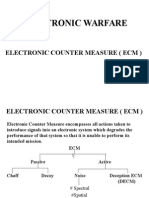
Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Classification of Buses
Enviado por
Aghil BuddyDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Classification of Buses
Enviado por
Aghil BuddyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
03-01-2014
CLASSIFICATION OF BUSES
CLASSIFICATION OF BUSES
Passenger carrying buses are classifies based
on:
Distance travelled by the vehicle
Capacity of the vehicle
Shape and Style of the vehicle
Distance travelled by the vehicle
Town bus
Town bus
Suburban bus
Long Distance Coaches
Touring Coaches
These buses are used for a short distance
of about 20 kms.
They are provided with large number of
standing places, two wide doors with large
entry and exit platform and hard seats
covered with durable plastic materials.
03-01-2014
Suburban bus
Long Distance Coaches
These buses are used for a distance of about
40 to 50 kms. They usually have reasonably
comfortable seats;
fairly small entry platform for the extra space
can be used for luggage and extra standing
passengers.
Usually one door is sufficient for this type of
operation.
These buses are used for a distance of about
200 kms and above.
They have comfortable seats with under floor
luggage space and roof racks for large items
of luggage.
Touring Coaches
Based on the capacity of the vehicle
For longer distance touring coaches, very
comfortable reclining seats are used.
Toilets, air conditioners, TV,etc are provided.
Additional windows in the roof are used to
improve visibility for the passengers.
Thermal and acoustic insulation is usually
elaborate
and
spacious
luggage
compartments are provided under the floor
and on the roof.
03-01-2014
Shape and Style of the vehicle
Classic type
Classic type
Single Decker
Double Decker
Split-level bus
Two-level single Decker
Articulated bus
The Classic or normal control bus has the engine in
front of the passenger carrying compartment.
This design, which was almost universal at one
time, has practically disappeared and is mainly of
historical interest.
low ratio of useful length to overall length.
It also has a high tare weight and poor aerodynamic
shape.
Single Decker
10
Double Decker
The full-length bodywork, i.e. single deck bus
or coach is almost universal today as this
layout eliminates all the disadvantages of
classic type.
11
These buses have a greater number of seats
for a given overall length than a single Decker
but stability is not so high as for the single
Decker.
12
03-01-2014
Split-level bus
Two-level single Decker
An intermediate solution between the two
is the split-level layout.
This layout has more seats than a single
Decker and more stability than the double
Decker.
However, owing to the small number of
variations that can be made from this basic
design, it has not been widely accepted.
Two-level single Decker has been used for
luxury coaches.
This layout provides good forward visibility for
all passengers, good luggage space and easy
installation of an under-floor or rear engine.
Again this type is only made for special
orders, as it is not easy to make derivations
from the same body shell.
13
14
Articulated bus
Bodies for very large coaches or in particular,
city buses are often made in two parts because
of axle load limitations.
The rear portion is articulated to the main vehicle
by a covered pivot allowing easy access
between the two sections.
A bi-articulated bus or double articulated
bus is an extension of an articulated bus in
that it has three passenger compartment
sections instead of two.
This also involves the addition of an extra axle.
Due to the extended length, bi-articulated
buses tend to be used on high frequency core
routes or bus rapid transit schemes rather than
conventional bus routes.
15
16
03-01-2014
AIS 052
Type I
Type II
Type III
Type IV
Low Capacity
Medium Capacity
High Capacity
NDX
SDX
DLX
ACX
17
Type I
Vehicles are the medium and high capacity
urban and sub urban / city transport with area
for standing passengers,
low capacity vehicles which are designed and
constructed for urban and sub urban / city
transport exclusively for carrying seated
passengers.
The low capacity vehicles in this type can carry
standee passengers if they meet provisions for
low capacity standee buses.
18
19
Type II
Vehicles are those designed and constructed
for inter-urban/inter-city transport without
specified area for standing passengers, but
can carry standing passengers over short
distance in the gangway; unless otherwise
prohibited by the State Transport Department.
20
03-01-2014
Type III Vehicles are those designed and
constructed for long distance passenger transport,
exclusively designed for comfort of seated
passengers and not intended for carrying standing
passengers.
Type IV Vehicles are those designed and
constructed for special purpose use
such as the following :
(1) School Bus: means vehicles designed and
constructed specially for schools, college, and other
educational Institutions.
(2) Sleeper Coaches: means vehicles designed and
constructed specially berth to accommodate sleeping
passengers.
(3) Tourist Bus: means vehicles designed and
constructed for the purpose of transportation of
passengers as tourists and may be classified in any one
Type of comfort levels.
21
Low Capacity Vehicles include
(1) Micro Bus : Seating capacity of maximum
12 passengers plus driver.
(2) Mini Bus : Seating capacity between 13 to
22 passengers plus driver.
22
Medium Capacity Vehicles include (1) Midi Bus : Seating capacity between
23 to 34 passengers plus
driver.
(2) Standard Bus : Seating capacity
between 35 to 70
passengers
23
24
03-01-2014
Non Deluxe Bus(NDX) means bus designed for
basic minimum comfort level.
Semi Deluxe Bus(SDX) means a bus designed
for a slightly higher comfort level and with
provision for ergonomically designed seats.
Deluxe Bus(DLX) means a bus designed for a
high comfort level and individual seats and
adjustable seat backs, improved ventilation and
pleasing interiors.
A.C. Deluxe Bus(ACX) means a Deluxe Bus
which is air conditioned.
High Capacity Vehicles are the vehicles with
seating capacity more than 70 passengers
plus driver and include vehicles such as Single
Deck Articulated Bus, Single Deck Double
Articulated Bus, Double Deck Bus, Double
Deck Articulated Bus and Single Deck
Tandem Axle Bus etc.
25
26
REFERENCES
Vehicle Body Engineering by J.Powloski
AIS 052
27
Você também pode gostar
- UNIT III Notes Bus BodyDocumento41 páginasUNIT III Notes Bus BodyRish RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Bus BodyDocumento27 páginasBus BodyDr. Vijay Singh ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of BusesDocumento4 páginasClassification of Busesrudey18Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit1 - Classification of Coachwork - S1Documento22 páginasUnit1 - Classification of Coachwork - S1Akash Singh100% (1)
- Bus Body Layout and TypesDocumento52 páginasBus Body Layout and Typesjayabalaji_775985% (20)
- VBE PPT Module 1. 168293764906011Documento63 páginasVBE PPT Module 1. 168293764906011Bhuvan s GaneshkarAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Kelompok - 20231030 - 122554 - 0000Documento19 páginasTugas Kelompok - 20231030 - 122554 - 0000zaipulrohimlubisAinda não há avaliações
- Vehicle Body Engineering: Bus Body DetailsDocumento12 páginasVehicle Body Engineering: Bus Body DetailsAnant ShivAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - IiDocumento57 páginasUnit - Iisiva kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Bus Body Regulations PDFDocumento106 páginasBus Body Regulations PDFUsha Kiran KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Bus BodyDocumento24 páginasBus BodyHarshdeepsinh Padhiyar100% (1)
- Overview of Transit VehiclesDocumento3 páginasOverview of Transit VehiclesAsjsjsjsAinda não há avaliações
- PES University Bangalore Scheme Solutions Body Chassis EngineeringDocumento8 páginasPES University Bangalore Scheme Solutions Body Chassis EngineeringvvvAinda não há avaliações
- Intermodal Shipping: What Is The Challenge?Documento2 páginasIntermodal Shipping: What Is The Challenge?zaamanishAinda não há avaliações
- Sky Bus TechnologyDocumento13 páginasSky Bus TechnologyJhanvi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Automobilechassisandbody 160622030425Documento95 páginasAutomobilechassisandbody 160622030425Thomas TamangAinda não há avaliações
- Man GN PDF 2Documento20 páginasMan GN PDF 2Adrian A UPD100% (1)
- Motor VehiclesDocumento19 páginasMotor VehiclesdaveAinda não há avaliações
- Motor Vehicle Engineering IntroductionDocumento39 páginasMotor Vehicle Engineering IntroductionKuma AlexoAinda não há avaliações
- HgjyDocumento1 páginaHgjykaru320Ainda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento50 páginasReport 1pramo_dassAinda não há avaliações
- ISBT - Library Study (GROUP1) PDFDocumento45 páginasISBT - Library Study (GROUP1) PDFTwinkle AhlawatAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - 14Documento5 páginas2 - 14annanovosolovvaAinda não há avaliações
- RSW-MT-01 - BusTerminal - Digman, Sean Elvin B.Documento18 páginasRSW-MT-01 - BusTerminal - Digman, Sean Elvin B.SEAN ELVIN DIGMANAinda não há avaliações
- Vehicle Body Engineering - Bus Body DetailsDocumento20 páginasVehicle Body Engineering - Bus Body DetailsAnkush khurana100% (1)
- Sky Bus TechnologyDocumento15 páginasSky Bus TechnologyDennyAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of VehiclesDocumento35 páginasClassification of Vehiclesdranita@yahoo.com0% (1)
- Bus Station Design ElementsDocumento31 páginasBus Station Design ElementsRapha RachoAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing MixDocumento8 páginasMarketing MixinvestokingAinda não há avaliações
- Public TransportationDocumento10 páginasPublic TransportationfendyAinda não há avaliações
- Bus StationDocumento9 páginasBus StationMark BaluyutAinda não há avaliações
- Motorcoaches, Car Rentals and Railway TransportDocumento51 páginasMotorcoaches, Car Rentals and Railway Transportgene roy hernandezAinda não há avaliações
- The Beamway (Monorail)Documento47 páginasThe Beamway (Monorail)onæssAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportDocumento16 páginasBasic Principles Function: Types of Driver's Cab Driver's Cab Concept International Long-Distance TransportAdrian A UPD100% (1)
- in Tro Du C T I On: Commuter Rail ServiceDocumento24 páginasin Tro Du C T I On: Commuter Rail ServiceKennyAinda não há avaliações
- Skybus Research PaperDocumento3 páginasSkybus Research Paperhiren50% (2)
- Transportation: 1.passenger Areas A. Ticketing and Queuing B. Passenger Waiting AreasDocumento3 páginasTransportation: 1.passenger Areas A. Ticketing and Queuing B. Passenger Waiting AreasAbhishek ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- A History of Buses and Their VariationsDocumento11 páginasA History of Buses and Their VariationsDianna SeregolaAinda não há avaliações
- Priyanka SinghDocumento20 páginasPriyanka Singhprakash11111Ainda não há avaliações
- Bus Terminal StandardsDocumento21 páginasBus Terminal StandardsJenish75% (4)
- Land TransportationDocumento25 páginasLand TransportationMonique EtquibalAinda não há avaliações
- Land TransportationDocumento3 páginasLand TransportationGenn rod PrancilisoAinda não há avaliações
- Rekayasa Desain TransportrasiDocumento17 páginasRekayasa Desain Transportrasinana jangAinda não há avaliações
- MiTR Bus Training Content v1Documento56 páginasMiTR Bus Training Content v1dhilonjimyAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation Modes & InfrastructureDocumento160 páginasTransportation Modes & InfrastructureArianne Najah ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Title: Design and Analysis of 3-Dimensional Pro-E Model of A Rear Engine Low Floor Team Registration No.: IN1423 NameDocumento10 páginasTitle: Design and Analysis of 3-Dimensional Pro-E Model of A Rear Engine Low Floor Team Registration No.: IN1423 NameavinitsharanAinda não há avaliações
- Bus Manufacturing, A Sector of The AutomotiveDocumento6 páginasBus Manufacturing, A Sector of The AutomotiveMarlon AliagaAinda não há avaliações
- Low Floor Bus DesignDocumento10 páginasLow Floor Bus DesignavinitsharanAinda não há avaliações
- BRT (Bus Rapid Transit) : " It's All About The Bus"Documento31 páginasBRT (Bus Rapid Transit) : " It's All About The Bus"Junith Jay CalinawanAinda não há avaliações
- HIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of HighwaysDocumento75 páginasHIGHWAYS, Geometric Design and Components of Highwaysabubakar100% (1)
- Bus Rapid Transit System: Case Studies: at Dr. MCR HRDI, HyderabadDocumento115 páginasBus Rapid Transit System: Case Studies: at Dr. MCR HRDI, HyderabadsatishsajjaAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER ONE (Modified)Documento39 páginasCHAPTER ONE (Modified)Ephrem AbabiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Straddling BussesDocumento2 páginasStraddling BussesAndrey FoxAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - IiiDocumento56 páginasUnit - Iiisiva kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cha 5Documento6 páginasCha 5May ThansinAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluating two-lane and multi-lane highway capacityDocumento2 páginasEvaluating two-lane and multi-lane highway capacityChristopher Toff LayupanAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation Systems Evolve Over TimeDocumento5 páginasTransportation Systems Evolve Over TimeJohn Philip Neri BesedillasAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture No 3Documento85 páginasLecture No 3Arman AliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter One Introduction To Car Body: 1.1.1 Importance of Vehicle Body EngineeringDocumento18 páginasChapter One Introduction To Car Body: 1.1.1 Importance of Vehicle Body EngineeringShuguta LatiAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Buckling Analysis of Composite Beams: A Simple Intuitive FormulationDocumento13 páginasPost-Buckling Analysis of Composite Beams: A Simple Intuitive FormulationAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 3Documento13 páginasTutorial 3Kelvin ChewAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesDocumento34 páginasA Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Buckling Strength of Structural Plates: Nasa Space Vehicle Desicn CriteriaDocumento50 páginasBuckling Strength of Structural Plates: Nasa Space Vehicle Desicn CriteriaAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- H 406 4 FailureDocumento29 páginasH 406 4 FailureHemanthKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Beginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC All PDFDocumento26 páginasBeginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC All PDFName100% (1)
- Linear Buckling Analysis: Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0Documento18 páginasLinear Buckling Analysis: Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0Aghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Compression Test of Steel Columns: Experiment # 5Documento14 páginasCompression Test of Steel Columns: Experiment # 5Aghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Stability and Design Course OverviewDocumento146 páginasStructural Stability and Design Course OverviewAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Advt 135 Roas PDFDocumento1 páginaAdvt 135 Roas PDFGyan BshnAinda não há avaliações
- Aircraft GalleysDocumento4 páginasAircraft GalleysAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Failure Theories..Documento93 páginasFailure Theories..adnanmominAinda não há avaliações
- Ce 579: Structral Stability and DesignDocumento16 páginasCe 579: Structral Stability and DesignAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Invitation Letter For ALUMNIDocumento1 páginaInvitation Letter For ALUMNIAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Model 208C01 ICP® Force Sensor Installation and Operating ManualDocumento17 páginasModel 208C01 ICP® Force Sensor Installation and Operating ManualSIVARAMANJAGANATHANAinda não há avaliações
- Bolts Screws Hex Hexagon Nuts Washers Threaded Rods DIN 933 934 7989 125 127 4034 975 555 ISODocumento43 páginasBolts Screws Hex Hexagon Nuts Washers Threaded Rods DIN 933 934 7989 125 127 4034 975 555 ISOgrover_ptAinda não há avaliações
- Steel Weight Optimisation Midship Stiffner Plate ThicknessDocumento161 páginasSteel Weight Optimisation Midship Stiffner Plate ThicknessmarcoAinda não há avaliações
- Fixed End MomentsDocumento1 páginaFixed End MomentsHarold DeanAinda não há avaliações
- Design Optimization of Stiffened Composite Panels With Buckling and Damage Tolerance ConstraintsDocumento14 páginasDesign Optimization of Stiffened Composite Panels With Buckling and Damage Tolerance ConstraintslumpertAinda não há avaliações
- A DLM-Based Flutter Simulator for T-Tail Aircraft Using Modal DescramblingDocumento18 páginasA DLM-Based Flutter Simulator for T-Tail Aircraft Using Modal DescramblingAghil Buddy100% (1)
- DsaDocumento112 páginasDsadgbooklover0766571100% (3)
- Bolt DetailsDocumento1 páginaBolt DetailsAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Patran 2010 Installation and Operations GuideDocumento160 páginasPatran 2010 Installation and Operations Guidek_4_khela1354Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic Warfare Support Measure (EsmDocumento8 páginasElectronic Warfare Support Measure (EsmAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- ECCM01Documento14 páginasECCM01Aghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- ECM01ADocumento24 páginasECM01AAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- COMNAVDocumento35 páginasCOMNAVAghil BuddyAinda não há avaliações
- Detect-Engage Fire Control SolutionDocumento22 páginasDetect-Engage Fire Control SolutionAghil Buddy100% (2)
- Submarine WarfareDocumento14 páginasSubmarine WarfareAghil Buddy100% (1)
- Collins Avionics Glossary - 933Documento57 páginasCollins Avionics Glossary - 933RzVaan ArfiAinda não há avaliações
- CSCDocumento20 páginasCSCSheheryar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Letter For Parents Drum and Lyre MattersDocumento1 páginaLetter For Parents Drum and Lyre MattersRon RealinAinda não há avaliações
- Q2 M1 w1 2 Physical Education and Health 3Documento19 páginasQ2 M1 w1 2 Physical Education and Health 3Andrea Klea ReuyanAinda não há avaliações
- List of Products with PricesDocumento1 páginaList of Products with PricesPlay ProjectAinda não há avaliações
- SST PureDocumento16 páginasSST PureQasim KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Kettlebell Training 12 WeekDocumento5 páginasKettlebell Training 12 WeekRenáta Kiss100% (3)
- Desarrollo Taller JackDocumento4 páginasDesarrollo Taller JackDaniel SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Volkswagen Tiguan Allspace, La Scheda TecnicaDocumento3 páginasVolkswagen Tiguan Allspace, La Scheda TecnicaBlogo MotoriAinda não há avaliações
- Flexor Tendon Repairs Zones I III 05-13-2013Documento3 páginasFlexor Tendon Repairs Zones I III 05-13-2013Mihaela DoniciAinda não há avaliações
- CXCDÑDocumento14 páginasCXCDÑRecursos EdicionesAinda não há avaliações
- CY 6102BG - 36 型柴油机备件目录: Model Cy6102Bg-36 Diesel Engine Spare Parts CatalogueDocumento72 páginasCY 6102BG - 36 型柴油机备件目录: Model Cy6102Bg-36 Diesel Engine Spare Parts Cataloguesobirin100% (1)
- Rogue Archetype: MisdirectorDocumento2 páginasRogue Archetype: MisdirectorPip TurenAinda não há avaliações
- Mitsubishi Xpander Vehicle SpecificationsDocumento6 páginasMitsubishi Xpander Vehicle Specificationskevin_lim90Ainda não há avaliações
- Leveling Guide from 1-85 in Lineage 2 ClassicDocumento50 páginasLeveling Guide from 1-85 in Lineage 2 Classicanon_986224999Ainda não há avaliações
- Despiece Mitsubishi y KubotaDocumento4 páginasDespiece Mitsubishi y KubotaOscar MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Brian Bowen II Rico ComplaintDocumento85 páginasBrian Bowen II Rico ComplaintDarren Adam HeitnerAinda não há avaliações
- African Elephant InstructionsDocumento4 páginasAfrican Elephant Instructionsscope_inf3957Ainda não há avaliações
- 316 US Colleges With Non-Binding Early Action PlansDocumento10 páginas316 US Colleges With Non-Binding Early Action PlanspalanitAinda não há avaliações
- Cruise Control System OverviewDocumento6 páginasCruise Control System OverviewDanielAinda não há avaliações
- Chest and TricepsDocumento7 páginasChest and TricepstareqAinda não há avaliações
- Ass AsDocumento21 páginasAss AsMukesh BishtAinda não há avaliações
- MR +SAXOBEAT+-+score+harmonieDocumento4 páginasMR +SAXOBEAT+-+score+harmonieluis floresAinda não há avaliações
- Weco Pneumatic Actuator Safety AlertDocumento2 páginasWeco Pneumatic Actuator Safety AlertRafael GranadoAinda não há avaliações
- Def Tank Replacement VolvoDocumento18 páginasDef Tank Replacement VolvoHarsimranSidhu75% (4)
- Walkthrough bw2 Bag 2Documento30 páginasWalkthrough bw2 Bag 2Ahmad WariAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar and vocabulary rules for complete sentencesDocumento3 páginasGrammar and vocabulary rules for complete sentencesshiomara jhamilet0% (2)
- Dv6 FC: EURO 6 Step 1 Diesel Engine Automotive Application VersionDocumento2 páginasDv6 FC: EURO 6 Step 1 Diesel Engine Automotive Application Versionargya AwangAinda não há avaliações
- Mario Kart CheatsDocumento4 páginasMario Kart CheatsKrisAinda não há avaliações
- Mirror GuideDocumento34 páginasMirror GuideIshtaraAinda não há avaliações
- Cricket Mandi 80 - Players List - 230204 - 144111Documento5 páginasCricket Mandi 80 - Players List - 230204 - 144111Hariharan BaskharAinda não há avaliações