Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Giardia Benchaid
Enviado por
Saad MotawéaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Giardia Benchaid
Enviado por
Saad MotawéaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
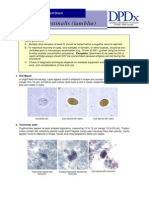
Laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis
Giardia intestinalis (lamblia)
Basic guidelines
A. Multiple stool samples (at least 3) should be tested before a negative result is reported.
B. To maximize recovery of cysts, stool samples in formalin should be concentrated prior to
microscopic examination (e.g., 10 min at 500 g when using the formalin-ethyl acetate
concentration procedure). Exception: Specimens to be used for EIA or rapid cartridge
assays should NOT be concentrated because antigens are lost during the procedure!
C. Choice of diagnostic techniques depends on available equipment and reagents, experience, and considerations of time and cost.
1. Wet mount
In bright-field microscopy, cysts appear ovoid to ellipsoid in shape and usually measure 11 to 14 m
(range: 8 to 19 m). Nuclei, 4 in mature cysts and 2 in immature cysts, and intracytoplasmic fibrils are
visible.
Unstained cyst
Cyst stained with iodine
Cyst stained with iodine
2. Trichrome stain
Trophozoites appear as pear-shaped organisms, measuring 12 to 15 m (range: 10 to 20 m). Trophozoites contain two anteriorly placed nuclei and 8 flagella (rarely seen because they stain poorly). Cysts
appear ovoid to ellipsoid in shape. Nuclei and intracytoplasmic fibrils are visible.
Trophozoite stained with
trichrome
Dividing trophozoite stained
with trichrome
Cyst stained with trichrome
Laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis
3. Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) assay
This technique offers the highest combination of sensitivity and
specificity and is considered the gold standard by many laboratories. For commercial DFA kits, it is recommended that a concentrated stool specimen be used to increase the probability of detection of low numbers of cysts. However, special equipment
(fluorescence microscope) and commercially available test kits are
required and it does not provide a permanently stained slide that
can be archived.
Giardia intestinalis labeled with immunofluorescent antibodies
4. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
The EIA does not rely on microscopy and is useful for screening large numbers of specimens. Borderline positives and questionable negatives obtained with this technique should be further confirmed by
DFA. Antigens of Giardia are detected in the feces using this method; therefore, specimens should not
be concentrated prior to testing. However, special equipment (microplate reader) and commercially
available test kits are required.
5. Rapid immunochromatographic cartridge assays
The rapid cartridge assays may be used with preserved specimens and are quick and easy to perform. Antigens of Giardia are detected in the feces using this method; therefore, specimens should not
be concentrated prior to testing. Borderline positives and questionable negatives obtained with this
technique should be further confirmed by DFA. No special equipment is needed.
The quality of reagents in commercially available kits may be variable or deteriorate under storage conditions;
for that reason external controls are necessary to determine whether the kit is properly performing.
Você também pode gostar
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesAinda não há avaliações
- Giardia Intestinalis (Lamblia) : Laboratory Diagnosis of GiardiasisDocumento2 páginasGiardia Intestinalis (Lamblia) : Laboratory Diagnosis of GiardiasisJulio Cesar SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Giardia BenchaidDocumento2 páginasGiardia BenchaidAnggun Rahmah Muthi'ahAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Parasitology: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University PARA 311Documento23 páginasDiagnostic Parasitology: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University PARA 311Moon YoungheeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Policies Culture Wounds Lab 3115Documento7 páginasLab Policies Culture Wounds Lab 3115Marj MendezAinda não há avaliações
- Protozoa - Sample PreparationDocumento31 páginasProtozoa - Sample PreparationRAinda não há avaliações
- Stool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'Documento27 páginasStool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'AnastasiaAinda não há avaliações
- Obi BCH ReportDocumento39 páginasObi BCH ReportErhueh Kester AghoghoAinda não há avaliações
- CDC - Stool ProcessingDocumento2 páginasCDC - Stool ProcessingC. HidalgoAinda não há avaliações
- PMLS 2 Chapter Summary - YraudaDocumento5 páginasPMLS 2 Chapter Summary - YraudaKeizzy YraudaAinda não há avaliações
- Stool AnalysisDocumento11 páginasStool AnalysisMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- 1 IntroductionDocumento37 páginas1 IntroductionJeffrey RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Microscopy Technical ManualDocumento10 páginasClinical Microscopy Technical ManualSharon ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- Specimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESDocumento43 páginasSpecimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESPrincewill SeiyefaAinda não há avaliações
- Parasitology Lab ManualDocumento33 páginasParasitology Lab ManualshericeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Parasitology LaboratoryDocumento18 páginasIntroduction To Parasitology LaboratoryCrisiant DolinaAinda não há avaliações
- CDC - DPDX - Diagnostic Procedures - Stool SpecimensDocumento2 páginasCDC - DPDX - Diagnostic Procedures - Stool SpecimensGaurav ChandrakarAinda não há avaliações
- Fob Cassette PDFDocumento2 páginasFob Cassette PDFHeang ChanryAinda não há avaliações
- NOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingDocumento4 páginasNOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingOdette G. TanAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesDocumento48 páginasPractical Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic DiseasesliliposhianAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Specimen Collection and Processing PDFDocumento107 páginas2 Specimen Collection and Processing PDFcloudiest euniceAinda não há avaliações
- (Para) المختبرDocumento48 páginas(Para) المختبرAhmed GaberAinda não há avaliações
- Stool SampleDocumento3 páginasStool SamplecgermaineeAinda não há avaliações
- SOP For Identification Techniques For Parasite Assays inDocumento68 páginasSOP For Identification Techniques For Parasite Assays inDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (1)
- Specimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDDocumento38 páginasSpecimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDRica Rebadomia100% (2)
- Cytology 3 ReportDocumento93 páginasCytology 3 ReportMoganambikai RagavanAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Operative Procedure For Collection, Transport and Processing and Inoculation of Extra-Pulmonary SpecimensDocumento10 páginasStandard Operative Procedure For Collection, Transport and Processing and Inoculation of Extra-Pulmonary SpecimensgauravAinda não há avaliações
- Pitfalls in The Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic InfectionsDocumento20 páginasPitfalls in The Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic InfectionsJasmen Sabroso PasiaAinda não há avaliações
- ParaDocumento21 páginasParaGEBEYAW ADDISUAinda não há avaliações
- WILDLIFE PATHOLOGY - Practical Laboratory Skills - 2012 - v2Documento49 páginasWILDLIFE PATHOLOGY - Practical Laboratory Skills - 2012 - v2Juliana MatheusAinda não há avaliações
- Para QuizDocumento5 páginasPara QuizEricsson CarabbacanAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For Sweat Test 24Documento14 páginasGuidelines For Sweat Test 24Ruy BorboremaAinda não há avaliações
- Hayat cp3Documento5 páginasHayat cp3hayatkuwaityAinda não há avaliações
- "Collection of Stool Specimen": Parasitology AssignmentDocumento10 páginas"Collection of Stool Specimen": Parasitology AssignmentOmar ElabdAinda não há avaliações
- Final Sop Manual-1-1Documento62 páginasFinal Sop Manual-1-1Dianne JoyAinda não há avaliações
- SMS 315 PRACTICAL HANDBOOK at MARCH 2021Documento25 páginasSMS 315 PRACTICAL HANDBOOK at MARCH 2021Raymond NyarkoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To FecalysisDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To FecalysisseanleeqtAinda não há avaliações
- H Pilory HecesDocumento2 páginasH Pilory HecesKarla SotoAinda não há avaliações
- Permanent stain - نسخة - نسخةDocumento22 páginasPermanent stain - نسخة - نسخةLê Huy HoàngAinda não há avaliações
- Ear Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2Documento2 páginasEar Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2SemeeeJuniorAinda não há avaliações
- 1 General 1Documento37 páginas1 General 1بلسم محمود شاكرAinda não há avaliações
- SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND TRANSPORT - ADocumento8 páginasSPECIMEN COLLECTION AND TRANSPORT - AJane Frances JabricaAinda não há avaliações
- BBL CLED Agar: ™ L007367 - Rev. 04 - May 2006Documento3 páginasBBL CLED Agar: ™ L007367 - Rev. 04 - May 2006Muhammad Hadi ArwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Semen ExaminationDocumento4 páginasSemen Examinationnitin tyagiAinda não há avaliações
- CLEDDocumento4 páginasCLEDMongiwethu DungeniAinda não há avaliações
- Ova and Parasite Examination StoolDocumento5 páginasOva and Parasite Examination StoolNazaqat FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- Accurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andDocumento4 páginasAccurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andManulat VicaiiAinda não há avaliações
- Cytogenetics Lecture Notes - SOPDocumento23 páginasCytogenetics Lecture Notes - SOPNeo Mervyn Monaheng100% (1)
- EXPERIMENTDocumento58 páginasEXPERIMENTYriel GuilaranAinda não há avaliações
- Workflow BactriologyDocumento48 páginasWorkflow BactriologyAl- ImanuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Lesson 16: The Kato-Katz Technique For Helminths EggsDocumento5 páginasLab Lesson 16: The Kato-Katz Technique For Helminths EggsRalph B. BarsanalinaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic CytologyDocumento32 páginasDiagnostic Cytologyclaw foreSK TeamAinda não há avaliações
- Sterile ProductsDocumento7 páginasSterile ProductsMUHAMMAD ZOHAIBAinda não há avaliações
- Monkeypox - Diagnostic Testing - GOV - UKDocumento7 páginasMonkeypox - Diagnostic Testing - GOV - UKEduardo Rios DuboisAinda não há avaliações
- Cb1 - Specimen Handling, Transport and ProcessingDocumento7 páginasCb1 - Specimen Handling, Transport and ProcessingAngelic AngelesAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment NO 2 BTI619Documento19 páginasAssignment NO 2 BTI619Mashal WakeelaAinda não há avaliações
- SOP For Parasitology Sample Collection and ExaminationDocumento11 páginasSOP For Parasitology Sample Collection and ExaminationDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines88% (8)
- 6.1. Stool Specimen 6.1. Stool Specimen: 9/18/21 Tafeseb - Tufa 1Documento67 páginas6.1. Stool Specimen 6.1. Stool Specimen: 9/18/21 Tafeseb - Tufa 1Worku KifleAinda não há avaliações
- Ohhc Obtaining Stool Specimens For Laboratory AnalysisDocumento8 páginasOhhc Obtaining Stool Specimens For Laboratory AnalysisDerick RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Patient HandbookDocumento29 páginasPatient HandbookOluwasegun OluwaletiAinda não há avaliações
- Biological WeaponsDocumento29 páginasBiological WeaponsSaad Motawéa100% (1)
- 3-Bioelectrical Stimulation For People With Patterns Consistent With Certain Chronic InfectionsDocumento8 páginas3-Bioelectrical Stimulation For People With Patterns Consistent With Certain Chronic InfectionsSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Session 1 - BT Epi Response Training - Outbreak InvestigationDocumento41 páginasSession 1 - BT Epi Response Training - Outbreak InvestigationSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- 2-Electrotherapy For Blood ElectrificationDocumento12 páginas2-Electrotherapy For Blood ElectrificationSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Outbreak Investigation Monday's ExerciseDocumento5 páginasOutbreak Investigation Monday's ExerciseSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Bioelectrical Stimulation For People With Patterns Consistent With Certain Chronic InfectionsDocumento8 páginas3-Bioelectrical Stimulation For People With Patterns Consistent With Certain Chronic InfectionsSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Common Intertinal Worms Found in Southern AfricaDocumento100 páginasCommon Intertinal Worms Found in Southern AfricaSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Parasites LectureDocumento22 páginasParasites LectureSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- 20 - Outbreak Investigation ReportDocumento26 páginas20 - Outbreak Investigation ReportSaad Motawéa50% (2)
- Pathogenomic Research in Hungary Present Stage and PerspectivesDocumento11 páginasPathogenomic Research in Hungary Present Stage and PerspectivesSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Julian Pe ToDocumento41 páginasJulian Pe ToSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- EpidemiologyDocumento7 páginasEpidemiologySaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Wong F Food OverviewDocumento25 páginasWong F Food OverviewSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- GM 05 TrypanosomDocumento30 páginasGM 05 TrypanosomSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- New York University School of Medicine Meeting of The Curriculum CommitteeDocumento2 páginasNew York University School of Medicine Meeting of The Curriculum CommitteeSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- A Cute Appendic ItsDocumento109 páginasA Cute Appendic ItsYosevine Noviana PeranginanginAinda não há avaliações
- Case 2Documento20 páginasCase 2Saad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Paraneoplastic SyndromeDocumento1 páginaParaneoplastic SyndromeSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- CasesDocumento18 páginasCasesSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- The Bizarre Claims of Hulda ClarkDocumento16 páginasThe Bizarre Claims of Hulda ClarkSaad Motawéa100% (1)
- ApplicationDocumento11 páginasApplicationSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Courses2006 2007Documento8 páginasCourses2006 2007Saad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- S P - O F: Yllabus RE Rder ORMDocumento1 páginaS P - O F: Yllabus RE Rder ORMSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Public Health Community Preparedness For SarsDocumento29 páginasPublic Health Community Preparedness For SarsSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Report 2005 PDFDocumento54 páginasAnnual Report 2005 PDFSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- GuideDocumento41 páginasGuideSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Writing A ReferenceDocumento1 páginaWriting A ReferenceSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Supportive SupervisionDocumento21 páginasSupportive SupervisionSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Hexamine Fuel TabletDocumento4 páginasHexamine Fuel TabletSaad MotawéaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Cells Under A MicroscopeDocumento3 páginasLab Cells Under A MicroscopeAndrea ColliaAinda não há avaliações
- Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Carbinoxamine Maleate and Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Oral SolutionDocumento2 páginasPseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Carbinoxamine Maleate and Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Oral SolutionK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Weight MarkersDocumento12 páginasMolecular Weight MarkersZecaValerianoAinda não há avaliações
- How Develop - Validate MethodsDocumento554 páginasHow Develop - Validate MethodsAdriana CiroAinda não há avaliações
- Integenx Rapid DnaDocumento14 páginasIntegenx Rapid Dnaapi-400796139Ainda não há avaliações
- Imaging Bio MoleculesDocumento48 páginasImaging Bio Moleculesakash meherAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Lesson MaterialsDocumento6 páginasCell Lesson Materialsapi-250804103Ainda não há avaliações
- Separation of The Components in A Mixture (File) 2Documento4 páginasSeparation of The Components in A Mixture (File) 2Lester PioquintoAinda não há avaliações
- Acellular PathogensDocumento17 páginasAcellular Pathogensjeraldine marceraAinda não há avaliações
- Genomic DNA Plug KitDocumento12 páginasGenomic DNA Plug KitsrijitkhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 315 Practice QuizzesDocumento9 páginasChem 315 Practice QuizzesLuke HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- 986.33 Mesofilos Aerobios-PetrifilmDocumento1 página986.33 Mesofilos Aerobios-PetrifilmBleidy NieblesAinda não há avaliações
- Title PageDocumento11 páginasTitle PageRaja Muaz AliAinda não há avaliações
- Feider Et Al 2019 Ambient Ionization Mass Spectrometry Recent Developments and ApplicationsDocumento25 páginasFeider Et Al 2019 Ambient Ionization Mass Spectrometry Recent Developments and ApplicationsBishoy F. YoussefAinda não há avaliações
- DistillationDocumento14 páginasDistillationThe MatrixAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Electron MicrosDocumento4 páginasResearch Paper On Electron Microslemvhlrif100% (1)
- Various Analysis Techniques For Organic Acids and Examples of Their Application. Application Note (Shimadzu)Documento16 páginasVarious Analysis Techniques For Organic Acids and Examples of Their Application. Application Note (Shimadzu)Maikel Perez NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Gel Electrophoresis of ProteinsDocumento4 páginasGel Electrophoresis of ProteinsRommel BauzaAinda não há avaliações
- Wa0000.Documento4 páginasWa0000.Jashandeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Gel Electrophoresis LabDocumento8 páginasGel Electrophoresis LabAmit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Pengantar Dan Sejarah KromatografiDocumento32 páginasPengantar Dan Sejarah KromatografiFenny rahmadhanyAinda não há avaliações
- Use of Eriochrome Cyanine R in Routine Histology and Histopathology: Is It Time To Say Goodbye To Hematoxylin?Documento10 páginasUse of Eriochrome Cyanine R in Routine Histology and Histopathology: Is It Time To Say Goodbye To Hematoxylin?Dušan StefanovićAinda não há avaliações
- HBsAg WantaiDocumento16 páginasHBsAg WantaiAnnisa UtamiAinda não há avaliações
- Questions HPLCDocumento10 páginasQuestions HPLCMariz MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Mass SpectrometryDocumento19 páginasMass SpectrometryArchieAinda não há avaliações
- MicrosDocumento6 páginasMicroshguytAinda não há avaliações
- MembraneDocumento26 páginasMembraneSurendranAinda não há avaliações
- GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY - Mass SpectrosDocumento29 páginasGAS CHROMATOGRAPHY - Mass SpectroslintasamimAinda não há avaliações
- IMMUNOELECTROPHORESISDocumento4 páginasIMMUNOELECTROPHORESISkiedd_0460% (5)
- Experiment 2dDocumento2 páginasExperiment 2dbillchen9929% (7)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (24)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (80)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!No EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (392)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (169)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNo EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningNo EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)No EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (378)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNo EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (51)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNo EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (58)