Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lipid Lowering Drugs
Enviado por
Tinesh RajahDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lipid Lowering Drugs
Enviado por
Tinesh RajahDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lipid Lowering Drugs
Dyslipidaemia
Primary
Common (polygenic)
Familial
Secondary
Disease
Hypothyroidism
DM
NS
CLD
Drugs
Isoretenoin
Thiazide
Alcohol
Anti psoriatic
Dyslipidaemia
Total Cholesterol (> 5.2 mmol)
TG (> 1.7 mmol)
LDL-cholesterol (> 4.2 mmol)
HDL-cholesterol (< 1.11 mmol)
Lipoproteins
Chylomicrons
Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
Low density lipoprotein (LDL)
Intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL)
High density lipoprotein (HDL)
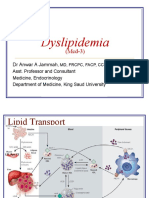
Lipoprotein metabolism
Exogenous pathways
Starts with intestinal absorption
Dietary cholesterol
Fatty acids
Endogenous pathways
Begins with synthesis of VLDL
(by liver)
Sources of Cholesterol Liver, Intestinal
Mediterranean Diet
Risk of heart disease (CHD)
Diet
High
Low Moderate
Fruits
Fish
Vegetables
Poultry
Whole grains
Dairy products
Nuts
Red meat
Seeds
Olive oil
Effects
Subsequent cardiac events
Inflammatory markers, insulin resistance
LDL oxidation
DASH Diet (Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension)
Diet
High
Moderate
Low
Fruits
Low-fat dairy products
Animal protein
Vegetables
Protein (plant source)
Legumes
Nuts
Effects
BP
LDL-cholesterol
Risk of Stroke, CHD
Lipid Lowering Drugs
HMG CoA reductase inhibitor
Fibrate
Resin
Nicotinic acid
Ezetimibe
Sites & Mechanisms Drugs for Hyperlipidaemia
Risk Factors CHD
Dyslipidaemia
Hypertension
Smoking
Treatment
Diet polymeal
Weight
Exercise
Smoking cessation
Alcohol cessation
Stress management
Lipid Lowering with Diet/ Dietary Supplements
Fish oil
Soy protein
Guggulipid
Garlic
Polyphenols
Products with trans fatty acids
Fiber
Nuts
Tea
Calcium
Lipid Lowering Drugs
HMG CoA Inhibitor (Statins)
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) ( t )
Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
Pravastatin (Pravachol)
Lovastatin (Mevacor)
Simvastatin (Zocor)
Fluvastatin (Lescol)
MOA
Competitive inhibitors of
hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase
(rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis)
Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis
( Cholesterol concentration within hepatocyte)
Homeostatic event restore intrahepatic cholesterol lvl
Production of LDL receptors
Enhanced clearance of LDL (plasma hepatocyte)
Effects
LDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol
Adverse Reactions (Common)
GIT Abdominal pain, constipation, flatulence, indigestion
Hepatic - Liver enzymes
Neurologic Headache
Musculoskeletal Myalgia, myopathy
Adverse Reactions (Serious)
Musculoskeletal Rhabdomyolysis, rupture of tendon
Avoid drugs assoc. w. rhabdomyolysis
(when taking statins)
Fibrates (esp. gemfibrazol)
Warfarin
Digoxin
Macrolide antibiotics
Niacin
Antifungals
Cyclosporine
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to atorvastatin
Liver disease (active)
Pregnancy, lactation (fetal harm)
Serum transaminases (unexplained persistent elevation)
Drug Interactions
Effect with Colestipol, Antacids
Adsorption with Cholestyramine
Level with CYP3A4 inhibitors
Amiodarone
Macrolide antibiotics
Cyclosporine
Ketoconazole
HIV protease inhibitors
Fibrates
Niacin
Grapefruit
Exchange Resin (Bile Acid Sequestrants)
Cholestyramine
Colestipol
Colesevelam (better GIT tolerability)
Exetimibe
Ezetimibe
Gemfibrozil
Bezafibrate
Ciprofibrate
Fenofibrate
Fibrate (Fibric acid derivatives)
Effects
LDL clearance from plasma (LDL receptor pathway)
LDL receptors (due to Intrahepatic cholesterol)
Interruption of enterohepatic circulation of bile acids
Conversion of cholesterol to bile acids
Intrahepatic cholesterol
Activated 2 homeostatic responses
(return intrahepatic cholesterol to normal)
LDL receptor activity
Cholesterol biosynthesis
Effects
LDL cholesterol
Inhibitor of cholesterol absorption (well tolerated)
Bind to intestinal brush border protein
(cholesterol influx transporer)
Cholesterol concentration within hepatocytes
Enhance clearance of LDL from plasma
(via LDL receptor pathway)
Pharmacokinetics
Absorbed in intestine
Peak level 12-14h
Effects
Less effective in LDL cholesterol (compared to others)
HDL cholesterol (more than statins)
Adverse Effects (Common)
GIT Abdominal discomfort, constipation, flatulence,
nausea, vomiting
Hematologic Blood coagulation disorder
(due to hypoprothrombinemia)
Adverse Effects (Common)
GIT Diarrhoea
Musculoskeletal Arthralgia, Myalgia
Respiratory Nasopharyngitis, Sinusitis, URTI
Adverse Effects (Serious)
Hepatic Hepatitis, LFT
Immunology Anaphylaxis
Musculoskeletal Disorder of muscle, Rhabdomyolysis
Adverse Effects (Common)
Dermatologic Rash
GIT Abdominal pain, Diarrhoea, Flatulence, Indigestion,
Xerostomia
Musculoskeletal Myalgia
Adverse Effects (Serious)
Hepatic LFT abnormal
Musculoskelatal Rhabdomyolysis
(esp. coadministered with statin)
Contraindications
Complete biliary obstruction
Hyperlipidaemia (ypes III, IV, V)
Hypersensitivity to bile-sequestering resins
Contraindications
Concomitant use with statin in
Pregnant, nursing mothers
Active liver disease
Unexplained persistent hepatic transaminase
Hypersensitivity to ezetimibe
Precautions (Use not recommended)
Use with fibrates (other than fenofibrate)
Hepatic impairment (moderate severe)
Myopathy (inc. rhabdomyolysis)
Contraindications
Concomitant gemfibrozil, cerivastatin
Preexisting gallbladder disease
Hepatic dysfunction (inc. primary biliary cirrhosis)
Hypersensitivity to gemfibrozil
Severe renal impairment
Precautions
Cholelithiasis
Concomitant use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statin)
(risk for rhabdomyolysis)
Type IIa Hyperlipidaemia (not recommended)( LDL)
Precautions
Bleeding tendency
(due to hypoprothrombinemia Vitamin K deficiency)
Interfere fat absorption ( Vitamin A,D, E, K)
Pre-existing constipation
Absorption of other drugs
Other Lipid Lowering Drugs
Nicotinic acid group (nicotinic acid, acipimox)
Fish oils (omega-3 marine triglycerides)
Soluble fibre (ispaghula husk)
Nicotinic acid (Vitamin B3) (Niacin)
MOA
Do not involve LDL receptor pathway
Binds to a G-protein-coupled receptor in adipocytes
cAMP levels
Hormone-sensitive lipase in adipocytes
( Delivery of fatty acids to liver)
( Hepatic synthesis, secretion of VLDL)
(Hormone-sensitive lipase = enzyme for hydrolysis of TG in adipose tissue)
Effects
LDL
VLDL
Remnants of VLDL
Lipoprotein (a)
HDL (most effective available drug)
Contraindications
Active liver disease
Active peptic ulcer disease
Hypersensitivity to Niacin
Adverse Effects
Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
Restlessness
Flushing, warmth sensation in face, neck, ears
Headache
Hypotension
Rash, tingling, itching, dry skin
Combination Therapy
No more effective than -dose statin monotherapy
Severe Hypercholesterolemia
Combination regimen for intensive of LDL level
Drugs must individually LDL
Must do so by different MOA
Bad HDL-cholesterol Responders
HDL-cholesterol (< 1.0 mmol/L or 30 mg/dL) during treatment
(despite higher HDL-cholesterol before treatment)
Bad HDL-cholesterol responders
Statins (higher)
Fibrates
Treatment for HDL-cholesterol levels
Maximize life habit changes
Cigarette smoking
Obesity
Physical inactivity
Favour fibrates over statins (patients with CHD, HDL-cholesterol)
Combine statins with fibrate/ nicotinic acid/ ezetimibe
(for risk patients with isolated HDL-cholesterol levels)
Drug Therapy for Dyslipidaemia
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- LipidsDocumento40 páginasLipidsKlimpoy WatashiewaAinda não há avaliações
- Atvbaha 114 305048Documento9 páginasAtvbaha 114 305048Sammy OhAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Notes For The MRCP 3rd PDFDocumento613 páginasEssential Notes For The MRCP 3rd PDFnayhtun2471100% (1)
- Biochemistry MCQ IIDocumento18 páginasBiochemistry MCQ IISidharta Chatterjee100% (2)
- Chemistry of Lipids-LECTUREDocumento88 páginasChemistry of Lipids-LECTUREKesha Marie TalloAinda não há avaliações
- Canine HyperlipidaemiaDocumento11 páginasCanine Hyperlipidaemiaheidy acostaAinda não há avaliações
- LipidDocumento31 páginasLipidahmed abd elazizAinda não há avaliações
- Lipid Profile: Dr. MD Razib HasanDocumento26 páginasLipid Profile: Dr. MD Razib HasanRazib HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Insert TRIGL 0020767107322COIN V11 en PDFDocumento4 páginasInsert TRIGL 0020767107322COIN V11 en PDFtechlabAinda não há avaliações
- NDT ReviewerDocumento111 páginasNDT ReviewerMay RodeoAinda não há avaliações
- Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento11 páginasLipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesLarry411100% (1)
- ABX Pentra Triglycerides CPDocumento4 páginasABX Pentra Triglycerides CPAstri AmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Is Darkfield Microscopic Examination of Fresh Capillary Blood A VDocumento137 páginasIs Darkfield Microscopic Examination of Fresh Capillary Blood A Vwtemple100% (3)
- Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyDocumento8 páginasDyslipidemia Dyslipidemia: PathophysiologyNur HaidagAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperlipidemia 1Documento54 páginasHyperlipidemia 1MarrkAinda não há avaliações
- A Lipid EmulsionDocumento9 páginasA Lipid Emulsionrahul2kAinda não há avaliações
- LIPIDS D PharmDocumento65 páginasLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarAinda não há avaliações
- Magazine: The LiverDocumento5 páginasMagazine: The LiverMariskaAinda não há avaliações
- Geria UNIT 3Documento5 páginasGeria UNIT 3Raiden VizcondeAinda não há avaliações
- A Retrospective Analysis of Lipid Laden Aqueous Humor in Dogs - 2019Documento9 páginasA Retrospective Analysis of Lipid Laden Aqueous Humor in Dogs - 2019Paula d'Avila C. CavalcantiAinda não há avaliações
- Mock Test Biochemapril 2016 DoneDocumento8 páginasMock Test Biochemapril 2016 DoneLamy SAinda não há avaliações
- Aerva Lanata A Review On Phytochemistry and PharmacologicalDocumento5 páginasAerva Lanata A Review On Phytochemistry and Pharmacologicalzan_anwarAinda não há avaliações
- Journal of EthnopharmacologyDocumento5 páginasJournal of Ethnopharmacologyluthfiyah putriAinda não há avaliações
- Efeitos Metab Licos Do Jejum Intermitente PDFDocumento197 páginasEfeitos Metab Licos Do Jejum Intermitente PDFLarisa JanušićAinda não há avaliações
- LDL and HDL Cholesterol: "Bad" and "Good" Cholesterol: Lowering Your RiskDocumento3 páginasLDL and HDL Cholesterol: "Bad" and "Good" Cholesterol: Lowering Your Risknidia rahmaAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem - LipidsDocumento21 páginasBiochem - Lipids813 cafeAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology MCQDocumento42 páginasPathology MCQJim Jose Antony100% (17)
- Nejmoa2309822 AppendixDocumento20 páginasNejmoa2309822 Appendixtristan_raoultAinda não há avaliações
- DR ReddyDocumento159 páginasDR ReddyIssa AvenaAinda não há avaliações
- RPA171824662021Documento12 páginasRPA171824662021manimeczAinda não há avaliações