Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Solution MT PS 01
Enviado por
asukachan8059Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Solution MT PS 01
Enviado por
asukachan8059Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
FM 300: Corporate Finance, Investments, and Financial Markets
Section A - Michaelmas Term - Michela Verardo
Classwork 1
Answer key
1.
RA = .01 + .80 RM + A
M = 0.20, A = .10 (A is the residual standard deviation).
The volatility of the return for stock A is
2A = .802 (2M )+ 2 = 0.0356, and A = .0356 = .1887
2.
The alphas of A and B are given by:
A = (E[rA] rf ) A (E[rM] rf) = 0.04 0.5 0.05 = 0.015
B = (E[rB] rf ) B (E[rM] rf) = 0.06 1.5 0.05 = 0.015
To find the variance of P, first find A and B.
Recall that the R2 is defined as the explained variance divided by the total variance:
Var[P + P(rM rf)] / Var[(rP rf)].
R2 = 2i 2M /2i
A = ( 2A 2M / R2 )= (0.52 0.22 /0.95) = .1026 = 10.26%
B = ( 2B 2M / R2 )= (1.52 0.22 /0.95) = .3078 = 30.78%
Cov(rA,rB) = A B 2M = 0.5 1.5 0.22 = 0.03
Var(rP) = wA2 A2 + wB2 B2 + 2 wA wB Cov(rA,rB)
= 0.72 0.0105 + 0.32 0.0947 + 2(0.7)(0.3) (0.03) = 0.0263
3.
RA = 3% + .7RM + A;
RB = -2% + 1.2RM + B;
M = 20%;
Rsq(A)=.20; Rsq(B)=.12;
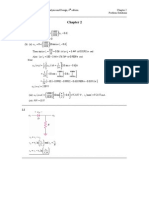
a) The standard deviation of each stock can be derived from the following equation
for R2:
i2 2M Explained variance
R =
= Total variance
i2
2
i
Therefore:
=
2
A
A2 M2
R A2
0.7 2 .20 2
=
= 0.098
0.20
A = 31.30%
1.2 2 .20 2
= 0.48
0.12
B = 69.28%
B2 =
b) The systematic risk for A is: A2 M2 = 0.70 2 .20 2 = 0.0196
The firm-specific risk of A (the residual variance) is the difference between As total
risk and its systematic risk: 0.098 0.0196 = 0.0784
The systematic risk for B is: B2 M2 = 1.20 2 .20 2 = 0.0576
Bs firm-specific risk (residual variance) is: 0.48 0.0576 = 0.4224
c) The covariance between the returns of A and B is (since the residuals are assumed
to be uncorrelated):
Cov(rA , rB ) = A B M2 = 0.70 1.20 0.04 = 0.0336
The correlation coefficient between the returns of A and B is:
AB =
Cov (rA , rB )
A B
0.0336
= 0.155
31.30% 69.28%
d) The non-zero alphas from the regressions are inconsistent with the CAPM. The
question is whether the alpha estimates reflect sampling errors or real mispricing. To
test the hypothesis of whether the intercepts (3% for A, and 2% for B) are
significantly different from zero, we would need to compute t-values for each
intercept.
4.
avg ret
std dev
beta
alpha
R2
General
Electric
0.154
0.236
IBM
0.147
0.294
Pepsi
0.153
0.168
Apple
0.307
0.625
Johnson
0.163
0.180
3M
0.128
0.134
Kellogg
0.112
0.216
Bank of
America
0.180
0.219
Fedex
0.160
0.216
DELL
0.471
0.703
Portfolio
0.198
0.156
1.328
0.042
0.864
0.678
0.069
0.146
0.381
0.092
0.150
0.673
0.230
0.031
0.492
0.096
0.222
0.199
0.077
0.059
0.237
0.058
0.033
0.500
0.112
0.141
0.629
0.085
0.212
1.285
0.362
0.091
0.640
0.122
0.471
The portfolio earns a positive risk-adjusted return of 12.2%.
Using regression analysis (instead of the slope and intercept functions) we can calculate the standard errors (and t-statistics) and see that alpha is
significantly different from zero.
Intercept
RM-rf
Coefficients
0.122
0.640
Standard
Error
0.028
0.170
t Stat
4.30
3.77
The R2 of a well-diversified portfolio should be higher than the R2 of an individual stock (the market can explain more of its total variance). This
should be true on average. However, in this case, there is a stock with a higher R2.
An R2 of 80% is unusually high for a regression of the SML type, when the data in question describe a single stock. It is much more usual for the
R2 of a single stock to be around 20-30%.
Você também pode gostar
- WS Simple Regression Analysis DownloadDocumento5 páginasWS Simple Regression Analysis DownloadAjeet YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8: Index Models: Problem SetsDocumento14 páginasChapter 8: Index Models: Problem SetsBiloni KadakiaAinda não há avaliações
- Investments 11Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasInvestments 11Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFWilliamCartersafg100% (8)
- Chapter 8: Index Models: Problem SetsDocumento14 páginasChapter 8: Index Models: Problem SetsAlyse97Ainda não há avaliações
- Task 2 + SolutionsDocumento8 páginasTask 2 + SolutionsS M Tanjilur RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 8 Bodie 9eDocumento14 páginasChap 8 Bodie 9eChristan LambertAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Science AssignmentDocumento4 páginasDecision Science AssignmentShivani MallikAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 252 Spring 2011 Problem Set 2 SolutionDocumento13 páginasEcon 252 Spring 2011 Problem Set 2 SolutionTu ShirotaAinda não há avaliações
- Single AssetsDocumento4 páginasSingle AssetsMega Pop LockerAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 - Problem Solving (Risk)Documento5 páginasChapter 6 - Problem Solving (Risk)Shresth KotishAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar 3Documento8 páginasSeminar 3EnnyAinda não há avaliações
- CH 2 - Return and RiskDocumento68 páginasCH 2 - Return and RiskZoe McKenzieAinda não há avaliações
- FINM2003 - Mid Semester Exam Sem 1 2015 (Suggested Solutions)Documento6 páginasFINM2003 - Mid Semester Exam Sem 1 2015 (Suggested Solutions)JasonAinda não há avaliações
- Index Models: Problem SetsDocumento14 páginasIndex Models: Problem SetsdomazzzAinda não há avaliações
- TSExamples PDFDocumento9 páginasTSExamples PDFKhalilAinda não há avaliações
- Study Questions 12 Risk and Return SolutionsDocumento4 páginasStudy Questions 12 Risk and Return SolutionsAlif SultanliAinda não há avaliações
- E120 FALL14 HW9SolsDocumento2 páginasE120 FALL14 HW9Solskimball_536238392Ainda não há avaliações
- Soln CH 10 Index ModelsDocumento9 páginasSoln CH 10 Index ModelsSilviu TrebuianAinda não há avaliações
- Solution q1 in q3 CapitalAssetPricingModelHomeworkDocumento14 páginasSolution q1 in q3 CapitalAssetPricingModelHomeworkAbdu AbdoulayeAinda não há avaliações
- On Linear ProgrammingDocumento49 páginasOn Linear Programmingh_badgujarAinda não há avaliações
- 3017 Tutorial 4 SolutionsDocumento3 páginas3017 Tutorial 4 SolutionsNguyễn HảiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 22 Solution To Problems 1Documento3 páginasChapter 22 Solution To Problems 1Jayvee M FelipeAinda não há avaliações
- QMCS 20 - 2 Exercises - FailureDocumento32 páginasQMCS 20 - 2 Exercises - FailureBeatriz LatorreAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Science Final AnswerDocumento8 páginasDecision Science Final AnswerBhavya PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Winkler Curved Beam TheoryDocumento21 páginasWinkler Curved Beam TheoryMuluken TemesgenAinda não há avaliações
- JUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-ParametersDocumento6 páginasJUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-Parameterssultan1786Ainda não há avaliações
- Consider A Second Order System Auto Regressive Moving Average (ARMA) Where The Polynomial Are in The Following General FormDocumento2 páginasConsider A Second Order System Auto Regressive Moving Average (ARMA) Where The Polynomial Are in The Following General FormyeshiwasAinda não há avaliações
- Micro4EXSol6 PDFDocumento22 páginasMicro4EXSol6 PDFDeivasigamani SubramaniyanAinda não há avaliações
- 智能机器人 第二次作业Documento12 páginas智能机器人 第二次作业Tongkai XuAinda não há avaliações
- Tolerance Analysis 09.04.03Documento26 páginasTolerance Analysis 09.04.03maddy_scribdAinda não há avaliações
- A D LN (2.000, 0.002) 2.000 0.002: EXAMPLE 20-7Documento12 páginasA D LN (2.000, 0.002) 2.000 0.002: EXAMPLE 20-7ABINAS NAYAKAinda não há avaliações
- Sulfuric AcidDocumento22 páginasSulfuric AcidEmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- PracticeProblems 4315 SolutionsDocumento9 páginasPracticeProblems 4315 SolutionsKashifRizwanAinda não há avaliações
- Standar Deviasi: RA E (RA) )Documento10 páginasStandar Deviasi: RA E (RA) )velisa ratna dillaAinda não há avaliações
- 01 TrabajoDocumento18 páginas01 TrabajoYuliza Carolina Capuñay SiesquenAinda não há avaliações
- HW5S FL16-2Documento7 páginasHW5S FL16-2alexAinda não há avaliações
- Demo Qs Topic 5 Part 1Documento6 páginasDemo Qs Topic 5 Part 1Triet NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Pareto Chart: Bonferroni Limit 3.08209Documento4 páginasPareto Chart: Bonferroni Limit 3.08209Rocio Andrea CasillaAinda não há avaliações
- Working With Phasors and Using Complex Polar Notation in MATLAB/OctaveDocumento5 páginasWorking With Phasors and Using Complex Polar Notation in MATLAB/Octaveel_ruso__83Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment Power ElectronicDocumento21 páginasAssignment Power ElectronicSeth RathanakAinda não há avaliações
- Sara LaFreniere P115 E7 Lab ReportDocumento7 páginasSara LaFreniere P115 E7 Lab ReportMickey AngeloAinda não há avaliações
- Chap54 7Documento6 páginasChap54 7balakaleesAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocumento15 páginasChapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bAinda não há avaliações
- HW 4 A 1Documento11 páginasHW 4 A 1draconnoxAinda não há avaliações
- Mohit Jetani 1270404 0Documento32 páginasMohit Jetani 1270404 0ronajoj120Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2 (Distributed Database Systems) (Due Thursday, July, 31, 2003)Documento2 páginasAssignment 2 (Distributed Database Systems) (Due Thursday, July, 31, 2003)Tapu Raihan SabujAinda não há avaliações
- Price (RS.) Probability: Expected Return ERDocumento6 páginasPrice (RS.) Probability: Expected Return ERShoaib with rAinda não há avaliações
- Microelectronics 4th Neaman Chpt2Documento26 páginasMicroelectronics 4th Neaman Chpt2mohammadarar100% (2)
- University of Maryland: Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocumento2 páginasUniversity of Maryland: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineeringqaiserkhan001Ainda não há avaliações
- Return Dan Risiko Aset TunggalDocumento4 páginasReturn Dan Risiko Aset TunggalDevi Anggraini IIAinda não há avaliações
- Risk and Return A - SolutionsDocumento3 páginasRisk and Return A - SolutionsmilotikyuAinda não há avaliações
- CORRECTION DE LA SERIE 3 Marchés Financiers Et Évaluation Des Actifs #1Documento8 páginasCORRECTION DE LA SERIE 3 Marchés Financiers Et Évaluation Des Actifs #1sihemAinda não há avaliações
- POQ:quizDocumento10 páginasPOQ:quizHarsh ShrinetAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Exercises in Chapter 8: 1.szm, xr8-1.wf1 and Xr8-1.sas, RespectivelyDocumento12 páginasSolutions To Exercises in Chapter 8: 1.szm, xr8-1.wf1 and Xr8-1.sas, RespectivelyKarthik Mohan KAinda não há avaliações
- Collection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems: IN IN IN O ODocumento37 páginasCollection of Solved Feedback Amplifier Problems: IN IN IN O Ogowri thumburAinda não há avaliações
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYAinda não há avaliações
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNo EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesNota: 1.5 de 5 estrelas1.5/5 (2)
- MBA 1.5 Outlines PDFDocumento148 páginasMBA 1.5 Outlines PDFMaQsud AhMad SaNdhuAinda não há avaliações
- Horse Racing Winning FormulaDocumento23 páginasHorse Racing Winning Formulaifandoot100% (2)
- Unit 2 Assignment Managing Financial Resources & Decisions SamDocumento9 páginasUnit 2 Assignment Managing Financial Resources & Decisions SamBenAinda não há avaliações
- Verma Panel FindingsDocumento17 páginasVerma Panel FindingsNaga Mani MeruguAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5.2-General Cost Classifications (Problem 2)Documento2 páginasLecture 5.2-General Cost Classifications (Problem 2)Nazmul-Hassan Sumon75% (4)
- Kinds of SharesDocumento16 páginasKinds of SharesMridulGodhaAinda não há avaliações
- Red Herring Prospectus - South West Pinnacle Exploration LimitedDocumento482 páginasRed Herring Prospectus - South West Pinnacle Exploration LimitedgoyalneerajAinda não há avaliações
- Monetary Policy in The 21st CenturyDocumento7 páginasMonetary Policy in The 21st CenturyRomeo RomeAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 PM P2Documento62 páginas2014 PM P2dashapuskarjovaAinda não há avaliações
- Question 1Documento5 páginasQuestion 1Yono SéAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Example Answers Paper 1Documento2 páginasEconomics Example Answers Paper 1mohdportmanAinda não há avaliações
- FA1 General JournalDocumento5 páginasFA1 General JournalamirAinda não há avaliações
- Edelweiss Banking ReportDocumento36 páginasEdelweiss Banking ReportAnand SarafAinda não há avaliações
- Bank of IndiaDocumento17 páginasBank of IndiaShawn BuckAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Social Science Economics Revision Notes Ch4Documento4 páginas10 Social Science Economics Revision Notes Ch4Proshumi BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Plaintiffs:: Court Use Only - Case NumberDocumento39 páginasPlaintiffs:: Court Use Only - Case NumberCircuit MediaAinda não há avaliações
- Great Cash Gain Ps en FW JoDocumento53 páginasGreat Cash Gain Ps en FW JoGobinath SubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- Data Per Acre Planted Soybeans Corn Corn WheatDocumento3 páginasData Per Acre Planted Soybeans Corn Corn WheatMohamed Mostafa AliAinda não há avaliações
- ISJ039Documento52 páginasISJ0392imediaAinda não há avaliações
- Oil and Gas IndustryDocumento6 páginasOil and Gas IndustryLuqman HadiAinda não há avaliações
- Option SellingDocumento5 páginasOption SellingSathishAinda não há avaliações
- GMO Grantham July 09Documento6 páginasGMO Grantham July 09rodmorleyAinda não há avaliações
- Company Profile of TATA Steel by (Anindya S Kundu)Documento16 páginasCompany Profile of TATA Steel by (Anindya S Kundu)anindya_kundu100% (5)
- V 13 I 30Documento37 páginasV 13 I 30Riswan FadhilahAinda não há avaliações
- Protocols For Economic Collapse in America by Al MartinDocumento12 páginasProtocols For Economic Collapse in America by Al Martininformationawareness100% (1)
- Surrender / Partial Withdrawal Form SRN No:: Surname First Name Middle Name TitleDocumento2 páginasSurrender / Partial Withdrawal Form SRN No:: Surname First Name Middle Name Titlesofich rosaAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial AccountingDocumento9 páginasManagerial AccountingChristopher Price100% (1)
- Timeline of Pinterest - Timelines2Documento13 páginasTimeline of Pinterest - Timelines2SennheiserAinda não há avaliações
- HedgingDocumento7 páginasHedgingSachIn JainAinda não há avaliações
- Session 1 (CH 1) SlidesDocumento33 páginasSession 1 (CH 1) SlidesBim BimAinda não há avaliações