Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Overpopulation
Enviado por
Monisha Sweetgurl0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
22 visualizações2 páginasOverpopulation is defined as having large numbers of people with too few resources. Poverty can also depend on the country's mix of population density and agriculture productivity. Bangladesh has one of the world's highest population densities with 1,147 persons per sq km. Many developing countries lack essential raw materials and the knowledge and skills gained through formal education and training.
Descrição original:
Título original
Overpopulation.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoOverpopulation is defined as having large numbers of people with too few resources. Poverty can also depend on the country's mix of population density and agriculture productivity. Bangladesh has one of the world's highest population densities with 1,147 persons per sq km. Many developing countries lack essential raw materials and the knowledge and skills gained through formal education and training.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
22 visualizações2 páginasOverpopulation
Enviado por
Monisha SweetgurlOverpopulation is defined as having large numbers of people with too few resources. Poverty can also depend on the country's mix of population density and agriculture productivity. Bangladesh has one of the world's highest population densities with 1,147 persons per sq km. Many developing countries lack essential raw materials and the knowledge and skills gained through formal education and training.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
Overpopulation
Overpopulation is defined as the situation of having large numbers of people with
too few resources and too little space. Overpopulation can result from either a
high population density (the ratio of people to land area) or from low amounts of
resources, or from both high population density pressures the available resources in
the country, as there sources can only support a certain number of people. Poverty
can also depend on the country's mix of population density and
agriculture productivity. For example, Bangladesh has one of the world's highest
population densities with 1,147 persons per sq km (2,970 persons per sq mi). A
large majority of the people of Bangladesh engage in low-productivity manual
farming, which contributes to the country extremely high level of poverty. However,
this only applies to third-world countries that do not have advanced technologies.
Distribution of resources
In many developing countries, the problems of poverty are massive and pervasive. In recent decades most
of these countries have tried to develop their economies with industry and technology with varying levels
of success. Many developing countries, however, lack essential raw materials and the knowledge and
skills gained through formal education and training. Because these things are necessary for the
development of industry, developing countries generally must rely on trade with developed countries for
manufactured goods, but they cannot afford much .Because people in developed nations may have more
wealth and resources than those in developing countries, their standard of living is also generally higher.
Thus, people who have what would be considered adequate wealth and resources in developing countries
may be considered poor in developed countries.
In contrast, people in developing countries may consider themselves to be doing
well if they have productive gardens, some livestock, and a house of thatch or mudbrick .In rural areas, people may be accustomed to not having plumbing, electricity,
or formal health care. By the standards of developed countries, such living
conditions are considered hallmarks of poverty.
According to reports, peoples incomes are not enough to cover the cost of their
basic necessities and provide them basic services such as water, electricity,
transportation and communication. It pointed out that recent surveys confirm that
80 percent of citizens expenses go for to food, most notably among vulnerable
groups that are deprived of basic services and luxury means.
Natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes have caused millions of
dollars worth of infrastructure and the loss of lives. Developing countries often
suffer much more extensive and acute crises at the hands of natural disasters,
because limited resources become obstacles for the construction of adequate
housing, infrastructure, and mechanisms for responding to crises. Natural disasters,
being uncontrollable by man, affect annual agricultural output, such as floods
destroying the fertility of soils by washing away mineral-rich topsoil, and take away
natural decomposing agents, rendering the soil infertile. Droughts cause the land to
become barren and unsuitable for cultivation. The states of the U.S.A situated in
Tornado Alley face constant fears of poor harvests in the face of frequent tornado
occurrences. In the case of the Sichuan Earthquake in 2008 and The 2004 Tsunami
catastrophe not only resulted in the loss of agriculture, but the destruction of
millions of dollars worth of infrastructure as well.
African countries, without an exception, are generally categorized among "third
world countries" which are characterized by underdevelopment of their human and
natural resources and the poor quality of life of the majority of their citizenry. There
is the general belief that education is an instrument for social, economic and
political development. Evidence in support of this assertion can be found in the
relationship between the level of educational development and the high standard of
living in developed nations of the world, such as the United States of America,
Britain, Canada and Japan, among others. They are industrialized, modern
economics and democracies mainly because they have well-educated, enlightened,
and skilled adult populations. Conversely, African countries remain underdeveloped
due mainly to a large percentage of illiterates and unskilled worker force within the
adult population.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Chap 002Documento73 páginasChap 002Tony TaiAinda não há avaliações
- Duties of Procurement HeadDocumento1 páginaDuties of Procurement HeadstephenogunladeAinda não há avaliações
- Intimation of Acquisition of Nichepro Technologies Private Limited (Company Update)Documento5 páginasIntimation of Acquisition of Nichepro Technologies Private Limited (Company Update)Shyam SunderAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Auditing Report (Audit of Receivables)Documento7 páginasApplied Auditing Report (Audit of Receivables)mary louise magana100% (1)
- Your August 2022 Bill: $102.30 $84.40 Summary of Current ChargesDocumento3 páginasYour August 2022 Bill: $102.30 $84.40 Summary of Current ChargesMarissa RempilloAinda não há avaliações
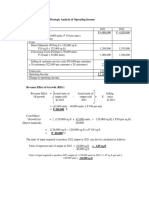
- Solution To Exercise Strategic Analysis of Operating IncomeDocumento4 páginasSolution To Exercise Strategic Analysis of Operating IncomeTONG, HANS KENNETH N.Ainda não há avaliações
- Ethics in Accounting A Decision Making Approach 1St Edition Klein Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento29 páginasEthics in Accounting A Decision Making Approach 1St Edition Klein Test Bank Full Chapter PDFLisaMartinykfz100% (10)
- XRP ExchangesDocumento2 páginasXRP ExchangesGaindesec snAinda não há avaliações
- Robotic Process Automation Mini ProjectDocumento34 páginasRobotic Process Automation Mini ProjectSipu100% (1)
- Analisis Daya Saing Jambu Mete Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Jawa TengahDocumento15 páginasAnalisis Daya Saing Jambu Mete Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Jawa TengahantoAinda não há avaliações
- Beam Telecom PVT LTD.: 8-2-610/A, Road No.10, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad-500034 Tel: +91-40-66272727Documento2 páginasBeam Telecom PVT LTD.: 8-2-610/A, Road No.10, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad-500034 Tel: +91-40-66272727Raghav Reddy NelloreAinda não há avaliações
- Hunting Endangered Species: Investing in The Market For Corporate Control Fall 2012 Strategy PaperDocumento15 páginasHunting Endangered Species: Investing in The Market For Corporate Control Fall 2012 Strategy PaperTobias Carlisle100% (1)
- Research Paper Word - Banking Sector FraudDocumento13 páginasResearch Paper Word - Banking Sector FraudMeena BhagatAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Name Number of Option Legs Direction: Bull Call Spread Two Moderatly BullishDocumento3 páginasStrategy Name Number of Option Legs Direction: Bull Call Spread Two Moderatly BullishMnvd prasadAinda não há avaliações
- Sales Quota - All Types of QuotaDocumento17 páginasSales Quota - All Types of QuotaSunny Bharatbhai Gandhi100% (2)
- L33 - Atal Pension YojanaDocumento5 páginasL33 - Atal Pension YojanaYATHARTH AGARWAL100% (1)
- Linde Bangladesh Limited-PtdDocumento14 páginasLinde Bangladesh Limited-PtdnasirAinda não há avaliações
- PT BEH - PCMU Lap - Adv.Gen - Material - FinalDocumento6 páginasPT BEH - PCMU Lap - Adv.Gen - Material - FinalDeny SaputraAinda não há avaliações
- Graham Fruit ShakeDocumento14 páginasGraham Fruit ShakeJykyll PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Strategy of Parle Company: Virendra SinghDocumento62 páginasMarketing Strategy of Parle Company: Virendra Singhsyed saadAinda não há avaliações
- Time-Based Competition For SCMDocumento3 páginasTime-Based Competition For SCMNicole HuangAinda não há avaliações
- Gaurav Gupta ResumeDocumento3 páginasGaurav Gupta ResumeGaurav GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 2part1Documento8 páginasAssignment 2part1Febri EldiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter # 7Documento32 páginasChapter # 7Rooh Ullah KhanAinda não há avaliações
- To Study Credit Appraisal in Home Loan Fin - Final - Docx 1Documento69 páginasTo Study Credit Appraisal in Home Loan Fin - Final - Docx 1Swapnil BhagatAinda não há avaliações
- Team Project 2: Chapter 8: Investment Decision Rules Fundamentals of Capital BudgetingDocumento61 páginasTeam Project 2: Chapter 8: Investment Decision Rules Fundamentals of Capital BudgetingБекФорд ЗакAinda não há avaliações
- Yocket Loan Assistance Documents RequiredDocumento1 páginaYocket Loan Assistance Documents RequiredMaulik SolankiAinda não há avaliações
- Rating Methodology: Evaluating The IssuerDocumento35 páginasRating Methodology: Evaluating The Issuerizi25Ainda não há avaliações
- Band Partnership AgreementDocumento7 páginasBand Partnership AgreementAustin Salisbury100% (1)
- The Workforce Playbook Embargoed Until 6.11 AspenDocumento72 páginasThe Workforce Playbook Embargoed Until 6.11 AspeninforumdocsAinda não há avaliações