Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
View
Enviado por
mohandass selvakumarDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
View
Enviado por
mohandass selvakumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
FINAL EXAMINATION
AUGUST 2013 SEMESTER
COURSE
COURSE CODE
DURATION
FACULTY
PROGRAM
LECTURER
:
:
:
:
:
:
FLUID MECHANICS 1
KJS 1214
3 HOURS
ENGINEERING
BACH. OF ENG. (HONS.) MECHANICAL
MR. MOHAMAD HAFIZ BIN ISMAIL
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
This paper consists of four (4) questions.
Answer all questions.
All answers must be written in answer booklet provided.
The answer for each question must start on a new page.
Candidates are NOT ALLOWED to bring any unauthorized items into the exam hall
except with the permission of your invigilator.
Do Not Open the Question Paper Until Instructed
This Question Paper Consists of FIVE (5) Printed Pages
CONFIDENTIAL
FoE/KJS1214/AUG13
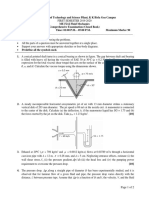
QUESTION 1
a)
A ball bearing with density s is dropped in a cylindrical tank filled with oil at
density o. The ball bearing fall by creeping flow which is define as
= whereas FD , U and R are drag force, velocity and radius of the
2
ball bearing. Show that the dynamic viscosity is given by 9 2 .
[5 marks]
b)
A 25 mm diameter shaft is pulled through a cylindrical bearing as shown in
Figure 1. The lubricant that fills the 0.3 mm gap between the shaft and bearing
is oil having a kinematic viscosity of 8 10-4 m2/s and a specific gravity of
0.91. Determine the force P required to pull the shaft at a velocity of 3m/s.
Assume the velocity distribution in the gap is linear.
Figure 1
[6 marks]
[Total: 11 marks]
CONFIDENTIAL/2
FoE/KJS1214/AUG13
QUESTION 2
a)
The density of a liquid is to be determined by an old 1-cm-diameter cylindrical
hydrometer whose division marks are completely wiped out (Figure 2). The
hydrometer is first dropped in water, and the water level is marked. The
hydrometer is then dropped into the other liquid, and it is observed that the mark
for water has risen 0.6 cm above the liquid-air interface. If the height of the
original water mark is 13.6 cm, determine the density of the liquid.
Figure 2
[4 marks]
b)
The dam in Figure 3 is a quarter-circle 50 m wide into the paper. Determine the
horizontal and vertical components of hydrostatic force against the dam and the
point CP where the resultant strikes the dam.
Figure 3
[8 marks]
[Total: 12 marks]
CONFIDENTIAL/3
FoE/KJS1214/AUG13
QUESTION 3
a)
A pitot-static probe is connected to a water manometer is used to measure the
velocity of air (Figure 4). If difference height between two arms is 7.3 cm,
determine the air velocity. Take the air density to be 1.25 kg/m3
Figure 4
[5 marks]
b)
A reducing elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to deflect water flow while
accelerating it as shown in Figure 5. The elbow discharge water into the
atmosphere. The mass of the elbow and the water in it is 50 kg. Determine the
anchoring force needed to hold the elbow in place. Take the momentum flux
correction factor to be 1.03 and mass flow rate 30 kg/s.
Figure 5
[10 marks]
[Total: 15 marks]
CONFIDENTIAL/4
FoE/KJS1214/AUG13
QUESTION 4
a)
Model tests are to be performed to study the flow through a large check valve
having a 0.6 m diameter inlet and carrying water at a flowrate of 0.85 m3/s as
shown in Figure 6 below. The working fluid in the model is water at the same
temperature as that in the prototype. Complete geometric similarity exists
between model and prototype, and the model inlet diameter is 7.5 cm.
Determine the required flowrate in the model.
Figure 6
[5 marks]
b)
Consider flow of an incompressible fluid of density and dynamic viscosity
through a long, horizontal section of round pipe of diameter D. The velocity
profile is given in Figure 7 below. V is the average speed across the pipe cross
section. The flow is fully developed. Because the frictional forces between the
fluid and the pipe wall, there exists a shear stress w on the inside of pipe wall.
We assume some constant average roughness height along the inside wall of
the pipe. Develop a non-dimensional relationship between shear stress w and
the other parameters in the problem.
Figure 7
[7 marks]
[Total: 12 marks]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
CONFIDENTIAL/5
Você também pode gostar
- Report Fluid Friction TestDocumento12 páginasReport Fluid Friction TestAbdul Fatah Najmi60% (5)
- Exam 2 2011 SummerDocumento8 páginasExam 2 2011 Summerfabankit100% (2)
- Debre Markos University Technology College Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocumento3 páginasDebre Markos University Technology College Mechanical Engineering Departmentanon_293092329Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 5 Thermo FluidsDocumento13 páginasLab 5 Thermo FluidsAimiWaniAinda não há avaliações
- UBC CHBE 251 - Fluid Mechanics - Problems From Past FinalsDocumento14 páginasUBC CHBE 251 - Fluid Mechanics - Problems From Past FinalsflybossladiAinda não há avaliações
- EML4304C - : Be Sure To Follow The Homework Format As Shown On The Website!Documento4 páginasEML4304C - : Be Sure To Follow The Homework Format As Shown On The Website!Kris GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1 2014Documento7 páginasTutorial 1 2014sotdeAinda não há avaliações
- Year 7 Activity Pack Samples - UNIT 7IADocumento11 páginasYear 7 Activity Pack Samples - UNIT 7IAAFuentesCaballeroAinda não há avaliações
- 9686-6160-JSA-000-0041 - B1 JSA For UPS & Batteries Pre-Com & CommissioningDocumento12 páginas9686-6160-JSA-000-0041 - B1 JSA For UPS & Batteries Pre-Com & CommissioningKhan Wasim100% (1)
- Waves Internship ReportDocumento36 páginasWaves Internship ReportIrfanInayatUllahLakAinda não há avaliações
- Fluids B48BB1 Coursework 2011-2012Documento8 páginasFluids B48BB1 Coursework 2011-2012Mohamed AbdullaAinda não há avaliações
- ME2109 Fluid May2011Documento6 páginasME2109 Fluid May2011Hafsa Khan0% (1)
- ME2109 Fluid May2012Documento7 páginasME2109 Fluid May2012Hafsa KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Universiti Tunku Abdul RahmanDocumento6 páginasUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanfreeloadAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures of Fluid MechanicsDocumento84 páginasLectures of Fluid MechanicsMarc AlamoAinda não há avaliações
- #3 Fluid MechanicsDocumento9 páginas#3 Fluid MechanicsRom PerezAinda não há avaliações
- UEME2123 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 1Documento3 páginasUEME2123 Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 1Ah WenAinda não há avaliações
- Relationship Between Pressure and Velocity of FluidsDocumento12 páginasRelationship Between Pressure and Velocity of FluidsNavinRajSakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocumento15 páginasFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsCik Tiem Ngagiman93% (29)
- Effect of Ejector Con Guration On Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Gas-Liquid Ejectors PDFDocumento11 páginasEffect of Ejector Con Guration On Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Gas-Liquid Ejectors PDFPan MachinneAinda não há avaliações
- OrificeDocumento7 páginasOrificePrasillaPrisiAinda não há avaliações
- Eng Trial ExamDocumento11 páginasEng Trial ExamudinjcAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank For 1 Unit Test Class:CH4G Sub:FFO (17426) : Chapter 1 (12 Marks)Documento3 páginasQuestion Bank For 1 Unit Test Class:CH4G Sub:FFO (17426) : Chapter 1 (12 Marks)rutvikAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics: Hydraulic BenchDocumento11 páginasFluid Mechanics: Hydraulic BenchAmar Hafiz83% (6)
- Appreciation: Fluid Friction TestDocumento10 páginasAppreciation: Fluid Friction TestLuqman Yusof100% (1)
- Politeknik MalayDocumento6 páginasPoliteknik MalaybrianlaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4 2Documento12 páginasExperiment 4 2ChongAinda não há avaliações
- θ, a, and H. Calculate the viscous torque using the dimensions shownDocumento2 páginasθ, a, and H. Calculate the viscous torque using the dimensions shownPransuAinda não há avaliações
- Actividad 4: Volumen de ControlDocumento5 páginasActividad 4: Volumen de ControlWoodyFernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet (6) Dimensional AnalysisDocumento4 páginasSheet (6) Dimensional AnalysisABDELRHMAN ALIAinda não há avaliações
- Major Probables MEE 290Documento5 páginasMajor Probables MEE 290m-772007Ainda não há avaliações
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocumento17 páginasFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsMuhammad Zulhusni Che RazaliAinda não há avaliações
- Mixing of Water in A Flat Bottom MixerDocumento20 páginasMixing of Water in A Flat Bottom MixerJorge Agüero LópezAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics For Mechanical Engineering: Tutorial 4Documento27 páginasFluid Mechanics For Mechanical Engineering: Tutorial 4mitulkindAinda não há avaliações
- AE-May-2015-04-BS-7Documento15 páginasAE-May-2015-04-BS-7umchem2Ainda não há avaliações
- Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman: Chapter 3: The Bernoulli EquationDocumento6 páginasUniversiti Tunku Abdul Rahman: Chapter 3: The Bernoulli EquationfreeloadAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4: Asst - Lectuer: Mohammed Abid JameelDocumento6 páginasExperiment 4: Asst - Lectuer: Mohammed Abid JameelSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mech Sheet 4 IAETDocumento11 páginasFluid Mech Sheet 4 IAET3bdo MahmoudAinda não há avaliações
- College of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination Special Semester 2013 / 2014Documento13 páginasCollege of Engineering Putrajaya Campus Final Examination Special Semester 2013 / 2014NabilahJasmiAinda não há avaliações
- FM Test 1Documento10 páginasFM Test 1ReginaldRemoAinda não há avaliações
- Test 1 QuestionsDocumento3 páginasTest 1 QuestionsqueenycypAinda não há avaliações
- Homework SolutionDocumento25 páginasHomework SolutionHirman De NovaAinda não há avaliações
- Orifice Meter ExperimentDocumento10 páginasOrifice Meter ExperimentAmoluck BhatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Yaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Documento10 páginasYaqub 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 458 012078Daniel MoraesAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Study On Hydraulic Fractures in Cohesive Soil Grounds by Slurry PressureDocumento7 páginasExperimental Study On Hydraulic Fractures in Cohesive Soil Grounds by Slurry PressureHarold TaylorAinda não há avaliações
- MM204 Assn3 2017Documento5 páginasMM204 Assn3 2017jayAinda não há avaliações
- 12P305Documento2 páginas12P305RAJAAinda não há avaliações
- Ijmet 10 01 008Documento15 páginasIjmet 10 01 008IAEME PUBLICATIONAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of The Flow Rate of Different Fluids by A RotameterDocumento8 páginasDetermination of The Flow Rate of Different Fluids by A RotameteracetilenAinda não há avaliações
- HydraulicsDocumento5 páginasHydraulicsAmit GhadeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab VortexDocumento13 páginasLab VortexDaniel RazakAinda não há avaliações
- InTech-Analysis of Cavitation Performance of InducersDocumento15 páginasInTech-Analysis of Cavitation Performance of InducersTGrey027Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid MechanicsDocumento2 páginasFluid MechanicsMD Manan RainAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment # 01 - (2023-24)Documento5 páginasAssignment # 01 - (2023-24)Mohd YamanAinda não há avaliações
- OpDocumento88 páginasOpMahmud Rahman BizoyAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics Lab Objective QuestionDocumento2 páginasHydraulics Lab Objective QuestionShan Cv0% (1)
- Aerodynamics Lab ManualDocumento42 páginasAerodynamics Lab ManualSathya Narayanan100% (2)
- Gas Hold-Up, Mixing Time and Circulation Time in InternalDocumento9 páginasGas Hold-Up, Mixing Time and Circulation Time in Internalali abdulrahman al-ezziAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Pipeline Hydraulics: Second EditionNo EverandLiquid Pipeline Hydraulics: Second EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2No EverandFluid Mechanics in Channel, Pipe and Aerodynamic Design Geometries 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Disc Brake ProjectDocumento3 páginasDisc Brake ProjectPathan ShamsheerkhanAinda não há avaliações
- SOP06 ACAD Final Year ProjectDocumento2 páginasSOP06 ACAD Final Year Projectmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- System DesignDocumento2 páginasSystem Designmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Thermal Ordinances in EuropeDocumento27 páginasSolar Thermal Ordinances in Europemohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- List of Panel - IAD3162Documento2 páginasList of Panel - IAD3162mohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Gantt ChartDocumento1 páginaGantt Chartmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Yes - The Fastest 4G Mobile Internet With VoiceDocumento2 páginasYes - The Fastest 4G Mobile Internet With Voicemohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial Training Programme: Student Personal DetailsDocumento1 páginaIndustrial Training Programme: Student Personal Detailsmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Form of E-Commerce: JN Musical (Jayasuthan A/l Jayabalan & Navakumar A/l Mohan)Documento2 páginasForm of E-Commerce: JN Musical (Jayasuthan A/l Jayabalan & Navakumar A/l Mohan)mohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- No4 PDFDocumento6 páginasNo4 PDFmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Statistics Malaysia: Labour Market in Malaysia, June 2015Documento4 páginasDepartment of Statistics Malaysia: Labour Market in Malaysia, June 2015mohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Online Shopping Cart SolutionsDocumento23 páginasAnalysis of Online Shopping Cart SolutionsmounicasrungaAinda não há avaliações
- ViewDocumento8 páginasViewmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Turorial 2Documento1 páginaTurorial 2mohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Design StrategiesDocumento15 páginasDesign Strategiesmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Section A - Company/Organization BackgroundDocumento3 páginasSection A - Company/Organization Backgroundmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- In Out: Import Public Class Public Static Void Int NewDocumento3 páginasIn Out: Import Public Class Public Static Void Int Newmohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1 AnswerDocumento22 páginasTutorial 1 Answermohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology: Prepared ForDocumento3 páginasFaculty of Computer Science and Information Technology: Prepared Formohandass selvakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study-Software RequirementDocumento69 páginasCase Study-Software RequirementNiyaishZahraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapt 03Documento35 páginasChapt 03Dwi AryantaAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Retardant Research PaperDocumento2 páginasFire Retardant Research Paperapi-318759920Ainda não há avaliações
- KSG 5K DMDocumento2 páginasKSG 5K DMGirasolar solarAinda não há avaliações
- LIFTCALC 30aDocumento101 páginasLIFTCALC 30aareks30% (1)
- Performance Curve: 2 PUMPS-60HZDocumento1 páginaPerformance Curve: 2 PUMPS-60HZWael BadriAinda não há avaliações
- Criostato CM1850 - en PDFDocumento50 páginasCriostato CM1850 - en PDFJuan Carlos Terrones NuñezAinda não há avaliações
- An Experimental Study On Usage of Hollow Glass Spheres (HGS) For Reducing Mud Density in Geothermal DrillingDocumento7 páginasAn Experimental Study On Usage of Hollow Glass Spheres (HGS) For Reducing Mud Density in Geothermal DrillingifebrianAinda não há avaliações
- Interrelated Function Bio MolecularDocumento2 páginasInterrelated Function Bio MolecularAlifah SyarafinaAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet 1 Solution SPC 307Documento15 páginasSheet 1 Solution SPC 307Ercan Umut DanışanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry MSCDocumento17 páginasChemistry MSCRajesh ShahiAinda não há avaliações
- Enedict Oliman Ineda: Curriculum VitaeDocumento6 páginasEnedict Oliman Ineda: Curriculum VitaeDaryll SanjoseAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical KineticsDocumento3 páginasChemical Kineticsvivek daveAinda não há avaliações
- Power System Stability Vol II KimbarkDocumento296 páginasPower System Stability Vol II KimbarkShashidhar Kasthala100% (11)
- Lista Stand Iec 60034Documento4 páginasLista Stand Iec 60034nikola CHECAinda não há avaliações
- 08-Com101 AMDocumento11 páginas08-Com101 AMHồng HoanAinda não há avaliações
- Continuity EquationDocumento9 páginasContinuity EquationEucharia100% (1)
- Seal of BushingDocumento6 páginasSeal of BushingB.k. BirtiaAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical EngineeringDocumento1 páginaMechanical EngineeringManjunatha EikilaAinda não há avaliações
- Sic Power Module: Bsm300D12P2E001Documento10 páginasSic Power Module: Bsm300D12P2E001doggaravi07Ainda não há avaliações
- Emailing Net Chemical Sciences Paper Dec. 2018Documento24 páginasEmailing Net Chemical Sciences Paper Dec. 2018Baban BaidyaAinda não há avaliações
- The Greening of Wal Mart's Supply ChainDocumento8 páginasThe Greening of Wal Mart's Supply ChainmuputismAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogue: Zeeta Electrical Engineering Pvt. LTDDocumento37 páginasCatalogue: Zeeta Electrical Engineering Pvt. LTDKamitkumar PatelAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineDocumento6 páginasThe Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineVinay GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Documento23 páginasScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Keith Genesis Ruiz AglubaAinda não há avaliações
- EC ElectromagneticsDocumento51 páginasEC ElectromagneticsNilamani Umashankar JenaAinda não há avaliações
- Pressure Loss AwwaDocumento1 páginaPressure Loss AwwaSashiAinda não há avaliações
- Infrared SpectrosDocumento3 páginasInfrared SpectrosAmanda CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações