Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
111 HW 11
Enviado por
Owl AppleKingDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
111 HW 11
Enviado por
Owl AppleKingDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
HOMEWORK: SET 11- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION PROBLEMS:
1) A body of mass 2 kg is suspended from a spring of negligible mass, and is found to stretch the spring
20 cm. (a) What is the force constant of the spring? (b) What is the period of oscillation of the body, if it
is pulled down and released? (c) What would be the period of a body of mass 4 kg hanging from the
same spring?
ans.
a) 98 N/m
b) 0.898 sec.
c) 1.27 sec
2) The scale of a spring balance reading from zero to 180 N is 9 cm long. A body suspended from the
balance is observed to oscillate vertically with a frequency of 1.5 Hz. What is the mass of the body?
Neglect the mass of the spring.
ans.
22.5 kg
3) A body is vibrating with simple harmonic motion of amplitude 15 cm and frequency 4 Hz. Compute
(a) the maximum values of the acceleration and the velocity, (b) the acceleration and velocity when the
position is 9 cm, and (c) the time required to move from the equilibrium position to a point 12 cm distant
from it.
ans. (a) 94.8 m/sec2; 3.77 m/sec. (b) 56.9 m/sec2, 3.02 m/sec (c) 0.0369 seconds
4) A body of mass 4 kg is attached to a coil spring and oscillates vertically with SHM. The amplitude of
the oscillations is 0.5 m, and at its highest point of the motion, the spring has its natural unstretched
length. Calculate the elastic potential energy of the spring, the kinetic energy of the body, and its
gravitational potential energy relative to the lowest point of the motion, and the sum of these 3 energies,
when the body is (a) at its lowest point, (b) at its equilibrium position, (c) at its highest point.
ans. a) 39.2, 0, 0, 39.2 J
b) 9.8, 9.8, 19.6, 39.2 J
c) 0, 0, 39.2, 39.2 J
5) A body of mass 10 gm moves with simple harmonic motion of amplitude 24 cm and a period of 4
seconds. The position (coordinate) is + 24 cm when t = 0. Compute (a) the position when t= 0.5 seconds,
(b) the magnitude & direction of the force acting on the body when t = 0.5 sec. (c) the minimum time
required for the body to move from its initial position to the point where x = - 12 cm, (d) the velocity of
the body at x = - 12 cm.
ans.
a) 17.0 cm
b) - 4.19 x 10-3 N
c) 1.33 sec
d) -32.6 cm/sec
6) A small block is executing SHM in a horizontal plane with an amplitude of 10 cm. At a point 6 cm
from its equilibrium position the block has a speed of 24 cm/sec. (a) What is the period of the motion?
(b) What is the displacement from equilibrium when the magnitude of the velocity is 12 cm/sec? (c) If
a small object placed on top of the oscillating block is just on the verge of slipping at the endpoint of the
motion, what is the coefficient of static friction between the object and the block?
ans.
a) 2.09 sec
b) 9.17 cm
c) 0.0918
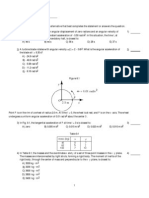
7) Two springs with the same unstretched length but
different force constants k1 and k2 are attached to a
block of mass m on a level frictionless surface.
Calculate the effective force constant in each of the 3
cases shown in the figure. In terms of k1 and k2 what
would be the ratios of the frequencies of case 2 to
case 1 ? Of case 3 to case 1 ?
ans.
a) k1 + k2
b) k1 + k2
c) (k1 k2)/(k1 + k2)
k1
k2
k2
8) The motion of the piston in an automobile engine is approximately simple harmonic motion.
a) If the stroke of the engine (twice the amplitude) is 10 cm, and the angular velocity is 3600
rev/minute, compute the acceleration of the piston at the end of its stroke.
b) If the piston has a mass of 0.5 kg, what resultant force must be exerted on it at this point?
c) What is the velocity of the piston, in kilometers per hour, at the midpoint of the stroke?
ans.
a) 7106 m/sec2
b) 3553 N
c) 67.9 km/hr
9) A force of 30 N stretches a vertical spring 15 cm. a) What mass must be suspended from the spring
so that the system will oscillate with a period of (/4) seconds?
b) If the amplitude of the motion is 5 cm, where is the body and in what direction is it moving
( /12) seconds after it has passed the equilibrium position, moving downward?
c) What force does the spring exert on the body when it is 3 cm below the equilibrium position,
moving upward?
ans.
a) 3.13 kg
b) 4.33 cm below, moving upward
c) 37 N
11) It is desired to construct a pendulum of period 10 seconds. (a) What is the length of a simple
pendulum which would have this period? (b) Suppose the pendulum must be mounted in a case not over
0.5 m high. Can you devise a pendulum, having a period of 10 seconds, that will satisfy this
requirement?
ans.
24.8 m
Você também pode gostar
- SHM Worksheet Solutions KaplanDocumento3 páginasSHM Worksheet Solutions KaplanNadeenMohamedAinda não há avaliações
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocumento4 páginasR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Documento4 páginasAnnual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Sumathi SrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- ProblemsDocumento4 páginasProblemsMonda Bw'OnchwatiAinda não há avaliações
- SHM WSDocumento3 páginasSHM WSTrishnee MunusamiAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Harmonic Motion and ElasticityDocumento15 páginasSimple Harmonic Motion and ElasticitySubho BhattacharyaAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Quiz AnswersDocumento37 páginasEngineering Mechanics Quiz AnswersAnanda BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational Motion by Kota Practice Test Iit JeeDocumento6 páginasRotational Motion by Kota Practice Test Iit JeeTEACHING TECHNICAL TIPSAinda não há avaliações
- AL Physics/S.H.M./P.1: DX DT BXDocumento4 páginasAL Physics/S.H.M./P.1: DX DT BXmiguelAinda não há avaliações
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSAinda não há avaliações
- SheetDocumento3 páginasSheetAly ElbarodyAinda não há avaliações
- Ss 1 PHDocumento3 páginasSs 1 PHPrince BurnaAinda não há avaliações
- Harmonic Motion HomeworkDocumento4 páginasHarmonic Motion HomeworkJennifer PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Harmonic Motion Problems With Answers FINALDocumento15 páginasSimple Harmonic Motion Problems With Answers FINALAngelAinda não há avaliações
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreDocumento5 páginasExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamAinda não há avaliações
- SHM Review-Exam 3Documento6 páginasSHM Review-Exam 3Ney CampoAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Questions in Physics 101Documento13 páginasRevision Questions in Physics 101lozzzzzAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises August 14, 2019Documento3 páginasExercises August 14, 2019Lester Patalinghug BernardinoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Forces and Motion Recitation LessonDocumento15 páginasPhysics Forces and Motion Recitation LessonRicard AltamirAinda não há avaliações
- Oscillations Question BankDocumento9 páginasOscillations Question Bankkrishnam rajuAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Harmonic Motion TutorialDocumento2 páginasSimple Harmonic Motion TutorialveluarasuAinda não há avaliações
- PHY 101 QuestionsDocumento3 páginasPHY 101 QuestionsEddy WilliamAinda não há avaliações
- I-Taalem Task - Chapter 8Documento3 páginasI-Taalem Task - Chapter 8ruzaimi98Ainda não há avaliações
- OscillationsDocumento4 páginasOscillationsNguyen Lam Uyen FX12223Ainda não há avaliações
- Force - STD XDocumento48 páginasForce - STD XSujoy SenAinda não há avaliações
- التنصيرDocumento4 páginasالتنصيرmaryanahmedfiidowAinda não há avaliações
- 17-09-23 Neet Ans.-1Documento6 páginas17-09-23 Neet Ans.-1yxfjmv862qAinda não há avaliações
- PHY11 CO2 Reviewer 1Documento3 páginasPHY11 CO2 Reviewer 1Tetsuya OkazakiAinda não há avaliações
- 1.0 Test On Circular MotionDocumento1 página1.0 Test On Circular Motionrsdiwane100% (1)
- Wilson, College Physics - Chapter 6, ExercisesDocumento23 páginasWilson, College Physics - Chapter 6, ExercisesJohnatan AgudeloAinda não há avaliações
- Phyc2122 Sem1 W1 10 GR12Documento85 páginasPhyc2122 Sem1 W1 10 GR12Diana Jane Lauzon LluragAinda não há avaliações
- (Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc-121 Week 1-10Documento84 páginas(Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc-121 Week 1-10Amanda Dinah RamilAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational Dynamics and EquilibriumDocumento16 páginasRotational Dynamics and EquilibriumSubho BhattacharyaAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Question MoreDocumento12 páginasRevision Question MoreFiedDinieAinda não há avaliações
- QuestionsDocumento25 páginasQuestionsSkye JabaAinda não há avaliações
- Wheat Fields Public School Ghudda, Bathinda S.A 1, Xi - PhysicsDocumento2 páginasWheat Fields Public School Ghudda, Bathinda S.A 1, Xi - PhysicsGurvinder SinghAinda não há avaliações
- ANSWER: (A) 30 S (B) 1.8Documento2 páginasANSWER: (A) 30 S (B) 1.8Thu HòaAinda não há avaliações
- Pay Roll SystemDocumento52 páginasPay Roll SystemMind-RelaxingAinda não há avaliações
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento19 páginasHapter: Conceptual Problemsadel0% (1)
- Midterm Spring 09Documento3 páginasMidterm Spring 09rubel_lincAinda não há avaliações
- 11 Physics Oscillations and Waves Test 01Documento1 página11 Physics Oscillations and Waves Test 01Edukondalu NamepalliAinda não há avaliações
- ECAT Unit 7 (Oscillations) - 1Documento3 páginasECAT Unit 7 (Oscillations) - 1MScIT2M1012 Jawad TariqAinda não há avaliações
- 3U Exam ReviewDocumento5 páginas3U Exam ReviewShivansh DharAinda não há avaliações
- Physics RequirementDocumento14 páginasPhysics RequirementVinky SantosAinda não há avaliações
- PSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsDocumento18 páginasPSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsamanAinda não há avaliações
- Circular MotionDocumento15 páginasCircular Motionpraveen alwisAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 Electric FieldsDocumento17 páginasChapter 15 Electric FieldsdrewAinda não há avaliações
- File 30-01-24 872Documento8 páginasFile 30-01-24 872himalacharya86Ainda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion Questions?Documento29 páginasCircular Motion Questions?Muhammad RafayAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 6Documento6 páginasAssignment 6CapsanneAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Choice Mechanics ExamDocumento5 páginasMultiple Choice Mechanics ExamAvnish GargAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheet 8Documento2 páginasTutorial Sheet 8fmukuka12Ainda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNo EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- 9 - Sewage Treatment PlantDocumento10 páginas9 - Sewage Treatment PlantOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- KSEW Internship ReportDocumento17 páginasKSEW Internship ReportOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Shipbuilding Quality Standard GuideDocumento59 páginasShipbuilding Quality Standard Guidenyaungzin100% (2)
- Ur p2 Oct 2018Documento39 páginasUr p2 Oct 2018Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Requirements Concerning Pipes and Pressure Vessels: International Association of Classification SocietiesDocumento72 páginasRequirements Concerning Pipes and Pressure Vessels: International Association of Classification SocietiesmahmudAinda não há avaliações
- Requirements Concerning Pipes and Pressure Vessels: International Association of Classification SocietiesDocumento72 páginasRequirements Concerning Pipes and Pressure Vessels: International Association of Classification SocietiesmahmudAinda não há avaliações
- KSEW Internship ReportDocumento17 páginasKSEW Internship ReportOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Ge Jenbacher Engines Specifications PDFDocumento110 páginasGe Jenbacher Engines Specifications PDFAnibal Rios100% (3)
- 9 - Sewage Treatment PlantDocumento10 páginas9 - Sewage Treatment PlantOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix 1 - Mechanical Specification PDFDocumento328 páginasAppendix 1 - Mechanical Specification PDFOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Ge Jenbacher Engines Specifications PDFDocumento110 páginasGe Jenbacher Engines Specifications PDFAnibal Rios100% (3)
- Ludeca-A Practical Guide To Shaft Alignment PDFDocumento0 páginaLudeca-A Practical Guide To Shaft Alignment PDFDelfinsh100% (1)
- 14264A ch6Documento50 páginas14264A ch6Carlos Andres Cifuentes Castro0% (1)
- QRD Series: Instruction ManualDocumento43 páginasQRD Series: Instruction ManualOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Man B&W S35Mc7: Project Guide Camshaft Controlled Two Stroke EnginesDocumento351 páginasMan B&W S35Mc7: Project Guide Camshaft Controlled Two Stroke EnginesOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Satellite Communication: Direct-to-Home Satellite Television Broadcasting and S-DARSDocumento35 páginasSatellite Communication: Direct-to-Home Satellite Television Broadcasting and S-DARSOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Man B&W S35Mc7: Project Guide Camshaft Controlled Two Stroke EnginesDocumento351 páginasMan B&W S35Mc7: Project Guide Camshaft Controlled Two Stroke EnginesOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Delta Lab Group Tri2s1516 Ver2Documento33 páginasDelta Lab Group Tri2s1516 Ver2Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Karachi Population From KMP 2020 - Vol IDocumento6 páginasKarachi Population From KMP 2020 - Vol IOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Delta Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver2Documento4 páginasDelta Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver2Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Gamma Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver3Documento30 páginasGamma Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver3Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Gamma Lab Group Tri2s1516 Ver1Documento24 páginasGamma Lab Group Tri2s1516 Ver1Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Epsilon Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver2Documento8 páginasEpsilon Lab Timetable Tri2s1516 Ver2Owl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- Runge Kutta4 DaniDocumento90 páginasRunge Kutta4 DaniOwl AppleKingAinda não há avaliações
- JMS901 USB 3.1 Gen 1 To UFS/UHS-1 Bridge: Product BriefDocumento10 páginasJMS901 USB 3.1 Gen 1 To UFS/UHS-1 Bridge: Product BriefBaron MunchausenAinda não há avaliações
- Unedited Actpc Event Feb 12Documento3 páginasUnedited Actpc Event Feb 12api-540635791Ainda não há avaliações
- XenServer Web Self Service Installation Guide 1.1.2Documento13 páginasXenServer Web Self Service Installation Guide 1.1.2lucozzadeAinda não há avaliações
- Infirmière Du New Jersey Veut Une Grosse Bite NoiDocumento1 páginaInfirmière Du New Jersey Veut Une Grosse Bite Noifranck petbeamAinda não há avaliações
- JCI Values Prayer and MissionDocumento4 páginasJCI Values Prayer and MissionnamasteamizadeAinda não há avaliações
- SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION EXERCISESDocumento11 páginasSENTENCE CONSTRUCTION EXERCISESMuthyala AkhilAinda não há avaliações
- DMELLOHTLDocumento1.023 páginasDMELLOHTLSneha RaoAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Job Order Costing-1Documento15 páginas05 Job Order Costing-1RodelLaborAinda não há avaliações
- Sanand GIDC Company List PDFDocumento3 páginasSanand GIDC Company List PDFMotka GhanshyamAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 2 - SolutionDocumento2 páginasProblem Set 2 - SolutionJohn ScarceAinda não há avaliações
- Epayslip 2023-07-27 31173270Documento1 páginaEpayslip 2023-07-27 31173270ryan robert mercadoAinda não há avaliações
- BSBOPS504 Student Guide (Ver. 1) PDFDocumento41 páginasBSBOPS504 Student Guide (Ver. 1) PDFanishAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To SLADocumento4 páginasAn Introduction To SLASaurabhChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- No. L-25177. October 31, 1969. THE PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Plaintiff-Appellee, Fugoso and Joventino Garces, Defendants-AppellantsDocumento7 páginasNo. L-25177. October 31, 1969. THE PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Plaintiff-Appellee, Fugoso and Joventino Garces, Defendants-AppellantsHarold Q. GardonAinda não há avaliações
- 365 SummaryDocumento1 página365 SummaryS MulaAinda não há avaliações
- G.R. No. 154554Documento7 páginasG.R. No. 154554KidMonkey2299Ainda não há avaliações
- HistoryDocumento5 páginasHistoryGrizell CostañosAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating key financial ratios and metricsDocumento4 páginasCalculating key financial ratios and metricsAccounting MaterialsAinda não há avaliações
- PWDApplication FormDocumento2 páginasPWDApplication FormJames LorenzoAinda não há avaliações
- Itr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification FormDocumento1 páginaItr-V: Indian Income Tax Return Verification FormVikash SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Sea Lion Case DigestDocumento2 páginasSea Lion Case DigestmrpowerplusAinda não há avaliações
- 266 Steelcase v. DISI (Galinato)Documento3 páginas266 Steelcase v. DISI (Galinato)Koko GalinatoAinda não há avaliações
- YNOT Vs Intermediate Appellate CourtDocumento8 páginasYNOT Vs Intermediate Appellate Courtricohizon99Ainda não há avaliações
- BMW F 850 GS SpecificationsDocumento7 páginasBMW F 850 GS SpecificationsBoby KumbAinda não há avaliações
- Thal Limited Result 12-09-2023Documento3 páginasThal Limited Result 12-09-2023zaid khanAinda não há avaliações
- LAW Salient Features Ra 3883 Business Name LAWDocumento24 páginasLAW Salient Features Ra 3883 Business Name LAWTan TanAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Instructions: C/o ©Shane-Michael: Dorn 3439 NE Sandy BLVD Suite 691 Portland, Oregon RepublicDocumento1 páginaAccounting Instructions: C/o ©Shane-Michael: Dorn 3439 NE Sandy BLVD Suite 691 Portland, Oregon RepublicjimAinda não há avaliações
- Sprint Communications Company LP v. Vonage Holdings Corp., Et Al - Document No. 345Documento2 páginasSprint Communications Company LP v. Vonage Holdings Corp., Et Al - Document No. 345Justia.comAinda não há avaliações
- Professional Chef ResumeDocumento2 páginasProfessional Chef ResumeShery TentionAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Key Section 1 To 5 Nov2022batchDocumento15 páginasAnswer Key Section 1 To 5 Nov2022batchICS Davao2 (Epyong)100% (1)