Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chapter 18 Vocab: Condyle Articular Cartilage Medial Meniscus Lateral Meniscus Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Enviado por
mph440Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 18 Vocab: Condyle Articular Cartilage Medial Meniscus Lateral Meniscus Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Enviado por
mph440Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 18 Vocab
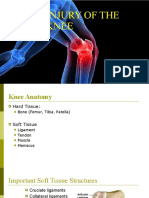
1. Condyle – the rounded prominence found at the point of articulation with another
bone
2. Articular cartilage – the thin layer of connective tissue over the ends of long
bones
3. Medial meniscus – cartilage in the knew between the femoral condyle and the
medial tibial plateau
4. Lateral meniscus- cartilage in the knee between the lateral femoral condyle and
the lateral tibial plateau
5. Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) – a ligament in the knee that attaches to the
anterior aspect of the tibial plateau restricting anterior movement of the tibia on
the femur
6. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) - a ligament in the knees that attaches to the
posterior aspect of the tibial plateau restricting posterior movement of the tibia on
the femur
7. Patella - kneecap
8. Crepitus- a grinding noise or sensation within a joint
9. Epiphyseal plate – the growth plate at the end of the bone
10. Valgus – outward bending or twisting force
11. Varus – inward bending or twisting force
Notes:
- 4 main ligaments (bone to bone)
o Anterior cruciate
o Posterior cruciate
o Medial collateral
o Lateral collateral
- Tendons to know
o Patella tendon
o Tendon of quadriceps
- Q angle – angle of pelvis with knee
o The greater the angle the more strain there is on the knees –
greater angle on woman so they can pop babies out
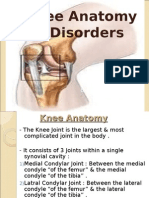
- Condyle
o Moon shaped
o Cushion
o Keeps bones from grinding
o End of bone that helps cushion in joint
- Meniscus
Has left or right
Can be torn easily
Between condyle
Cushion protect bone from bone
If gone – arthritis comes sooner
- Cartilage – connective tissue
- Patellofemoral Problems
Aching pain in front knee
Knee giving away
Crepitus
Walking up and down stairs – painful
Treatment:
Shoe insert to support the arch or low dye taping
Stretching
Tape the patella
Bracing
Rehab
- Patellar Tendonitis
Inflammation of the patellar tendon
Also known as jumpers knee
Anterior knee pain
Local tenderness
Over use
Treatment:
Give time to heal
Cycling and swimming – gives it time to
heal
Stretching
Ice
Bracing and taping
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) sprain
Caused by stretching and Valgus
Limited motion in full flexion and extension
Swelling
Tenderness
See table 18 –1
Treatment:
PRICE
Rehab
Surgery
- Chondromalacia
o Scrapping of under side of knee
o Maybe misalignment
o Also called movie sign
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) sprain
• Varus
• Tenderness to palpation
• Pain and laxity
• Treatment: see treatment for MCL
- Torn Anterior cruciate ligament
• Pop followed by swelling within the joint cavity
• Anterior drawer test – the athlete is in a supine position with the
knee bent to 90 degrees. The examiner applies anterior force to
the proximal tibia excessive movement may indicate ACL
damage, checks for torn ACL and ligaments in the ankle
• Ligament may be torn
• Treatment:
Splinting, icing, and compressive wrapping
Crutches
Surgery
- Meniscus Tears
• Mild knee swelling – takes hours
• Pain
• Popping
• Locking
• Giving away of knee
• Treatment:
Ice
Compressive wrap
Crutches
Knee supports
Physical therapy
Anti inflammation meds
Surgery
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
• Hyperflexion and serious accident
• Sag test
• MRI
• Treatment:
PRICE
Physical therapy
Knee brace
- Osgood- Schlatter Condition
o The quadriceps will exert undue
pressure on the growth center of the
tibia
o Usually moves too quick
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Inflammation of the Iliotibial band
Head of femur irritates the band
Band is too tight
Over use injury
Treatment:
Proper foot wear
Icing
Stretching
Training program
Você também pode gostar
- Knee Injury Seminar 2015Documento96 páginasKnee Injury Seminar 2015Aqilah Ab RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Warning: You May Want To Look Away at Times!: Youtube VideoDocumento47 páginasWarning: You May Want To Look Away at Times!: Youtube VideoRaffy B. MabilingAinda não há avaliações
- Knee ExaminationDocumento14 páginasKnee ExaminationAsimAinda não há avaliações
- Knee&Foot Part1Documento28 páginasKnee&Foot Part1SarkawtAinda não há avaliações
- Injuri & Trauma Saat Olahraga & Penatalaksanaannya (DR - Arief Faisal, SP - OT)Documento53 páginasInjuri & Trauma Saat Olahraga & Penatalaksanaannya (DR - Arief Faisal, SP - OT)Wulan Nindira WarasudiAinda não há avaliações
- Musculo-Skeletal System: Etiology: MobilityDocumento6 páginasMusculo-Skeletal System: Etiology: MobilityFev BanataoAinda não há avaliações
- MUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingDocumento82 páginasMUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingJan Clarisse RamosAinda não há avaliações
- AnatomyDocumento6 páginasAnatomyVarsha Mol MohananAinda não há avaliações
- Sprains, Strains, Dislocations & Subluxations, Carpal Tunnel & Other Related InjuriesDocumento26 páginasSprains, Strains, Dislocations & Subluxations, Carpal Tunnel & Other Related InjuriesLydia Lopz MsnrncdAinda não há avaliações
- TractionDocumento20 páginasTractionCharinelle MolinaAinda não há avaliações
- MCHT Leading and Managing Your Organisation Musculoskeletal Education IC3Documento49 páginasMCHT Leading and Managing Your Organisation Musculoskeletal Education IC3nickmirad2Ainda não há avaliações
- "Hip Dislocation": Short CaseDocumento38 páginas"Hip Dislocation": Short CaseGusty BahyAinda não há avaliações
- Common Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalDocumento71 páginasCommon Sports Injuries: Ukris Gunadham, MD, FRCOST Department of Orthopaedics Trang HospitalMohammed SaqoorAinda não há avaliações
- S T O P: Ports Rauma and Veruse ReventionDocumento37 páginasS T O P: Ports Rauma and Veruse ReventionNabiha AjmalAinda não há avaliações
- Musculoskeletal Exam - General Principles and Detailed Review of Knee and ShoulderDocumento48 páginasMusculoskeletal Exam - General Principles and Detailed Review of Knee and ShoulderGokul Krishna-21Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 - Knee DisordersDocumento85 páginas5 - Knee Disordersraed faisalAinda não há avaliações
- Qindeel Fatima Ankle Sprain TreatmentDocumento19 páginasQindeel Fatima Ankle Sprain TreatmentQindeel FatimaAinda não há avaliações
- DegenerativeDiskDisease (HNP) IDocumento2 páginasDegenerativeDiskDisease (HNP) Iapi-3822433Ainda não há avaliações
- LE Sports InjuriesDocumento42 páginasLE Sports InjuriesgmalangaAinda não há avaliações
- 891 Paediatric Idiopathic Flatfoot PDFDocumento51 páginas891 Paediatric Idiopathic Flatfoot PDFRobertus Dwi AtmokoAinda não há avaliações
- Affections of The Ankle and FootDocumento77 páginasAffections of The Ankle and FootJudy Ann Bahom SantiagoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Knee JointDocumento26 páginasAnatomy of The Knee JointSaghar AbroAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Soft TissueDocumento24 páginasPrinciples of Soft TissueEric Carlos YumulAinda não há avaliações
- Dislocation: Mohamad Syafiq Bin Mohamad BHAL 16044338Documento14 páginasDislocation: Mohamad Syafiq Bin Mohamad BHAL 16044338Joni NeohAinda não há avaliações
- Orthopedics PDFDocumento14 páginasOrthopedics PDFSam christenAinda não há avaliações
- Meniscal Pathology: Mr. Abdul WahabDocumento44 páginasMeniscal Pathology: Mr. Abdul WahabSoumashree MondalAinda não há avaliações
- Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 páginasPrecipitating FactorsCake ManAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17 VocabularyDocumento3 páginasChapter 17 Vocabularymph440Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 4949982050959491377 PDFDocumento48 páginas1 4949982050959491377 PDFAjay ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Foot and Ankle Injuries and Pain: Indranil Neel' Kushare, MDDocumento55 páginasFoot and Ankle Injuries and Pain: Indranil Neel' Kushare, MDrizwan.mughal1997Ainda não há avaliações
- Therapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Documento31 páginasTherapeutic Exercise: Foundation & Techniques: Resource Person: Dr. Rahat Ayub PT SHS.326.Lec.15Fatima YasirAinda não há avaliações
- ORTHOPEDICSDocumento6 páginasORTHOPEDICSJAY-AR DAITAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 1.3 Synovial Joints UpdatedDocumento24 páginasMod 1.3 Synovial Joints UpdatedNandhkishoreAinda não há avaliações
- Sport Traumatology-III Foot and Ankle Joint-15Documento47 páginasSport Traumatology-III Foot and Ankle Joint-15kamran aliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 36Documento3 páginasChapter 36Samantha QuintoAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Limb OrthosisDocumento47 páginasUpper Limb OrthosisPraneethaAinda não há avaliações
- Cad wk9-10 QsDocumento10 páginasCad wk9-10 Qsapi-468597987Ainda não há avaliações
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocumento41 páginasAnkylosing SpondylitisAaliyah ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Final MB Surgery O T MEQ All in OneDocumento35 páginasFinal MB Surgery O T MEQ All in OneChris Jardine LiAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Rehabilitation in Musculoskeletal Trauma - Prof. Dr. Dr. Angela BM Tulaar SPKFR (K)Documento41 páginasMedical Rehabilitation in Musculoskeletal Trauma - Prof. Dr. Dr. Angela BM Tulaar SPKFR (K)YanuarAinda não há avaliações
- Paediatric FlatfootDocumento53 páginasPaediatric FlatfootAmr HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Hip Disloc and Fem HeadDocumento60 páginasHip Disloc and Fem HeadZisuhAinda não há avaliações
- Knee Injury: By: Haspreet GillDocumento18 páginasKnee Injury: By: Haspreet GillRoshandiep GillAinda não há avaliações
- Knee Disorders: Mittul PatelDocumento45 páginasKnee Disorders: Mittul PatelmittulcpatelAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Documento143 páginasLecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Wilson HalimAinda não há avaliações
- Neuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaDocumento62 páginasNeuromusculosklatal Disorders FK UnayaSuci MayveraAinda não há avaliações
- DHP W. TableDocumento21 páginasDHP W. Tablejenika studiesAinda não há avaliações
- Shoulder Conditions in Agility Dogs: T T T TDocumento5 páginasShoulder Conditions in Agility Dogs: T T T TJuan-PabloChaperoArenasAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Quiz 2 Review - Luke GriffinDocumento6 páginasAnatomy Quiz 2 Review - Luke Griffinnategozdor58Ainda não há avaliações
- Disorder of Lower LimbDocumento76 páginasDisorder of Lower Limb074 Khola WaqarAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Shoulder JointDocumento50 páginas4 Shoulder Jointq77gkyhzs4Ainda não há avaliações
- CTEVDocumento25 páginasCTEVIceBearAinda não há avaliações
- Closed Reduction, Traction, and Casting Techniques: Jason Tank, MDDocumento75 páginasClosed Reduction, Traction, and Casting Techniques: Jason Tank, MDluckyariadneeAinda não há avaliações
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocumento31 páginasMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion Fracturessatya yudhayanaAinda não há avaliações
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocumento31 páginasMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesKalayo100% (1)
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocumento31 páginasMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesutisuryanjAinda não há avaliações
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocumento31 páginasMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesRasjad ChairuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocumento31 páginasMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesAzmi FarhadiAinda não há avaliações
- Traction: Presented By: Kristine Irish C. Almonte Tricia Nicole AlimatoDocumento26 páginasTraction: Presented By: Kristine Irish C. Almonte Tricia Nicole AlimatoAlex Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17 VocabularyDocumento3 páginasChapter 17 Vocabularymph440Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 VocabularyDocumento3 páginasChapter 14 Vocabularymph440Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 13 VocabDocumento3 páginasChapter 13 Vocabmph440Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 VocabularyDocumento3 páginasChapter 12 Vocabularymph440Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 VocabularyDocumento2 páginasChapter 11 Vocabularymph440Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Vocab and Notes: Athletes Circle of CareDocumento4 páginasChapter 1 Vocab and Notes: Athletes Circle of Caremph440Ainda não há avaliações
- BBB Month 25 Workout LogDocumento8 páginasBBB Month 25 Workout LogluniblueAinda não há avaliações
- Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Over-the-Top TechniquesDocumento12 páginasArthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Over-the-Top TechniquesSang PhạmAinda não há avaliações
- Shoulder ExaminationDocumento3 páginasShoulder ExaminationTausif HuqAinda não há avaliações
- One Move Too Many-Injuries+Overuse Syndroms-2003Documento117 páginasOne Move Too Many-Injuries+Overuse Syndroms-2003mr_raccoonAinda não há avaliações
- Arthrology: DR N. ChikumbaDocumento50 páginasArthrology: DR N. ChikumbaNatty ChikumbaAinda não há avaliações
- Shoulder ComplexDocumento7 páginasShoulder ComplexOscar NgAinda não há avaliações
- Total Knee Replacement: Guided By: Dr. Kratika Varshney P.TDocumento66 páginasTotal Knee Replacement: Guided By: Dr. Kratika Varshney P.THarshita SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- One Move Too ManyDocumento117 páginasOne Move Too ManyMZ100% (3)
- Kris Gethin WorkoutDocumento18 páginasKris Gethin WorkoutravindraAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 7 The Muscular SystemDocumento6 páginasCHAPTER 7 The Muscular SystemRenson S. HermoginoAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - Knee Joint - D3Documento28 páginas7 - Knee Joint - D3aslooclt100% (1)
- Scapular Stabilization ExercisesDocumento2 páginasScapular Stabilization ExercisesnimitrisAinda não há avaliações
- Proprioceptive ExercisesDocumento5 páginasProprioceptive Exerciseswalaa eldesoukeyAinda não há avaliações
- PDII Checklist Musculoskeletal StudentDocumento3 páginasPDII Checklist Musculoskeletal Studentmre07Ainda não há avaliações
- 2010 PublicationsLCSPMDDocumento6 páginas2010 PublicationsLCSPMDEvelyn AsencioAinda não há avaliações
- Fraktur ClaviculaDocumento23 páginasFraktur ClaviculaayuradityoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy: Synovial JointsDocumento20 páginasAnatomy: Synovial JointsJayricDepalobosAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Movement Scenario ExamplesDocumento1 páginaPassive Movement Scenario ExamplesMickey NgoAinda não há avaliações
- Golfer's Elbow Test Purpose: Patient PositionDocumento4 páginasGolfer's Elbow Test Purpose: Patient Positionherlitaandri annisaAinda não há avaliações
- Biomechanics of The KneeDocumento8 páginasBiomechanics of The KneeJorge LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Beginner & Advanced Rotator Cuff Exercises For Shoulder Pain - MyodetoxDocumento18 páginasBeginner & Advanced Rotator Cuff Exercises For Shoulder Pain - MyodetoxJustin Wigon100% (1)
- Muscle Testing Hip Extension AbductioDocumento26 páginasMuscle Testing Hip Extension AbductioHaruka HaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Joint DislocationsDocumento64 páginasJoint DislocationsSabrina Indri WardaniAinda não há avaliações
- Muscle Activity During The Gait CycleDocumento3 páginasMuscle Activity During The Gait CycleMarjorie Walker100% (1)
- Normal Gait Kinetics - 20 Questions-1Documento3 páginasNormal Gait Kinetics - 20 Questions-1rehab aymanAinda não há avaliações
- PJM NotesDocumento26 páginasPJM NotesLeamy Reyes100% (1)
- Gregory I. Bain, Eiji Itoi, Giovanni Di Giacomo, Hiroyuki Sugaya Eds. Normal and Pathological Anatomy of The ShoulderDocumento410 páginasGregory I. Bain, Eiji Itoi, Giovanni Di Giacomo, Hiroyuki Sugaya Eds. Normal and Pathological Anatomy of The ShoulderNikolaos Anastasopoulos100% (3)
- Range of Joint Motion Evaluation Chart OK PDFDocumento2 páginasRange of Joint Motion Evaluation Chart OK PDFcesamav100% (4)
- Biomechanics of Elbow ComplexDocumento9 páginasBiomechanics of Elbow ComplexKIARA VENICE DELGADOAinda não há avaliações
- 100 TOP Orthopaedics MCQ and AnswersDocumento18 páginas100 TOP Orthopaedics MCQ and AnswersAhmed Noori89% (157)