Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACS
Enviado por
Meita ReligiaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
12 Hours: Continue To Monitor: High-Risk NSTEACS
Enviado por
Meita ReligiaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
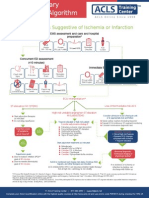
Chest discomfort suggestive
of Ischemia
Symptoms consistent with
ACS
EMS assessment and care and hospital preparation
- Monitor, support ABCs. Be prepare to provide COR and defibrillation
- Administer oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin, and morphine if need
- If available,, obtain 12 lead ECG; if ST-elevation:
o Notify receiving hospital with transmission or interpretation
o Begin fibrinolytic checklist
- Notified hospital should mobilized hospital resources to respond to NSTEMI
Immediate ED assessment (< 10 minutes)
- Check vital signs; evaluate oxygen saturation
- Establish IV access
- Obtain/view 12-lead ECG
- Perform brief, targeted history, physical exam
- Review/complete fibrinolytic checklist; check
contraindication
- Obtain initial cardiac marker levels, initial electrolytes and
coagulation studies
- Obtain portable chest x-ray (< 30 minutes)
Immediate ED general treatment
- Start oxygen at 4 L/min; maintain O2 sat > 90%
- Aspirin 160 325 mg (if not given by EMS)
- Nitroglycerin sublingual, spray, or IV
- Morphine IV if pain not relieved by
nitroglycerine
Review initial 12-lead ECG
ST elevation or new or
presumably new LBBB; strongly
suspicious for injury
ST-elevation MI (STEMI)
ST depression or dynamic T-wave inversion;
strongly suspicious for ischemia
High risk unstable angina/ non-ST-
elevation MI (UA/NSTEMI)
Normal or non-diagnostic change
in ST-segment or T-wave
Intermediate / low risk UA
Start adjunctive treatments as
Indicated (see text for contraindication)
Do not delay reperfusion
-adrenergic receptor
blockers
Clopidogrel
Heparin (UFH or LMWH)
Start adjunctive treatments as
Indicated (see text for contraindication)
Nitroglycerin
-adrenergic receptor
blockers
Clopidogrel
Heparin (UFH or LMWH)
Glycoprotein Iib/IIIa inhibitor
Develops high or
intermediate risk criteria
(Table)
OR
Troponin-positive?
Symptom onset
< 1 hour ago
PCI available with 1 hour?
1 3 houra ago
PCI available within 90 miniutes
3 -1 2 hours ago
PCI available within 90 minutes (onsite); or
2 hours (offsite, including transport time)?
YES NO YES NO YES NO
PCI Fibrinolysis
(unless contraindicated*)
PCI
Fibrinolysis
(unless contraindicated*)
PCI
Fibrinolysis
(unless contraindicated*)
Patients in whom fibrinolysis is contraindicated, or with ongoing symptoms
or instability, should be transferred for PCI
Continue adjunctive therapies and:
ACE inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) within 24 hours of
symptom onset
HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin therapy)
Admit to monitored bed
Assess risk status (Table)
High-risk patient (Table)
Refractory ischemic chest pain
Recurrent/persistent ST deviation
Ventricular tachycardia
Hemodynamic instability
Signs of pump failure
Early invasive strategy, including
catheterization and revascularization for
shock within 48 hours of an AMI
Continue ASA, heparin, and other therapies as
indicated.
ACE inhibitor/ARB
HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin
therapy)
Not at high risk: cardiology to risk-stratify
Continue to monitor:
chest pain
serial ECG
cardiac markers
Re-evaluate and risk stratify
(+/- cardiology consult)
High-risk NSTEACS
Presentation with clinical features consistent
with ACS and any of:
Repetitive or prolonged (>10 minutes)
ongoing
chest pain/discomfort
Elevation of at least 1 cardiac biomarker
(troponin or CK-MB)
Persistent or dynamic ST depression 0.5
mm
or new T wave inversion 2 mm
Transient ST segment elevation (0.5 mm)
in more than 2 contiguous leads
Haemodynamic compromise: systolic
blood
pressure <90 mmHg, cool peripheries,
diaphoresis,
Killip class >1 and/or new onset mitral
regurgitation
Sustained ventricular tachycardia
Syncope
LV systolic dysfunction (LVEF <40%)
Prior PCI within 6 months or prior CABG
surgery
Presence of known diabetes (with typical
symptoms of ACS)
Chronic kidney disease estimated GFR
<60 mL/
min (with typical symptoms of ACS)
Intermediate-risk NSTEACS
Presentation with clinical features
consistent with
ACS and any of:
Chest pain or discomfort within past 48
hours that
occurred at rest, or was repetitive or
prolonged
(but currently resolved)
Age >65 years
Known CHD: Prior MI with LVEF 40%
or known
coronary lesion >50% stenosed
No high risk ECG changes (see above)
Two or more of: known hypertension,
family
history, active smoking or
hyperlipidaemia
Presence of known diabetes (with
atypical
symptoms of ACS)
Chronic kidney disease estimated
GFR <60 mL/min (with atypical
symptoms of ACS)
Prior aspirin use
AND NOT meeting the criteria for high-
risk NSTEACS
Low-risk NSTEACS
Presentation with clinical features consistent
with
ACS without intermediate or high risk features
e.g.:
Onset of anginal symptoms within the last
month; or
Worsening in severity or frequency of
angina; or
Lowering in anginal threshold
Admit to coronary
care or other high
dependency unit and
treat with aggressive
medical management
Refer for angiography
PCI or CABG
Medical therapy
Stress test
(e.g. exercise ECG)
Recurrent ischaemia
or elevated troponin
at follow up testing
Appropriate period
of observation
Discharge with urgent
cardiac follow-up
(on upgraded
medical therapy)
YES
NO
+ -
>12
hours
Você também pode gostar
- ACS ChartDocumento1 páginaACS ChartJoey TingAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Risk Factors and ManagementDocumento54 páginasAcute Coronary Syndrome Risk Factors and Managementxiaou123100% (1)
- Cardio BBDocumento73 páginasCardio BBايات عبدالرحمنAinda não há avaliações
- Osce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionDocumento10 páginasOsce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionmmmalcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Tatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut Dengan Elevasi Segmen ST: Saharman Leman, Rony Y SyarifDocumento77 páginasTatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut Dengan Elevasi Segmen ST: Saharman Leman, Rony Y SyarifSigit_Rokhmadi100% (1)
- ACS Management GuidelinesDocumento56 páginasACS Management GuidelinesSabilul Huda100% (1)
- Cme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Documento36 páginasCme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Hakimah K. SuhaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Pain Protocol in EDDocumento3 páginasChest Pain Protocol in EDshahidchaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Lapkas PP (STEMI)Documento68 páginasLapkas PP (STEMI)KurbulAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocumento65 páginasAcute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimshintadeviiAinda não há avaliações
- ReferatDocumento50 páginasReferatvnAinda não há avaliações
- Perfusion, Class 11 ReviewedDocumento45 páginasPerfusion, Class 11 ReviewedMelissa GPAinda não há avaliações
- P ('t':'3', 'I':'669636497') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Documento56 páginasP ('t':'3', 'I':'669636497') D '' Var B Location Settimeout (Function ( If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') ( B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Muna NadiAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocumento1 páginaAcute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmRed JimenoAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Certification InstituteDocumento1 páginaAcute Coronary Syndrome: Certification InstituteFian Lingg-LunggAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Certification InstituteDocumento1 páginaAcute Coronary Syndrome: Certification InstituteAivi PhungAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome EditedDocumento38 páginasAcute Coronary Syndrome EditedSurgicalgownAinda não há avaliações
- Tatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut Dengan Elevasi Segmen STDocumento77 páginasTatalaksana Sindrom Koroner Akut Dengan Elevasi Segmen STQueenta SariAinda não há avaliações
- NSTEMIDocumento29 páginasNSTEMIGeanina CreangaAinda não há avaliações
- ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) PresentationDocumento39 páginasST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) PresentationRika Sartyca IlhamAinda não há avaliações
- ACS (Dr. Thamrin 2015)Documento43 páginasACS (Dr. Thamrin 2015)ok sogatenAinda não há avaliações
- Protocol 13: Chest Pain: A&E DoctorDocumento4 páginasProtocol 13: Chest Pain: A&E DoctorVanessa HermioneAinda não há avaliações
- CardiovascularDocumento23 páginasCardiovascularzacks nyirongoAinda não há avaliações
- Differences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaDocumento7 páginasDifferences BTW ACS, Stable AnginaCarmenhAinda não há avaliações
- Acutecoronary Syndrome: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocumento65 páginasAcutecoronary Syndrome: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimpuspayafelliAinda não há avaliações
- ACS LectureDocumento55 páginasACS LectureAyunda AlmiradaniAinda não há avaliações
- 11-Acs2 StemiDocumento33 páginas11-Acs2 Stemiمحمد بن الصادقAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndromes 2015Documento26 páginasAcute Coronary Syndromes 2015prototypeallhellAinda não há avaliações
- ACLS Algorithms SlideDocumento26 páginasACLS Algorithms SlidehrsoAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Shock Types and TreatmentsDocumento75 páginasUnderstanding Shock Types and TreatmentsaulianmediansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Pain Protocol StepsDocumento4 páginasChest Pain Protocol StepsArul ShanmugamAinda não há avaliações
- ACS (Dr. Thamrin 2015)Documento43 páginasACS (Dr. Thamrin 2015)Budianto Aj Ganteng DeweAinda não há avaliações
- Unstable Angina, STEMI, NSTEMI Diagnosis and ManagementDocumento21 páginasUnstable Angina, STEMI, NSTEMI Diagnosis and ManagementNabil Mosharraf Hossain100% (2)
- CardioDocumento9 páginasCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- Stephen Wijayanto: 405110198 Group 12Documento88 páginasStephen Wijayanto: 405110198 Group 12yinvilllAinda não há avaliações
- ACS Algorithm Guide Managing PatientsDocumento5 páginasACS Algorithm Guide Managing PatientsLiuk IrawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines on Management of STEMIDocumento5 páginasGuidelines on Management of STEMIningputAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento46 páginasAcute Coronary SyndromeEmma Andaya100% (1)
- STEMIDocumento34 páginasSTEMIefendiAinda não há avaliações
- AV Block Types, Causes, EKG Findings & TreatmentDocumento59 páginasAV Block Types, Causes, EKG Findings & Treatmentmmmmz100% (1)
- WI EMS Medical Guidelines BradycardiaDocumento2 páginasWI EMS Medical Guidelines BradycardiaCheewin KhawprapaAinda não há avaliações
- Tata Laksana Sindroma Koroner Akut: Cholid Tri TjahjonoDocumento84 páginasTata Laksana Sindroma Koroner Akut: Cholid Tri TjahjonoVio Alveolita PrimayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Coronary Syndrome by DR Anwar Ul HaqDocumento18 páginasAcute Coronary Syndrome by DR Anwar Ul HaqAnwar ul HaqAinda não há avaliações
- Angina and MIDocumento68 páginasAngina and MIAndrassy Twinkle AlineaAinda não há avaliações
- AcsDocumento20 páginasAcsTitanSeptiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- STEMI Extensive Anterior Onset >12 Hours KILLIP 2Documento30 páginasSTEMI Extensive Anterior Onset >12 Hours KILLIP 2dhinialfiandariAinda não há avaliações
- Stemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2Documento30 páginasStemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2Nurul Rezki Fitriani AzisAinda não há avaliações
- unstable-angina جاهز لللعرضDocumento9 páginasunstable-angina جاهز لللعرضshamaamo19Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiology Pharmacist Guide to Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento38 páginasCardiology Pharmacist Guide to Acute Coronary SyndromeAnonymous100% (1)
- ACS Algorithm SymptomsDocumento1 páginaACS Algorithm SymptomsJhon100% (1)
- Saudi CPR Guidlines in EnglishDocumento16 páginasSaudi CPR Guidlines in EnglishpiyushbamsAinda não há avaliações
- Unstable AnginaDocumento5 páginasUnstable AnginaAria AlysisAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Myocardial Infarction: Recognition and AssessmentDocumento7 páginasAcute Myocardial Infarction: Recognition and AssessmentHasnainKhimjiAinda não há avaliações
- Tony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014Documento4 páginasTony Cross CDU Low Risk ACS Proforma - V3.212 Review Due June 2014ED@HEFTAinda não há avaliações
- Vasovagal Reflex SyndromeDocumento19 páginasVasovagal Reflex SyndromeJalalludin AnAinda não há avaliações
- Stemi Extensive Anterior LBH 24 Hour Onset Killip IDocumento35 páginasStemi Extensive Anterior LBH 24 Hour Onset Killip IIta MaghfirahAinda não há avaliações
- ACLS Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Provider Manual 2023No EverandACLS Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Provider Manual 2023Ainda não há avaliações
- Nomor Abnama Peg 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4276 Ayu Annisn N N N TKS L P, S2 NDocumento4 páginasNomor Abnama Peg 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4276 Ayu Annisn N N N TKS L P, S2 NMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- FormatInputShiftNovember 2020Documento4 páginasFormatInputShiftNovember 2020Meita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- OutputDocumento2 páginasOutputMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- DP SarafDocumento2 páginasDP SarafMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Puri Kwitang Hotel VoucherDocumento2 páginasPuri Kwitang Hotel VoucherMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Critical Thinking Test Arguments QuestionsDocumento10 páginasFree Critical Thinking Test Arguments QuestionsMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Free Critical Thinking Test Interpreting Information SolutionsDocumento8 páginasFree Critical Thinking Test Interpreting Information SolutionsMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Pustaka Meita Bab 2-3Documento1 páginaDaftar Pustaka Meita Bab 2-3Meita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study on Knowledge and Stunting RatesDocumento1 páginaCase Study on Knowledge and Stunting RatesMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- G2P1A0H1 Labor Latent PhaseDocumento5 páginasG2P1A0H1 Labor Latent PhaseMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- DP Referat CA LaringDocumento1 páginaDP Referat CA LaringMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 páginasDaftar PustakaMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Percentile BB - U Dan TB - U PDFDocumento1 páginaPercentile BB - U Dan TB - U PDFQonita NahdiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 páginasDaftar PustakaMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Mrs. S Age: 21 Years Old Address: Penimbun Admitted: January 7 2016 No. RM: 572290Documento10 páginasName: Mrs. S Age: 21 Years Old Address: Penimbun Admitted: January 7 2016 No. RM: 572290Meita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Mrs. S Age: 21 Years Old Address: Penimbun Admitted: January 7 2016 No. RM: 572290Documento10 páginasName: Mrs. S Age: 21 Years Old Address: Penimbun Admitted: January 7 2016 No. RM: 572290Meita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Konsumsi DiesDocumento4 páginasKonsumsi DiesMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pengalaman: Klasifikasi Tahun Angkatab Klasifikasi Nilai Total CrosstabulationDocumento6 páginasPengalaman: Klasifikasi Tahun Angkatab Klasifikasi Nilai Total CrosstabulationMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Pustaka Fisiologi Jantung dan Sistem Sirkulasi DarahDocumento1 páginaDaftar Pustaka Fisiologi Jantung dan Sistem Sirkulasi DarahMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Pustaka Fisiologi Jantung dan Sistem Sirkulasi DarahDocumento1 páginaDaftar Pustaka Fisiologi Jantung dan Sistem Sirkulasi DarahMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Shock And/Or Map (Mean Arterial Pressure) 60 MMHG: Airway Circulation BreathingDocumento1 páginaShock And/Or Map (Mean Arterial Pressure) 60 MMHG: Airway Circulation BreathingMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Possible Mechanisms of Action of The Hypotensive Effect of Annona MuricataDocumento2 páginasPossible Mechanisms of Action of The Hypotensive Effect of Annona MuricataMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Terapi Kanker Dengan Daun Sirsak Tidak EfektifDocumento3 páginasTerapi Kanker Dengan Daun Sirsak Tidak EfektifMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Brosur PJKDocumento3 páginasBrosur PJKMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento3 páginasDaftar PustakaMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Cover Catatan TutorialDocumento2 páginasCover Catatan TutorialMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Discomfort Suggestive of IschemiaDocumento1 páginaChest Discomfort Suggestive of IschemiaMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulseless Arrest Algorythm: Symptoms PersistDocumento1 páginaPulseless Arrest Algorythm: Symptoms PersistMeita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- Dopaminergic System: Psikosis EP Prolactin EATING Behavior ??Documento5 páginasDopaminergic System: Psikosis EP Prolactin EATING Behavior ??Meita ReligiaAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 NSTE ACS Slide SetDocumento109 páginas2014 NSTE ACS Slide SetGiorgiana NicoletaAinda não há avaliações
- KillipsDocumento12 páginasKillipsNhorlyn Adante SoltesAinda não há avaliações
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Documento25 páginasCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24Ainda não há avaliações
- CABGDocumento25 páginasCABGkingafridiAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Compendi o Pascoe 2002Documento493 páginasCompendi o Pascoe 2002Pablo Matas Soria100% (2)
- Global Atlas About CV Disease by WHODocumento164 páginasGlobal Atlas About CV Disease by WHOLouisette AgapeAinda não há avaliações
- Stress-Induced (Takotsubo) CardiomyopathyDocumento13 páginasStress-Induced (Takotsubo) CardiomyopathyAdrian GeambasuAinda não há avaliações
- Packrat 15 - 2010Documento86 páginasPackrat 15 - 2010EmersonMoreno80% (5)
- Acupressure and Reflex Points For Common AilmentsDocumento15 páginasAcupressure and Reflex Points For Common AilmentsAnonymous j3gtTwAinda não há avaliações
- Angina PectorisDocumento33 páginasAngina PectorisRosse Del MundoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is An AneurysmDocumento2 páginasWhat Is An AneurysmAlejita CeronAinda não há avaliações
- ACS AMI FacilitatorDocumento21 páginasACS AMI FacilitatorPaul Zantua57% (7)
- Final Project ReportDocumento70 páginasFinal Project ReportManishankar Kumar50% (2)
- Case Eop Group A Year 3 MbbsDocumento7 páginasCase Eop Group A Year 3 MbbsKalaivaany RamachandranAinda não há avaliações
- New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationDocumento1 páginaNew York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationEjanZulqadMaulanaAinda não há avaliações
- CardiacDocumento47 páginasCardiacJoyzoey100% (2)
- 03-07 Lecture Coronary CirculationDocumento29 páginas03-07 Lecture Coronary Circulationaspalavista50% (2)
- 1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationDocumento21 páginas1 Preoperative Health Status EvaluationNuno CoelhoAinda não há avaliações
- Eur Heart J-2013 - 2949-3003Documento62 páginasEur Heart J-2013 - 2949-3003gekwahyuAinda não há avaliações
- New York Medicaid APG CrosswalkDocumento6.734 páginasNew York Medicaid APG CrosswalksdpetesrhsAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento16 páginasCoronary Artery Diseasehdaniel1196Ainda não há avaliações
- The American Journal of Cardiology Vol 107 Issue 4 February 2011Documento153 páginasThe American Journal of Cardiology Vol 107 Issue 4 February 2011ppappi12Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology and Investigation of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology and Investigation of Coronary Artery DiseasekartikaparamitaAinda não há avaliações
- Stable Angina PectorisDocumento11 páginasStable Angina Pectorismarco_bawAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Bypass GraftingDocumento9 páginasCoronary Artery Bypass GraftingRickCohen100% (1)
- Critical Care Medicine PDFDocumento153 páginasCritical Care Medicine PDFRadovanAinda não há avaliações
- II 2015 8Documento224 páginasII 2015 8tuni santeAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Revision Notes For MRCP PDFDocumento1.002 páginasEssential Revision Notes For MRCP PDFMontasir Ahmed100% (23)
- High Yield NotesDocumento191 páginasHigh Yield NotesAdnan MallickAinda não há avaliações