Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Assignment ADC
Enviado por
Vivek UpadhyayDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Assignment ADC
Enviado por
Vivek UpadhyayDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1.
Show that a band limited signal of finite energy which has no frequency components higher than
fm Hz is completely described by specifying values of the signals at instants of time separated by
1/2fm seconds and also show that if the instantaneous values of the signals are separated by
intervals larger than fm seconds, they fail to describe the signal. A bandpass signal has spectral
range that extends from 20 to 82 kHz.
Find the acceptable range of sampling frequency fs*
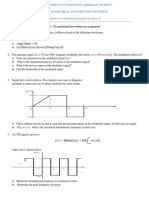
2. A bandlimited signal x(t) is sampled by a train of rectangular pulsed of width and period T.
(i)Find an expression for the sampled signal.
(ii)Determine the spectrum of the sampled signal and sketch it.
3. What is aliasing and how it is reduced?
4. A PCM system uses a uniform quantizer followed by a v bit encoder. Show that rms signal to
quantization noise ratio is approximately given as (1.8 + 6v) dB.
5. A television signal having a bandwidth of 4.2 MHz is transmitted using binary PCM system. Given
that the number of quantization level is 512. Determine:
(i)Code word length
(ii)Transmission bandwidth
(iii)Final bit rate
(iv)Output signal to quantization noise ratio.
6. The information in an analog signal voltage waveform is to be transmitted over a PCM system
with an accuracy of 0.1% (full scale). The analog voltage waveform has a bandwidth of 100 Hz
and an amplitude range of 10 to + 10 volts.
(i)Find the minimum sampling rate required.
(ii)Find the number of bits in each PCM words.
(iii)Find minimum bit rate required in the PCM signal.
(iv)Find the minimum absolute channel bandwidth required for the transmission of the PCM
signal.
7. A delta modulator system is designed to operate at five times the Nyquist rate for a signal
having a bandwidth equal to 3 kHz bandwidth. Calculate the maximum amplitude of a 2 kHz
input sinusoidal signal for which the delta modulator does not have slope over load. Given that
the quantizing step size is 250 mV. Also, derive the formula that you use.
8. A low pass signal of 3 kHz bandwidth and amplitude over 5 volts to + 5 volts range is sampled
at Nyquist rate and converted to 8-bit PCM using uniform quantization. The mean squared value
of message signal is 2 Volts-squared. Determine the following:
(i)the normalized power for quantization noise.
(ii)The bit transmission rate.
(iii)The signal to quantization noise ratio in dB.
(iv)Derive the expression used in (i) and (ii)
9. If a voice frequency signal is sampled at the rate of 32,000 samples/sec and characterized by
peak value of 2 Volts, determine the value of step size to avoid slope overload. What is
quantization noise power Nq and corresponding SNR? Assume bandwidth of signal as 4 kHz.
10. Explain Delta modulation in detail with suitable diagram. Also, explain ADM and compare its
performance with DM.
11. What is the slope overload distortion and granular noise in delta modulation and how it is
removed in ADM.
12. Explain Differential pulse code modulation.
13. Derive Power Spectral Density (PSD) of NRZ Polar Format.
14. Derive Power Spectral Density (PSD) of the Manchester Format.
15. Explain Eye Diagram.
16. Explain the Nyquist criteria for distortionless baseband binary transmission.
17. Explain ISI. Give Nyquist criterion for zero ISI raised cosine spectrum.
18. Find out the power spectral density of NRZ and AMI signal format.
19. Draw and explain Eye pattern diagram.
20. Explain Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization procedure, with a suitable example.
21. Verify whether two signals are orthogonal over one time period of the signal with smallest
frequency signal:
X1(t) = Cos 2ft and X2(t) = Sin 2ft
X1(t) = Cos 2ft and X2(t) = Cos (2ft + /3)
X1(t) = Cos 2ft and X2(t) = Cos (4ft + /4)
X1(t) = Sin 4ft and X2(t) = - Cos (ft /6)
22. Explain correlation receiver and Maximum Likelihood detection process.
23. Discuss properties of the Matched Filter. Explain how SNR maximization and minimization of
average symbol error probability can be achieved using a Matched Filter receiver?
Você também pode gostar
- Central College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiDocumento8 páginasCentral College of Engineering & Management Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Course:-B.E. (6 Sem.) Subject: Communication System-IiqweweAinda não há avaliações
- BEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsDocumento3 páginasBEC Communication Theory Previous QuestionsSiam hasanAinda não há avaliações
- QB 2Documento10 páginasQB 2Abhishek RaoAinda não há avaliações
- QB 2Documento10 páginasQB 2Abhishek RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2Documento2 páginasAssignment 2somojit dasAinda não há avaliações
- Nemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1Documento7 páginasNemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1pauliAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Communication CSP-310 Homework Assignment 2: (Submission Deadline: October 28, 2017)Documento1 páginaWireless Communication CSP-310 Homework Assignment 2: (Submission Deadline: October 28, 2017)Sachin AkhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Practice QuestionsDocumento4 páginasPractice Questionspratik shuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015Documento3 páginasDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 3012 Digital Communication-Monsoon 2015shreyas_stinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Question BankDocumento6 páginasQuestion Banksweetkhushboo786_592Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 4-SolutionDocumento11 páginasTutorial 4-SolutionZaidi Mat ZainuddinAinda não há avaliações
- DCDocumento8 páginasDCharshit420Ainda não há avaliações
- DC-Tutorial Sheet 2Documento2 páginasDC-Tutorial Sheet 2Allanki Sanyasi Rao100% (2)
- DC Tutorial Sheet 1Documento2 páginasDC Tutorial Sheet 1Sabir SankhlaAinda não há avaliações
- TutorialDocumento2 páginasTutorialthevin arokiarajAinda não há avaliações
- Digital CommunicationDocumento16 páginasDigital CommunicationAli Najim Al-AskariAinda não há avaliações
- Analog CommunicationsDocumento6 páginasAnalog CommunicationsSri KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Extra Tut 5 SolsDocumento4 páginasExtra Tut 5 SolsNOMPUMELELO MTHETHWAAinda não há avaliações
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocumento11 páginasAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise Chap 2Documento3 páginasExercise Chap 2chantinh_hd190Ainda não há avaliações
- Answer 1.1%Documento29 páginasAnswer 1.1%Anonymous 7puVtTdpVAinda não há avaliações
- Iecep EsatDocumento29 páginasIecep EsatIvy Cee100% (1)
- Numericals DCNDocumento2 páginasNumericals DCNShanzay AbbasiAinda não há avaliações
- 2022 (E.s.) - 2Documento2 páginas2022 (E.s.) - 2Nikhil Kumar JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- ExtraDocumento44 páginasExtraJosephine Pinlac Junio100% (1)
- Baseband Questions StudentsDocumento3 páginasBaseband Questions StudentsRishi JhaAinda não há avaliações
- VI Sem ECE AssignmentsDocumento11 páginasVI Sem ECE AssignmentsManoj VarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet SamplingDocumento3 páginasSheet SamplingAhmed MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- DCS SolnDocumento6 páginasDCS SolnSandeep Kumar100% (1)
- Chuong 5 - 6 - Full - ENDocumento4 páginasChuong 5 - 6 - Full - ENKỳ TrầnAinda não há avaliações
- Work Sheet 2: School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocumento1 páginaWork Sheet 2: School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringfikaduAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless PregtuFINAL 2018Documento7 páginasWireless PregtuFINAL 2018Tej SarvaiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasTutorial 1 AssignmentbaaaaNDSAinda não há avaliações
- Data Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.HaniyDocumento8 páginasData Communication: By:Eng - Alaa I.Haniypömo cAinda não há avaliações
- Modulation Techniques For Mobile RadioDocumento3 páginasModulation Techniques For Mobile RadioAbhinav0% (1)
- Comm AssntIIDocumento6 páginasComm AssntIIkalAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Documento4 páginasAssignment 3 Communication Theory EE304: Submit QTS.: 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 11Sourav kumar MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.10 Practice Set: Review QuestionsDocumento4 páginas3.10 Practice Set: Review QuestionsscpAinda não há avaliações
- AssignmentDocumento5 páginasAssignmentpaper.2014Ainda não há avaliações
- DCS Tutorial Ii NewDocumento4 páginasDCS Tutorial Ii NewARTHIAinda não há avaliações
- Iecep EsatDocumento29 páginasIecep EsatChaeyoung YooAinda não há avaliações
- Solution For Assignment 3Documento3 páginasSolution For Assignment 3Faizan 'Fezar' RabbaniAinda não há avaliações
- Adc QB 2020Documento14 páginasAdc QB 2020priyaroopaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento1 páginaAssignment 1Sabir SankhlaAinda não há avaliações
- T2 BookDocumento4 páginasT2 Bookirain04Ainda não há avaliações
- Digi Comm Model QP P1Documento3 páginasDigi Comm Model QP P1bku14677Ainda não há avaliações
- Chhhpppttteeerrr 55555Documento12 páginasChhhpppttteeerrr 55555S Ahson ASAinda não há avaliações
- T3-Physical LayerDocumento95 páginasT3-Physical Layerutkarsh.shrivastav202002Ainda não há avaliações
- Iii Part A BDocumento115 páginasIii Part A BDivya SreeAinda não há avaliações
- ECE4313 Worksheet EndsemDocumento5 páginasECE4313 Worksheet EndsemBereketeab ZinabuAinda não há avaliações
- AllProblemSets PDFDocumento16 páginasAllProblemSets PDFMaxamed CabdiraximAinda não há avaliações
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationAinda não há avaliações
- Error-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsNo EverandError-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsAinda não há avaliações
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDAinda não há avaliações
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneNo EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneAinda não há avaliações
- Telescope Trainee HagarDocumento2 páginasTelescope Trainee HagarVivek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- DispersionDocumento10 páginasDispersionVivek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarDocumento6 páginasFiber Optics: Prof. R.K. ShevgaonkarVivek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Disease: Benign THE Anus, Rectum and ColonDocumento6 páginasDisease: Benign THE Anus, Rectum and ColonVivek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Forensics: Omveer SinghDocumento74 páginasMobile Forensics: Omveer SinghVivek UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Balfour Castle EstateDocumento20 páginasBalfour Castle EstatejahumphriesAinda não há avaliações
- Drinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2Documento31 páginasDrinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2josephsedAinda não há avaliações
- BIO CH04 FoundationsDocumento12 páginasBIO CH04 FoundationsDyuana Stevenson0% (1)
- 329 Cryogenic Valves September 2016Documento8 páginas329 Cryogenic Valves September 2016TututSlengeanTapiSopanAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Documento4 páginasWelcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Niño Jay C. GastonesAinda não há avaliações
- Fractal Approach in RoboticsDocumento20 páginasFractal Approach in RoboticsSmileyAinda não há avaliações
- Table of SpecificationDocumento2 páginasTable of SpecificationAya AlisasisAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Colonial Philippine ArtDocumento5 páginasPre-Colonial Philippine Artpaulinavera100% (5)
- BEGONTES, MESSY PORTFOLIO BATCH 2023 Episode 1-7Documento34 páginasBEGONTES, MESSY PORTFOLIO BATCH 2023 Episode 1-7Messy S. BegontesAinda não há avaliações
- 2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFDocumento782 páginas2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFAnoif Naputo Aidnam100% (1)
- Debit Note and Credit NoteDocumento2 páginasDebit Note and Credit Noteabdul haseebAinda não há avaliações
- Differentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2Documento186 páginasDifferentialequations, Dynamicalsystemsandlinearalgebra Hirsch, Smale2integrationbyparths671Ainda não há avaliações
- OXE Training - Complete (2011)Documento94 páginasOXE Training - Complete (2011)Dhexter Villa75% (4)
- MOOT 1 (Principal Sir)Documento3 páginasMOOT 1 (Principal Sir)vaibhav jainAinda não há avaliações
- Osssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001Documento7 páginasOsssc JR Clerk Odia Paper 2015 - 20171207 - 0001songspk100Ainda não há avaliações
- A Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceDocumento16 páginasA Guide To Energy Efficiency ComplianceOARIASCOAinda não há avaliações
- People Vs CorreaDocumento2 páginasPeople Vs CorreaRmLyn Mclnao100% (1)
- Thermo Exam QuestionsDocumento4 páginasThermo Exam QuestionssiskieoAinda não há avaliações
- BE 503 - Week 1 - Analysis 7.18.11Documento6 páginasBE 503 - Week 1 - Analysis 7.18.11dwoodburyAinda não há avaliações
- HSE Inspection Report-07Documento32 páginasHSE Inspection Report-07najihahAinda não há avaliações
- Ev Conversion PDFDocumento2 páginasEv Conversion PDFShannonAinda não há avaliações
- JapanDocumento15 páginasJapanceazar BugtongAinda não há avaliações
- Visco GraphDocumento4 páginasVisco GraphwamlinaAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Documento79 páginasRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoAinda não há avaliações
- Times Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Documento49 páginasTimes Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Joseph HoukAinda não há avaliações
- Jibachha's Textbook of Animal Health Volume-IIDocumento16 páginasJibachha's Textbook of Animal Health Volume-IIjibachha sahAinda não há avaliações
- 1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018Documento5 páginas1. Mạch điện đồng hồ santafe 2014-2018PRO ECUAinda não há avaliações
- AI LabDocumento17 páginasAI LabTripti JainAinda não há avaliações
- BasicsDocumento1 páginaBasicsRishi Raj100% (1)