Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Wastewater Treatment
Enviado por
libbissujessyTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Wastewater Treatment
Enviado por
libbissujessyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ChE 302 WASTEWATER TREATMENT
SEMESTER 2, 2009
DESIGN PROJECT
GROUP MEMBERS:
Melissa Rosdiana Dewi (7D6B4040 / 13786801)
Chew Khai Liong (7D7A4397/13757768)
Faizah Othman (7D7A4585 / 13785138)
Fung Dar Kiong (7D7A4675 / 13785028)
Name of Lecturer: Michelle Fam
Due Date: 8th November 2009
ChE 302 Wastewater Treatment 2009
1.0
INTRODUCTION
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants in wastewater. It
involves number of stages which include physical, chemical and biological processes
with an objective of producing treated effluent which is suitable for discharge or reuse.
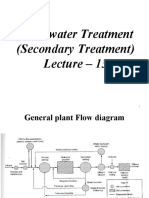
Below is the flow diagram of a common wastewater treatment plant:
Bar rack / Screens
Grit Chamber
Primary Sedimentation
Basin
Biological Treatment
Secondary
Sedimentation Basin
Advanced Wastewater
Treatment
In this project, a new Complete Mix Activated Sludge (CMAS) is to be designed to
upgrade the existing CMAS in one of the cities in Victoria, Australia. The design must be
able to handle population of 700,000 with a 2.048% population growth per year through
the year of 2028.
2.0
OBJECTIVES
The objective of this project is to design a wastewater treatment plant which can handle a
population of 700,000 with a 2.048% population growth each year.
ChE 302 Wastewater Treatment 2009
3.0
DESCRIPTION OF DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
In this section, the stages involved in wastewater treatment plant are briefly discussed.
Below are the brief explanations:
3.1
Bar Rack or Screens
Bar racks or screens are the first facility used in treating wastewater in which its
function is to remove coarse or large objects. Bar rack has an opening of about 15
mm or larger while screens opening is approximately 15 mm or smaller. Thus,
when untreated water is passed through bar rack, the larger objects are removed.
The slightly smaller objects which passed through the bar rack can be removed by
screen.
3.2
Grit Chamber
Located after the bar racks and before primary sedimentation basins, grit chamber
is utilized to remove grit or inert inorganic materials such as glass pieces, sand
and road grit. Grit chamber is also used to prevent abrasion in moving mechanical
equipment as well as to lessen heavy deposits formation in pipelines. Excessive
accumulations of grit which leads to high frequency of digester can also be
reduced by grit chamber.
3.3
Primary Sedimentation Basin
Besides containing coarse objects and grits, untreated water also contains
suspended solids and organic matter which need to be removed in order to obtain
clean and safe treated water. In order to do so, primary sedimentation basin is
needed. Primary sedimentation basin applies the principle of specific gravity and
density. When wastewater enters the primary sedimentation basin, solids present
in the wastewater that have a higher density than the liquid will settle at the
bottom of the tank. On the other hand, solids with smaller density than the liquid
will rise. The settleable solids and the floating materials are then removed from
the wastewater and hence reducing the organic suspended solids content.
ChE 302 Wastewater Treatment 2009
3.4
Biological Treatment
Biological treatment involves biological processes in which dissolved organic
solids are converted into flocculants and biological slimes. These flocculants are
then removed in sedimentation basins. Biological treatment utilizes different types
of microorganisms such as bacteria and protozoans to reduce Biological Oxygen
Demand (BOD), remove nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus as well as to
remove dissolved and colloidal organic matter.
3.5
Secondary Sedimentation Basin
Secondary sedimentation basin uses the same principle as primary sedimentation
basin. The only difference between the secondary and primary sedimentation
basins is that in secondary sedimentation basins, biological slimes from the
biological treatment are the settleable solids which will then be removed.
3.6
Advanced Wastewater Treatment
This treatment is an additional treatment applied to remove suspended and
dissolved substances that remained after the secondary treatment. The substances
may include inorganic ions such as potassium and nitrate or they may be organic
suspended solids. There are a number of technologies or facilities that can be
applied in this treatment such as Granular-Medium Filtration and Microscreening
to remove residual suspended solids.
In this design project, the facilities involved in the wastewater treatment plant are to be
designed. The design should include Grit Chamber, Primary Sedimentation Basin,
Activated Sludge System for biological treatment and Secondary Sedimentation Basin.
The detailed calculations of the design are shown in the next section.
4.0
FACILITIES DESIGN AND CALCULATIONS
5.0
SUMMARY
6.0
APPENDICES
4
Você também pode gostar
- Sanitary Engineer II: Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandSanitary Engineer II: Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Liu Yi-Design and Construction of Biogas Digester 2017Documento74 páginasLiu Yi-Design and Construction of Biogas Digester 2017Stanley Wishmore MukuraAinda não há avaliações
- Mini Project ReportDocumento5 páginasMini Project ReportSaj BhaiAinda não há avaliações
- Manual On The Causes and Contril of Activated SludgeDocumento21 páginasManual On The Causes and Contril of Activated SludgeRiianti WidiiAinda não há avaliações
- Sugar IndustryDocumento27 páginasSugar IndustryChali HaineAinda não há avaliações
- Aerated BiofiltersDocumento18 páginasAerated BiofiltersNataliaKAinda não há avaliações
- CPI BrochureDocumento2 páginasCPI Brochuremashonk okAinda não há avaliações
- Reverse Osmosis System FaridDocumento30 páginasReverse Osmosis System FaridAchFaridWadjdiAinda não há avaliações
- Pulsator - P ER 003 EN 1603 - v2 PDFDocumento2 páginasPulsator - P ER 003 EN 1603 - v2 PDFpjrapanutAinda não há avaliações
- Sizing of InterceptorDocumento11 páginasSizing of InterceptorLorence GabayanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento3 páginasAssignment 1Victor Megong JakiAinda não há avaliações
- V3i4 Ijertv3is040786 PDFDocumento5 páginasV3i4 Ijertv3is040786 PDFsarikagAinda não há avaliações
- About Sewage Treatment PlantDocumento47 páginasAbout Sewage Treatment PlantShumank SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- CAP 15 - 3 Design of Water Resource Recovery Facilities, Sixth Edition Nitrogen-Removal-Sidestream-Process-DesignDocumento4 páginasCAP 15 - 3 Design of Water Resource Recovery Facilities, Sixth Edition Nitrogen-Removal-Sidestream-Process-DesignNICOLAS SANCHEZ GOMEZAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling of Activated Sludge With ASM1 Model, Case Study On Wastewater Treatment Plant of South of IsfahanDocumento10 páginasModeling of Activated Sludge With ASM1 Model, Case Study On Wastewater Treatment Plant of South of IsfahanAnish GhimireAinda não há avaliações
- Addis Ababa University: Institute of TechnologyDocumento17 páginasAddis Ababa University: Institute of Technologyashe zinabAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of Softdrink Industry Wastewater Using An Integrated Anaerobicaerobic Membrane BioreactorDocumento154 páginasTreatment of Softdrink Industry Wastewater Using An Integrated Anaerobicaerobic Membrane BioreactorAbiodun Gbenga100% (1)
- Desalting Water Treatment Membrane Manual PDFDocumento172 páginasDesalting Water Treatment Membrane Manual PDFCelenia BejaranoAinda não há avaliações
- Lab DI Water SystemsDocumento6 páginasLab DI Water SystemsHaidee Che RizminAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Engineering SyllabusDocumento49 páginasChemical Engineering Syllabusyugal sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Water Treatment Process Disinfection PDFDocumento6 páginasWater Treatment Process Disinfection PDFAriff JasniAinda não há avaliações
- Shortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationNo EverandShortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Water TreatmentDocumento12 páginasChemical Water TreatmentEderango JackAinda não há avaliações
- DBDocumento25 páginasDBAbhijit MondalAinda não há avaliações
- Today'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"Documento57 páginasToday'S Topic "Cooling Water Treatement" "Condenser Leak Detection" "Chlorination Plant" AND "Effluent Treatment"saravan1891Ainda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word - Festo Rain Water Harvesting Flow ChartDocumento5 páginasMicrosoft Word - Festo Rain Water Harvesting Flow Chartjeykumar.BalannairAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1 WastewaterDocumento2 páginasTutorial 1 WastewaterAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Tank Recirculation Pump SizingDocumento1 páginaFire Tank Recirculation Pump SizingAkhil VijaiAinda não há avaliações
- Water Pricing in Water SupplyDocumento8 páginasWater Pricing in Water SupplySuwash AcharyaAinda não há avaliações
- Epa Water Treatment MGT Coag Flocc Clar2Documento104 páginasEpa Water Treatment MGT Coag Flocc Clar2Hemanth Kumar RamachandranAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRDocumento39 páginasModule - 9 Secondary Treatment AS, EAAS, SBRFaran Masood100% (1)
- Water Treatment Plant Performance Evaluations and OperationsNo EverandWater Treatment Plant Performance Evaluations and OperationsAinda não há avaliações
- SO2 Removal Using Packed Column Scrubber TowerDocumento60 páginasSO2 Removal Using Packed Column Scrubber TowerAbrahamChongAinda não há avaliações
- Boq 196423Documento87 páginasBoq 196423sanjaygkpAinda não há avaliações
- ENVI Trickling FiltersDocumento23 páginasENVI Trickling FiltersbaBy daBy AnNetTeAinda não há avaliações
- A. Standard Membrane Bioreactor Computations: 2.1. Design Flowrates and Maximum Monthly Loading RatesDocumento7 páginasA. Standard Membrane Bioreactor Computations: 2.1. Design Flowrates and Maximum Monthly Loading RatesshekharshindeAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Documento4 páginasTreatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Dương Ánh100% (1)
- Chernicharo Et Al Anaerobic Sewage Treatment 2015Documento32 páginasChernicharo Et Al Anaerobic Sewage Treatment 2015Luiz Marcos Oliveira Junior100% (1)
- Chlorine Energy 2520 BalanceDocumento4 páginasChlorine Energy 2520 Balancetonzz10Ainda não há avaliações
- Study Guide Suspended GrowthDocumento44 páginasStudy Guide Suspended GrowthVineet ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Final Final Expt 3 - Part 1Documento6 páginasFinal Final Expt 3 - Part 1Florecita CabañogAinda não há avaliações
- Activated Sludge ProblemDocumento3 páginasActivated Sludge ProblemCamille LeiAinda não há avaliações
- Aeration Solutions Comparison Chart - VlightDocumento2 páginasAeration Solutions Comparison Chart - VlightprannoyAinda não há avaliações
- Air Stripper Brochure WEBDocumento8 páginasAir Stripper Brochure WEBMark McClureAinda não há avaliações
- Removal of Removal of Iron (Fe) and Manganese (MN) : DR Liu YuDocumento20 páginasRemoval of Removal of Iron (Fe) and Manganese (MN) : DR Liu YuChuah Chong YangAinda não há avaliações
- Sewage FacilitiesDocumento31 páginasSewage FacilitiesNataliaKAinda não há avaliações
- Systematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsNo EverandSystematic Methods of Water Quality Parameters Analysis: Analytical MethodsAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Water Treatment Plant Design For Small and Midsized CommunitiesDocumento33 páginasWaste Water Treatment Plant Design For Small and Midsized CommunitieskassyAinda não há avaliações
- ClarifierDocumento7 páginasClarifiersuleman205Ainda não há avaliações
- SBR DesignDocumento10 páginasSBR DesignQuốc TuyênAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 8 NeutralizationDocumento32 páginasLec 8 Neutralizationhaseeb tahirAinda não há avaliações
- Ozone Based Waste Water TreatmentDocumento10 páginasOzone Based Waste Water TreatmentZafar BukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Handover Document - Yaden KatunayakeDocumento39 páginasHandover Document - Yaden KatunayakeUTY ENGAinda não há avaliações
- Water Treatment SchemesDocumento26 páginasWater Treatment SchemesCao Xuan CanhAinda não há avaliações
- Anoxic TankDocumento12 páginasAnoxic TankpragatheeskAinda não há avaliações
- Anaerobic Treatment and Biogas (Short)Documento61 páginasAnaerobic Treatment and Biogas (Short)Dinda SyafidahAinda não há avaliações
- Read Your Bible Through in A YearDocumento2 páginasRead Your Bible Through in A YearlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graduate Sample CV PDFDocumento2 páginasEngineering Graduate Sample CV PDFferozAinda não há avaliações
- Heat and Mass TransferDocumento1 páginaHeat and Mass TransferlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Journal 1 Speaker: Ms. June Roy Date: August 10, 2010 (Tuesday) Title: Process Engineering ServicesDocumento13 páginasJournal 1 Speaker: Ms. June Roy Date: August 10, 2010 (Tuesday) Title: Process Engineering ServiceslibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- S H e C: Afety Ealth Nvironment OmmunityDocumento16 páginasS H e C: Afety Ealth Nvironment OmmunitylibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Design Project Memo 2: Leverage Engineering Consultancy Sdn. BHDDocumento10 páginasDesign Project Memo 2: Leverage Engineering Consultancy Sdn. BHDlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- PEM AssignmentDocumento6 páginasPEM AssignmentlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Developing Growth Strategies To Become A Market Leader IMI GroupDocumento8 páginasDeveloping Growth Strategies To Become A Market Leader IMI GrouplibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Momentum Transport - Understanding Flow: DS ChaudharyDocumento18 páginasMomentum Transport - Understanding Flow: DS ChaudharylibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Standards VesselDocumento1 páginaStandards VessellibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2Documento1 páginaAssignment 2libbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Page 3 of 4: Fig. 3. Divided-Wall Technology Applied To The Butadiene Distillation SectionDocumento1 páginaPage 3 of 4: Fig. 3. Divided-Wall Technology Applied To The Butadiene Distillation SectionlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- PPE AssignmentDocumento16 páginasPPE AssignmentlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Basic First AidDocumento49 páginasBasic First AidlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Thiophane (1) (Report) - Edited by FaizahDocumento5 páginasThiophane (1) (Report) - Edited by FaizahlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 2Documento1 páginaTutorial 2libbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Log Book Week 1 Week 2Documento12 páginasLog Book Week 1 Week 2libbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Final Compilation of Assing 3 - Vignes ShanmuganathanDocumento28 páginasFinal Compilation of Assing 3 - Vignes ShanmuganathanlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1-Process Creation Process Flow DiagramDocumento2 páginasTutorial 1-Process Creation Process Flow DiagramlibbissujessyAinda não há avaliações
- G10 Lesson2 DLPDocumento13 páginasG10 Lesson2 DLPAngeles, Mark Allen CAinda não há avaliações
- The Rise of Australian NovelDocumento412 páginasThe Rise of Australian NovelSampath Kumar GummadiAinda não há avaliações
- Sale Counter List JuneDocumento9 páginasSale Counter List Junep6a4nduAinda não há avaliações
- Alfa Week 1Documento13 páginasAlfa Week 1Cikgu kannaAinda não há avaliações
- Continuing Professional Development PlanDocumento4 páginasContinuing Professional Development Planvviki50% (2)
- Mathmatcs Joint Form TwoDocumento11 páginasMathmatcs Joint Form TwoNurudi jumaAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical PaperDocumento16 páginasGeotechnical PaperTxavo HesiarenAinda não há avaliações
- European Asphalt Standards DatasheetDocumento1 páginaEuropean Asphalt Standards DatasheetmandraktreceAinda não há avaliações
- Subject OrientationDocumento15 páginasSubject OrientationPearl OgayonAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Control of Rigid Pavements 1Documento58 páginasQuality Control of Rigid Pavements 1pranjpatil100% (1)
- Healthy Apps Us New VarDocumento9 páginasHealthy Apps Us New VarJESUS DELGADOAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Learning Module As PatternDocumento23 páginasSample Learning Module As PatternWilliam BulliganAinda não há avaliações
- HUMSS - Introduction To World Religions & Belief Systems CGDocumento13 páginasHUMSS - Introduction To World Religions & Belief Systems CGAliuqus SirJasper89% (18)
- Gis Data Creation in Bih: Digital Topographic Maps For Bosnia and HerzegovinaDocumento9 páginasGis Data Creation in Bih: Digital Topographic Maps For Bosnia and HerzegovinaGrantAinda não há avaliações
- World War II D-Day Invasion by SlidesgoDocumento55 páginasWorld War II D-Day Invasion by SlidesgoPreston SandsAinda não há avaliações
- Kissoft 15,69,0.4Documento10 páginasKissoft 15,69,0.4Daggupati PraveenAinda não há avaliações
- Loctite 586 PDFDocumento9 páginasLoctite 586 PDForihimieAinda não há avaliações
- 11.3.1 Some Special CasesDocumento10 páginas11.3.1 Some Special CasesSiddharth KishanAinda não há avaliações
- Universal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukDocumento3 páginasUniversal Ultrasonic Generator For Welding: W. Kardy, A. Milewski, P. Kogut and P. KlukPhilip EgyAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryDocumento17 páginasLesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryNAPHTALI WILLIAMS GOAinda não há avaliações
- Magic Bullet Theory - PPTDocumento5 páginasMagic Bullet Theory - PPTThe Bengal ChariotAinda não há avaliações
- Application of The Strain Energy To Estimate The Rock Load in Non-Squeezing Ground ConditionDocumento17 páginasApplication of The Strain Energy To Estimate The Rock Load in Non-Squeezing Ground ConditionAmit Kumar GautamAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Problems - Electrochemical CellDocumento5 páginasPractice Problems - Electrochemical CellYehia IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Ateneo de Manila University: Submitted byDocumento5 páginasAteneo de Manila University: Submitted byCuster CoAinda não há avaliações
- Enlightened ExperimentationDocumento8 páginasEnlightened ExperimentationRaeed HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Niveshdaily: From Research DeskDocumento53 páginasNiveshdaily: From Research DeskADAinda não há avaliações
- Mcdaniel Tanilla Civilian Resume Complete v1Documento3 páginasMcdaniel Tanilla Civilian Resume Complete v1api-246751844Ainda não há avaliações
- Common Core Content and Training Objectives For Basic AIS Training - Phase 2 - SpecialistDocumento82 páginasCommon Core Content and Training Objectives For Basic AIS Training - Phase 2 - SpecialistjlferreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Very Narrow Aisle MTC Turret TruckDocumento6 páginasVery Narrow Aisle MTC Turret Truckfirdaushalam96Ainda não há avaliações
- Active Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023Documento119 páginasActive Hospital Network List For Vidal Health Insurance Tpa PVT LTD As On 01 Feb 2023jagdeepchkAinda não há avaliações