Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Physics II Problems
Enviado por
BOSS BOSS0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
2K visualizações1 páginaThis document contains multiple circuit analysis problems involving resistors, batteries, capacitors, and measuring instruments like ammeters and voltmeters. The problems involve calculating currents, potential differences, emfs and conversions between different types of measuring instruments. Diagrams of the circuit setup are provided for each problem.
Descrição original:
Título original
Physics II Problems (52)
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document contains multiple circuit analysis problems involving resistors, batteries, capacitors, and measuring instruments like ammeters and voltmeters. The problems involve calculating currents, potential differences, emfs and conversions between different types of measuring instruments. Diagrams of the circuit setup are provided for each problem.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
2K visualizações1 páginaPhysics II Problems
Enviado por
BOSS BOSSThis document contains multiple circuit analysis problems involving resistors, batteries, capacitors, and measuring instruments like ammeters and voltmeters. The problems involve calculating currents, potential differences, emfs and conversions between different types of measuring instruments. Diagrams of the circuit setup are provided for each problem.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
Exercises
Figure E26.34
Figure E26.27
2.00 A
+
20.0 V
E1
17 V
E2
+
6.00 V
5.00 A
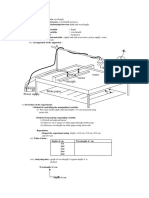
26.28 .. In the circuit shown Figure E26.28
in Fig. E26.28, nd (a) the cur2.00 V 10.00 V
rent in each branch and (b) the
3.00 V
+ a
potential difference Vab of
1.00 V 5.00 V
point a relative to point b.
4.00 V
+
26.29 . The 10.00-V battery
b
in Fig. E26.28 is removed
10.00 V
from the circuit and reinserted
with the opposite polarity, so
that its positive terminal is now next to point a. The rest of the circuit is as shown in the gure. Find (a) the current in each branch
and (b) the potential difference Vab of point a relative to point b.
26.30 . The 5.00-V battery in Fig. E26.28 is removed from the
circuit and replaced by a 20.00-V battery, with its negative terminal next to point b. The rest of the circuit is as shown in the gure.
Find (a) the current in each branch and (b) the potential difference
Vab of point a relative to point b.
26.31 .. In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.31 the batteries have
negligible internal resistance and the meters are both idealized.
With the switch S open, the voltmeter reads 15.0 V. (a) Find the
emf E of the battery. (b) What will the ammeter read when the
switch is closed?
Figure E26.31
30.0 V
+
20.0
V
+
E5?
25.0 V
S
50.0
V
V
6.0 V 20.0 V
25 V
3.0 V
13 V
19 V
A
1.0 V
Section 26.3 Electrical Measuring Instruments
26.35 . The resistance of a galvanometer coil is 25.0 , and the
current required for full-scale deection is 500 mA. (a) Show in a
diagram how to convert the galvanometer to an ammeter reading
20.0 mA full scale, and compute the shunt resistance. (b) Show
how to convert the galvanometer to a voltmeter reading 500 mV
full scale, and compute the series resistance.
26.36 . The resistance of the coil of a Figure E26.36
pivoted-coil galvanometer is 9.36 , and a
RG
current of 0.0224 A causes it to deect full
scale. We want to convert this galvanomeR
ter to an ammeter reading 20.0 A full scale.
Shunt
The only shunt available has a resistance of
0.0250 . What resistance R must be connected in series with the
coil (Fig. E26.36)?
26.37 . A circuit consists of a series combination of 6.00-k and
5.00-k resistors connected across a 50.0-V battery having negligible internal resistance. You want to measure the true potential
difference (that is, the potential difference without the meter present) across the 5.00-k resistor using a voltmeter having an internal resistance of 10.0 k. (a) What potential difference does the
voltmeter measure across the 5.00-k resistor? (b) What is the
true potential difference across this resistor when the meter is not
present? (c) By what percentage is the voltmeter reading in error
from the true potential difference?
26.38 . A galvanometer having a resistance of 25.0 has a
1.00- shunt resistance installed to convert it to an ammeter. It is
then used to measure the current in a circuit consisting of a 15.0-
resistor connected across the terminals of a 25.0-V battery having
no appreciable internal resistance. (a) What current does the
ammeter measure? (b) What should be the true current in the circuit (that is, the current without the ammeter present)? (c) By what
percentage is the ammeter reading in error from the true current?
26.39 . In the ohmmeter in Fig. E26.39 M is
Figure E26.39
a 2.50-mA meter of resistance 65.0 . (A
2.50-mA meter deects full scale when the
M
current through it is 2.50 mA.) The battery B
a b
B
has an emf of 1.52 V and negligible internal
Rx
R
resistance. R is chosen so that when the terminals a and b are shorted 1Rx = 02, the meter reads full scale.
When a and b are open 1Rx = q 2, the meter reads zero. (a) What
is the resistance of the resistor R? (b) What current indicates a
resistance Rx of 200 ? (c) What values of Rx correspond to meter
deections of 14, 12, and 34 of full scale if the deection is proportional to the current through the galvanometer?
+
26.32 .. In the circuit shown Figure E26.32
in Fig. E26.32 both batteries
12.0 V
have insignicant internal
+
E5?
resistance and the idealized
48.0
+
ammeter reads 1.50 A in the
15.0
V
75.0 V
V
direction shown. Find the emf
A
E of the battery. Is the polarity
shown correct?
26.33 . In the circuit shown Figure E26.33
in Fig. E26.33 all meters are
100.0 V
a
idealized and the batteries
15.0
have no appreciable internal
+
S
V
25.0 +
resistance. (a) Find the readV
75.0
V
ing of the voltmeter with the
A
V
switch S open. Which point is
b
at a higher potential: a or b?
(b) With the switch closed, nd the reading of the voltmeter and
the ammeter. Which way (up or down) does the current ow
through the switch?
26.34 .. In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.34, the 6.0- resistor is
consuming energy at a rate of 24 J/s when the current through it ows
as shown. (a) Find the current through the ammeter A. (b) What are
the polarity and emf E of the battery, assuming it has negligible internal resistance?
E5?
3.00 V
4.00 V
3.00 A
75.0
V
877
Section 26.4 R - C Circuits
26.40 . A 4.60-mF capacitor that is initially uncharged is connected in series with a 7.50-k resistor and an emf source with
E = 245 V and negligible internal resistance. Just after the circuit
is completed, what are (a) the voltage drop across the capacitor;
Você também pode gostar
- Solution 08Documento44 páginasSolution 08楊顗融Ainda não há avaliações
- Class XI XII Laboratory Manual SolutionDocumento106 páginasClass XI XII Laboratory Manual SolutionRajibul Islam78% (129)
- Circuits WorksheetDocumento3 páginasCircuits Worksheettuvvac67% (3)
- Physics Practical Class 12Documento14 páginasPhysics Practical Class 12Sahil Midha100% (2)
- WavesDocumento30 páginasWavesExotic EagleAinda não há avaliações
- Resistance Electricity Class X Science Ncert Ncert Questions Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Ncert Notes Electrical ResistivityDocumento2 páginasResistance Electricity Class X Science Ncert Ncert Questions Science Class 10 Chapter 1 Ncert Notes Electrical ResistivityPranavMehtaAinda não há avaliações
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Networks MCQ Bank and Free Study MaterialDocumento68 páginasComputer Networks MCQ Bank and Free Study MaterialVikasSainiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Project File 2222333333Documento12 páginasPhysics Project File 2222333333Harsh Arora100% (1)
- Hooke's Law and The Spring ConstantDocumento4 páginasHooke's Law and The Spring ConstantJuan Carlos Mejia Macias0% (1)
- Chap 23Documento24 páginasChap 23bryarAinda não há avaliações
- Neals Token InstrumentDocumento39 páginasNeals Token InstrumentVikas Srivastav100% (2)
- PR Closed System 2Documento2 páginasPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ProblemsDocumento3 páginasPhysics ProblemsKathiresan ManickamAinda não há avaliações
- 69 75Documento10 páginas69 75Carlos Moran CepedaAinda não há avaliações
- Cheeto LabDocumento2 páginasCheeto Labapi-213645632100% (1)
- 10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsDocumento6 páginas10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsBharti KakkarAinda não há avaliações
- Tshoga Lo PDFDocumento11 páginasTshoga Lo PDFlehlabileAinda não há avaliações
- Paulino, Paul Tyrone R. Assignment 2Documento14 páginasPaulino, Paul Tyrone R. Assignment 2Tyrone PaulinoAinda não há avaliações
- TOS 06 Student's PDFDocumento1 páginaTOS 06 Student's PDFCed Calzado0% (1)
- Laboratory 1Documento13 páginasLaboratory 1Rn NatAinda não há avaliações
- Math4 170513085146Documento47 páginasMath4 170513085146jucar fernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Tuto 6Documento13 páginasSolution Tuto 6Abood AtiyatAinda não há avaliações
- Integration Using Algebraic SolutionDocumento6 páginasIntegration Using Algebraic SolutionAANAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Internal Assessment OoDocumento7 páginasMathematics Internal Assessment OoSigne Sofia PersdotterAinda não há avaliações
- Ideal Gas ProcessDocumento1 páginaIdeal Gas ProcessGood Game100% (1)
- CIEM5390 Problem Set 2 - SolutionDocumento10 páginasCIEM5390 Problem Set 2 - SolutionMatthew LiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento15 páginasChapter 1سعيد بن إدريس100% (1)
- Formulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017Documento11 páginasFormulas For Pre-Olympiad Competition Math: Eashan Gandotra 4 August 2017jehovisti100% (1)
- Unit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment0Documento4 páginasUnit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment0Prasenjit DeyAinda não há avaliações
- Solucionario Cap 10 Circuitos Dorf Sodoba 5 EdicionDocumento40 páginasSolucionario Cap 10 Circuitos Dorf Sodoba 5 EdicionJersson Emyr Camacho GomezAinda não há avaliações
- Theoretical Problems in PhysicsDocumento9 páginasTheoretical Problems in PhysicsbananasausageAinda não há avaliações
- S PDFDocumento90 páginasS PDFAmritha V100% (1)
- Day 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Documento51 páginasDay 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Free student100% (1)
- 610 Midterm 2 S11 02 With SolDocumento6 páginas610 Midterm 2 S11 02 With SolabuzarAinda não há avaliações
- The Advantages of AC Power Over DC PowerDocumento2 páginasThe Advantages of AC Power Over DC PowershafibhaiAinda não há avaliações
- HW1 A SolutionsDocumento5 páginasHW1 A SolutionsAli Abbas SheriffAinda não há avaliações
- ECE 3074 AC Circuits Lab Lab 2: Winding Your Own Inductors & Making AC Measurements With An OscilloscopeDocumento6 páginasECE 3074 AC Circuits Lab Lab 2: Winding Your Own Inductors & Making AC Measurements With An OscilloscopeZiad Mohmed FawzyAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Ch1 ProblemDocumento5 páginasTutorial Ch1 ProblemKiat HauAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Economics Questions Problem SolvingDocumento4 páginasEngineering Economics Questions Problem SolvingLouie Jay LayderosAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Homework #1Documento34 páginasPhysics Homework #1RowlenaAinda não há avaliações
- Jessica Agar: Search Subjects LOG INDocumento7 páginasJessica Agar: Search Subjects LOG INJamiel CatapangAinda não há avaliações
- Activity # 1Documento20 páginasActivity # 1BIG BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Series Circuits: Pspice Tutorials Available at LoydDocumento49 páginasSeries Circuits: Pspice Tutorials Available at LoydSanda Kinithi0% (1)
- Assignment 2 - 2023 - SolutionsDocumento23 páginasAssignment 2 - 2023 - SolutionsLinhan ChuAinda não há avaliações
- MSE 227 HW9 F10 SolutionsDocumento5 páginasMSE 227 HW9 F10 Solutionsputri nur shahidaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No 2 Name: Muhammad Ali Reg Id: 12249 Section: ES Semester: 1 Course: BSSE Subject: Applied Physics Teacher Name: Qazi Haseeb YousufDocumento11 páginasAssignment No 2 Name: Muhammad Ali Reg Id: 12249 Section: ES Semester: 1 Course: BSSE Subject: Applied Physics Teacher Name: Qazi Haseeb YousufAli KhanAinda não há avaliações
- D.C. Machin BaidaDocumento53 páginasD.C. Machin BaidaLeonard ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- Of The Bar by Equating The Strain: Problem 2.7-9Documento16 páginasOf The Bar by Equating The Strain: Problem 2.7-9EDiane LlanosAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Problems of EEDocumento9 páginasSample Problems of EEEdson MilanoAinda não há avaliações
- HjjooDocumento28 páginasHjjooJohn Patrick DagleAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2Documento3 páginasAssignment 2MubynAfiqAinda não há avaliações
- Kirchhoff Current Law (KCL)Documento3 páginasKirchhoff Current Law (KCL)Kiran KarthikAinda não há avaliações
- Statics Chpt.3Documento105 páginasStatics Chpt.3safeer_siddickyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 ThermodynamicsDocumento94 páginasChapter 12 ThermodynamicsNitish MehraAinda não há avaliações
- WasaaapppDocumento29 páginasWasaaapppManoy BermeoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 13. Filter Inductor DesignDocumento29 páginasChapter 13. Filter Inductor DesignNestor EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Problemas Cinetica PDFDocumento7 páginasProblemas Cinetica PDFMoisés DuranAinda não há avaliações
- 2-3 Time Value of Money - Arithmetic Gradient SeriesDocumento19 páginas2-3 Time Value of Money - Arithmetic Gradient SeriesKyzer GardiolaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1 - Electric CircuitsDocumento70 páginasTopic 1 - Electric CircuitsKavinesh AnanthanAinda não há avaliações
- Physics II ProblemsDocumento1 páginaPhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Physics II Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Circuits-Worksheet 101Documento5 páginasCircuits-Worksheet 101wassimfakAinda não há avaliações
- Physics II Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDocumento1 páginaCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Additional One Marks Question Paper 1Documento1 páginaAdditional One Marks Question Paper 1BOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeDocumento2 páginasCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- Albert EinsteinDocumento2 páginasAlbert EinsteinBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDocumento1 páginaTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- KVSTUDY6Documento10 páginasKVSTUDY6OnlineDownloadsAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Paper 1 DR Ken ChanDocumento19 páginasPhysics Paper 1 DR Ken Chansuperpooh-1Ainda não há avaliações
- 12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Documento32 páginas12 Electricity and Magnetisium - 1Harsh GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion of Charge in Magnetic FieldDocumento18 páginasMotion of Charge in Magnetic FieldAsif HameedAinda não há avaliações
- To Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Documento4 páginasTo Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Sulman Abbasi0% (2)
- Sec. 4-2 Torque and Deflection of The GalvanometerDocumento9 páginasSec. 4-2 Torque and Deflection of The GalvanometerMohammadKazaalAinda não há avaliações
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocumento9 páginasMapúa Institute of Technology: Familiarization With Electrical Measuring InstrumentsJohn FerreAinda não há avaliações
- Eksperiman FizikDocumento26 páginasEksperiman FizikNUR BATRISYIA AMALYAAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Manual For classXII (2022-2023)Documento46 páginasPhysics Lab Manual For classXII (2022-2023)studies for sundarAinda não há avaliações
- Meter BridgeDocumento5 páginasMeter BridgeSandhya67% (9)
- Comparator SDocumento68 páginasComparator SMuraliAinda não há avaliações
- GalvanometerDocumento8 páginasGalvanometerAnkit ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Class Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementDocumento8 páginasClass Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementRafaelAinda não há avaliações
- Idoc - Pub - Cbseclass 12thphysics Practical File Readings PDFDocumento45 páginasIdoc - Pub - Cbseclass 12thphysics Practical File Readings PDFRishabh MalviyaAinda não há avaliações
- Optical RecordingDocumento17 páginasOptical RecordingArijit MitraAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking Type Questions: Moving Charges and MagnetismDocumento4 páginasCritical Thinking Type Questions: Moving Charges and MagnetismMurthi ChandhuAinda não há avaliações
- Faraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetDocumento1 páginaFaraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetAnahita SinghAinda não há avaliações
- MCQSDocumento14 páginasMCQSqasimAinda não há avaliações
- WWW Elprocus Com What Is PMMC Instrument Construction Its WorkingDocumento7 páginasWWW Elprocus Com What Is PMMC Instrument Construction Its WorkingAayush “Ashu”Ainda não há avaliações
- Torque On A CoilDocumento24 páginasTorque On A CoiledithAinda não há avaliações
- Sensors and Transducers Lab Sample QuestionsDocumento2 páginasSensors and Transducers Lab Sample QuestionsNaik RhAinda não há avaliações
- Half DeflectionDocumento4 páginasHalf DeflectionUdit AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Multimeter Working PrincipalsDocumento3 páginasMultimeter Working PrincipalsSanjivee SachinAinda não há avaliações
- Investigatory Project of Physics 2022-23Documento14 páginasInvestigatory Project of Physics 2022-23MediaxAinda não há avaliações
- Angel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsDocumento3 páginasAngel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsAtul Verma0% (1)