Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Android Application Development
Enviado por
alvachristiDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Android Application Development
Enviado por
alvachristiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Build Your Android App in 7 Easy Steps
www.mobilepundits.com
Build your first Android App in 7 simple steps
Overview of Android
Mobile application development is the hottest thing and in boom in the programming world right
now. The two most popular mobile platforms which are most commonly used these days are
Android and iOS (Apple). Although the numbers tend to fluctuate frequently, it seems that
Android has taken the top spot from Apple.
Android is an open source platform and Linux-based Operating System for mobile devices such
as Smartphones and tablet computers. Android application development is in great demand
these days. It provides a rich application framework that allows you to build highly innovative
apps and games for mobile devices in a Java language environment.
If the overall ratio is to be compared then the demand for Android is much higher. In the United
States, at least 50% of all Smartphone users are having Android devices. Globally, almost 70%
of people uses Android. It is the most popular platform from where you could start building your
android apps.
Not only is Android popular, but it could also become a very profitable platform for users once
you start creating your own apps. Many companies are also moving towards outsourcing
Android apps development.
Building Your First App
Before you start with the class make sure that you have development environment set up. For
this follow the below steps as shown:
1. Download the Android SDK.
2. Install the ADT plugin for Eclipse (if you are using the Eclipse IDE).
3. Download the latest SDK tools and platforms using the SDK Manager.
Create Your Android Project with the help of Eclipse
In Eclipse, create a new Android project and name it as shown:
1. Click New in the toolbar.
2. In the window that appears, open the Android folder, select Android Application
Project, and click on Next button.
The New Android App Project wizard in Eclipse.
Below are the details of the form:
Application name - The user-friendly name of the application that will be
displayed in the Applications tab of the Android UI. For this project, use "My
First App."
Project name - The name of the project you need to enter in it.
Package name - The name of the package. This name will be used as the package
name in your Java files. Package name must be fully qualified. The convention is
to use your company's domain name in reverse order.
Minimum Required SDK is the lowest version of Android that your app
supports. To support as many devices as possible, you should set this to the lowest
version available that allows your app to provide its core feature set.
Target SDK indicates the highest version of Android
As new versions of Android become available, while testing your app prefer the
new version in order to take advantage of new platform features.
Compile With is the platform version against which you will compile your app.
By default, this is set to the latest version of Android available in your SDK. You
can also build your app in the lower version but it will not contain new features
and if you prefer the latest version it will give your app the latest user experience
with new and innovative features.
Theme specifies the Android UI style to apply for your app. You can also leave it
blank also. These themes are nothing but some pre defined color schemes, which
you can use to improve your application's User Interface.
Click Next.
3. On the next screen to configure the project, leave the default selections and click
Next. The screen will appear as shown below:
If you have checked the create custom launcher check box, next screen will be for the creation
of launcher icon.
4. The next screen can help you create a launcher icon for your app.
5. You can customize an icon in several ways and the tool generates an icon for all screen
densities.
On this screen, you can configure different options to create a launcher icon. You can choose
your own image, Text or even your clip-arts. In the Right pane, you can see the demo of the icon
Click Next.
6. Now you can select an activity template from which to begin building your app.
Blank Activity: This will create a blank activity with just 1 textview.
Full Screen Activity: This is typically used for games. This activity hides the status bar
and then your activity takes all screen space.
Master Detail Flow: This template creates advanced navigation, based on fragments,
which will work on tablets and phones as well without any change.
For this project, select Blank Activity and click on Next button.
7. Leave all the details for the activity by default and click Finish.
Your Android project is now a basic "Hello World" app that contains some of the default files.
To run the app see the next section as mentioned below:
Running Your App
If you followed the previous lesson to create an Android project, it includes a default set of
"Hello World" source files that allow you to immediately run the app.
How you run your app depends on two things: whether you have a real Android-powered device
and whether you're using Eclipse. This lesson shows you how to install and run your app on a
real device with either Eclipse or the command line tools.
Before running an app, you must be aware about the few files and directories that will be helpful
while creating the Android project:
AndroidManifest.xml
The AndroidManifest.xml file is an application configuration file that contains detailed
information about your application, such as the number of activities you have in your
application, the version information of your application, the types of permissions your
application needs, and so on. Here you will learn about the various declarations in a file.
One of the most important elements your manifest should include is the <uses-sdk> element.
This declares your app's compatibility with different Android versions using the android:
minSdkVersion and android: targetSdkVersion attributes. For your first app, it should look
like this:
You should always set the android: targetSdkVersion as high as possible and test your app on
the corresponding platform version.
src/
Directory for your app's main source files. By default, it includes an Activity class that runs
when your app is launched using the app icon.
res/
Contains several sub-directories .Some of them are mentioned here:
drawable-hdpi/
Directory for drawable objects (such as bitmaps) that are designed for high-density (hdpi)
screens. Other drawable directories contain assets designed for other screen densities.
layout/
Directory for files that define your app's UI.
When you build and run the default Android app, the default Activity class starts and loads a layout file
that says "Hello World." Through this you will understand how to run your app before start developing
it.
Run on a Real Device
If you have a real Android-powered device, here are the below steps so that you can install and
run your app easily:
1) Plug in your device to your development machine with a USB cable. If you're developing
on Windows, you might need to install the appropriate USB driver for your device.
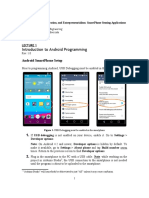
2) Enable USB debugging on your device.
On most devices running which are following the android older version such as 3.2 or
older you will get the option under Settings > Applications > Development.
In Android 4.0 or the latest version you will get the option under Settings > Developer
options.
Note: On Android 4.2 and in the newer version, Developer options are hidden by
default. To make it available, follow the steps as shown:
Go to Settings > About phone and tap Build number seven times. Return to the
previous screen to find Developer options.
To run the app from Eclipse:
1. Open one of your project's files and click Run from the toolbar.
2. In the Run as window that appears, select Android Application and click on OK
button. Your app will now be deployed on your device. It will look as below if deployed
in an AVD. (Android Virtual Device)
Eclipse will install the app on your connected device and starts it accordingly.
Or
There is another method too. You can run your app from a command line:
1. Change directories to the root of your Android project and execute:
ant debug
2. Make sure the Android SDK platform-tools/ directory is included in your PATH
environment variable, then execute:
adb install bin/MyFirstApp-debug.apk
3. On your device, locate MyFirstActivity and open it.
That's how you can build and run your Android app on a device successfully.
Você também pode gostar
- L1 - Intro To Android ProgrammingDocumento14 páginasL1 - Intro To Android ProgrammingppphreAinda não há avaliações
- Android Developers 1Documento4 páginasAndroid Developers 1Praveen KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Building Your First Android App: Create A Project With EclipseDocumento4 páginasBuilding Your First Android App: Create A Project With Eclipsemanoj22490Ainda não há avaliações
- MAD Mod1-5@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocumento137 páginasMAD Mod1-5@AzDOCUMENTS - inVaishnavi G . RaoAinda não há avaliações
- MAD Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - in PDFDocumento26 páginasMAD Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - in PDFNAGARAJ S C1525Ainda não há avaliações
- Mobile Application Development LabDocumento47 páginasMobile Application Development LabDEENBANDHUAinda não há avaliações
- Android App DevelopmentDocumento40 páginasAndroid App Developmentnaman sethiAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile App Development ManualDocumento56 páginasMobile App Development Manual209X1A04D2 SHAIK ASMAAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Android Application DevelopmentDocumento116 páginasReport On Android Application DevelopmentArnoldVaz27100% (1)
- Android Mobile Application DevelopmentDocumento43 páginasAndroid Mobile Application DevelopmentprogrammerAinda não há avaliações
- Annex A: Android Module IntroductionDocumento6 páginasAnnex A: Android Module IntroductionSkyzer BlueAinda não há avaliações
- Akshat GuptaDocumento23 páginasAkshat GuptaAkshat GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Getting Started With Android Development IndexDocumento55 páginasGetting Started With Android Development IndexAman guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 1 Aim: Theory:: Anubha Gajargaonkar Be-A 118CP1334B ROLL NO-11Documento14 páginasExperiment No. 1 Aim: Theory:: Anubha Gajargaonkar Be-A 118CP1334B ROLL NO-11yo fireAinda não há avaliações
- Android Programming For BeginnersDocumento94 páginasAndroid Programming For BeginnersMuhammad Irfan50% (2)
- CS6611-Mobile Application Development Lab-ManualDocumento108 páginasCS6611-Mobile Application Development Lab-ManualVIJAY VIDHYA SAGAR SAinda não há avaliações
- Building Andriod App StepsDocumento40 páginasBuilding Andriod App StepsAbdulrazaq Saleh OkumuAinda não há avaliações
- Android Studio Project CreationDocumento98 páginasAndroid Studio Project CreationSumit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Mobileorchard Com Introduction To Android DevelopmentDocumento15 páginasMobileorchard Com Introduction To Android Developmentomprakkash1509Ainda não há avaliações
- FDDGDocumento54 páginasFDDGAngel CabillanAinda não há avaliações
- Android Application Development Cookbook - Second Edition - Sample ChapterDocumento29 páginasAndroid Application Development Cookbook - Second Edition - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento23 páginasChapter 1Zain IjazAinda não há avaliações
- 6 ChaptersDocumento25 páginas6 Chaptersumesh patilAinda não há avaliações
- Creating React Native Application 1) The React Native CLI: Preparing The Android DeviceDocumento7 páginasCreating React Native Application 1) The React Native CLI: Preparing The Android DeviceAnuj GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Android Development FundamentalsDocumento23 páginasAndroid Development FundamentalsShubham BargudeAinda não há avaliações
- Getting Started With AndroidDocumento30 páginasGetting Started With AndroidNSKumarAinda não há avaliações
- LAB1Documento6 páginasLAB1Ishaan SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Class VII - Computer - Lesson 12 - Application Development-1Documento9 páginasClass VII - Computer - Lesson 12 - Application Development-1Rhythm VlogsAinda não há avaliações
- Cowgate Telangiectasis CraniometricalDocumento2 páginasCowgate Telangiectasis Craniometricalchristian villaramaAinda não há avaliações
- Microcoleoptera_mycosis_tripwireDocumento2 páginasMicrocoleoptera_mycosis_tripwirealejandroleaharneeAinda não há avaliações
- AMP Practical ManualDocumento81 páginasAMP Practical ManualShubham KandwalAinda não há avaliações
- 1.4. Android Hello World App ExampleDocumento9 páginas1.4. Android Hello World App ExampleAbdullah Al Mamun ParvezAinda não há avaliações
- MAD Full Manual PDFDocumento182 páginasMAD Full Manual PDFYashAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1-App Design and Development: Installation of Required SoftwareDocumento16 páginasModule 1-App Design and Development: Installation of Required Softwarekishorekumar123123Ainda não há avaliações
- Development Project (AutoRecovered)Documento26 páginasDevelopment Project (AutoRecovered)Rushi WalgudeAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Android?: Linux KernelDocumento7 páginasWhat Is Android?: Linux KernelInnoxent NafeesAinda não há avaliações
- R20ep070 TDDocumento20 páginasR20ep070 TDKing KingAinda não há avaliações
- Android Programming - The Fast Way - Learn Android Programming, Start Coding TODAY With The Ultimate Android Programming For Beginners GuideDocumento25 páginasAndroid Programming - The Fast Way - Learn Android Programming, Start Coding TODAY With The Ultimate Android Programming For Beginners GuideMỹ TiênAinda não há avaliações
- Miltos Sighten KaoliniteDocumento2 páginasMiltos Sighten KaolinitejhasudAinda não há avaliações
- Create Hello World App in Android StudioDocumento28 páginasCreate Hello World App in Android StudioSivasai DandeAinda não há avaliações
- Calling Built inDocumento56 páginasCalling Built inramalalliAinda não há avaliações
- Android Assingment Unit 1Documento16 páginasAndroid Assingment Unit 1Ayush PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Alternativeness Kahle PenmanshipsDocumento2 páginasAlternativeness Kahle PenmanshipsMaitri shahAinda não há avaliações
- Android App Development - A Beginners GuideDocumento60 páginasAndroid App Development - A Beginners GuideAquila MobiTech100% (1)
- Mad Report22Documento19 páginasMad Report224GH19CS004- AMRUTHA M VAinda não há avaliações
- Printout DocumentDocumento63 páginasPrintout Documentsuchdev darshanAinda não há avaliações
- Android Industrail Training ReportDocumento8 páginasAndroid Industrail Training ReportAnkit KarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Computing Lab ManualDocumento63 páginasMobile Computing Lab Manualsuchdev darshanAinda não há avaliações
- Korunas_flayers_guidsireDocumento2 páginasKorunas_flayers_guidsirealejandroleaharneeAinda não há avaliações
- Aromal Valero - AbodingDocumento2 páginasAromal Valero - Abodingnitish365Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 MCADDocumento36 páginasUnit 2 MCADNisarg ShrimaliAinda não há avaliações
- Bogsucker Cutcherries RehideDocumento2 páginasBogsucker Cutcherries RehideShagun ShettyAinda não há avaliações
- Unconvolutely Underscrupulous CraftsmenshipDocumento2 páginasUnconvolutely Underscrupulous CraftsmenshipdevzAinda não há avaliações
- Android Interview Questions, NKNKJNDocumento49 páginasAndroid Interview Questions, NKNKJNHassan KhwilehAinda não há avaliações
- Android StudioDocumento34 páginasAndroid StudioJayachandra Jc100% (1)
- Mad Lab Manual - FormattedDocumento56 páginasMad Lab Manual - FormattedasfgashjhkAinda não há avaliações
- UB - Android Development Boot Camp 01Documento60 páginasUB - Android Development Boot Camp 01Ronald RamosAinda não há avaliações
- AP Narender Singh LabDocumento64 páginasAP Narender Singh LabNarender Singh ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Android Programming For Beginners: The Ultimate Android App Developer's GuideNo EverandAndroid Programming For Beginners: The Ultimate Android App Developer's GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Android For Beginners. Developing Apps Using Android StudioNo EverandAndroid For Beginners. Developing Apps Using Android StudioNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- ABAP Select For All Entries What Is Happening in SQL ServerDocumento10 páginasABAP Select For All Entries What Is Happening in SQL ServerVaibhav SambareAinda não há avaliações
- JCL ExampleDocumento8 páginasJCL ExampleSathish JanarthananAinda não há avaliações
- iR-ADV-C3800 BrochureDocumento4 páginasiR-ADV-C3800 Brochuresanjay4u4allAinda não há avaliações
- PTEq-X v1.0.2 User ManualDocumento10 páginasPTEq-X v1.0.2 User ManualRbn DchsnAinda não há avaliações
- Assembly Program's FileDocumento30 páginasAssembly Program's FileHirdesh80% (5)
- Understanding the Importance of SAP LandscapeDocumento3 páginasUnderstanding the Importance of SAP LandscapeMohammed Nawaz ShariffAinda não há avaliações
- 1493266679p6m35 EtextDocumento21 páginas1493266679p6m35 EtextMuskan Roy 16Ainda não há avaliações
- Cloning DatabaseDocumento6 páginasCloning Databaseapi-3745837100% (2)
- C# Flicker Free AnimationDocumento10 páginasC# Flicker Free AnimationsatyendrashahAinda não há avaliações
- 06 20R300 1 C200 Hardware ConfigurationDocumento44 páginas06 20R300 1 C200 Hardware Configurationavandetq15Ainda não há avaliações
- Word AssignDocumento9 páginasWord AssignSandip PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Sinamics g120 at s7-300400-pn Doku v23 en PDFDocumento67 páginasSinamics g120 at s7-300400-pn Doku v23 en PDFGlauco SantiagoAinda não há avaliações
- DDCA Ch6Documento129 páginasDDCA Ch6Dheer MehrotraAinda não há avaliações
- FSUIPC Lua LibraryDocumento41 páginasFSUIPC Lua LibraryCaptain XrayAinda não há avaliações
- LVP605 Series User S Manual ENGDocumento42 páginasLVP605 Series User S Manual ENGEntonces Dijo Bla Bla MoisésAinda não há avaliações
- OS Concepts Chapter 1 Solutions To Practice Exercises Part 1Documento2 páginasOS Concepts Chapter 1 Solutions To Practice Exercises Part 1Alfred Fred100% (2)
- Testing SyallabusDocumento10 páginasTesting Syallabusudaychandu520Ainda não há avaliações
- U Kbuild PDFDocumento4 páginasU Kbuild PDFOkecha StepheneAinda não há avaliações
- Configure Your New Slackware System: Create A User AccountDocumento11 páginasConfigure Your New Slackware System: Create A User Accountina_mitrovicAinda não há avaliações
- COMP1 Lab Act4. Algorithm Loop CS For Do While v2Documento5 páginasCOMP1 Lab Act4. Algorithm Loop CS For Do While v2Joshua SedaAinda não há avaliações
- Scanner Tool SummaryDocumento3 páginasScanner Tool Summaryraspberries1Ainda não há avaliações
- Fujifilm LTO Ultrium SeminarDocumento46 páginasFujifilm LTO Ultrium SeminarLeandro MussoAinda não há avaliações
- RightScale State of The Cloud Report 2013Documento15 páginasRightScale State of The Cloud Report 2013arms8586Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual Object Oriented Programming: University of Lahore, Sargodha CampusDocumento29 páginasLab Manual Object Oriented Programming: University of Lahore, Sargodha CampusM.Bilal ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- AlabangClearance 12618Documento13 páginasAlabangClearance 12618Joseph Gene LalasAinda não há avaliações
- 3BHS233287 E80 AbbDocumento15 páginas3BHS233287 E80 Abbsabah nooriAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Manual For Android How To Program 3rd Edition Deitel 0134444302 9780134444307Documento5 páginasSolution Manual For Android How To Program 3rd Edition Deitel 0134444302 9780134444307rosaAinda não há avaliações
- QualiTest - Network Functions Virtualization - Testing Best Practices - QualiTestDocumento15 páginasQualiTest - Network Functions Virtualization - Testing Best Practices - QualiTestSajad PourmohseniAinda não há avaliações
- RF 6705 Sw001 Tactical Chat Ip DsDocumento4 páginasRF 6705 Sw001 Tactical Chat Ip Dsruslan100% (1)
- Object-Oriented Programming (Oop) With C++Documento13 páginasObject-Oriented Programming (Oop) With C++Sahil AliAinda não há avaliações