Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Homework1 2015
Enviado por
lelouch_damienTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Homework1 2015
Enviado por
lelouch_damienDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MCDB 126B/226B -- Winter 2015
Homework 1A (10 pts)--Due in section (either Wednesday Jan 14 or Friday Jan 16)
Please read the article on the class website from the Dougherty group at Caltech:
Xiu et al. (2009) Nicotine binding to brain receptors requires a strong cation-
interaction. Nature 458, 534.
Two summary pages are also included with the article to help with your understanding. This
article describes exciting work that explores the remarkable specificty of nicotine for the brain,
and explains at the molecular level why nicotine binds to brain nACh, but not muscle nACh
receptor.
We plan to organize this weeks section meeting in a discussion format, so please be prepared
to discuss the article. Reading journal articles takes practice, and one of the goals of this class
is to develop those skills. You arent expected to understand all of the details of the article, but
do your best. (For additional information on methods and background see the Dougherty lab
website: http://www.its.caltech.edu/~dadgrp/research/ Unnatural Amino Acid Mutagenesis).
Also, bring any questions you have to discuss with members of your section and your TA.
Your written homework assignment (below) will be due at the beginning of discussion section:
1. What is a cation- interaction? In this paper, what are the cation and the that are
being studied?
2. What do the authors conclude is the reason that nicotine can bind to brain nACh
receptors but not to muscle nACh R?
3. What is the key experimental evidence that supports their conclusion?
4. What are unnatural amino acids, and why are they employed in the study?
5. What is nonsense suppression? How is nonsense suppression helpful for incorporating
unnatural amino acids into a protein?
6. In carrying out this study, the authors needed to overcome several technical hurdles in
order to express the nAChR proteins in Xenopus (frog) oocytes. For one of these
hurdles, they used the property of inward rectification.
As background information, rectification refers to asymmetry in the ability of an ion
channel to carry ions across the membrane, and inward rectification means that the
channel can carry ions into the cell better than out of the cell. Whether a channel
rectifies or not can be determined by measuring the ratio of the current through the
channel at positive voltage (outward current) compared to current at negative voltages
(inward current), and a low ratio (<0.1) was used as an indicator of inward rectification.
In this paper, why did the authors measure inward rectification and what did it tell them
about the ACh receptor that they expressed?
MCDB 126B/226B -- Winter 2015
Homework Problems 1B (10 pts) --Due in lecture Friday Jan 16
Please make the Double reciprocal plot (#3) by hand using graph paper in order to practice
setting up your axes; other questions can be done by computer if desired.
1) (2 pts) A binding experiment is made with an isolated receptor. Using a variety of ligand
concentrations, the equilibrium concentrations of free ligand and receptor-ligand complex were
determined as shown below.
a) Plot [LR] vs. [L].
b) What would you estimate for the Kd for the binding of this ligand to the receptor?
c) What do you estimate for the total concentration of receptors, [Rt]?
[L]
10 M
20 M
30 M
40 M
50 M
where
[LR]
50 nM
81 nM
99 nM
115 nM
125 nM
[L]= concentration of ligand
[LR]= concentration of receptor-ligand complex
[Rt]= [R] + [LR] = total concentration of receptor, including bound & free receptor
Note: M = 10-6 M; nM= 10-9 M. Your graphing will be most successful if you convert
[L] and [LR] to the same units before analysis and plotting.
2) (2 pts) Plot the data above using a semi-logarithmic plot of [LR] vs. log[L], and again
estimate Kd and [Rt].
3) (2 pts) Now plot the same data with a double reciprocal plot, and again determine Kd and
[Rt].
4) (2 pts) Plot again using a Scatchard plot, and determine Kd and the total concentration of
receptors, [Rt].
5) (2 pts) Compare the estimates of Rt and Kd obtained for problems 1-4. Are they the same?
Which method(s) gives the better estimate for this data set?
Você também pode gostar
- Abstract Book For WebDocumento113 páginasAbstract Book For WebArihant JainAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write An AbstractDocumento5 páginasHow To Write An AbstractCuong LeAinda não há avaliações
- Script Intracellular 2017Documento14 páginasScript Intracellular 2017Brew-sam ABAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis EnergyDocumento7 páginasThesis Energyjillturnercincinnati100% (2)
- BISC110P-F22 Homework-9Documento4 páginasBISC110P-F22 Homework-9otded360Ainda não há avaliações
- Performance Check 1. The Nature and Scope of Analytical ChemistryDocumento4 páginasPerformance Check 1. The Nature and Scope of Analytical ChemistryMaden betoAinda não há avaliações
- Exfin Sol PDFDocumento11 páginasExfin Sol PDFDavid ValeroAinda não há avaliações
- HW 1 PDFDocumento3 páginasHW 1 PDFsuudfiinAinda não há avaliações
- Action Research Session GuideDocumento14 páginasAction Research Session GuideJulien AmbidAinda não há avaliações
- Ftir PHD ThesisDocumento7 páginasFtir PHD Thesisteishahickspeoria100% (1)
- Jean Faber and Gilson A. Giraldi - Quantum Models For Artifcial Neural NetworkDocumento8 páginasJean Faber and Gilson A. Giraldi - Quantum Models For Artifcial Neural Networkdcsi3Ainda não há avaliações
- HH ThesisDocumento6 páginasHH Thesismrlsikiig100% (2)
- Dissertation Page LimitDocumento7 páginasDissertation Page LimitPaperWritingWebsiteCharleston100% (1)
- Biotechnology Thiel Bissen Lyons PDFDocumento182 páginasBiotechnology Thiel Bissen Lyons PDFhendrikmuskusuprAinda não há avaliações
- Segon Examen Parcial Pep Gener 2016Documento6 páginasSegon Examen Parcial Pep Gener 2016geri10Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology 355 Exam 1 Study GuideDocumento2 páginasBiology 355 Exam 1 Study GuideNgoc Minh NgoAinda não há avaliações
- SBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistryDocumento6 páginasSBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistrySukhvir AujlaAinda não há avaliações
- Protocol ATAC SeqDocumento8 páginasProtocol ATAC Seqcnoutsos316Ainda não há avaliações
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideDocumento22 páginasMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211Ainda não há avaliações
- Actividad Motores MolecularesDocumento4 páginasActividad Motores MolecularesLINA MARCELA ALVAREZ PALLARESAinda não há avaliações
- Ue ThesisDocumento7 páginasUe Thesisafknqbqwf100% (1)
- Bezaire. Quantitative Assessment of CA1 Local CircuitsDocumento35 páginasBezaire. Quantitative Assessment of CA1 Local Circuitsmaariamunoz9Ainda não há avaliações
- Planning Chemical Syntheses With Deep Neural Networks and Symbolic AI PDFDocumento16 páginasPlanning Chemical Syntheses With Deep Neural Networks and Symbolic AI PDFMarce VeraAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS 400 Exam 1 SolutionsDocumento4 páginasPHYS 400 Exam 1 Solutionsjm6006232Ainda não há avaliações
- Solutions1 2Documento3 páginasSolutions1 2Ali NajmaldinAinda não há avaliações
- PHD Thesis VertalingDocumento4 páginasPHD Thesis Vertalingaflnzefdqbrevm100% (2)
- L6 MattDocumento46 páginasL6 MattasdfghjklAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Biology Exam Review Questions OnlyDocumento20 páginasAp Biology Exam Review Questions Onlyapi-57781915100% (1)
- Chemistry Lab Research PaperDocumento4 páginasChemistry Lab Research Paperxvszcorif100% (1)
- BMEDocumento7 páginasBMEJabeen ThazAinda não há avaliações
- Wegleitung Bachelor Thesis FHNWDocumento5 páginasWegleitung Bachelor Thesis FHNWpzblktgld100% (2)
- Iec Exp 10 Student ManualDocumento3 páginasIec Exp 10 Student ManualprinceiutAinda não há avaliações
- EEG Brain Signal Classification for Epileptic Seizure Disorder DetectionNo EverandEEG Brain Signal Classification for Epileptic Seizure Disorder DetectionAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Topics For Bachelor DegreeDocumento6 páginasThesis Topics For Bachelor Degreecourtneybennettshreveport100% (2)
- 2011 Assignment 1 2Documento9 páginas2011 Assignment 1 2Rayhanul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Gamma Ray SpectrosDocumento3 páginasGamma Ray SpectrosWeiyu TongAinda não há avaliações
- Neural Data Science: A Primer with MATLAB® and Python™No EverandNeural Data Science: A Primer with MATLAB® and Python™Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- How To Write A Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasHow To Write A Lab ReportEthan ZhengAinda não há avaliações
- Research Papers On Qsar StudiesDocumento7 páginasResearch Papers On Qsar Studiesgz8reqdc100% (1)
- Dissertation SynthesisDocumento4 páginasDissertation Synthesisdnhrm565100% (2)
- Bachelor Thesis HTW ChurDocumento7 páginasBachelor Thesis HTW Churxxsfomwff100% (1)
- Roe A 40Documento10 páginasRoe A 40Prakash KatwalAinda não há avaliações
- Formative Question AnswerDocumento9 páginasFormative Question AnswerjasonlAinda não há avaliações
- Electrophysiology Measurements for Studying Neural InterfacesNo EverandElectrophysiology Measurements for Studying Neural InterfacesAinda não há avaliações
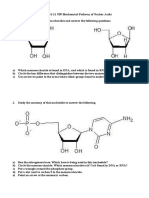
- SEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Documento6 páginasSEHH2231-22 T09 Biochemical Pathway of Nucleic Acid Exercise (Question)Brian Chi Yan Cheng 鄭智仁Ainda não há avaliações
- 340Documento17 páginas340alem010100% (1)
- Dna Replication For Science Session GuideDocumento14 páginasDna Replication For Science Session GuideTiffany MooreAinda não há avaliações
- Bioinformatics Pratical FileDocumento63 páginasBioinformatics Pratical FileSudheshnaAinda não há avaliações
- Error in PHD ThesisDocumento5 páginasError in PHD Thesiskllnmfajd100% (2)
- Nbti ThesisDocumento7 páginasNbti Thesisangiejorgensensaltlakecity100% (2)
- First Round of Review Reviewer 1Documento8 páginasFirst Round of Review Reviewer 1YanjiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Directions:: Print Your Name: Your Laboratory Section: DAY TimeDocumento6 páginasDirections:: Print Your Name: Your Laboratory Section: DAY TimeSunny ShahAinda não há avaliações
- Genetic Algorithm For Protein Folding Simulations in 2D HP ModelDocumento11 páginasGenetic Algorithm For Protein Folding Simulations in 2D HP ModelToño GonzálezAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis SubmittedDocumento5 páginasThesis Submittedjennifermoserreno100% (1)
- PracticeQuestions Exam1 Sp2015 KEYDocumento7 páginasPracticeQuestions Exam1 Sp2015 KEYsyuhadahAinda não há avaliações
- Nanosensors For Neurotransmitters: ReviewDocumento15 páginasNanosensors For Neurotransmitters: ReviewValeria ZárateAinda não há avaliações
- Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses: Physioex 9.0 Review Sheet ExerciseDocumento6 páginasNeurophysiology of Nerve Impulses: Physioex 9.0 Review Sheet ExerciseAna Lucia BerganzaAinda não há avaliações
- EEMB 116 Invertebrate Zoology Syllabus Spring 2015Documento1 páginaEEMB 116 Invertebrate Zoology Syllabus Spring 2015lelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid Hormones: - Iodine (I)Documento7 páginasThyroid Hormones: - Iodine (I)lelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Low River Flow Alters The Biomass and Population Structure of A Riparian Predatory InvertebrateDocumento2 páginasLow River Flow Alters The Biomass and Population Structure of A Riparian Predatory Invertebratelelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Hypothalamus Pituitary Oxytocin-4ppDocumento7 páginas18 Hypothalamus Pituitary Oxytocin-4pplelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- 20 CortisolAdrenal-4ppDocumento5 páginas20 CortisolAdrenal-4pplelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Beta 3 Agonist SDocumento9 páginasBeta 3 Agonist Slelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- 05 GABA-extra Slide PropofolDocumento1 página05 GABA-extra Slide Propofollelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Do Not Open Exam Until Instructed To Do SoDocumento6 páginasDo Not Open Exam Until Instructed To Do Solelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- TPR H Verbal WB 2011Documento290 páginasTPR H Verbal WB 2011Nathaniel Zhu50% (2)
- Drug NameDocumento3 páginasDrug Namelelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Read Me FirstDocumento2 páginasRead Me Firstwilliam1230Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecology Concepts and ApplicationsDocumento12 páginasEcology Concepts and Applicationslelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Campaign Marketing ToolkitDocumento2 páginasCampaign Marketing Toolkitlelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Flavi Viridae - Hepatitis CDocumento2 páginasFlavi Viridae - Hepatitis Clelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas For The MCAT: General ChemistryDocumento1 páginaFormulas For The MCAT: General Chemistrymissee728Ainda não há avaliações
- Rhabdo Viri DaeDocumento7 páginasRhabdo Viri Daelelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Genome Variation Among Individuals and Molecular Analysis of Traits (Chpt. 11)Documento40 páginasGenome Variation Among Individuals and Molecular Analysis of Traits (Chpt. 11)lelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Tools For Genome Analysis (Chapter 9: Digital Analysis of DNA)Documento40 páginasMolecular Tools For Genome Analysis (Chapter 9: Digital Analysis of DNA)lelouch_damienAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology Ain Shams 123 - Compress 1Documento552 páginasPharmacology Ain Shams 123 - Compress 1ahmed hoty100% (1)
- Martin 1991 - The Egg and The SpermDocumento17 páginasMartin 1991 - The Egg and The SpermYolly ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Pharmacology in PsychiatryDocumento278 páginasClinical Pharmacology in Psychiatryanon_633561647Ainda não há avaliações
- Pub - Signal Transduction Protocols 3rd Edition Methods PDFDocumento445 páginasPub - Signal Transduction Protocols 3rd Edition Methods PDFboonlueAinda não há avaliações
- Komunikasi Sel PDFDocumento64 páginasKomunikasi Sel PDFMuhammad RizaldiAinda não há avaliações
- Update Pharma Graf GDocumento3 páginasUpdate Pharma Graf GSyamil Azhar100% (1)
- Vol 1 - Drug DiscoveryDocumento946 páginasVol 1 - Drug Discoveryjoshigauta100% (2)
- Mechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)Documento138 páginasMechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)geniousmasud721Ainda não há avaliações
- Katzung End of Chapter Questions-ModifiedDocumento110 páginasKatzung End of Chapter Questions-ModifiedLicensed to Heal0% (1)
- Chemical Signal: Hormone 1: Biosignaling (WEEK 2)Documento27 páginasChemical Signal: Hormone 1: Biosignaling (WEEK 2)Fenny Aulia SugianaAinda não há avaliações
- Phar0011 Radioligand Binding Analysis 2022Documento5 páginasPhar0011 Radioligand Binding Analysis 20224wqzcq7p9xAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology Notes CH 1 IntroductionDocumento4 páginasPharmacology Notes CH 1 Introductionridley45Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Biochemistry: by Zaheer Uddin (Pharm-D, M Phil (Pharmacy Practice) MBA (MARKETING)Documento63 páginasIntroduction To Biochemistry: by Zaheer Uddin (Pharm-D, M Phil (Pharmacy Practice) MBA (MARKETING)Izat KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Snyder - Science and Psychiatry - Groundbreaking Discoveries in Molecular Neuroscience PDFDocumento514 páginasSnyder - Science and Psychiatry - Groundbreaking Discoveries in Molecular Neuroscience PDFuterw100% (1)
- 3rd Ccpbiosimconference Abstract BookletDocumento82 páginas3rd Ccpbiosimconference Abstract BookletRajeev Ranjan RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Thomas L. Pazdernik, Laszlo Kerecsen-Rapid Review Pharmacology, 3rd Edition-Mosby (2010)Documento784 páginasThomas L. Pazdernik, Laszlo Kerecsen-Rapid Review Pharmacology, 3rd Edition-Mosby (2010)dtech2Ainda não há avaliações
- Mission Memo - Cell Biology Act III Lab InstructionsDocumento14 páginasMission Memo - Cell Biology Act III Lab Instructionscarolyn0% (6)
- Cell SignalingDocumento25 páginasCell SignalingSai SridharAinda não há avaliações
- PHARMACOLOGYDocumento42 páginasPHARMACOLOGYrbishestaAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry of Cancer Biochemistry of Cancer: DR Madiha Soban BiochemistryDocumento36 páginasBiochemistry of Cancer Biochemistry of Cancer: DR Madiha Soban BiochemistryTalha MohsinAinda não há avaliações
- Tissue Engineering IIDocumento344 páginasTissue Engineering IILeonardo Garro100% (1)
- 1general Principles of Pharmacology Types of ReceptorsDocumento1 página1general Principles of Pharmacology Types of ReceptorskondajagadishAinda não há avaliações
- CH 11 PPT Cell Communication 1Documento77 páginasCH 11 PPT Cell Communication 1api-270681964Ainda não há avaliações
- Consumer Chemistry q4 Module 1 Week 1-2Documento6 páginasConsumer Chemistry q4 Module 1 Week 1-2Tiffany Moore80% (10)
- Full Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFDocumento41 páginasFull Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFalvin.vincent421100% (15)
- Pharmacodynamics: DR Narendra KumarDocumento76 páginasPharmacodynamics: DR Narendra KumarsivaAinda não há avaliações
- Phle Reviewer Module 4 - Pharmacology-PharmacokineticsDocumento134 páginasPhle Reviewer Module 4 - Pharmacology-PharmacokineticsMhiel Bhon RamzAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Revesion PDFDocumento80 páginas7 Revesion PDFMd Sakil AminAinda não há avaliações
- Equilibrium: Application To Drug Design: Nature BiotechnologyDocumento5 páginasEquilibrium: Application To Drug Design: Nature BiotechnologysgybleeAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Pharmacology Therapeutics 6Th Edition Derek G Waller Download PDF ChapterDocumento51 páginasMedical Pharmacology Therapeutics 6Th Edition Derek G Waller Download PDF Chaptervicki.krause300100% (17)