Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Exam of Applied Mechanics
Enviado por
putex247Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Exam of Applied Mechanics
Enviado por
putex247Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Set No.
Code No: RR10105
I B.Tech Semester Supplimentary Examinations, June 2009
APPLIED MECHANICS
(Civil Engineering)
Time: 3 hours
Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Explain various force systems with neat sketches.
(b) A roller of radius r = 0.3 m and weight Q = 2000 N is to be pulled over a
curb of height h = 0.15 m.by a horizontal force P applied to the end of a
string woundaround the circumference of the roller. Find the magnitude of P
required to start the roller over the curb.
[6+10]
{As shown in the Figure1b}
Figure 1b
2. The three flat blocks are positioned on the 300 incline as shown in Figure2, and
a force P parallel to the incline is applied to the middle block. The upper block
is prevented from moving by a wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The
coefficient of static friction for each of the three pairs of mating surfaces is shown.
Determine the maximum value which P may have before any slipping takes place.
[16]
Figure 2
3. A cross belt drive is to transmit 7.5 KW at 1000 r.p.m of the smaller pulley.
The diameter of the smallest pulley is 250mm and velocity ratio is 2. The centre
distance between the pulley is 1250mm. A flat belt of thickness 6 mm and of
coefficient friction 0.3 is used over the pulleys. Determine the necessary width of
1 of 3
Set No. 1
Code No: RR10105
the belt if the maximum allowable stress in the belt is 1.75N/mm2 and density of
the belt is 1000Kg/m3 .
[16]
4. (a) Locate the centroid of given parabola bounded by x- axis the line x = a.
{As shown in the Figure 4a}
Figure 4a
(b) Locate the centroid of the wire bent as shown in figure 4b.
[8+8]
Figure 4b
5. (a) Prove that the mass moment of inertia of a right circular cone of base radius
R and height h, with respect to a diameter of the base is M (3R2 + 2h2 )/20
where M is the mass of the cone.
(b) Calculate the mass moment of inertia of a circular cone of base radius 300mm
and height 600mm about a line which passes through the mass centre of the
cone and which is parallel to the base of the cone. The mass density of the
cone is 2500 kg/m3 .
[8+8]
6. (a) A car starts from the rest on a straight road and travels with uniform acceleration of 0.8m/s2 for the first 10sec and then travels with uniform velocity for
the next 30 sec. It then decelerates at the rate of 0.5m/s2 and comes to rest.
Determine
i. Total time taken to complete the trip
ii. Total distance travelled
(b) A fighter plane is directly over an antiaircraft gun at time t=0 and at an
altitude of 1800m. The plane is moving with a speed of 600 km/hour. A shell
2 of 3
Set No. 1
Code No: RR10105
is fired at time t=0 in an attempt to hit the plane. If the muzzle velocity is
1000m/sec, find out the angle at which the gun should be held.
[8+8]
7. (a) A body weighing 20 N is projected up a 200 inclined plane with a velocity of
12 m/s, coefficient of friction is 0.15. Find
i. The maximum distance S, that the body will move up the inclined plane
ii. Velocity of the body when it returns to ist original position.
(b) Find the acceleration of the moving loads as shown in figure 7b. Take mass
of P=120 kg and that of Q=80 Kg and coefficient of friction between surfaces
of contact is 0.3 .Also find the tension in the connecting string.
[8+8]
Figure 7b
8. A clock with a seconds pendulum is running correct time at a place where the
acceleration due to gravity is 9.81m/s2 . Find the length of the pendulum. This
clock is taken at a place where the acceleration due to gravity is 9.80m/s2 . Find
how much the clock will loose or gain in a day at this place?
[16]
3 of 3
Set No. 2
Code No: RR10105
I B.Tech Semester Supplimentary Examinations, June 2009
APPLIED MECHANICS
(Civil Engineering)
Time: 3 hours
Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. Determine the tensions in wires AB, AC and AD,{As shown in Figure 1}.
[16]
Figure 1
2. (a) Explain the types of friction with examples.
(b) Two equal bodies A and B of weight W each are placed on a rough inclined
plane. The bodies are connected by a light string. If A = 1/2 and B = 1/3,
show that the bodies will be both on the point of motion when the plane is
inclined at tan1 (5/12).
[6+10]
3. (a) Distinguish between initial tension and centrifugal tension in a belt.
(b) An open belt of width 80 mm connects a pulley of diameter 600 mm on the
secondary shaft to a pulley of diameter 400 mm on the machine shaft. The
shafts are three meters apart. The secondary shaft has a speed of 100 r.p.m.
Find the maximum permissible stress in the belt if the safe working tension is
15 N/mm width and = 0.3.
[6+10]
4. (a) State and prove parallel axis theorem.
(b) Find the centroid of the shaded lamina shown in Figure4b.
Figure 4b
1 of 3
[6+10]
Set No. 2
Code No: RR10105
5. The area shown in figure5 is revolved about x axis to form a homogeneous solid of
revolution of mass m. Determine the mass moment of inertia of the solid about
x-axis.
[16]
Figure 5
6. A ladder AB of 3m length remains in contact with the vertical wall and horizontal
floor and the angle of inclination of the ladder with horizontal is 600 . The ladder
moves such that its ends remain in contact with the vertical wall at B and horizontal
floor at A. If the end A moves with a linear velocity of 0.1m/s, find the velocity
of its upper end B. If the linear acceleration of the end A is 0.05m/s2 , find the
acceleration of the end B and the resultant acceleration of the ladder AB.
[16]
7. (a) A homogeneous solid cylinder of weight 100 N whose axis is horizontal rotates
about its axis, in frictionless bearings under the action of the weight of a 10N
block which is carried by a rope wrapped around the cylinder. What will be
angular velocity of cylinder two seconds after the motion starts? Assume the
diameter of cylinder as 100cm.
(b) A block of mass 5Kg resting on a 300 inclined plane is released. The block after
travelling a distance of 0.5m along the inclined plane hits a spring of stiffness
15N/cm. Find the maximum compression of spring. Assume coefficient of
friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.2. As shown in the
Figure 7b.
[8+8]
Figure 7b
8. A small ball of weight W is attached to the middle of a tightly stretched perfectly
flexible wire AB of length 2l, connected between two horizontal rigid surfaces.
2 of 3
Set No. 2
Code No: RR10105
(arrangement is vertical). Prove that for small lateral displacements and high initial
tension in the wire, the ball will have a simple harmonic motion, and calculate the
period.
[16]
3 of 3
Set No. 3
Code No: RR10105
I B.Tech Semester Supplimentary Examinations, June 2009
APPLIED MECHANICS
(Civil Engineering)
Time: 3 hours
Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
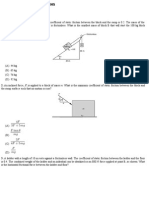
1. (a) A ball of weight Q = 12 N rests in a right-angled trough, as shown in figure1a.
Determine the forces exerted on the sides of the trough at D and E if all
surfaces are perfectly smooth.
Figure 1a
(b) A pulley A is supported by two bars AB and AC which are hinged at points
B and C to a vertical mast EF. Over the pulley hangs a flexible cable DG
which is fastened to the mast at D and carries at the other end G a load Q =
20 KN. Neglecting friction in the pulley, determine the forces produced in the
bars AB and AC. The angles between the various members are shown in the
figure1b.
[6+10]
Figure 1b
2. The three flat blocks are positioned on the 300 incline as shown in Figure2, and
a force P parallel to the incline is applied to the middle block. The upper block
is prevented from moving by a wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The
coefficient of static friction for each of the three pairs of mating surfaces is shown.
Determine the maximum value which P may have before any slipping takes place.
[16]
1 of 3
Set No. 3
Code No: RR10105
Figure 2
3. An open belt drive connects two pulleys 1200mm and 500mm diameter on parallel
shafts 4000mm apart. The belt weigh 9N/m length and maximum tension in it is
not to exceed 2000N. The coefficient of friction is 0.3. The 1200mm pulley, which is
the driver runs at 200r.p.m Due to belt slip on one of the pulleys, the velocity of the
driven shafts is only 450 r.p.m Calculate the torque on each of the two shafts, the
power transmitted and power lost in friction. What is the efficiency of the drive.
[16]
4. Determine the moment of inertia of a triangle about x x axis as shown in figure
4.
[16]
Figure 4
5. A cylinder of diameter 400mm and height 1000mm rests vertically. Over this, a
cone of base diameter 400mm and height 500mm is placed such that the axis of the
cone coincides with the axis of the cylinder. Find out the mass moment of inertia
of this composite solid about a line which passes through the vertex of the cone
and which is parallel to the base of the cylinder if the mass density is 4000kg/m3 .
[16]
6. (a) A train is traveling at a speed of 60 km/hr. It has to slow down due to certain
repair work on the track. Hence, it moves with a constant retardation of 1
km/hrper second until its speed is reduced to 15 km/hr. It then travels at
a constant speed of for 0.25 km/hr and accelerates at 0.5 km/hr per second
until its speed once more reaches 60 km/hr. Find the delay caused.
(b) The motion of a particle in rectilinear motion is defined by the relation
s = 2t3 9t2 + 12t 10 where s is expressed in metres and t in seconds. Find
i. the acceleration of the particle when the velocity is zero
2 of 3
Set No. 3
Code No: RR10105
ii. the position and the total distance traveled when the acceleration is zero.
[8+8]
7. (a) A homogeneous sphere of radius of a=100 mm and weight W=100 N can
rotate freely about a diameter. If it starts from rest and gains, with constant
angular acceleration, an angular speed n=180rpm, in 12 revolutions, find the
acting moment. .
(b) A block starts from rest fromA. If the coefficient of friction between all surfaces of contact is 0.3, find the distance at which the block stop on the horizontal plane. Assume the magnitude of velocity at the end of slope is same as
that at the beginning of the horizontal plane.
As shown in the Figure7b.
[8+8]
Figure 7b
8. A gun is so designed that on firing, the barrel recoils against a spring. A dashpot,
at the end of the recoil, allows the barrel to come back to its initial position within
the minimum time without any oscillation. A gun barrel has a mass of 500kg and
a recoil spring of 300 N/mm. The barrel recoils 1m on firing. Determine
(a) the initial recoil velocity of the gun barrel and
(b) the critical damping coefficient of the dashpot engaged at the end of the recoil
strike.
[16]
3 of 3
Set No. 4
Code No: RR10105
I B.Tech Semester Supplimentary Examinations, June 2009
APPLIED MECHANICS
(Civil Engineering)
Time: 3 hours
Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions
All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) A 1000 N cylinder is supported by a horizontal rod AB and a smooth uniform
rod CD which weighs 500 N as shown in figure 1a. Assuming the pins at
A,B,C and D to be friction less and weight of AB negligible Find the reactions
at C and D.
Figure 1a
(b) A uniform ladder AB whose weight is 200 N and length 6 m rests against a
smooth vertical wall making with it an angle of 30o . The other end rests on
the ground surface. Find the reactions given to the ladder by the wall and the
floor and their inclination to the vertical, when a man weighing 700 N climbs
the ladder by a distance 1.5 m along the length of the ladder.
[8+8]
2. The vertical position of the 100kg block is adjusted by the screw activated wedge
{As shown in the Figure2}. Calculate the moment M which must be applied to
the handle of the screw to raise the block. The single threaded screw has square
threads with a mean diameter of 30 mm and advances 10 mm for each complete
turn. The coefficient of friction for the screw threads is 0.25, and the coefficient of
friction for all mating surfaces of the block and wedge is 0.40. Neglect friction at
the ball joint A.
[16]
1 of 3
Set No. 4
Code No: RR10105
Figure 2
3. A leather belt is required to transmit 9kW from a pulley 1200 mm in diameter
running at 200 r.p.m The angle embraced is 1650 and the coefficient of friction
between leather belt and pulley is 0.3. If the safe working stress for the leather belt
is 1.4N/mm2 the weight of leather is 1000Kg/m3 and the thickness of the belt is
10mm, determine the width of the belt taking the centrifugal tension in to account.
[16]
4. (a) From first principles deduce an expression to determine the centroid of a triangle of base b and height h.
(b) Determine the centroidal co-ordinates of the shaded area as shown in figure
4b.
[8+8]
Figure 4b
5. (a) Define mass moment of inertia and explain Transfer formula for mass moment
of inertia.
(b) Derive the expression for the moment of inertia of a homogeneous sphere of
radius r and mass density w with reference to its diameter.
[8+8]
6. (a) The motion of a disk rotating about a fixed point is given by the relation
= 2(1 + e3t ) where is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the
angular coordinates, velocity and acceleration of the disk when
i. t=0 and
ii. t=2secs.
2 of 3
Set No. 4
Code No: RR10105
(b) A projectile is aimed at a mark on the horizontal plane through the point of
projection and falls 12m short when the angle of projection is 150 while it
overshoots the mark by 24m when the angle of projection is 450 . Find the
angle of projection to hit the mark neglecting the resistance of air.
Take g = 9.81 m/s2 .
[8+8]
7. If Wa :Wb :Wc is in the ratio of 3:2:1 , find the accelerations of the blocks A, B, and
C. Assume that the pulleys are weightless. {As shown in the Figure7}.
[16]
Figure 7
8. (a) A homogeneous circular disk of radius r and weight W hangs in a vertical
plane from a pin O at its circumference. Find the period for small angles
of swing in the plane of the disk
(b) A slender wire 0.90 m long is bent in the form of a equilateral triangle and
hangs from a pin at O as shown in the figure8b. Determine the period for
small amplitudes of swing in the plane of the figure.
[16]
Figure 8b
3 of 3
Você também pode gostar
- 2015 12 GETRAG Lecture Modular Hybrid Transmission KitDocumento25 páginas2015 12 GETRAG Lecture Modular Hybrid Transmission Kitputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- HCP A C Ratio PDFDocumento16 páginasHCP A C Ratio PDFInderpal SinghAinda não há avaliações
- DS350 Tadano Faun 1368Documento61 páginasDS350 Tadano Faun 1368Mohamed Harb100% (2)
- Tensile Test Lab ReportDocumento13 páginasTensile Test Lab Reportahmad adnanAinda não há avaliações
- Cantilever Flex ExperimentDocumento8 páginasCantilever Flex ExperimentJhonattan PardoAinda não há avaliações
- PHY10L - Resolution of ForcesDocumento14 páginasPHY10L - Resolution of Forcesdenzel94Ainda não há avaliações
- Achidram, Ashwamedham & KatakamDocumento228 páginasAchidram, Ashwamedham & KatakamSubhash Sharma100% (9)
- Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocumento18 páginasPharmaceutical Analysisak gamingAinda não há avaliações
- Roll Forging.Documento36 páginasRoll Forging.jaydee420Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - FIR Filters - Digital Filter Design - Mikroelektronika PDFDocumento114 páginasChapter 2 - FIR Filters - Digital Filter Design - Mikroelektronika PDFAnimesh NagrareAinda não há avaliações
- Inclined Plane Experiment NewestDocumento3 páginasInclined Plane Experiment Newestapi-238942037Ainda não há avaliações
- HVAC Control in The New MillenniumDocumento389 páginasHVAC Control in The New Millenniumnicky1213aAinda não há avaliações
- Final PPT of Carbon NanotubesDocumento29 páginasFinal PPT of Carbon Nanotubesmkumar_5481450% (2)
- Experiment 9 Young S ModulusDocumento4 páginasExperiment 9 Young S ModulusLIEW ZHUN KIT MoeAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Stresses in BeamDocumento6 páginas8 Stresses in BeamAnkit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment - Buckling of StrutDocumento2 páginasExperiment - Buckling of StrutKubenKrishAinda não há avaliações
- Concurrent Forces Vs Non-Concurrent ForcesDocumento15 páginasConcurrent Forces Vs Non-Concurrent ForcesInocent FarrukhAinda não há avaliações
- EM PPT II SemDocumento398 páginasEM PPT II SemsridharanAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3 Fluids 1Documento9 páginasExperiment 3 Fluids 1JOSE FERNANDO GEMPERLEAinda não há avaliações
- Buckling TestDocumento19 páginasBuckling TestMEjiNasRizAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Method of JointDocumento45 páginasChapter 1 - Method of JointJAinda não há avaliações
- To Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Documento4 páginasTo Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Apu Sarkar0% (2)
- Assignment # 1Documento19 páginasAssignment # 1Khaled Al-sAinda não há avaliações
- LEP 4.1.03 Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceDocumento4 páginasLEP 4.1.03 Internal Resistance and Matching in Voltage SourceJohn CraftAinda não há avaliações
- 8.simple Harmonic Motion and ElasticityExercise PDFDocumento81 páginas8.simple Harmonic Motion and ElasticityExercise PDFSubbalakshmi Yeleswarapu 010311100% (1)
- Experiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesDocumento6 páginasExperiment No.: 5 Test of Slender Column: 1. ObjectivesAsad UzzamanAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveDocumento2 páginasExperiment 5 Title: Acceleration of Free Fall by Means of The Simple Pendulum. ObjectiveReam MairAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 1 G5Documento24 páginasExp 1 G5Abdullah Helmi100% (1)
- Physics ProjectDocumento16 páginasPhysics ProjectAhigya Khandelwal100% (2)
- Experiment 3 - Prism SpectrometerDocumento6 páginasExperiment 3 - Prism SpectrometerTATENDA GOTOAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Friction: Experiment #13Documento8 páginasKinetic Friction: Experiment #13kate anne del castroAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Materials: 3.1 IntroductionDocumento49 páginasMagnetic Materials: 3.1 IntroductionCurious ManAinda não há avaliações
- UEME1132/UEME1323 Statics Assignment (30%)Documento20 páginasUEME1132/UEME1323 Statics Assignment (30%)shintanAinda não há avaliações
- Mass Moment Inertia LabDocumento5 páginasMass Moment Inertia LabVinay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Lab ManualDocumento44 páginasEngineering Mechanics Lab ManualengrburhanAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Methods LabDocumento6 páginasExperimental Methods LabIbraheem OlugbadeAinda não há avaliações
- Resistance Lab ReportDocumento14 páginasResistance Lab Reportalsaffar2010100% (4)
- Homework 4 NewDocumento4 páginasHomework 4 NewnooraAinda não há avaliações
- Metacentre and Metacentric HeightDocumento4 páginasMetacentre and Metacentric HeightleonAinda não há avaliações
- Exp. 6, Theory Rigid Body EquilibriumDocumento4 páginasExp. 6, Theory Rigid Body Equilibriumdayangmyra100% (2)
- Experimental Lab Principles of Superposition ObjectiveDocumento6 páginasExperimental Lab Principles of Superposition ObjectiveAizat HermanAinda não há avaliações
- PPSDocumento94 páginasPPSaamirAinda não há avaliações
- Truss Imp QuestionsDocumento3 páginasTruss Imp QuestionsIrfan ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- Practical 222Documento4 páginasPractical 222Faris 2806100% (1)
- Lab Manual Engineering MechanicsDocumento34 páginasLab Manual Engineering MechanicsBrajesh Kumar Sahu100% (2)
- TechometryDocumento49 páginasTechometryMuhammad Usman RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Hawassa University: Department of Hydraulic and Water Resources EngineeringDocumento2 páginasHawassa University: Department of Hydraulic and Water Resources EngineeringAmanuel AlemayehuAinda não há avaliações
- Examples of Beams For Non-Uniformly Distributed LoadsDocumento2 páginasExamples of Beams For Non-Uniformly Distributed LoadsBikila TerefeAinda não há avaliações
- Rolling Disk Lab Report Applied DynamicsDocumento7 páginasRolling Disk Lab Report Applied DynamicsAliAinda não há avaliações
- Bending Moment For MechatronicsDocumento14 páginasBending Moment For MechatronicsMorapedi D. KealebogaAinda não há avaliações
- Momentum Problem Set PDFDocumento3 páginasMomentum Problem Set PDFNirmaan ShankerAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1:tacheometric SurveyDocumento29 páginasModule 1:tacheometric SurveyveereshAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4 LEVELLINGDocumento6 páginasExperiment 4 LEVELLINGbestyAinda não há avaliações
- Solution For Online Exam1 ProblemDocumento2 páginasSolution For Online Exam1 ProblemAl Christopher SaturAinda não há avaliações
- FE Statics PDFDocumento6 páginasFE Statics PDFMiguel Analuisa0% (1)
- Friction Horizontal PlaneDocumento4 páginasFriction Horizontal Planepiyushmathur50% (2)
- Mechanics of Materials - Principal Stresses and StrainsDocumento14 páginasMechanics of Materials - Principal Stresses and StrainsDavid Clark100% (5)
- HWK 5 Solution PDFDocumento3 páginasHWK 5 Solution PDFJohn Miko JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6 and Experiment 7Documento5 páginasExperiment 6 and Experiment 7Gebre TensayAinda não há avaliações
- Hookes Law ExperimentDocumento3 páginasHookes Law ExperimentKhairul Razmin AbdurakmanAinda não há avaliações
- Elasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceDocumento11 páginasElasticity & Oscillations: Ut Tension, Sic Vis As Extension, So Force. Extension Is Directly Proportional To ForceJustin Paul VallinanAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Structures Final ExamDocumento2 páginasTheory of Structures Final ExamErnel CamantigueAinda não há avaliações
- Water Absorption of BrickDocumento2 páginasWater Absorption of BrickKCC Buildcon Purnea LabAinda não há avaliações
- Bending Stress in A Beam PDF FreeDocumento11 páginasBending Stress in A Beam PDF FreeGTRCDEAinda não há avaliações
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsAinda não há avaliações
- Rr10105 Applied MechanicsDocumento13 páginasRr10105 Applied MechanicsSrinivasa Rao GAinda não há avaliações
- 1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsDocumento11 páginas1429r05210804 Engineering MechanicsSaivenkat PenuguduruAinda não há avaliações
- Applied MechanicsDocumento13 páginasApplied Mechanicsapi-26349602100% (1)
- DimensionsDocumento1 páginaDimensionsputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- BR Series ERDocumento16 páginasBR Series ERputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Properties of CastDocumento1 páginaProperties of Castputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Design ProcedureDocumento16 páginasDesign Procedureputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 - Basic MATLAB CommandsDocumento7 páginasChapter 1 - Basic MATLAB CommandsKrishna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - Programming StructuresDocumento5 páginasChapter 2 - Programming StructuresKrishna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Basic Graphing RoutinesDocumento3 páginasChapter 3 - Basic Graphing RoutinesKrishna KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Product Redesign Based On An Axiomatic PRESENTATIONDocumento20 páginasProduct Redesign Based On An Axiomatic PRESENTATIONputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- EX-1733 TankCalDocumento4 páginasEX-1733 TankCaljacquesmayolAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Papers PHD GuideDocumento4 páginas3 Papers PHD GuideMiss_BayesAinda não há avaliações
- Om Life Plan BrochureDocumento2 páginasOm Life Plan Brochureputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Monarch Steel Catalogue PDFDocumento36 páginasMonarch Steel Catalogue PDFputex24774% (19)
- DFMDocumento4 páginasDFMMarko BrkicAinda não há avaliações
- Solidworks 2015 PDFDocumento226 páginasSolidworks 2015 PDFputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Design Data BookDocumento69 páginasMechanical Design Data Bookvenugopalmanga100% (1)
- Module 2 Lesson 3Documento11 páginasModule 2 Lesson 3putex247Ainda não há avaliações
- CXP 023e Acid Low Acid CannedDocumento85 páginasCXP 023e Acid Low Acid CannedMonching AdecerAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Simple StressesDocumento25 páginas4 Simple StressesPRASAD326Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Introduction To StaticsDocumento26 páginasUnit 1 Introduction To Staticsputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 Compound Stresses in Machine PartsDocumento15 páginas5 Compound Stresses in Machine PartsPRASAD326Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 StructuresDocumento27 páginasUnit 4 Structuresputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Distributed ForcesDocumento27 páginasUnit 5 Distributed Forcesputex247100% (1)
- Adams Se 2013 Doc PidDocumento4 páginasAdams Se 2013 Doc PidMahesh DevasigamaniAinda não há avaliações
- EIM 116 Course Outline (2015-2016)Documento4 páginasEIM 116 Course Outline (2015-2016)putex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Force SystemsDocumento46 páginasUnit 2 Force Systemsputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- ThesisDocumento79 páginasThesisputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- Conceptual Design of A Bus Emergency Exit RampDocumento4 páginasConceptual Design of A Bus Emergency Exit Rampputex247Ainda não há avaliações
- IISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Documento22 páginasIISER Aptitude Test 17th Sept 2021Muskaan KathuriaAinda não há avaliações
- Aerodyn2 Discussion 11 Ceilings Ant Time To ClimbDocumento26 páginasAerodyn2 Discussion 11 Ceilings Ant Time To Climbshop printAinda não há avaliações
- NSEJS Mini Test-1 OlympiadsDocumento4 páginasNSEJS Mini Test-1 OlympiadsNarenthran RameshAinda não há avaliações
- ISCSI OptimizationDocumento28 páginasISCSI OptimizationrahulhclAinda não há avaliações
- Iteration: Chapter GoalsDocumento46 páginasIteration: Chapter GoalsAni AniAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling and Optimization of FermentativDocumento13 páginasModeling and Optimization of FermentativThayna Rhomana da Silva CandidoAinda não há avaliações
- KinematicsDocumento5 páginasKinematicsUnicornpop PopAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0960077922005665 MainDocumento8 páginas1 s2.0 S0960077922005665 MainSajjad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Remote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Documento16 páginasRemote Terminal Viewer Software Release Note 1101192-A: © Foxboro Australia 2000 ACN 000 522 26Mochamad EffendiAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of LiOH and LiNO3 Aqueous SolutionsDocumento13 páginasProperties of LiOH and LiNO3 Aqueous Solutionstim tengAinda não há avaliações
- Iconnect v3.1 User ManualDocumento105 páginasIconnect v3.1 User Manualcjamiz2006Ainda não há avaliações
- 1520 0477 Bams D 22 0164.1Documento22 páginas1520 0477 Bams D 22 0164.1Slobodna DalmacijaAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei KPIs 10thsep2011Documento15 páginasHuawei KPIs 10thsep2011Amr Mohamed Abd El-baryAinda não há avaliações
- For And: Viterbi Decoding Satellite Space CommunicationDocumento14 páginasFor And: Viterbi Decoding Satellite Space CommunicationRosi Marleny Machuca rojasAinda não há avaliações
- CodeDocumento8 páginasCodenikhil18salviAinda não há avaliações
- Ready To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaDocumento25 páginasReady To Use Therapeutic Food in RwandaKABERA RENEAinda não há avaliações
- ALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuDocumento67 páginasALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuMeghaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Practice Worksheet 0625Documento6 páginasPhysics Practice Worksheet 0625emmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- ASAP2Documento119 páginasASAP2hacvuaAinda não há avaliações
- The Best Itext Questions On StackoverflowDocumento361 páginasThe Best Itext Questions On Stackoverflowadaf8850% (2)
- Gauss Contest: Grade 7Documento4 páginasGauss Contest: Grade 7irwan syahAinda não há avaliações
- The Chemistry Maths Book: Erich SteinerDocumento16 páginasThe Chemistry Maths Book: Erich SteinerDewi MariyamAinda não há avaliações
- VSANDocumento16 páginasVSANaksbehalAinda não há avaliações