Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Brazilian Test
Enviado por
Justin NgDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Brazilian Test
Enviado por
Justin NgDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and
Rock Mechanics
Brazilian Test
NG KWOK CHAK (3035009926)
12/9/2012
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
OBJECTIVE
To determine the uniaxial tensile strength of prepared rock specimens indirectly by the Brazil
Test.
Figure 1
INTRODCTION
The justification for the test is based on the experimental fact that the most rocks in biaxial
stress fields fail in tension at their uniaxial tensile strength.
Compression Load
Cracking
Tension
Tension
Compression Load
Figure 2
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
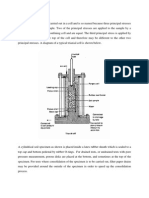
APPARATUS
DGM loading machine
It has a control panel showing the instantaneous
applied load. At the moment when the rock
specimen fails, one of the pointers will stop
showing the failure compressive load (Fig. 3).
Steel Loading Jaws
This is the apparatus where the specimens are
mounted (Figure 4).
Electronic Calipers
It is used to measure the diameter and thickness
of each rock specimen (Figure 5).
Masking Tape
They are used for wrapping the periphery of the
rock specimens to reduce contact irregularities.
They are also used to prevent the specimens from
breaking into pieces after failure, so that the
failure plane can be observed (Figure 6).
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
THEORY
The tensile strength of a material is a measure of its ability to resist uniaxial tensile loads without yielding
or fracture. A direct-pull uniaxial test is difficult to apply to rock and in many cases some type of indirect
test is employed to determine tensile strength. The Brazilian test, where a disc of the test material is
loaded across a diameter, is often employed. The figure below illustrates the principle of the test and
Equation 1 is used to calculate the equivalent tensile strength (T*).
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
Figure 7
Figure 8
Basically, the technique involves loading disc-shaped specimens in compression across their diameter.
Such loading generates a tensile stress at the center of the disc in a direction perpendicular to the direction
of applied load (in the plane of the disc face). When the applied load reaches a critical level, the disc splits
lengthwise in tension. Apparent tensile strength is calculated using the following equation:
where T0* is the tensile strength, P is the maximum compressive load recorded during the test, D is the
diameter, and t is the thickness of the test specimen.
Notes:
1. Only the small circular disc of rock would be used (but D is not less than 50 mm) in the Brazilian
Test to ensure the rock specimen to be an intact rock and relatively free from cracks and joints.
2. The ration between D and t is about 2: 1.
3. The disc circumference should be wrapped in masking tape.
4. The rock specimen should be loaded at in constant rate, 200N/s is recommended, so that the
specimen within a reasonable time.
There are two possible modes of failure:
1. Axial splitting along vertical failure
2. Shear and crushing failure at loading
Figure 9
Figure 10
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
PROCEDURE
1.
2.
3.
4.
Eight test specimens shall be cut and prepared using clean water.
The test specimens shall be wrapped around its periphery with one layer of the masking tape
Each specimen shall be coded. The diameter and thickness shall be measured.
The specimens shall be mounted squarely in the test apparatus such that the curved platens
load the specimen diametrically with the axes of rotation for specimen and apparatus
coincident.
Load on the specimen shall be applied continuously at a constant rate. A loading rate of 200N/s
is recommended.
The failure compressive load shall be recorded and the corresponding tensile strength was
calculated.
5.
6.
DESCRIPTION OF SAMPLE
Lithological description
8 rock specimens have been tested in this experiment. Specimens 33-36 were tested by our group
(Group J) whereas specimens 37-40 are tested by another group, Group I. In general, all the
specimens are very similar in appearance and their properties are as follows:
1.
2.
3.
4.
The rocks are grey in colour with white pattern
No visible cracks are observed
No weathering is observed on the surface
The grains cannot be identified easily by naked eyes
Remarks:
For Specimen 38, it seems to have a joint, which is perpendicular to the pen.
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
RESULTS
a) Dimension of Specimens and Tensile Strength
By the Equation,
2P
0.636 P
Dt
Dt
The data of our group (Group J):
The data of group I:
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
b) Mode of failure
Axial Failure
Figure 11
Figure 13
Figure 12
Figure 14
For the specimen 34, 35, 36, 37, they almost got pure axial failure. It can be observed that they split
along the plane of applied compressive force as the blue line illustrate. The reason for the specimen
that can`t get the perfect axial failure may due to the multi-point contact suffer the compressive
force when it was nearly to fail. As we can see that, most specimens are not a perfect circle as it did
before the experiment, especially for the contact position.
6
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
Shear and crushing failure
Figure 15
Figure 17
Figure 16
Figure 18
Figure 19
7
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
For the specimen 33,38,39,40, they fail in a mixing failure mode with both of axial and shear factors. It is
observed that these specimen as a relative low ultimate tensile strength. It might due to their
composition difference, such as different grain size and grain arrangement. For the specimen 38, 39 and
40, they have more black patterns then others. Also, it might due to their internal joint and fracture. For
the specimen 38, as the Figure 17 and Figure 18 shown (the direction of the pen pointing to respect to
the specimen are same in both), the vertical rupture plane due to shear is parallel to the fracture in
Figure 17.
Average Tensile Strength
As the Experiment is based on the assumption of specimen in axial tensile failure, only the data of
specimen 34, 35, 36 and 37 are taken for the calculation of the tensile strength for the intact rock
the specimen.
Average Tensile Strength = (8.089+9.347+6.804+4.622)/ 6= 7.216 MPa
DISCUSSION, SUGGESTI ON, COMMENT
a) Comment on preparation of rock specimen
As observed, the rock specimens used in this experiment have smooth and straight sides and there
are no observable tool marks on the surface of the specimens. Furthermore, all the diameters of the
specimens are greater than 60 mm which fits our requirement that the specimens should be larger
than 50 mm. However the thickness of the specimen is about the 55% of the diameter instead on
the 50% suggested. Nevertheless, the rock specimens are generally well prepared and agree with
the instructions.
b) Source of error
From the results of the Brazil test, the tensile strengths of the specimens range from 4.372MPa to
9.347MPa. There is large deviation of the tensile strength form the average tensile strength
(7.216MPa). The deviation can be explained by the following sources of error:
1.
Rock is heterogeneous in nature. Also, it is an aggregate rather than a single material. As a
result, even the specimens are taken from the same rock mass, the rock specimens may vary
in physical properties.
2.
The assumptions that the rock specimens are intact and relatively free from cracks and joints
or other discontinuities are not true. There are discontinuities in the rock, like joints and
fissures.
3.
The compressive load may be subjected to eccentricity due to technical problems of the
loading machine or imperfect steel jaws manufacturing.
CIVL 2002
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
4.
The contact between the specimen and jaws was not perfectly point contact as assumed in
the derivation of the formula.
5.
As friction was present within the hydraulic ram of the loading machine, the indicated load
was likely to be higher than the actual applied load.
6.
The specimens are not having perfect vertical and horizontal surfaces.
7.
The crack initiation load is usually smaller that the peak load because the test does not
ensure crack initiation occurs at maximum tensile stress. A 4-point-beam test or 3-pointbeam test should be used instead to ensure crack initiation is accompanied by peak load. It is
often, however, difficult to obtain an intact rock beam sample from nature.
8.
Induction of the tensile stress is hindered as the masking tape is confining the specimen. In
other words, compressive stress is induced by the masking tape and true induced tensile
stress cannot be revealed.
9.
Although there are no signs of weathering were observed on the surface, weathering may
exist within the rock specimens. Weathering might weaken the interactions among the
mineral grains and thus lower the tensile strength of the specimens. More fraction of the
specimen is weathered, lower tensile strength are resulted.
10.
As shown in the result of the experiment, the value of the diameters of the rock specimens
measured are quite varied. The diameter measured may be smaller than the actual one. To
avoid this, we should record the diameter until the largest value is measured.
c) Precautions
The following precautions should be noted when carrying out the experiment:
1.
The applied compressive load should not larger than the induced tensile stress by three
times, or the specimen may not fail by tension in the lateral direction.
2.
The measured tensile strength depends on the width of contact area between the specimen
and the loading jaws. If the width is larger than 10o at failure, its effect should be taken into
account when calculating the tensile stress.
CIVL 2002
3.
Engineering Geology and Rock Mechanics
If failure involves cracking, crushing or splitting perpendicular to or at an oblique angle to the
line of loading, the test of that rock specimen should be rejected. Sample anisotropy in the
form of foliation, bedding, etc. should be noted with respect to the direction of loading.
d) Improvements
Following improvements can be done to increase the accuracy of the result of the experiment:
1.
The tensile strength obtained through the Brazil test highly depends on the rate of the
applied load. As a result, the tensile strength obtained in the above section only represents
the tensile strength of a particular applied rate. Therefore, tests with different loading rate
should be carried out in order to improve the accuracy of the experiment.
2.
The result of Brazil test may have a large deviation during the experiment. More samples
(more than 10 samples) should be tested so as to obtain a more accurate result.
3.
It is better to measure the dimension with more times so as to increase the accuracy. When
measuring the diameter of the specimen, we should shift the Electronic Calipers until largest
value is gained which indicates the diameter.
CONCLUSION
Actually, the result in these experiment is a question, as there is only four sets of data can fulfill the
assumption which is far from enough as the requirement, 10 set of data. It might need to do it again with
the improvements mentioned above.
Then, I would like to conclude with the importance of Brazilian test. It is the method to find the tensile
strength of the rock. By knowing the tensile strength of the rock material, Engineer can determine
whether the material is a suitable choice for the application is their mind. This is extremely important for
the safety of in the design.
REFERENCE
1. Charles Jaegar, Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2nd Edition 1979, Cambridge University Press;
2. Stagg & Zienkiewiez, Rock Mechanics in Engineering Practice, John Wiley & Sons Limited;
3. Richard E. Goodman, Introduction to Rock Mechanics, 2nd Edition
10
Você também pode gostar
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985No EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Ainda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear Box and Ring Shear Test Comparison Why Does Internal Friction Angle VaryDocumento17 páginasDirect Shear Box and Ring Shear Test Comparison Why Does Internal Friction Angle VaryBarry OcayAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Built Environment: Full ReportDocumento10 páginasFaculty of Civil Engineering and Built Environment: Full ReportShahida RasliAinda não há avaliações
- Nanyang Technological University School of Civil and Structural EngineeringDocumento44 páginasNanyang Technological University School of Civil and Structural EngineeringZhwan AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- Lab7 ReportDocumento4 páginasLab7 ReporthelensongyAinda não há avaliações
- Three-Pinned Arch LaboratoryDocumento16 páginasThree-Pinned Arch LaboratoryHoo Yuen Fong100% (1)
- Lab Report Setting Out PDFDocumento10 páginasLab Report Setting Out PDFsaraa sharanAinda não há avaliações
- Failure of Retaining Wall - Case StudyDocumento4 páginasFailure of Retaining Wall - Case StudyRaghavAinda não há avaliações
- Brazilian TestDocumento55 páginasBrazilian TestGoh Ching SoonAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory+3+ +Point+Load+TestDocumento6 páginasLaboratory+3+ +Point+Load+TestFalahiah JudgeAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Impact ValueDocumento8 páginasAggregate Impact ValueAnis Nurfarahanim Abdul HalimAinda não há avaliações
- Sand Replacement Test Lab ManualDocumento3 páginasSand Replacement Test Lab Manualmm100% (1)
- Laboratory Report Standard Penetration Test - SPTDocumento6 páginasLaboratory Report Standard Penetration Test - SPTJc Aviles MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Flakiness and Elongation Index For The Given Aggregate Sample.Documento4 páginasDetermination of Flakiness and Elongation Index For The Given Aggregate Sample.Huma AliAinda não há avaliações
- LabEx No. 7 Los Angeles Abrasion TestDocumento4 páginasLabEx No. 7 Los Angeles Abrasion TestianzkieeAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Angularity Number For The Given Aggregate SampleDocumento4 páginasDetermination of Angularity Number For The Given Aggregate SampleEngr Muhammad TariqAinda não há avaliações
- Pull Out TestDocumento20 páginasPull Out TestTareq Al ShyoukhyAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Manual - Triaxial CD TestDocumento3 páginasLaboratory Manual - Triaxial CD TestMarcos Morrison50% (2)
- Direct Shear Test ResultDocumento7 páginasDirect Shear Test ResultDeepak Kr GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 7 Field Density (Sand Replacement Method) PDFDocumento21 páginasExp 7 Field Density (Sand Replacement Method) PDFAnonymous DR3NznAinda não há avaliações
- Unconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Documento8 páginasUnconfined Compression Test: Experiment No. 7Carmela Ayessa PiguerraAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Mix Design Report PDFDocumento32 páginasConcrete Mix Design Report PDFMohamed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Material LaboratoryDocumento14 páginasMaterial LaboratoryAnonymous tLXKwTAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of PenetrationDocumento57 páginasDetermination of Penetrationtunlaji0% (2)
- Lab 3 QuestionDocumento2 páginasLab 3 QuestionMadihah MB100% (2)
- Cube TestDocumento10 páginasCube Testridhuanzainal100% (1)
- Lab Report 4Documento16 páginasLab Report 4anon_68203647100% (1)
- L2 Full PDFDocumento22 páginasL2 Full PDFMas Idayu RosliAinda não há avaliações
- Constant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualDocumento3 páginasConstant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualmmAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear TestDocumento4 páginasDirect Shear TestNajihaharifAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear TestDocumento19 páginasDirect Shear Testshahrolhazrien75% (4)
- Geot. Report Basha Wolde Site 8.18.2017Documento32 páginasGeot. Report Basha Wolde Site 8.18.2017Minilik Tikur SewAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear TestDocumento23 páginasDirect Shear TestRajesh KhadkaAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMDocumento13 páginasSoalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMliyana2030Ainda não há avaliações
- Te Lab Shape of AggregateDocumento8 páginasTe Lab Shape of AggregateShivpreet SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Report Silt Test For SandDocumento10 páginasReport Silt Test For SandZanne Rose100% (1)
- Unconfined Compression TestDocumento11 páginasUnconfined Compression TestAmiruddin JSAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear TestDocumento2 páginasDirect Shear TestUtkarsh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear Test ReprtDocumento4 páginasDirect Shear Test ReprtShivaraj SubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- C2-Consistency Cement PasteDocumento4 páginasC2-Consistency Cement PasteMuhamad FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Full As Contoh Member AkashahDocumento29 páginasFull As Contoh Member AkashahWayen Bulat100% (1)
- Unit 5 - Shear Strength of SoilDocumento66 páginasUnit 5 - Shear Strength of SoilMr.Bhaskar Wabhitkar100% (1)
- (COMPLETE) Ring Ball and Penetration Test PDFDocumento10 páginas(COMPLETE) Ring Ball and Penetration Test PDFAthirah DinataAinda não há avaliações
- Report-Direct Shear Test 1Documento20 páginasReport-Direct Shear Test 1Ash BlackForest50% (2)
- Triaxial Test IntroductionDocumento4 páginasTriaxial Test IntroductionAshadi Hamdan100% (3)
- D2573-01-2007 Standard Test Method For Field Vane Shear Test in Cohesive SoilDocumento8 páginasD2573-01-2007 Standard Test Method For Field Vane Shear Test in Cohesive SoilBobAinda não há avaliações
- Shrinkage Limit Test Lab ManualDocumento2 páginasShrinkage Limit Test Lab ManualmmAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 1 DETERMINATION OF AGGREGATE IMPACT VALUE (AIV) (BS 812-112)Documento3 páginasLab Report 1 DETERMINATION OF AGGREGATE IMPACT VALUE (AIV) (BS 812-112)Kashif IqbaljAinda não há avaliações
- Permiability Test Aim of The ExperimentDocumento7 páginasPermiability Test Aim of The ExperimentArif AzizanAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Structure and Material Engineering Lab MaterialDocumento19 páginasFaculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Structure and Material Engineering Lab Materialalnz100% (1)
- Bending Test On WoodDocumento8 páginasBending Test On WoodShekharappa MallurAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidation TestDocumento9 páginasConsolidation Testdatonizam0% (1)
- Direct Shear TestDocumento14 páginasDirect Shear TestAmin SaufiAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Retaining Wall - QuestionDocumento6 páginasAssignment Retaining Wall - QuestionbadrulAinda não há avaliações
- Vane Shear Test: Dr. B. Munwar BashaDocumento17 páginasVane Shear Test: Dr. B. Munwar BashaArif AzizanAinda não há avaliações
- Los Angeles Abrasion TestDocumento5 páginasLos Angeles Abrasion Testদেওয়ানসাহেবAinda não há avaliações
- Brazilian TestDocumento11 páginasBrazilian TestJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- 7strength Properties of Rocks and Rock MassesDocumento16 páginas7strength Properties of Rocks and Rock MassesSheshu BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Rock Mechanics Lab Manual PDFDocumento43 páginasRock Mechanics Lab Manual PDFYasmine Safitri100% (1)
- Modelling Ship Grounding With Finite ElementsDocumento4 páginasModelling Ship Grounding With Finite ElementsSiddhant AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Ground AnchorDocumento79 páginasGround AnchorLaughlikesiao HeheAinda não há avaliações
- Freeze and Cherry 1979-Smaller PDFDocumento624 páginasFreeze and Cherry 1979-Smaller PDFAndrew Kim67% (3)
- Engineering Rock Mass Classifications - Z T Bieniawski PDFDocumento250 páginasEngineering Rock Mass Classifications - Z T Bieniawski PDFanon_102990793100% (2)
- Paper Crawer CraneDocumento10 páginasPaper Crawer CraneJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Feasibility ReportDocumento59 páginasFeasibility ReportJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- SUOS2011Documento270 páginasSUOS2011Wong ChingAinda não há avaliações
- Building Construction CAP 123B PDFDocumento28 páginasBuilding Construction CAP 123B PDFJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Malaysian FYPDocumento138 páginasMalaysian FYPJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Econ Chapter6Documento61 páginasEcon Chapter6Justin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Explosives DesignDocumento31 páginasExplosives Designsukhoi200900100% (1)
- Brazilian TestDocumento11 páginasBrazilian TestJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Pollution Problems: Table 1 Noise Level Caused by Various Construction EquipmentsDocumento2 páginasPollution Problems: Table 1 Noise Level Caused by Various Construction EquipmentsJustin NgAinda não há avaliações
- 1002-ch07-presentation (相容模式)Documento55 páginas1002-ch07-presentation (相容模式)Justin NgAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete BasementsDocumento184 páginasConcrete BasementsMohan BhalmeAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Atomic StructureDocumento43 páginasRevised Atomic StructureUdy MaudyAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic Analysis & Bolt ConnectionDocumento22 páginasPlastic Analysis & Bolt ConnectionceportalAinda não há avaliações
- Jackson 5 20Documento3 páginasJackson 5 20David Becerril RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Flexural Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Beam Using Finite Element AnalysisDocumento85 páginasFlexural Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Beam Using Finite Element AnalysisBranchi IkyureAinda não há avaliações
- Acta Biechanica: (Received July 4, 1984)Documento23 páginasActa Biechanica: (Received July 4, 1984)Maiman LatoAinda não há avaliações
- STRUKTUR GABLE FRAME BAJA OKDocumento26 páginasSTRUKTUR GABLE FRAME BAJA OKpriyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Berger and Loutre QSRDocumento21 páginasBerger and Loutre QSRFabian MolinaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Parameters: MD Helalur Rahman Executive Engineer Titas 50 MW Power Plant BPDB, Titas, CumillaDocumento54 páginasElectrical Parameters: MD Helalur Rahman Executive Engineer Titas 50 MW Power Plant BPDB, Titas, CumillaHelal RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- MECH 343 Lab 3 ReportDocumento32 páginasMECH 343 Lab 3 ReportYousef MeguidAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento16 páginasChapter 1Junaidah Mohamad RamliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 FractureDocumento19 páginasChapter 11 FractureSimulation CAEAinda não há avaliações
- CZM Formulation and ABAQUSDocumento44 páginasCZM Formulation and ABAQUSaravind kumarAinda não há avaliações
- 507 33 Powerpoint-Slides Ch8 DRCSDocumento70 páginas507 33 Powerpoint-Slides Ch8 DRCSArun GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- ISS Motion Control SystemDocumento3 páginasISS Motion Control Systemzmei23Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009Documento2 páginasAssignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009DSGAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture1460085501 2Documento526 páginasLecture1460085501 2Smruti Ranjan Pattanayak100% (1)
- Practical Skills 1 QDocumento17 páginasPractical Skills 1 QJack BornAinda não há avaliações
- Emd ImpDocumento7 páginasEmd ImpErAmolDhakaneAinda não há avaliações
- Physics (Work and Energy) Class IXDocumento3 páginasPhysics (Work and Energy) Class IXAditya SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Timber GradingDocumento16 páginasTimber GradingDevansh MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- CM1Documento16 páginasCM1WASHIPONG LONGKUMER 2147327Ainda não há avaliações
- SARDS Rescursive SimulationDocumento43 páginasSARDS Rescursive SimulationChristineNyambeAinda não há avaliações
- AISC ASD Manual 9th EditionDocumento41 páginasAISC ASD Manual 9th EditionjxsnyderAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 - Intro To Thermo - Student-3Documento3 páginasLesson 1 - Intro To Thermo - Student-3OreoDaChickenPlayz YTAinda não há avaliações
- Science 8 Quarter 1 Learning Activity Sheet 01 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2Documento7 páginasScience 8 Quarter 1 Learning Activity Sheet 01 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2shawnmiguel065Ainda não há avaliações
- PENG 219 - Production Engineering: Vahid AtashbariDocumento45 páginasPENG 219 - Production Engineering: Vahid AtashbariGilbertAinda não há avaliações
- CALCULATION 10 MVA Short Circuit PDFDocumento4 páginasCALCULATION 10 MVA Short Circuit PDFLevi Franco Carvalho100% (2)
- 28Documento12 páginas28physicsdocsAinda não há avaliações
- Foundation Design For ChimneyDocumento5 páginasFoundation Design For ChimneyAmit100% (2)