Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Evolution and Genetics 12-13 Handout 2 Slides Per Page
Enviado por
Phoebe XieDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Evolution and Genetics 12-13 Handout 2 Slides Per Page
Enviado por
Phoebe XieDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
06/03/2014
Biological Psychology
DNA, Genetics & Evolution
Is this what makes you human?
06/03/2014
Chromosomes
Each chromosome is a
double stranded
molecule of
deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA).
The structure of the
molecule was described
in 1953 by James Watson
and Francis Crick.
06/03/2014
DNA
The two strands are held together by nucleotide bases which
are attracted to each other.
So that:
Adenine links to Thymine
Guanine links to Cytosine
06/03/2014
So what are genes?
Genes are sequences of nucleotide bases.
Imagine a simple alphabet made up of only 4 letters
A, T, C, G
Genes are words made up of sequences of these bases
Interesting Facts
It has been estimated that the human genome (the
total complement of all 23 pairs of chromosomes)
contains over 3,000 million base pairs (A-T, C-G).
To enable over 3,000 million base pairs to exist, each
cell in the body contains about 6 feet of DNA crammed
into a nucleus that is 0.005mm in diameter.
It is estimated that our 23 pairs of chromosomes
contain around 30,000 genes.
This is the amount of information required to build a
human being from a single egg and to maintain it
through life.
06/03/2014
The Importance of DNA
Genes provide a code to make amino
acids.
Amino acids are the building blocks of
proteins.
Our genes can only make 20 different
amino acids.
All our proteins are made from these 20
amino acids
DNA and Proteins
So:
The instructions for making
proteins are stored on
chromosomes locked away in the
cells nucleus.
However, protein manufacture
does not take place in the
nucleus, but in the surrounding
cytoplasm. How?
06/03/2014
The Answer
Thanks to another nucleic acid ribonucleic
acid (RNA).
Similar to DNA, but it exists as a single strand,
enabling it to move in and out of the nucleus.
Has the base URACIL instead of thymine.
The Process
MESSENGER RNA (mRNA) transports the DNAs instructions
from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
The genes are translated into amino acids.
Each amino acid is added to a lengthening strand.
When the length of the mRNA is finally translated, the
completed protein is released.
06/03/2014
Why are proteins important?
They are vital constituents of all living things.
A typical mammalian cell may have as many
as 10,000 different proteins, each with its
own unique role.
One of the most important roles of proteins
is as enzymes
Where do we get our DNA from?
DNA is passed on from parent to child.
But you do not get all your parents DNA, you
get half from you mother and half from your
father.
This allows you to have different combinations
of genes than your siblings.
This allow for variation between and within
species.
06/03/2014
Human Reproduction
Humans have 23 matched pairs of chromosomes in the
nucleus of all cells with one exception
The Egg and Sperm Cells
DIPLOID CELLS
46 chromosomes (most cells in the body)
HAPLOID CELLS
23 chromosomes (the egg in the female, sperm in the
male)
Human Reproduction
Diploid cells replicate by a process called MITOSIS
Mitosis generates a complete copy of the cells genetic
information
All new cells contain copies of all 23 matched pairs of
chromosomes.
06/03/2014
Human Reproduction
Haploid cells (sperm and egg) are created by a process celled
MEIOSIS
Only half the number of chromosomes
1 of each rather than 2 are assigned to each cell
The chromosome are randomly assigned to each
gamete
Human Reproduction
When the sperm fertilises an egg,
chromosomes from the mother pair up with
the relevant partner chromosome from the
father.
Therefore the resulting offspring inherits half
its genetic information from its mother and
half from its father.
06/03/2014
Human Reproduction
Why is this important?
VARIATION
New gene combinations are constantly produced.
No two individuals are the same.
Is this always true?
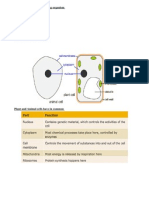
Genes and Chromosomes
Genes are located on CHROMOSOMES, which are
present in the nucleus of every cell.
Chromosomes occur in matched pairs.
The 2 genes (alleles) that control each trait are situated
at the same locus on each chromosome of a particular
pair.
Each species has a characteristic number of pairs of
chromosomes in each of its body cells.
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
10
06/03/2014
A bit more variation
Variation is further
promoted by the
phenomenon of crossing
over.
This occurs during
meiosis.
11
06/03/2014
Mendel 1822-1884
Published his work in 1866.
In his revolutionary work, he did not
deal with variation, but rather
consistent traits.
He showed that traits can be passed
from Grandparent to offspring,
bypassing the parental
generation.
He showed that traits were carried
through something other than
blood as had been assumed.
We will consider the work of Mendel
in the seminar
Charles Darwin
Not a natural Biologist.
Not a natural academic.
But now known as the
founder of modern day
biology.
12
06/03/2014
Pre-Darwinian Thought
19th
Century Britain
Creationism was accepted unchallenged by the general
public
However, much of the evidence Darwin used to develop his
theory was known
Geologists and Palaeontologists had evidence that life had
existed on Earth for a long time AND that it had changed
over time.
Members of a species look similar to each other
when compared to another species.
BUT when compared to each other, there are
differences between members of a species.
Theory of Inheritance of Acquired
Traits
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (17441829)
Suggested that the giraffes
neck grow because the
muscles in the parent stretch
as it reached for food and that
this trait was passed on to the
offspring.
This is now disregarded as we
know that only sperm and egg
cells can pass on information.
13
06/03/2014
Charles Darwin (1809 1882)
Darwin returned from his world trip on the Beagle in 1837
By 1838 he had developed his theory of Evolution
Alfred Russell Wallace independently developed the same
theory
In 1859 Darwin published his book On the Origin of Species
by Means of Natural Selection, or The Preservation of
Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. Known As Origins of
the Species
Darwins Theory
Evolution decent with modification
Evolution has occurred by branching so that different
species share common ancestral species.
Natural Selection
The main mechanism of evolution. This is where
random changes to an individual occur. Those
which are beneficial will be passed on to the next
generation.
14
06/03/2014
Natural Selection
Members of a species vary greatly in their structure,
physiology and behaviour, traits that are associated
with survival are more likely to be passed onto the
next generation. Therefore natural selection leads to
the evolution of species which are better able to
surviving and reproducing in their particular
environment.
The Reaction
Caricature in Hornet taken from
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Dar
win
Is evolution universally accepted
now?
Do YOU accept the theory of
evolution?
Have you examined the evidence
for evolution?
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/education/7612152.
stm
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/education/7619670.
stm
15
06/03/2014
1. Darwins Evidence
He documented the
evolution of fossil
records through
progressive geological
layers
2. Darwins Evidence
Taken from Carlson (2001) Physiology of Behaviour
16
06/03/2014
3. Darwins Evidence
Darwin argued that if
dogs and horses could be
bred to produce offspring
with desirable
characteristics, then why
could this not happen
naturally.
NATURAL SELECTION
Further Evidence
Science has moved on since Darwin. Can you
think of any other ways of testing the theory
of evolution?
Remember Darwin did not know about how
information was passed on from parents to
offspring. He had not seen the work of
Mendel.
17
06/03/2014
Example of Natural Selection
The Case of the disappearing (white) English Peppered
Moth
KEY FACTS
The English Peppered Moth (Biston Betularia) is whitish with
black speckles on its wings.
They are camouflaged on speckled lichen on trees.
A genetic mutation can cause some moths to be all black,
these are said to be melanistic.
Melanistic moths not camouflaged on lichen.
1800s Industrial Revolution.
Lichens sensitive to air pollution and die.
Black soot turns trees black
Example of Natural Selection
And the White Moths Disappeared.
What has caused this mysterious disappearance?
The white moths, no longer have an advantage and are being eaten.
The Black moths have an advantage and are not been eaten, so are able to
reproduce and pass on the mutation.
There were however white moths in the countryside.
In the 20th Century The Clean Air acts, changed the
environment again.
The white moths re-appear
18
06/03/2014
Survival of the Fittest
The individual best suited to their
environment will survive to pass on these
genes to the next generation.
This is a phrase coined by Herbert Spencer
and was used to justify Social Darwinism.
Human Evolution: A big brain?
Adult human brain weighs between 1200g and
1400g
Adult elephant brain weighs between 5,000g and
8,000g
Brain Body Ratio
Humans 2.33%
Elephant 0.2%
Shrew 3.33%
19
06/03/2014
Human Evolution
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Animal
Chordate
Mammal
Primate
Hominid
Homo
Sapiens
The Ape who Evolved to be Human
What key factors separate humans and apes?
20
06/03/2014
Human Evolution
From Kenyon http://www.flyfishingdevon.co.uk/salmon/
Evolutionary Psychology
Explains human behaviour in terms of
evolution.
Darwin himself believed that human
behaviour could be explained in terms of
evolution.
21
06/03/2014
Whose Genes?
From Kenyon http://www.flyfishingdevon.co.uk/salmon/
Evolution Facts
Evolution is not a straight line
Evolution does not progress to preordained perfection
Humans are the last surviving species of a family that has existed for a
very short time
Evolution can be rapid
Fewer than 1% of known species are in existence
Not all existing behaviours or structures are adaptive
22
06/03/2014
Conclusion
Darwin developed his theory of evolution to explain
the diversity that he saw around him
DNA was identified by Watson and Crick in the
1950s
Traits are passed from one generation to the next by
genes located on chromosomes
We now understand that many human traits involve
many genes (Polygenic)
And genes often provide just a predisposition to a
condition or trait.
23
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Add: Subtract 5 PDFDocumento1 páginaAdd: Subtract 5 PDFPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Add:subtract 3 PDFDocumento1 páginaAdd:subtract 3 PDFPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet Collection: Fractions, Decimals, LCM and MoreDocumento7 páginasWorksheet Collection: Fractions, Decimals, LCM and MorePhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- 2700 7634Documento44 páginas2700 7634Phoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Add/Subtract Three Mixed Numbers: Try The Skill Name - DateDocumento1 páginaAdd/Subtract Three Mixed Numbers: Try The Skill Name - DatePhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Genetic Terms+ DefinitionsDocumento4 páginasGenetic Terms+ DefinitionsPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplying+Dividing Fractions and Mixed NumbersDocumento2 páginasMultiplying+Dividing Fractions and Mixed NumbersPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- For Good Music and Lyrics by Stephen SchwartzDocumento16 páginasFor Good Music and Lyrics by Stephen SchwartzPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Cognitive Psychology SAQ Essay QuestionDocumento5 páginasCognitive Psychology SAQ Essay QuestionPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Attention Through Failures and SuccessesDocumento44 páginasUnderstanding Attention Through Failures and SuccessesDrew Wilson100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Modern TechnologyDocumento6 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Modern TechnologyPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- UE1 Ass.2 CorrectedDocumento5 páginasUE1 Ass.2 CorrectedPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7Documento30 páginasChapter 7Phoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet Number PyramidDocumento1 páginaWorksheet Number PyramidPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Atom FirstDocumento93 páginasChem Atom FirstPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- IA Student Guide From IBODocumento13 páginasIA Student Guide From IBOPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Revision NotesDocumento3 páginasBiology Revision NotesPhoebe XieAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Introduction To Bioinformatics: Database Search (FASTA)Documento35 páginasIntroduction To Bioinformatics: Database Search (FASTA)mahedi hasanAinda não há avaliações
- Pain PathwayDocumento17 páginasPain PathwaySalsabila Al-BasheerAinda não há avaliações
- The Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology of Muscular SystemDocumento55 páginasThe Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology of Muscular SystemAnisaAinda não há avaliações
- Non-symbiotic Nitrogen FixersDocumento21 páginasNon-symbiotic Nitrogen Fixersrajiv pathakAinda não há avaliações
- 皮膚病介紹Documento93 páginas皮膚病介紹MK CameraAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanDocumento7 páginasChemical Composition of Meat and Nut Water of Major Coconut in PakistanSkyle VoAinda não há avaliações
- Uits PDFDocumento36 páginasUits PDFCrystal ParkerAinda não há avaliações
- Egg Quality Manual Web PDFDocumento44 páginasEgg Quality Manual Web PDFVeterinario La EsperanzaAinda não há avaliações
- Muscle Energy Techniques ExplainedDocumento2 páginasMuscle Energy Techniques ExplainedAtanu Datta100% (1)
- Geology of Malta and GozoDocumento6 páginasGeology of Malta and GozoCarolina Pérez P.Ainda não há avaliações
- Parts, Functions and Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDocumento32 páginasParts, Functions and Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive SystemsZephie100% (1)
- The Science of NeglectDocumento20 páginasThe Science of NeglectdrdrtsaiAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Documento6 páginasPlant Transport - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Zhi En LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Kenya's Natural Capital AtlasDocumento139 páginasKenya's Natural Capital AtlasElvis Ole Sankale Ntimama100% (7)
- Determination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanDocumento4 páginasDetermination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanSutirtho MukherjiAinda não há avaliações
- Stress BreakerDocumento7 páginasStress BreakerEshan Verma33% (3)
- Biology of Implant OsseointegrationDocumento11 páginasBiology of Implant OsseointegrationAmIrAinda não há avaliações
- Dna Finger PrintingDocumento23 páginasDna Finger PrintingSanjay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Flowering PlantsDocumento43 páginasFlowering Plantskingbanakon100% (1)
- Young Children's Biological Predisposition To Learn in Privileged DomainDocumento6 páginasYoung Children's Biological Predisposition To Learn in Privileged DomainVeronica Dadal0% (1)
- Evolution of Pharmacy in the PhilippinesDocumento2 páginasEvolution of Pharmacy in the PhilippinesRosemarie OngAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Perkecambahan Biji PDFDocumento14 páginasJurnal Perkecambahan Biji PDFKinad Danik50% (2)
- MR Spectroscopy: Technical Aspects and Clinical ApplicationsDocumento5 páginasMR Spectroscopy: Technical Aspects and Clinical ApplicationsNotariana Kusuma AAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiological Test of Medical DevicesDocumento5 páginasMicrobiological Test of Medical Devicesbijendra_sinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Genetics of Colorectal Cancer - UpToDateDocumento41 páginasMolecular Genetics of Colorectal Cancer - UpToDateToweran ToweraneAinda não há avaliações
- The Antibacterial Properties of Isothiocyanates PDFDocumento15 páginasThe Antibacterial Properties of Isothiocyanates PDFSasicha DoungsuwanAinda não há avaliações
- Amazing Facts - Exercises 1Documento3 páginasAmazing Facts - Exercises 1Alina DorobatAinda não há avaliações
- Cu EnzymesDocumento8 páginasCu EnzymesVINEESHA VKAinda não há avaliações
- Behaviour of Great Apes Studied by Three Female ScientistsDocumento12 páginasBehaviour of Great Apes Studied by Three Female ScientistsSani AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- The Story of OrchidDocumento7 páginasThe Story of OrchidLilian Kimwell SastadoAinda não há avaliações