Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Defects of Timber
Enviado por
Richelle Simangan0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
195 visualizações5 páginasThis document classifies and describes various defects that can occur in timber. It divides defects into five categories: those caused by natural forces, fungi, insects, the conversion process, and seasoning. Defects caused by natural forces include chemical stains, knots, shakes, twisted fibers, ring galls, upsets, and burls. Defects from fungi include blue stain, brown rot, dry rot, heart rot, wet rot, and white rot. Insect-caused defects are discussed for beetles, marine borers, and termites. Defects from conversion are chip marks, diagonal grain, and torn grain. Seasoning can cause twists, cups, bows, checks, splits,
Descrição original:
defects in timber for timber design
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document classifies and describes various defects that can occur in timber. It divides defects into five categories: those caused by natural forces, fungi, insects, the conversion process, and seasoning. Defects caused by natural forces include chemical stains, knots, shakes, twisted fibers, ring galls, upsets, and burls. Defects from fungi include blue stain, brown rot, dry rot, heart rot, wet rot, and white rot. Insect-caused defects are discussed for beetles, marine borers, and termites. Defects from conversion are chip marks, diagonal grain, and torn grain. Seasoning can cause twists, cups, bows, checks, splits,
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
195 visualizações5 páginasDefects of Timber
Enviado por
Richelle SimanganThis document classifies and describes various defects that can occur in timber. It divides defects into five categories: those caused by natural forces, fungi, insects, the conversion process, and seasoning. Defects caused by natural forces include chemical stains, knots, shakes, twisted fibers, ring galls, upsets, and burls. Defects from fungi include blue stain, brown rot, dry rot, heart rot, wet rot, and white rot. Insect-caused defects are discussed for beetles, marine borers, and termites. Defects from conversion are chip marks, diagonal grain, and torn grain. Seasoning can cause twists, cups, bows, checks, splits,
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
1.
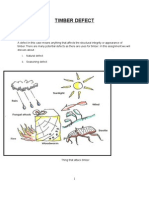
Defects of Timber
A defect is an irregularity or abnormality occurring in or on wood which
is responsible for its Strength reduction; Lowering of durability;
Lowering of utility; Poor appearance; and, Decay
Classification of Defects:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Caused
Caused
Caused
Caused
Caused
due
due
due
due
due
to
to
to
to
to
natural forces
insects
fungi
conversion
seasoning
a) Defects due to natural forces:
Chemical stain - the wood is sometimes discolored by the chemical
action caused with it by some external agency. This is known as
chemical stain.
Knots - these are the bases of branches or limbs which are broken or
cut off from the tree. The portion from which the branch is removed
receives nourishment from the stem for a pretty long time and it
ultimately results in formation of dark hard rings which are known as
knots. As continuity of wood fibers are broken by knots, they form a
source of weakness
Shakes - these are longitudinal separations in wood between the
annual rings. These are cracks which partly or completely separate
fibers of wood. The separations make the wood undesirable when
appearance is important
Twisted fibers - these are known as wandering hearts and caused by
twisting of young trees by fast blowing wind. The timbers with twisted
fibers is unsuitable for sawing
Ring galls - the rind means bark and gall indicates abnormal growth.
Hence peculiar curved swellings found on the body of tree are known
as rind gall. They develop at points from where branches are
improperly cut off or removed. They are rarely found in a tree and the
timber in this part is very weak and not durable.
Upsets - these indicate wood fibers which are injured by crushing or
compression. The upsets are mainly due to improper felling of tree and
exposure of tree in its young age to fast blowing wind
Burls - they are particularly formed when a tree receives shock or
injury in its young age. Due to its injury, the growth of tree is
completely upset and irregular projections appear on the body of
timber
b) Defects due to Fungi:
Blue stain - the sap of wood is stained to bluish color by the action of
certain type of fungi
Brown rot - the term rot is used to indicate decay or disease of timber,
the fungi of certain type removes cellulose compounds from wood and
hence wood assumes the brown color
Dry rot - some types of fungi feed on woods and during feeding they
attack on wood and convert it into dry powder form. This is known as
dry rot.
Heart rot -this is formed when branch has come out of the tree. In such
case, the heart wood is exposed to attack of atmospheric agents.
Ultimately the tree becomes weak and it gives hollow sound when
struck with hammer.
Wet rot - some kind of fungi caused chemical decomposition of wood of
timber and in doing so convert timber into grayish brown powder
White rot -it is just opposite of brown rot. In this certain type of fungi
attack lignin of wood and wood assumes the appearance of a white
mass consisting of cellulose compounds
c) Defects due to insects:
Defects caused by beetles
- They form pin holes of size about 2mm dia in wood
- Tunnel formation is done in sap wood by larvae of beetle
- Conversion of timber into flour like powder
- They do not disturb outer shell or cover
Defects due to marine boarders
-They are found in salty water
-They form tunnels or bores to take shelters
-Diameter and length of holes are as high as 25mm and 60 mm
respectively
-Affected wood loses its color and strength
-No timber is completely immune from attack of marine
boarders
Defects caused by termites
Lives in colony and very fast in eating away the wood from core
of cross-section
Makes tunnels in different directions and usually not disturb the
outer shell or cover.
The timber piece attacked by termites may look sound until it
completely fails
Few good timbers like teak, Sal, etc can resist the action of
termites
d) Defects due to conversion
Chip mark - this defect is indicated by mark or signs placed on finished
surface of timber. They may be formed by planning machine
Diagonal grain - the defect is formed due to improper sawing of timber.
It is indicated by diagonal marks on straight grained surface of timber
Torn grain - defect caused when a small depression is formed on a
finished surface of timber by falling a timber or so
Wane - this defect is denoted by presence of original rounded surface
on manufactured part of timber
e) Defects due to seasoning
Twist - when a piece of timber has spirally distorted along its length, it
is known as a twist
Cup - this defect is indicated by curvature formed in transverse
direction of timber
Bow - this defect is indicated by curvature formed in direction of length
of timber
Check -a crack which separates fibers of wood. It does not extend from
one end to the other
Split - when check extends from one end to other, it is known as a split
Honey combing - due to stress developed during drying, various radial
and circular cracks develop in the interior portion of timber, which
resembles with honey-comb texture
_slideshare.net
Timber Species and Properties(Timber Manual Datafile1, National Association of
Forest Industries)
Você também pode gostar
- Parts of TimberDocumento11 páginasParts of TimberAliAinda não há avaliações
- Wood EngineeringDocumento45 páginasWood EngineeringBLANCE CECILLE M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Defects of TimberDocumento27 páginasDefects of TimberMadhavi Latha0% (1)
- Wood DefectsDocumento10 páginasWood DefectsTegha LucasAinda não há avaliações
- Timber Assignment (Ruiles)Documento12 páginasTimber Assignment (Ruiles)Mary Joy RuilesAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation No 1Documento9 páginasPreparation No 1Jessa Mae Jamito EncinasAinda não há avaliações
- Consturction Matarial Assignment - Assingnment - 1Documento14 páginasConsturction Matarial Assignment - Assingnment - 1adnan maqboolAinda não há avaliações
- Aircraft Materials Construction and Repair: AENG 213Documento24 páginasAircraft Materials Construction and Repair: AENG 213Vince Gabriel AladoAinda não há avaliações
- Defects of TimberDocumento10 páginasDefects of TimberSandro Soriano100% (1)
- Abbas AssignmentDocumento11 páginasAbbas AssignmentFaisal KhanAinda não há avaliações
- TIMBERDocumento15 páginasTIMBERSadaf khanAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Defects in Timber As A Construction MaterialDocumento21 páginasTypes of Defects in Timber As A Construction MaterialManish ShashikantAinda não há avaliações
- Week 7 Tutorial Timber DefectsDocumento1 páginaWeek 7 Tutorial Timber DefectsSarahAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop Theory Report Clo 1Documento9 páginasWorkshop Theory Report Clo 1Anas SattiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6N TreesDocumento4 páginasLesson 6N TreesJake CanlasAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Technology (BSC Che-2Nd) : Assignment No 1Documento12 páginasMechanical Technology (BSC Che-2Nd) : Assignment No 1Iqra MaqsoodAinda não há avaliações
- Fe ReviewerDocumento3 páginasFe Reviewerzskhyzeia30Ainda não há avaliações
- SAfal CM AssignmentDocumento22 páginasSAfal CM AssignmentSafal PanthyAinda não há avaliações
- Timber DefectsDocumento2 páginasTimber Defectsarancypp100% (2)
- Defects in WoodDocumento56 páginasDefects in WoodJaypee TanAinda não há avaliações
- BFT Section 4 - Timber Technology (Presentation)Documento9 páginasBFT Section 4 - Timber Technology (Presentation)DontaeAXAinda não há avaliações
- Timber As Structural MaterialDocumento9 páginasTimber As Structural MaterialShayne Olaguer RoquidAinda não há avaliações
- Natural DefectsDocumento8 páginasNatural Defectswan8789100% (1)
- Timber Lesson 1 PDFDocumento59 páginasTimber Lesson 1 PDFdummya790Ainda não há avaliações
- Timber DefectsDocumento14 páginasTimber DefectsKemaro Morgan100% (1)
- Materials and Construction - I: Lecture No. 02 Dated: 20/02/2020Documento12 páginasMaterials and Construction - I: Lecture No. 02 Dated: 20/02/2020awais anjumAinda não há avaliações
- Timber Notes PDFDocumento56 páginasTimber Notes PDFAnjitha cAinda não há avaliações
- CMTDocumento45 páginasCMTstephannie montoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Construction MaterialsDocumento17 páginasConstruction MaterialsBisrateab FekaduAinda não há avaliações
- UEBE 1213-Building Materials: Topic 3-TimberDocumento67 páginasUEBE 1213-Building Materials: Topic 3-TimberTZShengAinda não há avaliações
- UEBE 1213-Building Materials: Topic 3-TimberDocumento67 páginasUEBE 1213-Building Materials: Topic 3-TimberTZShengAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of TreesDocumento16 páginasClassification of TreesKevinAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-Ii: Timber: Building Construction - VDocumento71 páginasUnit-Ii: Timber: Building Construction - VKittur AkshayAinda não há avaliações
- Wood Workshop: TimberDocumento22 páginasWood Workshop: TimberBilal AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Timber: Building Constrction and MaterailsDocumento70 páginasTimber: Building Constrction and MaterailsWilliam Arpit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Lect#7 TimberDocumento48 páginasLect#7 TimberTaimoor AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Defects in Timber - 1Documento20 páginasTypes of Defects in Timber - 1Joe NjoreAinda não há avaliações
- FAQ's Why Storing Timber Properly Is Important?: Common IssuesDocumento4 páginasFAQ's Why Storing Timber Properly Is Important?: Common IssuesJananiAinda não há avaliações
- WS PresentationDocumento60 páginasWS PresentationtechnologicaluniversityyangonAinda não há avaliações
- WoodDocumento41 páginasWoodJulius CodiamatAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Defects in Timber As A Construction MaterialDocumento17 páginasTypes of Defects in Timber As A Construction MaterialJustin MusopoleAinda não há avaliações
- Woods PresentationDocumento18 páginasWoods PresentationRie DeocampoAinda não há avaliações
- Palestine University: Building MaterialDocumento35 páginasPalestine University: Building MaterialMuhammad Irfan KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Defects in TimberDocumento17 páginasDefects in TimberAasim AzmiAinda não há avaliações
- Building Material - Timber & WoodDocumento47 páginasBuilding Material - Timber & WoodSaurav ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- Yaba College of Technology School of Environmental Studies Estate Management and Valuation LevelDocumento9 páginasYaba College of Technology School of Environmental Studies Estate Management and Valuation LevelGloriaAinda não há avaliações
- TIMBERDocumento43 páginasTIMBERgouri pmAinda não há avaliações
- TIMBER DEFECT SiapDocumento18 páginasTIMBER DEFECT Siapndali_2Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento11 páginasChapter 7engineeringnotes38480Ainda não há avaliações
- Nikhil, Abhishek, Soumya, Manav, Madhav, Divyaj, PrachiDocumento31 páginasNikhil, Abhishek, Soumya, Manav, Madhav, Divyaj, PrachiKulmani PadhiAinda não há avaliações
- Defects of Timber (Final Class)Documento20 páginasDefects of Timber (Final Class)Parth AnajwalaAinda não há avaliações
- Defects in TimberDocumento4 páginasDefects in TimberAnushkaAinda não há avaliações
- Growth of TreeDocumento16 páginasGrowth of TreeJohn EgbongAinda não há avaliações
- Carpentary Note by Ripan MondalDocumento7 páginasCarpentary Note by Ripan MondalSumanta DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Wood - : 1. Identify The Different Properties of WoodDocumento5 páginasWood - : 1. Identify The Different Properties of Woodrowell naragAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation 6 WOOD DEFECTSDocumento19 páginasPresentation 6 WOOD DEFECTSJohn ProtoctisAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Woodwork for Laboratory Technicians: Pergamon Series of Monographs in Laboratory TechniquesNo EverandPractical Woodwork for Laboratory Technicians: Pergamon Series of Monographs in Laboratory TechniquesAinda não há avaliações
- SRDS - PIM 03 As of 11 24 2020Documento1 páginaSRDS - PIM 03 As of 11 24 2020Richelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- SRDS - PIM 01 As of 11 24 2020Documento2 páginasSRDS - PIM 01 As of 11 24 2020Richelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- SRDS - PIM 05 As of 11 24 2020 2Documento2 páginasSRDS - PIM 05 As of 11 24 2020 2Richelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- SRDS - PIM 02 As of 11 24 2020Documento2 páginasSRDS - PIM 02 As of 11 24 2020Richelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- For ReviewDocumento8 páginasFor ReviewRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- Weather: For Other Uses, See - "Snowfall" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento3 páginasWeather: For Other Uses, See - "Snowfall" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- MJ ReviewDocumento29 páginasMJ ReviewRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- M.E. EngrDocumento66 páginasM.E. EngrRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- Proposed Small Water Impounding Project: Feasibility Study OnDocumento11 páginasProposed Small Water Impounding Project: Feasibility Study OnRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- HinahanapDocumento4 páginasHinahanapRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- Narrative ReportDocumento15 páginasNarrative ReportRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- Say It AgainDocumento2 páginasSay It AgainRichelle SimanganAinda não há avaliações
- GROUP1 MicroscaleDocumento3 páginasGROUP1 MicroscalefsfdsAinda não há avaliações
- My Ideal Home: Name No. Class Date Mark TeacherDocumento5 páginasMy Ideal Home: Name No. Class Date Mark TeacherQuadrado MágicoAinda não há avaliações
- Material Control Procedure - TemplateDocumento5 páginasMaterial Control Procedure - TemplateHernandito Rahmat KusumaAinda não há avaliações
- PRICELIST E Katalogs IVD 06042023 INDOPUTRA - PDF TerbaruDocumento6 páginasPRICELIST E Katalogs IVD 06042023 INDOPUTRA - PDF Terbaruseksi sspk sarprasAinda não há avaliações
- Aqa Econ3 QP Jan12Documento8 páginasAqa Econ3 QP Jan12api-247036342Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter Eight - Vapour Compression CycleDocumento37 páginasChapter Eight - Vapour Compression Cyclealhusseny100% (1)
- Pharma Iii To Viii PDFDocumento57 páginasPharma Iii To Viii PDFRaja PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- Full List of Oil Companies in Nigeria & Websites - Nigerian Infopedia PDFDocumento6 páginasFull List of Oil Companies in Nigeria & Websites - Nigerian Infopedia PDFBoma EvansAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Toe Treatments On The Fatigue Resistance of Structural Steel WeldsDocumento12 páginasEffect of Toe Treatments On The Fatigue Resistance of Structural Steel WeldsVicente Palazzo De MarinoAinda não há avaliações
- Zelio Control Relays - RM22TR33Documento7 páginasZelio Control Relays - RM22TR33SIVARAMANJAGANATHANAinda não há avaliações
- GenesDocumento33 páginasGenesJerick RoxasAinda não há avaliações
- ABB Photovoltaic DisconnectorsDocumento6 páginasABB Photovoltaic DisconnectorsBog PenAinda não há avaliações
- Heating and Cooling Load Calculations-ReportDocumento20 páginasHeating and Cooling Load Calculations-ReportEhtisham Tanvir100% (1)
- X-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationDocumento13 páginasX-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationVence MeraAinda não há avaliações
- Fagor CNC 8025 - 8030Documento255 páginasFagor CNC 8025 - 8030alvhann_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Science of Guilen Barren SyndromeDocumento2 páginasClinical Science of Guilen Barren SyndromemanakimanakuAinda não há avaliações
- The Effective SpanDocumento4 páginasThe Effective SpanMohamed FarahAinda não há avaliações
- TNB Ar2011Documento334 páginasTNB Ar2011Duncan LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Divine Child International School, Adalaj Revision Worksheet Grade 6, Maths Choose The Correct OptionDocumento2 páginasDivine Child International School, Adalaj Revision Worksheet Grade 6, Maths Choose The Correct OptionNatasha VidhaniAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Câu Viết Lại Câu Ôn Thi Vào Lóp 6Documento10 páginas100 Câu Viết Lại Câu Ôn Thi Vào Lóp 6Nguyễn Thanh PhươngAinda não há avaliações
- Heart of Dankness by Mark Haskell Smith - ExcerptDocumento29 páginasHeart of Dankness by Mark Haskell Smith - ExcerptCrown Publishing GroupAinda não há avaliações
- HK USP CompactDocumento56 páginasHK USP CompactJonathan CrenshawAinda não há avaliações
- Maxon - Gas Electro-Mechanical ValvesDocumento4 páginasMaxon - Gas Electro-Mechanical ValvesThiagoAinda não há avaliações
- TNM Sites May 2023Documento24 páginasTNM Sites May 2023Joseph ChikuseAinda não há avaliações
- Pipe Support Span CalculationDocumento14 páginasPipe Support Span Calculationrajeevfa100% (3)
- Rate List of 1-June-2015 To 31-May-2016: S.No Code Test Name Standard Rates 15% Discounted RatesDocumento25 páginasRate List of 1-June-2015 To 31-May-2016: S.No Code Test Name Standard Rates 15% Discounted RatesMirza BabarAinda não há avaliações
- SC607 Assignment2Documento2 páginasSC607 Assignment2Tirthankar AdhikariAinda não há avaliações
- F115a'12 Fl115a'12: (68VB) (68WB)Documento96 páginasF115a'12 Fl115a'12: (68VB) (68WB)AlexDiazAinda não há avaliações
- Dell Inspiron 16 5000 (5625) Laptop - Dell IndiaDocumento5 páginasDell Inspiron 16 5000 (5625) Laptop - Dell IndiamubbunAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Placa Mae Ga 945gcmx-s2 6.6Documento72 páginasManual Placa Mae Ga 945gcmx-s2 6.6luisb3toAinda não há avaliações