Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
An Go La
Enviado por
cbellsnlDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
An Go La
Enviado por
cbellsnlDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Angola
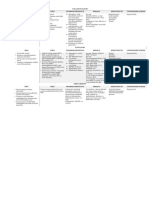
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 16,557 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Africa, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 3,082 (2006) undernutrition
260 260 Causes of neonatal
Unmet need for family planning (%) ---
Births (000) 792 (2006) Obstructed labor Contraceptive
Injuries Pneumonia deaths Abortion 6
250 1% 25% Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) --- Anaemia 4% prevalence rate Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 29 (2006) HIV/AIDS
Diarrhoea 5% 4%
Congenital 5% 4% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 260 (2006) 200 2% Tetanus 6% (1 or more) 66 Pregnancy
Other 7% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) ---
Measles Hypertensive Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 154 (2006) 5% disorders Haemorrhage 45 Birth
150 Asphyxia 24% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 34%
at birth
54 (2000) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) ---, ---, ---
22% *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 206 (2006) 100 Malaria
Sepsis/Infections,
8% Preterm 25% Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) --- Exclusive
87 including AIDS 11 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 1,400 (2005) 50 breastfeeding
MDG Target Other 16%
12 (2005) Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) 17% Infection 29% Other causes
48
0 Diarrhoea
Total maternal deaths 11,000 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 19% 30%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 51 (2001) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 77 (2001) 100 100 100
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 8 (2001) Low birthweight incidence (%) 12 (2000) 80 80 80
80
66
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
45
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses
40 40 40
At least one dose Two doses 23
100 100 100 20 20 20
88
94 100 75 77 79
80 80 80 68 0 0
64 65 2001 1996 2001 1983 1988 1993 1998 2003 2006
60 60 60 68 MICS MICS MICS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
37
40 40 40
28
20 20 11 20 0
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
0 0 0
0 0 0
1996 2001 2001 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
MICS MICS MICS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100 100
CHILD HEALTH
80 75 80 80
61
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 53 60 56
60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs transmission of HIV 40 40
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 36 40 29 31 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib
23
18 16
20 20 20
100 25
0 0 0
80 20 1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 15 14 2001
Percent
Percent
48 No data MICS
40 44
10 POLICIES SYSTEMS
20 5
3 Coverage gap (%) 55
International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 Substitutes No Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 38 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 1.6
Source: WHO/UNICEF Other NS Other NS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea No poorest-wealthiest (%) 25
% of total government expenditure (%) 4 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics No Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 21 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age No
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.4 (2004)
100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Partial Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 per child (US$) 11 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
Angola
58
60 60 life saving interventions Yes Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Percent
Percent
neonatal health per live birth (US$) 16 (2005)
No data Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
40 32 40
Convention 183 No National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
20 20 services (% of recommended minimum) ---
Specific notification of maternal deaths Yes
0 0
2001
MICS
2001
MICS
Countdown to 2015
2008 Report
Você também pode gostar
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Guinea BissauDocumento1 páginaGuinea BissaucbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Burkina FasoDocumento1 páginaBurkina FasocbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ye MenDocumento1 páginaYe MencbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Country Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in FijiDocumento4 páginasCountry Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in Fijipaperpin27Ainda não há avaliações
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocumento4 páginasLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Ainda não há avaliações
- Maternal CZEDocumento4 páginasMaternal CZEYajie LuoAinda não há avaliações
- Major causes of death in children under five globally in 2008Documento1 páginaMajor causes of death in children under five globally in 2008raissa leeAinda não há avaliações
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Documento35 páginasReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationAinda não há avaliações
- Child Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaDocumento24 páginasChild Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaSolomon JosephAinda não há avaliações
- G Minaccia Parto PretDocumento64 páginasG Minaccia Parto PretEleonora Francesco Consalvo DonzelliAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocumento2 páginasNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaAinda não há avaliações
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Documento63 páginasKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiAinda não há avaliações
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalDocumento5 páginasThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapDocumento84 páginasEssential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapShane Lim GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Infertility Among Productive AgeDocumento18 páginasInfertility Among Productive Ageari gunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Jamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsDocumento4 páginasJamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsZineil BlackwoodAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDocumento2 páginasMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- STD Clinical CliniciansDocumento69 páginasSTD Clinical Cliniciansayush231195Ainda não há avaliações
- Par To GraphDocumento15 páginasPar To GraphcarAinda não há avaliações
- Pakistan 2015Documento2 páginasPakistan 2015shujahkianiAinda não há avaliações
- Situation Analysis (1) FinalDocumento5 páginasSituation Analysis (1) Finalsitikantha sahooAinda não há avaliações
- WOMEN AND CHILD HEALTH GUIDEDocumento45 páginasWOMEN AND CHILD HEALTH GUIDEjulianaAinda não há avaliações
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Documento2 páginasMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiAinda não há avaliações
- HMIS Data Analysis - 2015 - 16 Karnataka - BangaloreDocumento27 páginasHMIS Data Analysis - 2015 - 16 Karnataka - BangaloreholysaatanAinda não há avaliações
- Cuba Cancer Profile 2020Documento2 páginasCuba Cancer Profile 2020axelAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition LCADocumento2 páginasNutrition LCAShernia EliboxAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisDocumento2 páginasPROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisEpie marcAinda não há avaliações
- Nicaragua: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 6 150 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 29 000Documento1 páginaNicaragua: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 6 150 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 29 000Jordan SamputonAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer Burden and Trends in SudanDocumento2 páginasCancer Burden and Trends in SudanmohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherDocumento16 páginasMaternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherFatima IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Maharashtra - Disease Burden ProfileDocumento4 páginasMaharashtra - Disease Burden ProfileMeghdoot DeherkarAinda não há avaliações
- 24 Angola Fact SheetsDocumento2 páginas24 Angola Fact SheetsHigidio EduardoAinda não há avaliações
- WHO CancerReport 2020 MEXDocumento2 páginasWHO CancerReport 2020 MEXAldo Leonardo De Jesus GarduzaAinda não há avaliações
- Cervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020Documento2 páginasCervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020nour abdallaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Infertility, Evaluations, and Treatment OptionsDocumento112 páginasUnderstanding Infertility, Evaluations, and Treatment OptionswaleedaliAinda não há avaliações
- Contraception HandoutDocumento4 páginasContraception HandoutKazia BryantAinda não há avaliações
- Poster CFRDocumento1 páginaPoster CFRIka Rara RositaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocumento2 páginasNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoAinda não há avaliações
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudDocumento52 páginasStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640Ainda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- The GambiaDocumento1 páginaThe GambiacbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ye MenDocumento1 páginaYe MencbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ye MenDocumento1 páginaYe MencbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDocumento1 páginaTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Sierra LeoneDocumento1 páginaSierra LeonecbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Burkina FasoDocumento1 páginaBurkina FasocbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Ben inDocumento1 páginaBen incbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- DemographicsDocumento1 páginaDemographicscbellsnlAinda não há avaliações
- Valgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsDocumento2 páginasValgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsiSmayli (smyle-smayl)Ainda não há avaliações
- Tuberculous MeningitisDocumento23 páginasTuberculous MeningitisAsma KhmAinda não há avaliações
- "Double Stigma": Forced Sterilization of Women Living With HIV in Kenya and NamibiaDocumento4 páginas"Double Stigma": Forced Sterilization of Women Living With HIV in Kenya and NamibiaPopulation & Development Program (PopDev)Ainda não há avaliações
- AIDS Taught Me How To Scream (Not Yodel!)Documento2 páginasAIDS Taught Me How To Scream (Not Yodel!)larrybobsfAinda não há avaliações
- Polansky SKRRT PDFDocumento619 páginasPolansky SKRRT PDFAstrud Labrador100% (1)
- CHN Compilation of ExamsDocumento59 páginasCHN Compilation of ExamsSteph100% (1)
- Tugas Prof08Documento9 páginasTugas Prof08dianaAinda não há avaliações
- HTTP Healthmedicinet Com II 2013 10 PDFDocumento314 páginasHTTP Healthmedicinet Com II 2013 10 PDFtuni santeAinda não há avaliações
- Antenatal AssessmentDocumento7 páginasAntenatal Assessmentmohapatra devAinda não há avaliações
- Handout1 - Normal Changes of AgingDocumento3 páginasHandout1 - Normal Changes of Agingpissednachos0123Ainda não há avaliações
- AVN19941999Documento96 páginasAVN19941999Kate SquiresAinda não há avaliações
- The Corrupted Blood IncidentDocumento13 páginasThe Corrupted Blood IncidentGabriel Andrei StanAinda não há avaliações
- Bethesda Health Personnel Provider Services Service ContractDocumento3 páginasBethesda Health Personnel Provider Services Service ContractKi RilAinda não há avaliações
- Thurstone Scaling: The Method of Equal-Appearing IntervalsDocumento10 páginasThurstone Scaling: The Method of Equal-Appearing IntervalsMuthukumar KalyanaramanAinda não há avaliações
- IDSPDocumento5 páginasIDSPShreyaswi M KarthikAinda não há avaliações
- The Future of Tourism: Planning for Climate Change and Health IssuesDocumento8 páginasThe Future of Tourism: Planning for Climate Change and Health IssuesPhil Jayve50% (2)
- 5096 w06 QP 1Documento16 páginas5096 w06 QP 1mstudy123456Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 - HBC207 - HIV-AIDS-Mukondombera 2013Documento50 páginas1 - HBC207 - HIV-AIDS-Mukondombera 2013HeruAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To The IDDRSDocumento772 páginasIntroduction To The IDDRSccentroamérica100% (1)
- DR Akin Moses Chief Consultant & Head, Family Medicine, NationalDocumento44 páginasDR Akin Moses Chief Consultant & Head, Family Medicine, Nationalayodeji78Ainda não há avaliações
- Callen Lorde TG ProtocolsDocumento43 páginasCallen Lorde TG ProtocolsafsdfasdfasddfaoewrerAinda não há avaliações
- Persuasive techniques in sentences on teenage pregnancy and sex educationDocumento2 páginasPersuasive techniques in sentences on teenage pregnancy and sex educationMs-Devashia T WhyteAinda não há avaliações
- OSHAD-SF - TG - New and Expectant Mothers - A Guide For Employers - V3.1 EnglishDocumento30 páginasOSHAD-SF - TG - New and Expectant Mothers - A Guide For Employers - V3.1 EnglishNiel Brian VillarazoAinda não há avaliações
- Ipr F300 Re V12.0Documento6 páginasIpr F300 Re V12.0gtmlpatelAinda não há avaliações
- Respirasi. 1 (1) :22.: Daftar PustakaDocumento2 páginasRespirasi. 1 (1) :22.: Daftar PustakaMichael KichAinda não há avaliações
- Gilead FCA LawsuitDocumento68 páginasGilead FCA LawsuitAlex Kacik100% (5)
- Christian Response To AIDS, Homophobia and Violence Against WomenDocumento62 páginasChristian Response To AIDS, Homophobia and Violence Against WomenbobbyramakantAinda não há avaliações
- Male and Female Condom GuideDocumento10 páginasMale and Female Condom GuideDevi Claudia PalupiAinda não há avaliações
- Ishola & OlleyDocumento9 páginasIshola & Olleypavlov2Ainda não há avaliações
- Hiv / Aids Education & Prevention ProgramDocumento36 páginasHiv / Aids Education & Prevention ProgramselvianaAinda não há avaliações
- What No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodNo EverandWhat No One Tells You: A Guide to Your Emotions from Pregnancy to MotherhoodNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (30)
- Menopause: All you need to know in one concise manualNo EverandMenopause: All you need to know in one concise manualNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (11)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- The Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismNo EverandThe Menopause Manifesto: Own Your Health With Facts and FeminismNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (18)
- Breaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodNo EverandBreaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (33)
- Younger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondNo EverandYounger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (110)
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouNo EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfNo EverandBrain Body Diet: 40 Days to a Lean, Calm, Energized, and Happy SelfNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- A Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersNo EverandA Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (71)
- Perimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopauseNo EverandPerimenopause Power: Navigating your hormones on the journey to menopauseNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)No EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Hypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthNo EverandHypnobirthing Meditations: Relaxation And Mindfulness Techniques For Expectant Mothers To Experience A Natural And Positive ChildbirthNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- All in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayNo EverandAll in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- The Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenNo EverandThe Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (153)
- I'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionNo EverandI'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (123)
- Women, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainNo EverandWomen, Food, And Hormones: A 4-Week Plan to Achieve Hormonal Balance, Lose Weight, and Feel Like Yourself AgainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (14)
- The 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthNo EverandThe 21-Day Self-Love Challenge: Learn How to Love Yourself Unconditionally, Cultivate Confidence, Self-Compassion and Self-WorthAinda não há avaliações
- I'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItNo EverandI'm So Effing Hungry: Why We Crave What We Crave – and What to Do About ItAinda não há avaliações
- Bumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondNo EverandBumpin': The Modern Guide to Pregnancy: Navigating the Wild, Weird, and Wonderful Journey From Conception Through Birth and BeyondNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (38)
- Sacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyNo EverandSacred Womb Healing Meditation Divine feminine alignment: heal ancestral traumas deep wounds, release blocked sexual energies, flow to creativity, overcome the energies of birthing, joy love happyNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteNo EverandThe Strength and Conditioning Bible: How to Train Like an AthleteAinda não há avaliações
- Dark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnoreNo EverandDark Feminine Energy: Free Your Femme Fatale Ignite Your Irresistible Allure Through Mystique, Sexuality, Femininity, and Elegance to Become the Dark Diva No One Can IgnoreNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Mindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondNo EverandMindful Birthing: Training the Mind, Body, and Heart for Childbirth and BeyondNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (24)
- Skinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!No EverandSkinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Nota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (488)
- After Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindNo EverandAfter Birth: What Nobody Tells You - How to Recover Body and MindNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- 9 Months Is Not Enough: The Ultimate Pre-Pregnancy Checklist to Create a Baby-Ready Body and Build Generational HealthNo Everand9 Months Is Not Enough: The Ultimate Pre-Pregnancy Checklist to Create a Baby-Ready Body and Build Generational HealthAinda não há avaliações
- The Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and ChildbirthNo EverandThe Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and ChildbirthNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (21)
- The Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesNo EverandThe Better Period Food Solution: Eat Your Way to a Lifetime of Healthier CyclesAinda não há avaliações