Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chapter 2: Body Coordination: Month Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes February 1
Enviado por
Anonymous b0gP6mDaqTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 2: Body Coordination: Month Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes February 1
Enviado por
Anonymous b0gP6mDaqDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Month
Week
Learning Area
Learning Outcomes
Chapter 2: Body Coordination
February
Body Coordination
A student is able to :
Body systems that control and
Describe what body coordination
regulate coordination
is
Importance of body
Identify the body systems that
coordination
control and regulate coordination
Human nervous system
State the importance of body
Component parts of the human
coordination
nervous system
Identify the component parts of
Neurones and its function
the human nervous system
Nervous coordination
Receptors and effectors
Reflex action and reflex arc
Proprioceptors
Proprioceptors and its
importance
Human brain and its complexity
Main parts and functions of
human brain
Voluntary and involuntary
actions
Hormonal coordination in the body
Hormone and endocrine
glands
Functions of hormones
secreted by the endocrine
glands
Effects of hormonal imbalance
on health
Coordination between nervous
system and the endocrine system
State the function of each
component part of the nervous
system
State what neurone is
Identify the parts of a neurone
State the function of each part of
the neurone
Identify the different types of
neurone
State the fuction of each type of
neurone
Compare and contrast the
different types of neurone
A student is able to :
State what receptors and
effectors are
State the functions of receptors
and effectors
Explain with examples what a
reflex action is
Describe a reflex arc
Illustrate the path taken by an
impulse in the reflex arc
Explain what proprioceptors are
Explain the importance of
proprioceptors
A student is able to :
Identify the main parts of the
human brain
State the functions of each
main part of the human brain
Explain what voluntary action is
Give examples of voluntary
action
Explain what involuntary action
is
Give examples of involuntary
action
Explain the effects of injuries to
specific parts of the human
brain
Importance of coordination
between nervous system and
the endocrine system in
response to a specific stimulus
Effects of a drug abuse on body
coordination and health
Examples of drugs
Drug abuse and its effects on
body coordination and health
Sound and healthy mind
Mind and factors that affect
mind
Describe what a hormone is
Describe what endocrine glands
are
Identify the main endocrine
glands and their respective
locations in the body
State the functions of hormones
secreted by the endocrine
glands
Describe the effects of
hormonal imbalance on health
Compare and contrast nervous
coordination with hormonal
coordination
Explain with examples the
coordination between the
nervous system and the
endocrine system in response
to a specific stimulus
Explain the importance of
coordination between the
nervous system and the
endocrine system in response
to a specific stimulus
A student is able to :
Define what drugs are
List examples of drugs
Explain what drug abuse is
Describe the effects of drug
abuse on body coordination
Describe the effects of drug
abuse on health
State what mind is
Identify factors that effect the
mind
Explain how substance abuse
can effect the mind
Justify the importance of a
healthy and sound mind
Chapter 3: Heredity and Variation
March
Cell division
Genes, deoxyribonucleic acids
(DNA) and chromosomes
Mitosis and meiosis
The principles and mechanism of
inheritance
Dominant genes and recessive
genes
Dominant traits and recessive
traits
Mechanism of inheritance of
A student is able to :
State what genes ,
deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
and chromosomes are
Describe the relationship
between gene, DNA and
chromosome
State what mitosis is
State what meiosis is
Describe the process of mitosis
Describe the process if meiosis
Compare and contrast mitosis
traits
Genotype and phenotype
ratios of a monohybrid cross
Sex determination and the
occurrence of twins in human beings
Sex chromosomes
Determination of sex
Identical and nonidentical
twins deficiency on plant
growth
Mutation
Type of mutation
Factors that causes mutation
Advantages and
disadvantages of mutation
Effects of genetic research on
human life
Contributions of genetic
research in various fields
Selective breeding in plants
and livestock
Present arguments for and
against genetic research
Variation among living things
Types of variation; continuous
and discontinuous variation
Factors that cause variation
Importance of variation
with meiosis
Explain the importance of
mitosis and meiosis
Explain what dominant genes
and recessive genes are
Identify dominant traits and
recessive traits in human
Illustrate the mechanism of
inheritance of traits using
schematic diagram
Predict the genotype and
phenotype ratios of a
monohybrid cross
A student is able to :
Explain what sex chromosomes
are
Explain how sex is determined
Explain the formation of identical
and non-identical twins
Compare and contrast identical
with non- identical twins
Explain what Siamese twins are
State what mutation is
State the types of mutation
List examples of mutation
Identify causes of mutation
State the advantages and
disadvantages of mutation
A student is able to :
List the contributions of genetic
research in various fields
Explain selective breeding in
plants and livestock
State the importance of
selective breeding in plants and
livestock
Describe the technology used
for selective breeding
Present arguments for and
against genetic research
State what variation is
List variation in humans
Classify variation into
continuous and discontinuous
variation
Identify factors that cause
variation
Explain
Chapter 4 : Matter and Substance
4
Changes in the states of matter
Kinetic theory of matter
Relate changes in heat to
A student is able to :
Explain the kinetic theory of
matter
changes in kinetic energy of
the particles in matter
Interconversion of the three
states of matter based on the
kinetic theory of matter
Structure of the atom
Subatomic particles
Proton number and nucleon number
in atoms of elements
Proton number and nucleon
number
Number of protons, neutrons
and electrons
Isotopes
March
Classification of elements in the
Periodic Table
Arrangement of elements in
the Periodic Table
Groups and periods
Location of metals, non-metals
and semi-metals
Importance of the Periodic
Table
Properties of substances based on
the particles present in them
Atoms, molecules and ions
Substances made of atoms,
molecules and ions
Relate the physical properties
of substance to the
arrangement of particles and
the forces of attraction
between them
Relate changes in heat to
changes in kinetic energy of the
particles in matter
Explain the interconversion of
the three states of matter based
on the kinetic theory of matter
Describe the structure of an
atom
Identify the subatomic particles
Compare and contrast the
subatomic particles
State what proton number is
State what nucleon number is
Relate the number of protons,
neutrons and electrons in an
atom to its proton number and
nucleon number
Deduce the number of protons,
electrons and neutrons in atom
of different elements
Make a generalization on the
numbers in atom of different
elements
State what isotopes are
Give example of isotopes
A student is able to :
Describe the arrangement of
elements in the Periodic table
Describe what is meant by
groups and periods in the
Periodic Table
Identify the locations of metals,
non- metals and semimetals in
the Periodic table
State the importance of the
Periodic Table
Describe what atoms ,
molecules and ions are
Identify the particles in
substances as atoms ,
molecules and ions
State examples of substances
made of atoms, molecules and
ions
Compare and contrast
substance that are made of
atoms, molecules and ions
based on their physical
properties
Relate the physical properties pf
substances made up of atoms,
molecules and ions to the
arrangement of particles and the
forces of attraction between
them.
Metals and non-metals
Properties of metals and nonmetals
Uses of metals and nonmetals
Relate the physical properties
of metals and non-metals to
their uses in daily life
Methods of purifying substances
Characteristics of pure
substances
Different methods of
purification of substances
Relate the characteristics of
substances to the method of
purification used
Methods of purification used to
produce substances used in
daily life
A student is able to :
List examples of metals and
non- metals
List the properties of metals and
non- metals
List the uses of metals and nonmetals in daily life
Compare and contrast metals
and non-metals based on their
physical properties
Relate the physical properties of
metals and non-metals to their
uses in daily life
Methods of purifying substances
Characteristics of pure
substances
Different methods of
purification of substances
Relate the characteristics of
substances to the method of
purification used
Methods of purification used to
produce substances used in
daily life
A student is able to :
State the characteristics of
pure substances
Describe the different
methods of purification of
substances
Relate the characteristics of
substance to the methods of
purification used to produce
substance used in daily life
Chapter 5: Energy and Chemical Changes
4
Physical and chemical changes
A student is able to :
Physical and chemical
Explain what physical
changes and the examples in
change is
daily life
Explain what chemical
change is
Heat change in chemical reactions
Give examples of
Chemical reaction involving
physical changes in daily life
heat change
Give example of
Reactions involving heat loss
chemical changes in daily life
and heat gain
Compare and contrast physical
Exothermic and endothermic
changes and chemical changes
reactions
State that chemical reactions
Heat changes that occur
involve heat change
during industrial chemical
Identify reactions involving heat
reactions
loss
Identify reactions involving heat
gain
Relate changes in temperature
of reactants to exothermic reactions
Relate the changes in
temperature of reactants to
endothermic reactions
Explain through
examples heat changes that occur
during industrial chemical reactions
Reactivity series of metals
A student is able to :
Reactivity of metals with water,
Describe the reactivity of metals
acids and oxygen
with water
Arrangement of metals in order
Describe the reactivity of metals
of reactivity
with acids
Position of carbon in the
Describe the reactivity of metals
reacitivity series
with oxygen
Concepts of reactivity series of
Compare and contrast the
metals
reactivity of metals with water,
Relate the position of metals in
acids and oxygen
the reactivity series to the
Arrange metals in order of
method of extraction of metals
reactivity
from their ores
Construct the reactivity series of
Process of extraction of metals
metals based on reactivity of
from its ore using carbon
metals with oxygen
Importance of the reactivity
Identify the position of carbon in
series
the reactivity series
Relate the position of metals in the
reactivity series to the method of
extraction of metals from their ores
Explain with examples the process
of extraction of a metal from its ore
using carbon
April
State the importance of the
reactivity series
Electrolysis
Anode, cathode, anion, cation
and electrolyte
Electrolysis using carbon
electrodes
Uses of electrolysis in industry
Production of electrical energy from
chemical reactions
Generation of electrical energy
using simple cell
Various types of cells and their
uses
Advantages and disadvantages
of various types of cells
A student is able to :
State what electrolysis is
State what anode, cathode, anion,
cation and electrolyte are
Describe the electrolysis of an
electrolyte using carbon
electrodes
Explain the uses of electrolysis in
industry
Describe how a simple cell works
List the various types of cells and
their uses
State the advantages and
disadvantages of various types of
cells
Chemical reactions that occur in the
A student is able to:
presence of light
Give example of chemical
Chemical reactions which
reactions which require light
require light
Explain the effect of light on
Effect of light on photosensitive
photosensitive chemicals
chemicals
Explain why certain chemicals
Storage of certain chemicals in
are stored in dark bottles
dark bottles
Chapter 6 : Nuclear Energy
May
Radioactive substances
Radioactive substances and the
process of radioactive decay
Radioactive radiations
Radioisotopes
Production of nuclear energy and its
uses
Production of energy through
nuclear fission and fusion
Uses of nuclear energy
Process of generating electricity
from nuclear energy
Awareness of the need for proper
handling of radioactive substances
Effects of radioactive radiations
on living things
Proper handling of radioactive
substances and radioactive
waste
A student is able to :
State what radioactive substances
are
Give examples of radioactive
substances
Describe the process of
radioactive decay
Name the three types of each type
of radiations
Describe the characteristics of
each type of radioactive radiation
Compare and contrast radioactive
radiations
Explain what radioisotopes are
Give examples of radioisotopes
Explain the uses of radioactive
substances
A student is able to :
Describe the production of nuclear
energy through fission
Describe the production of nuclear
energy through fusion
Sate the uses of nuclear energy
Describe the process of
generating electricity from nuclear
energy
Explain the effects of nuclear
energy production
State the effects of radioactive
radiations on living things
Describe the correct way of
handling radioactive substances
and radioactive waste
explain the need fro proper
handling of radioactive substances
and radioactive waste
Chapter 7 : Light, Colour and Sight
2
Formation of image by plane mirrors
A student is able to :
and lenses
State the characteristics of
Images formed by plane mirror,
images formed by a plane mirror
convex lens and concave lens
State the characteristics of
Draw a labelled ray diagram to
image formed by a convex lens
show the formation of image by
State the characteristics of
light rays passing through convex
images formed by a concave lens
and concave lens
Compare and contrast images
Determination of focal length of a
of distant objects formed by convex
convex lens
lenses and concave lenses
Draw a labelled ray diagram to
show the formation of image by light
rays passing through a convex lens
Draw a labelled ray diagram to
show the formation of image by light
Jun
Formation of image by optical
instruments
Parts of instruments involved in
image formation
Draw ray diagrams for light rays
passing through an optical
instrument
Mechanism in focusing and
controlling the amount of light
that enters human eyes and a
camera
Structure and function of various
parts of the eye using camera as
an analogy
Light dispersion
Examples on how dispersion of
light occurs
rays passing through a concave
lens
Draw ray diagrams to explain
how characteristics of images
formed by convex lenses vary with
object distance
Determine the focal length of a
convex lens
A student is able to :
Identify the parts of
optical instruments involved in
image formation
Draw ray diagrams
for light rays passing through an
optical instrument
Compare and
contrast the mechanisms in
focusing and controlling the
amount of light that enters human
eyes and a camera
Explain the structure and
function of various parts of the eye
using a camera as an analogy
State what light dispersion is
Explain through
examples how dispersion of light
occurs
Light scattering
A student is able to :
Examples of phenomena related to light
State what light scattering is
scattering
Give examples of phenomena
related to light scattering
Addition and subtraction of colored
Explain through examples how
lights
scattering of light occurs in
Primary and secondary colours
natural phenomena
Identify primary and secondary
colours
Explain how addition of primary
colours produces secondary
colours
Explain the subtraction of
colours by coloured filters
Principle of subtraction of coloured
A student is able to;
light to explain the appearance of
Explain subtraction of coloured
coloured objects
light by coloured objects
Subtraction of coloured lights by
Explain the appearance of
coloured objects
coloured objects under white light
Appearance of coloured objects
Explain the appearance of
under white light and coloured
coloured objects under coloured
lights
lights
Function of rod and cone cells in
State the function of rod and cone
the eye
cells in the eye
Mixing pigments
A student is able to ;
Uses of pigments
State what pigment is
Comparison between mixing of
List the uses of pigments
pigments with the addition of
coloured lights
Effects of pigments on light
Importance of colour in daily life
Uses of colour in daily life
Importance of colour to living
things
Compare and contrast the
mixing of pigments with the addition
of coloured lights
Explain through examples the
effects of pigments on light
Make conclusions about the
mixing of pigmnets
A student is able to ;
list the uses of colour in
daily life
state with examples the
importance of colour to living things
justify the importance of
colour to living things
Chapter 8 : Chemical in industry
Jul
Properties of alloys and their uses in
industry
Definition and examples of alloy
Formation of alloy that can
change the properties of metals
Relate the properties of alloys to
their uses in daily life
Importance of alloy
Superconductor alloys
Production and uses of ammonia in
industry
Uses of ammonia and its
compounds in daily life
Production of ammonia in
industry
Production of ammonium salt
fertilisers and urea using
ammonia
A student is able to :
State what an alloy is
Give examples of alloys
Explain how the formation of
alloy can change the properties
of metals
Relate the changes in the
properties of metals when they
are converted to alloys to the
arrangement of particles in the
alloys
Relate the properties of alloys
to their uses in daily life
Describe the importance of
alloys in industry
State what superconductor
alloys are
A student is able to :
List the uses of
ammonia and its compounds in
daily life
Describe how
ammonia is produced in industry
State the factors
which affect the production of
ammonia in industry
State the industrial
uses of ammonia
Describe how
ammonia is used to produce
ammonium salt fertilizers and urea
Effects of industrial waste disposal on A student is able to :
the environment
Identify manufacturing activities
Manufacturing activities, the
which are sources of pollution
source of pollution
Explain the effects of improper
Effects of improper industrial
industrial waste disposal
waste disposal
Relate the effects of industrial
Methods of controlling industrial
waste disposal to the survival of
waste disposal to avoid pollution
Recap the chapter
living things
State with examples the
methods of controlling industrial
waste disposal to avoid pollution
Você também pode gostar
- Unit 3 Ap Biology Review GuideDocumento23 páginasUnit 3 Ap Biology Review Guideapi-605991044Ainda não há avaliações
- Starship Troopers Skinnies Army BookDocumento66 páginasStarship Troopers Skinnies Army BookDougBirtles100% (5)
- Minimal Knowledge QuestionsDocumento5 páginasMinimal Knowledge QuestionsLorena IzabellaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology I (BIO201) Course MaterialsDocumento18 páginasAnatomy and Physiology I (BIO201) Course MaterialsAnnie Minnie0% (1)
- Muscle Energy Techniques ExplainedDocumento2 páginasMuscle Energy Techniques ExplainedAtanu Datta100% (1)
- Physiology SyllabusDocumento11 páginasPhysiology SyllabusBarney Cordova100% (1)
- Cambridge Year 8 Science Curriculum FrameworkDocumento2 páginasCambridge Year 8 Science Curriculum FrameworkAimanRiddle100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDocumento5 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Course SyllabusDanna ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- Biology IntroductionDocumento122 páginasBiology Introductioncpantsula0% (1)
- Richard Western Price List 2015Documento40 páginasRichard Western Price List 2015Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Introspect For DealersDocumento13 páginasIntrospect For DealersOBERON-INTROSPECT-BIOSPECTAinda não há avaliações
- Pain PathwayDocumento17 páginasPain PathwaySalsabila Al-BasheerAinda não há avaliações
- History of Industrial Microbiology PDFDocumento11 páginasHistory of Industrial Microbiology PDFOni Port43% (7)
- Microbiological Test of Medical DevicesDocumento5 páginasMicrobiological Test of Medical Devicesbijendra_sinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly TP f4 2012Documento9 páginasYearly TP f4 2012Haffiuzdin Bin Abd AzizAinda não há avaliações
- RPT Science FRM 4Documento16 páginasRPT Science FRM 4Siraj Ul-Akmal YusriAinda não há avaliações
- f4 Yearly Plan 2011Documento18 páginasf4 Yearly Plan 2011Zuraida Bt Zainol AbidinAinda não há avaliações
- RPT: Science Form 3Documento15 páginasRPT: Science Form 3Ani AhwaiAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO SyllabusDocumento8 páginasIJSO SyllabusMohini Deep RetreatAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Study Guide CP BiologyDocumento1 páginaMidterm Study Guide CP BiologyCrystalAinda não há avaliações
- Year 11 Jan Mock Revision ListDocumento9 páginasYear 11 Jan Mock Revision Listbseddon6969Ainda não há avaliações
- Cluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Documento3 páginasCluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Baby Jane AnayAinda não há avaliações
- Cluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Documento3 páginasCluster/Subject/Competency: 1. Biological Science 1-Plant and Animal Biology 1Baby Jane AnayAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Exam 1 Study GuideDocumento3 páginasUnit 1 Exam 1 Study Guideguisellvazquez36Ainda não há avaliações
- Mid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyDocumento8 páginasMid Term Study Guide For 2022 Without EcologyAniya HarriottAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy OutlineDocumento6 páginasAnatomy OutlineLena KhayoAinda não há avaliações
- BIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideDocumento3 páginasBIO 101 Exit Exam Study GuideOlaide Seun Akintade100% (1)
- BCH 439 Pharmaceutical Biochemistry CourseDocumento22 páginasBCH 439 Pharmaceutical Biochemistry CourseAkpemi Musa50% (2)
- A&P Review Questions for Behavioral CliniciansDocumento20 páginasA&P Review Questions for Behavioral Cliniciansphillip_galinsyAinda não há avaliações
- Obe Chem 103L 2015-2016Documento11 páginasObe Chem 103L 2015-2016Joseph AndaganAinda não há avaliações
- Dewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Documento12 páginasDewan Aminul Islam BME Assignment1Towsif Muhtadi KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 2017-18 Anatphys SyllabusDocumento7 páginas2017-18 Anatphys Syllabusapi-266971550Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Topic Questions Term OneDocumento5 páginasScience Topic Questions Term OneLaiba FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching & Learning Contract For Yearly Scheme of Work For Form Five Biology 2014Documento13 páginasTeaching & Learning Contract For Yearly Scheme of Work For Form Five Biology 2014halimi_foaedAinda não há avaliações
- BiologyDocumento7 páginasBiologyLuis VasquezAinda não há avaliações
- GCE O Level Biology Syllabus OverviewDocumento25 páginasGCE O Level Biology Syllabus OverviewWayne WeeAinda não há avaliações
- SMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)Documento8 páginasSMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)pooyenpengAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Biology - 1st Year: ObjectivesDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To Biology - 1st Year: ObjectivesAiza ArcenaAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly Plan 2011 Biology Form 4: Week Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes NotesDocumento7 páginasYearly Plan 2011 Biology Form 4: Week Learning Area Learning Objective Learning Outcomes NotesYeexin HoongAinda não há avaliações
- SMK Sultan Abdul Samad Science Lesson PlanDocumento17 páginasSMK Sultan Abdul Samad Science Lesson PlanRosalmi AyuAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1Documento8 páginasGrade 9 / Year 10 Biology Course Syllabus 2020-2021course Outline Term 1CanioAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy 1st Semester ReviewDocumento23 páginasAnatomy 1st Semester ReviewMonia AliAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding biochemistry basicsDocumento16 páginasUnderstanding biochemistry basicsGadzikaAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly Plan 2012Documento8 páginasYearly Plan 2012Rosni SelamonAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly Teaching PlanDocumento7 páginasYearly Teaching PlanrarmaaAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Science 6Documento6 páginasDLL Science 6Emil SayseAinda não há avaliações
- BIO-107Documento11 páginasBIO-107lizawillam2023Ainda não há avaliações
- RPT: Science Form 4 Rancangan Pelajaran TahunanDocumento21 páginasRPT: Science Form 4 Rancangan Pelajaran TahunanChuah Siew HoonAinda não há avaliações
- 5d83b684c0fa4b974de9b431 - HS Biology 1 - Course #2000310Documento7 páginas5d83b684c0fa4b974de9b431 - HS Biology 1 - Course #2000310Lerante LaubaxAinda não há avaliações
- 2022 Final Version TTO Reader1 Scheikunde T3Documento72 páginas2022 Final Version TTO Reader1 Scheikunde T3maxvandorsser07Ainda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full Biology Concepts and Investigations 3rd Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 páginasDwnload Full Biology Concepts and Investigations 3rd Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual PDFjunemojarrazqmxj100% (17)
- 2018 - Year 11 Chemistry Research Assessment TaskDocumento4 páginas2018 - Year 11 Chemistry Research Assessment TaskgeeeelooAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide For Biology MidtermDocumento5 páginasStudy Guide For Biology Midtermkal51Ainda não há avaliações
- RPT Biology Form 5Documento18 páginasRPT Biology Form 5Mohamad Khairie Rano IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis Science Paper 2 SPMDocumento2 páginasAnalysis Science Paper 2 SPMKelvin Tan100% (1)
- Year 8 High-Detail Topic List Nov23Documento3 páginasYear 8 High-Detail Topic List Nov2322hzamanAinda não há avaliações
- Form One Biology: Introduction and Key ConceptsDocumento54 páginasForm One Biology: Introduction and Key ConceptsoyooAinda não há avaliações
- Teacher's Name: Hildah Makori Grade 12, Biology Curriculum Map 2016Documento4 páginasTeacher's Name: Hildah Makori Grade 12, Biology Curriculum Map 2016api-302059687Ainda não há avaliações
- Yearly Plan 2008Documento22 páginasYearly Plan 2008rickysuAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Action Plan: Key Knowledge and SkillsDocumento5 páginasRevision Action Plan: Key Knowledge and SkillsIan AndersonAinda não há avaliações
- YEARLY SCHEME AND STUDENTS’ EXERCISE CONTRACT 2012 SCIENCE FORM 4Documento12 páginasYEARLY SCHEME AND STUDENTS’ EXERCISE CONTRACT 2012 SCIENCE FORM 4halizayani73Ainda não há avaliações
- AHS 101 Anatomy and Physiology SyllabusDocumento14 páginasAHS 101 Anatomy and Physiology SyllabusJuan ConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology Objectives DetailedDocumento35 páginasPhysiology Objectives DetailedSOOOS94Ainda não há avaliações
- Topics For MEDadmission Test&interviewDocumento5 páginasTopics For MEDadmission Test&interviewGuzay OzverirAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Processes ChecklistDocumento2 páginasCell Processes Checklistapi-324166624Ainda não há avaliações
- Life Science Final Exam Review-May 2015Documento8 páginasLife Science Final Exam Review-May 2015api-230330590Ainda não há avaliações
- Introductory Experiments on Biomolecules and their InteractionsNo EverandIntroductory Experiments on Biomolecules and their InteractionsAinda não há avaliações
- Maths File 3 PDFDocumento19 páginasMaths File 3 PDFAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Planning f3Documento12 páginasLesson Planning f3Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Birth Control or Contraception: Note: Please Insert Pictures For All The MethodDocumento10 páginasBirth Control or Contraception: Note: Please Insert Pictures For All The MethodAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Big Data Analytics MDEC PDFDocumento34 páginas02 Big Data Analytics MDEC PDFAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Trial Sains PT3 Penang PDFDocumento22 páginasSoalan Trial Sains PT3 Penang PDFAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- TemplateDocumento1 páginaTemplateAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2013 Subject: Science Form: 3 Weeks Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning OutcomesDocumento22 páginasYearly Lesson Plan 2013 Subject: Science Form: 3 Weeks Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning OutcomesAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Exchange & OTC Market DifferencesDocumento3 páginasExchange & OTC Market DifferencesAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Calendar Landscape 2 PagesDocumento2 páginas2016 Calendar Landscape 2 PagesAnonymous b0gP6mDaq100% (1)
- Book Inventory 2014Documento69 páginasBook Inventory 2014Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- KeyLearningPoints Prince2Documento12 páginasKeyLearningPoints Prince2Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Adoption GuideDocumento16 páginasAdoption GuideGustavo PalaciosAinda não há avaliações
- DogDocumento2 páginasDogRaja Prathap Singh0% (1)
- KeyLearningPoints Prince2Documento12 páginasKeyLearningPoints Prince2Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Smart TelecasterDocumento2 páginasSmart TelecasterAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
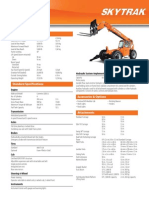
- SkyTrak 10054 Telehandler Spec SheetDocumento2 páginasSkyTrak 10054 Telehandler Spec SheetAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Technology and The CCSS in The Foreign Language Class DecDocumento40 páginasTechnology and The CCSS in The Foreign Language Class DecAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 - File Processing: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocumento72 páginasChapter 14 - File Processing: 2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All Rights ReservedAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Red Bull Media House Sales Catalog V12 13Documento58 páginasRed Bull Media House Sales Catalog V12 13Anonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- 1.04.1 The Various Resources On Earth: Kepelbagaian Sumber Di BumiDocumento12 páginas1.04.1 The Various Resources On Earth: Kepelbagaian Sumber Di BumiAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- 1.04.1 The Various Resources On Earth: Kepelbagaian Sumber Di BumiDocumento12 páginas1.04.1 The Various Resources On Earth: Kepelbagaian Sumber Di BumiAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
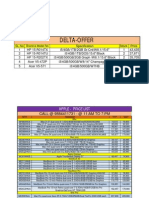
- Delta-Offer: Brand & Model NoDocumento17 páginasDelta-Offer: Brand & Model NoAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Accenture Mobility Services Brochure Low Res FinalDocumento8 páginasAccenture Mobility Services Brochure Low Res FinalAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Using Technology To Enhance Student LearningDocumento28 páginasUsing Technology To Enhance Student LearningAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Converged Enterprise Mobility SolutionsDocumento12 páginasConverged Enterprise Mobility SolutionsAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- Techol BsDocumento20 páginasTechol BsMarin507sAinda não há avaliações
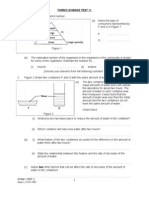
- Form 2 Science Test 11: (Choose Your Answers From The Following Numbers: 2000, 80, 3)Documento5 páginasForm 2 Science Test 11: (Choose Your Answers From The Following Numbers: 2000, 80, 3)Hasmi MohamadAinda não há avaliações
- What's Cooking?: It Starts With A Plan and A ListDocumento12 páginasWhat's Cooking?: It Starts With A Plan and A ListAnonymous b0gP6mDaqAinda não há avaliações
- MOKUSAKU APPLICATIONS (Version 1)Documento1 páginaMOKUSAKU APPLICATIONS (Version 1)api-19621568Ainda não há avaliações
- HistamineDocumento16 páginasHistaminevg03ik2Ainda não há avaliações
- Full Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasFull Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manualgambolrapinous.ggqcdr100% (39)
- PRACTICE TEST - Gen - EdDocumento93 páginasPRACTICE TEST - Gen - EddispacitoteamoAinda não há avaliações
- The Antibacterial Properties of Isothiocyanates PDFDocumento15 páginasThe Antibacterial Properties of Isothiocyanates PDFSasicha DoungsuwanAinda não há avaliações
- Explaining Butterfly MetamorphosisDocumento13 páginasExplaining Butterfly MetamorphosisCipe drAinda não há avaliações
- Biology ss2Documento2 páginasBiology ss2DanielAinda não há avaliações
- Follicular Dynamics in Bovine and Ovine 1Documento19 páginasFollicular Dynamics in Bovine and Ovine 1israr yousafAinda não há avaliações
- 4546-LacOperon InstsDocumento14 páginas4546-LacOperon InstsScribd_is_GreatAinda não há avaliações
- Non-symbiotic Nitrogen FixersDocumento21 páginasNon-symbiotic Nitrogen Fixersrajiv pathakAinda não há avaliações
- Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) PropertiesDocumento13 páginasCharacterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) PropertiesEsteban ArayaAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Sleep Deprivation among Students in Saint Francis of Assisi CollegeDocumento50 páginasEffects of Sleep Deprivation among Students in Saint Francis of Assisi College• Cielo •Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento40 páginasCardiovascular SystemMudasir Hussain TuriAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis Kualitatif Dan Kuantitatif Kandungan Kimia Dari Ekstrak Heksan, Aseton, Etanol Dan Air Dari Umbi Bawang Putih (Allium Sativum Linn.)Documento11 páginasAnalisis Kualitatif Dan Kuantitatif Kandungan Kimia Dari Ekstrak Heksan, Aseton, Etanol Dan Air Dari Umbi Bawang Putih (Allium Sativum Linn.)Tari PratiwiAinda não há avaliações
- Perkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurDocumento7 páginasPerkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurNurma YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- IN SEARCH OF SEXUAL ENHANCEMENT THROUGH PILLS AND DRUGSDocumento16 páginasIN SEARCH OF SEXUAL ENHANCEMENT THROUGH PILLS AND DRUGSJakob AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- Science Holidays Homework Class 9Documento2 páginasScience Holidays Homework Class 9nileshAinda não há avaliações
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocumento24 páginasBiology: Pearson EdexcelAhmad MohdAinda não há avaliações
- Pengantar Mikrobiologi LingkunganDocumento28 páginasPengantar Mikrobiologi LingkunganAhmad SyahrulAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanDocumento7 páginasChemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanSkyle VoAinda não há avaliações
- NSABB Final Report Recommendations Evaluation Oversight Proposed Gain of Function Research May 2016Documento109 páginasNSABB Final Report Recommendations Evaluation Oversight Proposed Gain of Function Research May 2016Jim Hoft100% (1)
- 421 Reproduction Developmental Toxicity Screening TestDocumento10 páginas421 Reproduction Developmental Toxicity Screening TestAshishAinda não há avaliações
- 皮膚病介紹Documento93 páginas皮膚病介紹MK CameraAinda não há avaliações
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocumento13 páginasMorphology of Flowering Plantschiragbhaskar16Ainda não há avaliações