13Documento9 páginasFolder No:: WRITTEN EXAM: Pharmacology With Toxicology Pharmacology: Questions 1-10 Toxicology: Questions 11-13John KirubakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Questions:: Activity Sheet No.1Documento14 páginasQuestions:: Activity Sheet No.1Raniey MayolAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ. Each Worth 1 Mark - There Will Be 15 QuestionsDocumento2 páginasMCQ. Each Worth 1 Mark - There Will Be 15 QuestionsChristopher Ezekiel LaiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5: Gizmos Lab Simulation: Cell Energy CycleDocumento6 páginasUnit 5: Gizmos Lab Simulation: Cell Energy Cyclejibityy junnnAinda não há avaliações
- Third Quarter Exam in Science 10Documento3 páginasThird Quarter Exam in Science 10roselyn acpacAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Model Exam - Feb 2022 1Documento2 páginas11 Model Exam - Feb 2022 1GokulAinda não há avaliações
- Ease 2 Biology Grade 9 2020 2021 FinalDocumento16 páginasEase 2 Biology Grade 9 2020 2021 FinalfajarAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis WorksheetDocumento3 páginasCell Cycle, Mitosis Worksheetrosellevalerio2014Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio A Final Review 2023Documento3 páginasBio A Final Review 2023nbairAinda não há avaliações
- ds24 Enzyme Review AssessmentDocumento8 páginasds24 Enzyme Review Assessmentapi-110789702Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 2 Textbook Written ComponentDocumento2 páginasModule 2 Textbook Written Componentwilliam rileyAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 1 Final Exam Review 2020Documento8 páginasBiology 1 Final Exam Review 2020Laarni GeeAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis WorksheetDocumento3 páginasCell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheetjulia.dukeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsDocumento9 páginasChapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsdarthAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Biology NotesDocumento10 páginasChapter 11 Biology Notestherenam825Ainda não há avaliações
- Parade Through The KingdomsDocumento17 páginasParade Through The KingdomsKevinBcnAinda não há avaliações
- 4th Week 4.1 LAS Science 10Documento5 páginas4th Week 4.1 LAS Science 10James YamAinda não há avaliações
- LS-CBB-5530 Cellular and Molecular Biology Gogol Exam 2 Nov. 4, 2014Documento8 páginasLS-CBB-5530 Cellular and Molecular Biology Gogol Exam 2 Nov. 4, 2014goutham278Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Endocrine System Review GuidemwDocumento3 páginas1 Endocrine System Review GuidemwdfgvsfdsfAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Modeling ToobersDocumento10 páginasProtein Modeling ToobersBecky KoshyAinda não há avaliações
- LMSG 10Documento6 páginasLMSG 10Jasmen Mohawk CheaseAinda não há avaliações
- Dna Review Packet UpdatedDocumento4 páginasDna Review Packet Updatedapi-259727482Ainda não há avaliações
- Effect of Watching Advertisement On ChildrenDocumento7 páginasEffect of Watching Advertisement On ChildrenSwapnil MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 6 GuideDocumento5 páginasExam 6 Guidetalbw05Ainda não há avaliações
- Bennett First Sem Final SG 15-16Documento3 páginasBennett First Sem Final SG 15-16api-292964277Ainda não há avaliações
- Division Enhanced Activity Genbio Week8Documento3 páginasDivision Enhanced Activity Genbio Week8Jheremy Charles Morales MorteraAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 09 Cell DivisionDocumento9 páginasLAB 09 Cell DivisionGlaiza Nicole CuarteronAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules Review W KeyDocumento6 páginasBiological Molecules Review W KeyJulius PanayoAinda não há avaliações
- Medicinal Chemistry 5220Documento11 páginasMedicinal Chemistry 5220وديع الرقيبAinda não há avaliações
- QuizDocumento2 páginasQuizydnar pokovlogskyAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis GR 2017Documento2 páginasPhotosynthesis GR 2017api-440268289Ainda não há avaliações
- Double Double Toil and ToubleDocumento1 páginaDouble Double Toil and ToubleDa BomshizAinda não há avaliações
- AP Lang Weasel Multiple ChoiceDocumento1 páginaAP Lang Weasel Multiple ChoiceKatara HokaidaAinda não há avaliações
- In The Gloaming. - . Finding Peace in Indecision Day and Night Pass Each Other, Pale Blues Fade Into DarknessDocumento1 páginaIn The Gloaming. - . Finding Peace in Indecision Day and Night Pass Each Other, Pale Blues Fade Into DarknessKatara HokaidaAinda não há avaliações
- Song of The WitchesDocumento1 páginaSong of The WitchesKatara HokaidaAinda não há avaliações
- Iphone and Ipad Development TU GrazDocumento2 páginasIphone and Ipad Development TU GrazMartinAinda não há avaliações
- 5066452Documento53 páginas5066452jlcheefei9258Ainda não há avaliações
- Ajmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalDocumento45 páginasAjmera - Treon - FF - R4 - 13-11-17 FinalNikita KadamAinda não há avaliações
- CORP2165D Lecture 04Documento26 páginasCORP2165D Lecture 04kinzi chesterAinda não há avaliações
- Formula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointDocumento24 páginasFormula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointRedgie Mark UrsalAinda não há avaliações
- National Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBDocumento33 páginasNational Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBMick StukesAinda não há avaliações
- Feasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTDocumento42 páginasFeasibility Study For Cowboy Cricket Farms Final Report: Prepared For Prospera Business Network Bozeman, MTMyself IreneAinda não há avaliações
- Business-Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Documento8 páginasBusiness-Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Pavan Sai Krishna KottiAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Repair Manual (2017)Documento59 páginasConcrete Repair Manual (2017)Fernando EscriváAinda não há avaliações
- Bad Memories Walkthrough 0.52Documento10 páginasBad Memories Walkthrough 0.52Micael AkumaAinda não há avaliações
- Power Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Documento18 páginasPower Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Ecs h61h2-m12 Motherboard ManualDocumento70 páginasEcs h61h2-m12 Motherboard ManualsarokihAinda não há avaliações
- EKC 202ABC ManualDocumento16 páginasEKC 202ABC ManualJose CencičAinda não há avaliações
- Account Statement 250820 240920 PDFDocumento2 páginasAccount Statement 250820 240920 PDFUnknown100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Documento23 páginasChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeAinda não há avaliações
- Back Propagation Neural NetworkDocumento10 páginasBack Propagation Neural NetworkAhmad Bisyrul HafiAinda não há avaliações
- 1B20 40Documento4 páginas1B20 40Electrival TcatallerAinda não há avaliações
- Ducted Split ACsDocumento31 páginasDucted Split ACsHammadZaman100% (1)
- Moquerio - Defense Mechanism ActivityDocumento3 páginasMoquerio - Defense Mechanism ActivityRoxan MoquerioAinda não há avaliações
- WHO Guidelines For Drinking Water: Parameters Standard Limits As Per WHO Guidelines (MG/L)Documento3 páginasWHO Guidelines For Drinking Water: Parameters Standard Limits As Per WHO Guidelines (MG/L)114912Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 - Basic ProbabilityDocumento37 páginasChapter 4 - Basic Probabilitynadya shafirahAinda não há avaliações
- The Wayland News October 2014Documento16 páginasThe Wayland News October 2014Julian HornAinda não há avaliações
- Matka Queen Jaya BhagatDocumento1 páginaMatka Queen Jaya BhagatA.K.A. Haji100% (4)
- Biology Key Stage 4 Lesson PDFDocumento4 páginasBiology Key Stage 4 Lesson PDFAleesha AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Not A Toy Sample PDFDocumento37 páginasNot A Toy Sample PDFMartha Paola CorralesAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry 1Documento265 páginasOrganic Chemistry 1Israk Mustakim IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Specifications (018-001) : WarningDocumento6 páginasSpecifications (018-001) : WarningRómulo Simón Lizarraga LeónAinda não há avaliações
- Acc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 1Documento6 páginasAcc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 12022825274100% (1)
- FinalDocumento18 páginasFinalAkash LadAinda não há avaliações
- 82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULEDocumento2 páginas82686b - LOAD SHARING MODULENguyễn Đình ĐứcAinda não há avaliações