Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Physic Homework 13
Enviado por
Miftah ShidqiDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Physic Homework 13
Enviado por
Miftah ShidqiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
PHYSIC HOMEWORK 13
PR 13. Optik Geometri (Pembentukan Bayangan)
Kerjakan soal di Halliday:
Bab 34 no 1, 7, 16, 24, 40, 41, 47, 52, 60, 70, 82, 90.
1) You look through a camera toward an image of a humming-bird in
a plane mirror. The camera is 4.30 m in front of the mirror. The bird is
at camera level, 5.00 m to your right and 3.30 m from the mirror. What is
the distance between the camera and the apparent position of the
bird's image in the mirror?
d=
(d + d ) + (d )
2
( 4,30 m+ 3,30 m) +( 5,00 m )
82,76 m2
= 9,097
9,10 m
7.) A concave shaving mirror has a radius of curvature of 35.0 cm. It is
positioned so that the (upright) image of a man's face is 2.50 times the
size of the face. How far is the mirror from the face?
1
1
p pm =
p =
r
1
(1
2
m )=
1
f =
35,0 cm
2
2
r
1
(1 2,50 = 10,5 cm
16) Diketahui: p=+17
Miror Convex, 14
Ditanya:a. r=?
b. i=?
c. m=?
e.I/NI=?
d. Real/Virtual=? f. Letak Bayangan=?
Jawab:
a. Fokus = -14; p= +17
Radius mirror= r=2f= 2 -14= -28 cm
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
b. i= pf/(p f) = (17)(-14) /(17+14)=
7,67 cm
7,7
cm
c. m=-i/p = 7,7/17= +0,45
d. Selama jarak negatif, maka bayangan akan selalu virtual (V)
e. Perbesaran yang dihasilkan kaca positif berarti tegak keatas
(NI/Not Inverted / Tidak dibalik)
f. Bayangan akan terbentuk disisi berlawanan object dengan kaca
24) Diketahui: p=+60
M= - 0,50
Ditanya:
Bayangan=?
a. Tipe kaca=?
b. Fokus=?
c. Radius =?
d. i=?
g.
Letak
e. Real/Virtual=?
f. I/NI=?
Jawab:
a. M= -0,5<0 maka bayangan akan terbalik,
Kaca
cekung
memiliki
hasil
bayangan
dibalik
maka
kemungkinan kaca pada soal ini
adalah Kaca Cekung
b. i= pf/(p f); i= 30cm (dari jawaban c)
f= ip/(p+i)= (30)(+60)/(60+30) =+20 cm
c. r= 2f = +40 cm
d. m=i/p; i=mp = +(60)(0,5)= 30 cm
e. Selama i>0, bayangan akan real/ nyata(R)
f. Pada jawaban a sudah dibahas bahwa bayangan akan terbalik
karena m<0 (I/Inverted)
g. Bayangan real akan berada disisi yang sama dengan benda
40) A glass sphere has radius R = 5.0 cm and index of refraction 1.6. A
paperweight is constructed by slicing through the sphere along a
plane that is 2.0 cm from the center of the sphere, leaving height p =
3.0 cm. The paperweight is placed on a table and viewed from
directly above by an observer who is distance d = 8.0 cm from the
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
tabletop. When viewed through the paperweight, how far
away does the tabletop appear to be to the observer?
n1=1,6; n2=1
1,6 1
+
p i =
11,6
r
1,6 1
+
3,0 i =
11,6
5,0
1
i =
0,6
5,0
1,6
3,0
i= -2,4 cm
Jadi yang diliat oleh observator jarak meja dengan dirinya menjadi =
|r|+|i| = 5,4 cm
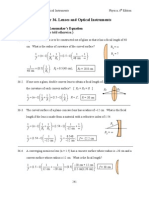
41)A lens is made of glass having an index of refraction of 1.5. One
side of the lens is fiat, and the other is convex with a radius of curvature
of 20 cm. (a) Find the focal length of the lens. (b) If an object is placed
40 cm in front of the lens, where is the image?
a. Fokus lensa
f=
[ ( )]
1 1
( n1 )
r1 r2
1
1
(1,51 )
20
)]
= +40cm
b. Bayangan benda
i=
[( ) ]
1 1
f p
1 1
f p
1
1
40 cm 40 cm
47) A double-convex lens is to be made of glass with an index of
refraction of 1.5. One surface is to have twice the radius of curvature of
the other and the focal length is to be 60 mm. What is the (a) smaller 6
and (b) larger radius?
a)
1
1 1
=( n1 )
f
r1 r2
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
( n1 )
( r1 + 21r )
1
3 ( n1 )
2 r1
r 1=
3 f ( n1 )
2
3 (60)( 1,51 )
2
45 mm
b)
|r 2|=|2r 1|
2 ( 45 )
90 mm
52) Thin lenses. Object 0 stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric
lens. For this situation, gives object distance p (centimeters), the type of
lens (C stands for converging and D for diverging), and then the distance
(centimeters, without proper sign) between a focal point and the lens
(P=+25, Lens C,35). Find (a) the image distance i and (b) the lateral
magnification m of the object, including signs. Also, determine whether
the image is (c) real (R) or virtual (V), (d) inverted (I) from object 0 or
noninverted (NI), and (e) on the same side of the lens as object 0 or on
the opposite side.
a)
1 1 1
= +
f p i
1 1
1
=
i 35 25
2
175
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
i=87,5 cm
i
b) m= p
87.5
25
3,5
c) karena i nya negative maka bayangan virtual (maya)
d) karena nilai m positif maka bayangan not inverted (tidak terbalik)
e) bayangan di sisi yang sama dengan benda
60) Lenses with given radii. Object o stands in front of a thin lens, on the
central axis. For this situation, gives object distance p, index of refraction
n of the lens, radius 1'1 of the nearer lens surface, and radius 1'2 of the
farther lens surface (P=+6; n=1.70; r 1=+10; r2= -12). (All distances are in
centimeters.) Find (a) the image distance i and (b) the lateral
magnification m of the object, including signs. Also, determine whether
the image is (c) real (R) or virtual (V), (d) inverted (I) from object 0 or
noninverted (NI), and (e) on the same side of the lens as object 0 or on
the opposite side.
1 1 1
a) f = p + i
1
1 1
1
=( n1 ) ( )
i
r1 r 2 6
( 1,71 ) (
1
1
1
)
10 12 6
1 77 1
=
i 600 6
23
600
i=26,087 cm
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
i
b) m= p
26,087
6
4,348
c) karena i nya negative maka bayangan virtual (maya)
d) karena nilai m positif maka bayangan not inverted (tidak terbalik)
e) bayangan di sisi yang sama dengan benda
70) More lenses. Object 0 stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric
lens. Refers to (a) the lens type, converging (C) or diverging (D), (b) the
focal distance t, (c) the object distance P, (d) the image distance i, and (e)
the lateral magnification m (f=20; p=+8; m<1; I/NI= NI). (All distances
are in centimeters.) It also refers to whether (f) the image is real (R) or
virtual (V), (g) inverted (I) or noninverted (NI) from 0, and (h) on the same
side of the lens as 0 or on the opposite side. Fill in the missing
information, including the value of m when only an inequality is given.
Where only a sign is missing, answer with the sign.
a) karena m<1 dan bayangan tidak terbalik, berarti lensa yang dipakai
tidak diverging(menyebar)
b) karena lensa diverging(menyebar) maka f nya minus = -20cm
c) p=8 cm
d)
1 1 1
= +
f p i
1 1 1
=
i 20 8
7
40
i=5,714 cm
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
i
e) m= p
5,714
8
0,714
f) karena i nya negative maka bayangan virtual (maya)
g) karena nilai m positif maka bayangan not inverted (tidak terbalik)
h) bayangan di sisi yang sama dengan benda
82) Two-lens systems. In picture, stick figure 0 (the object) stands on the
common central axis of two thin, symmetric lenses, which are mounted in
the boxed regions. Lens 1 is mounted within the boxed region closer to 0,
which is at object distance Pl' Lens 2 is mounted within the farther boxed
region, at distance d. Refers to a different combination of lens and
different values for distances (p1=+8; lensa 1=D,6; d=12; lensa 2=C,6),
which are given in centimeters. The type of lens is indicated by C for
converging and D for diverging; the number after C or D is the distance
between a lens and either of its focal points (the proper sign of the focal
distance is not indicated). Find (a) the image distance i2 for the image
produced by lens 2 (the final image produced by the system) and (b) the
overallia teral magnification M for the system, including signs. Also,
determine whether the final image is (c) real (R) or virtual (V), (d) inverted
(I) from object 0 or noninverted (NI), and (e) on the same side of lens 2 as
object 0 or on the opposite side.
a) f1 karena divergen adalah =-6 cm
maka
1 1 1
= +
f 1 p1 i 1
1 1 1
=
i1 6 8
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
7
24
i 1=3,428 cm
f2 karena convergen adalah=6 cm, dengan
p2=d i1
123,428
8,572 cm
1 1 1
= +
f 2 p 2 i2
1 1
1
=
i 2 6 8,572
643
12858
i 2=19,997 cm
b)
M =m 1 m2
i1 i 2
(
)
p1 p 2
3,428(19,997)
8 (8,572)
1
c) karena i nya positif maka bayangan real (nyata)
d) karena nilai m negatif maka bayangan inverted (terbalik)
e) bayangan di sisi yang berseberangan dengan benda (dari lensa 2)
Petra Elang Pradana
1106023096
90) In picture shows the basic
structure of a camera. A lens can be
moved forward or back to produce an
image on film at the back of the
camera. For a certain camera, with
the distance i between the lens and
the film set at f = 5.0 cm, parallel
light rays from a very distant object 0 converge to a point image on the
film, as shown. The object is now brought closer, to a distance of p = 100
cm, and the lens-film distance is adjusted so that an inverted real image
forms on the film (Fig. b). (a) What is the lens-film distance i now? (b) By
how much was distance i changed?
a)
1 1 1
=
i f p
1
1
=5,35
5 100
19
i=5,263 cm=0,3 cm
100
b)
i=if
Você também pode gostar
- TUTO 1 Geometrical OpticsDocumento10 páginasTUTO 1 Geometrical OpticsTuyenITAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 34, Example Problems: (34.14) Spherical Concave Mirror, With - R - 32.0 CM, Gives F +16.0 CM (+ Sign BecauseDocumento5 páginasChapter 34, Example Problems: (34.14) Spherical Concave Mirror, With - R - 32.0 CM, Gives F +16.0 CM (+ Sign Becausechamp delacruzAinda não há avaliações
- Geometrical OpticsDocumento35 páginasGeometrical Opticsthinkiit90% (10)
- Reflection QuestionsDocumento13 páginasReflection QuestionsSaransh Goyal100% (1)
- Self Evalution Test-OpticsDocumento5 páginasSelf Evalution Test-OpticsBHAAJI0001Ainda não há avaliações
- Geometrical OpticsDocumento12 páginasGeometrical OpticsApex Institute100% (1)
- NCERT-Ray Optics-Plane and Spherica Mirror-DPP-01Documento3 páginasNCERT-Ray Optics-Plane and Spherica Mirror-DPP-01potatoadityaAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions 17Documento7 páginasSolutions 17Patrick GareauAinda não há avaliações
- Geometrical Optics 1Documento10 páginasGeometrical Optics 1S Prasad Shiva PulagamAinda não há avaliações
- Light and Sound Worksheet With Solutions AnswersDocumento8 páginasLight and Sound Worksheet With Solutions AnswersKANCHAN KONDEKARAinda não há avaliações
- Refraction QuestionsDocumento18 páginasRefraction QuestionsSaransh Goyal100% (2)
- OPTICSDocumento5 páginasOPTICSNandan vadiAinda não há avaliações
- Cwps-Refraction at Spherical Surfaces & Lenses - SolutionsDocumento12 páginasCwps-Refraction at Spherical Surfaces & Lenses - Solutionsthalassophobic11Ainda não há avaliações
- Anschp 36Documento13 páginasAnschp 36pashelo00188% (17)
- Light QUESTIONSDocumento5 páginasLight QUESTIONSKANCHAN KONDEKARAinda não há avaliações
- Geometrical OpticsDocumento76 páginasGeometrical OpticsnehnegAinda não há avaliações
- 12 OpticsDocumento46 páginas12 OpticsSivakumar SarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Kvpy OpticsDocumento17 páginasKvpy OpticsAlokShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Geometric OpticDocumento8 páginasGeometric OpticSharonAinda não há avaliações
- Geometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersDocumento6 páginasGeometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersHarsh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Optics & Modern Physics: Solutions ofDocumento19 páginasOptics & Modern Physics: Solutions ofAshutosh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Optics Critical ThinkingDocumento9 páginasRay Optics Critical Thinkingvishal_kalraAinda não há avaliações
- Optics & Wave MechanicsDocumento95 páginasOptics & Wave MechanicsxanshahAinda não há avaliações
- NEET Ray Optics Important Questions - Free PDF DownloadDocumento28 páginasNEET Ray Optics Important Questions - Free PDF DownloadkavithavenkatesanAinda não há avaliações
- Optics and Modern Physics: Section A: Straight Objective TypeDocumento23 páginasOptics and Modern Physics: Section A: Straight Objective TypeAnkit RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Manual Experiments SECTION B EXPERIMENTS 2022-23Documento9 páginasPhysics Lab Manual Experiments SECTION B EXPERIMENTS 2022-23Dhairya PrabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Test Optics 1Documento4 páginasTest Optics 1Anant KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Sarthak Classes, Part Test-1, Optics, Seniors, PhyDocumento4 páginasSarthak Classes, Part Test-1, Optics, Seniors, PhySanthosh Siva KumarAinda não há avaliações
- EPH105C Questions +SOlutions - Optics - 2023Documento8 páginasEPH105C Questions +SOlutions - Optics - 2023Charity ChazAinda não há avaliações
- JEE Main Ray Optics Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocumento7 páginasJEE Main Ray Optics Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFJanakiraman SanthoshAinda não há avaliações
- Wave and Ray Optics Test Answer KeyDocumento27 páginasWave and Ray Optics Test Answer KeynithishmjmmAinda não há avaliações
- Optics 10Documento24 páginasOptics 10Uday Prakash SahuAinda não há avaliações
- JEE Main Previous Year Solved Questions On Ray OpticsDocumento5 páginasJEE Main Previous Year Solved Questions On Ray OpticsVPNAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment-4 With solution-EP-IIDocumento10 páginasAssignment-4 With solution-EP-IIadimeghaAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Documento9 páginasCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Krupa Mariam BijuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 34. Reflection and MirrorsDocumento14 páginasChapter 34. Reflection and MirrorsEmanuel GonzálezAinda não há avaliações
- Curved SurfaceDocumento6 páginasCurved SurfaceveebaAinda não há avaliações
- Exam1 Solutions 1Documento14 páginasExam1 Solutions 1Sai PragathiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics (E) 2024Documento54 páginasPhysics (E) 2024Dev RajAinda não há avaliações
- Physic Calculation: Amilia Lee Fang Zi - 5BDocumento88 páginasPhysic Calculation: Amilia Lee Fang Zi - 5BCapricornzzAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCDocumento59 páginas2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCazamchishty796Ainda não há avaliações
- Solucionario Capitulo 25 Física Serway and FaughnDocumento15 páginasSolucionario Capitulo 25 Física Serway and FaughnRafael Colindres0% (1)
- PhysDocumento41 páginasPhysAna PerezAinda não há avaliações
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Documento4 páginasDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingAinda não há avaliações
- Interference PatternsDocumento8 páginasInterference PatternsAsa mathewAinda não há avaliações
- Solucionario Capitulo 23 Física Serway and FaughnDocumento15 páginasSolucionario Capitulo 23 Física Serway and FaughnRafael ColindresAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Documento7 páginasCBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)kumarisimon2Ainda não há avaliações
- Light (HOT) PDFDocumento7 páginasLight (HOT) PDFEOTVAinda não há avaliações
- Physics: PpendicesDocumento27 páginasPhysics: PpendiceskankirajeshAinda não há avaliações
- (7028) Sheet 1 Geometrical Optics BDocumento83 páginas(7028) Sheet 1 Geometrical Optics BmanishAinda não há avaliações
- LB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIDocumento37 páginasLB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIMahesh YogamAinda não há avaliações
- Stat & Prob - OKDocumento96 páginasStat & Prob - OKMiftah ShidqiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Homework 10Documento6 páginasPhysics Homework 10Miftah ShidqiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Homework 11Documento8 páginasPhysics Homework 11Miftah ShidqiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Homework 10Documento6 páginasPhysics Homework 10Miftah ShidqiAinda não há avaliações
- GHZ-THZ Electronics: By-Pranav Yadav 1509131072 (Ec-Ii, Vi Sem)Documento20 páginasGHZ-THZ Electronics: By-Pranav Yadav 1509131072 (Ec-Ii, Vi Sem)PranavAinda não há avaliações
- LEExposure 07 SpreadsDocumento38 páginasLEExposure 07 SpreadsAlejandro Contreras100% (1)
- RiprocDocumento1 páginaRiprocChemGuyAinda não há avaliações
- Galen Rowell Camera BagDocumento3 páginasGalen Rowell Camera BagbhaumiksauravAinda não há avaliações
- Slits CanDocumento3 páginasSlits CanSteo0315Ainda não há avaliações
- Canon Autozoom 1014 BrochureDocumento4 páginasCanon Autozoom 1014 BrochureBolek827Ainda não há avaliações
- Sylvania BKD Dual BeamKat HID Floodlight Spec Sheet 1-87Documento4 páginasSylvania BKD Dual BeamKat HID Floodlight Spec Sheet 1-87Alan MastersAinda não há avaliações
- Fluent HeatTransfer WS05a Headlamp DODocumento43 páginasFluent HeatTransfer WS05a Headlamp DOAbhishek yadavAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Analysis Using ATR-FTIRDocumento6 páginasQuantitative Analysis Using ATR-FTIRribotsAinda não há avaliações
- Near-Infrared II Plasmonic Porous Cubic Nanoshells For in Vivo Noninvasive SERS Visualization of Sub-Millimeter MicrotumorsDocumento11 páginasNear-Infrared II Plasmonic Porous Cubic Nanoshells For in Vivo Noninvasive SERS Visualization of Sub-Millimeter MicrotumorsdfdffAinda não há avaliações
- Investigating Astronomy 2nd Edition Slater Solutions ManualDocumento25 páginasInvestigating Astronomy 2nd Edition Slater Solutions ManualCarolynFritzskwp100% (50)
- BTP Report PDFDocumento18 páginasBTP Report PDFAbhishekk lalnaikkAinda não há avaliações
- E AllDocumento104 páginasE AllCHRISTIANAinda não há avaliações
- Catálogo Solaris 2018Documento34 páginasCatálogo Solaris 2018JoseZamoraAinda não há avaliações
- Gea32131 mv1q Borescope Adapter r3Documento2 páginasGea32131 mv1q Borescope Adapter r3Maximiliano Ezequiel LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Uno Minda Pricelist All SegmentsDocumento460 páginasUno Minda Pricelist All SegmentsSunesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 40 ProblemsDocumento11 páginasChapter 40 ProblemsVeera Manoharan RAinda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Second Periodical TestDocumento6 páginasScience 10 Second Periodical TestMarl Rina EsperanzaAinda não há avaliações
- AJB 30203: Radar Principles: Assoc. Prof. Ts. Dr. Harlisya Harun Harlisya@unikl - Edu.myDocumento39 páginasAJB 30203: Radar Principles: Assoc. Prof. Ts. Dr. Harlisya Harun Harlisya@unikl - Edu.myMuhammad HaziqAinda não há avaliações
- DC30-091 DRX-Ascend System Operator Manual - MDocumento66 páginasDC30-091 DRX-Ascend System Operator Manual - MRaquel BedoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsDocumento16 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Communication SystemsMelz WiggieAinda não há avaliações
- Pinhole Camera 10 Common ProblemsDocumento1 páginaPinhole Camera 10 Common Problemsapi-235556762Ainda não há avaliações
- Dual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDocumento64 páginasDual Nature of Radiation: in 1 ShotDisney DoreamonAinda não há avaliações
- Structure of AtomDocumento20 páginasStructure of AtomSachin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Atoms in Electromagnetic Fields 2ndDocumento769 páginasAtoms in Electromagnetic Fields 2ndDewald MurrayAinda não há avaliações
- CH 111 Tutorial 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasCH 111 Tutorial 1 PDFShandrah KeiAinda não há avaliações
- Mandatory Appendix V - Asme VDocumento2 páginasMandatory Appendix V - Asme VAngelTinocoAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteria MorphologyDocumento6 páginasBacteria MorphologyMae Lislie Canonigo - FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Foucault's Method in New Settings: September 2014Documento10 páginasFoucault's Method in New Settings: September 2014anie bragaAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection RefractionDocumento17 páginasReflection RefractionDhira GunawanAinda não há avaliações