Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cataracts Prevention Technology Implications Society
Enviado por
Cindy VoDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cataracts Prevention Technology Implications Society
Enviado por
Cindy VoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
3.
The clarity of the signal transferred can
affect interpretation of the intended visual
communication
Explain how the production of two different images of a view can
result in depth perception
Some animals have forward facing eyes
Each eyes sees an image of an object in the light
path
There is overlap b/w the 2 views.
Death perception vision of objects as they exist in 3D space
Due to focusing of objects at different distances
from the eye.
When these images from both eyes ( +both visual
fields) are fused object will appear in 3D.
Stereoscopic vision: each eye is separated horizontally so they
have slightly different views.
Fusion = putting together 2 images from left + right visual
fields + from 2 eyes as they reach the brain.
HSC Questions:
Process and analyse information from
secondary sources to describe cataracts and
the technology that can be used to prevent
blindness from cataracts and discuss the
implications of this technology for society
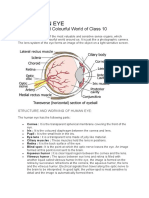
Cataracts = visual defect caused by clouding
of lens
Loss of lens transparency
Interferes with ability for eye to transmit clear signal by
obstructing path of light through the eye.
Total blindness can result if not treated
Cause
Natural consequence of aging
Present at birth (CONGENITAL)
Develop form disease (diabetes, thyroid disorders)
Excessive use of certain drugs
Excessive exposure to UV rays.
SYMPTOMS
Clouding of the pupil
Vision become blurred
Double vision
Halos around images
Loss of colour vision
Impaired night vision
Statistics:
African American + Caribbean people most likely to get this
In Aus : Overall = 11%
90+ 60-70%
50-59- 4%
Infants 1 in 4500
Indigenous Aus 3x more likely.
Surgical procedure
Local anaesthetic, sometimes general
Eye drops given to dilate pupil
In most cataract surgeries, removed lens is replaced by intra
ocular lens which can be made of plastic, silicon or acrylic
compound.
Intra capsular surgery
Involves surgically removing entire lens + capsule
( outer covering of lens)
Extra capsular surgery
Removing lens but leaving intact half of capsule
Slightly longer incision on side of cornea
Hard centre of lends removed in one piece
Remainder of lens ( softer lens cortex) removed by
suction
Phacoemulsification
Most advanced = small incision, no stitch
Tint probe inserted into eye
Probe emits ultrasonic waves that soften+ break up
lens
Debris is removed by a syringe
Artificial lens inserted into space left in existing lens
capsule
SOCIAL IMPLICATION
Cost of surgery is minimal
Tremendous contribution to self-esteem of patients
1. Prevent loss of vision
2. Contributes to a better quality of life
3. Happy person = happy society
Economic benefits:
1. People can continue working life + pay tax
2. Less welfare payments
3. Gov can allocate funds to other areas
Eliminates need carers:
1. Loss of jobs
Australian scientists in field of microsurgical replacement of
lenses
Dr Fred Hollows
1. Developed cheap corneal replacements to cure
certain types of blindness that are common in
developing countries.
2. Work is being carried through Fred Hollows
Foundation
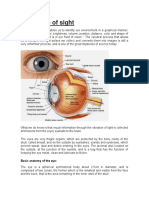
4. The light signal reaching the retina is
transformed into an electrical impulse.
Identify photoreceptor cells as those containing light
sensitive pigments and explain that these cells convert light
images into electrochemical signals that the brain can
interpret.
Varies among species but is able to absorb light and convert
them into electrical impulses that can be interpreted by the
brain.
Humans
Complex single lens eye:
capable of accommodation
to produce image on retina
Rods : sensitive to low
intensity of lights
Cones: colour vision
Flatworms
Bees
Only detect presence of
light no colour.
For direction
Ommatidium:
Describe the differences in distribution, structure and function of the
photoreceptor cells in the human eye
Outline the role of rhodopsin in rods
Made up of protein opsin + derivative of vitamin A retinal ( if
this is lacking, vision is affected + condition night blindness
can result)
Absorb light and undergoes photo-excitation
Separates into 2 parts: opsin + retinal
Generates nerve impulse that travels to the brain via optic
nerve.
Allow new image to be received
Identify that there are three types of cones, each
containing a separate pigment sensitive to either
blue, red or green light
Explain that colour blindness in humans results
from the lack of one or more of the colour-sensitive
pigments in the cones.
Red Green colour blindness
Sex linked
Caused by defect in red-green decoder
Red + green are confused as redness is taken out of red light
+ greenness is taken out of green light both will appear
brownish
Red colour shifted towards green + green shifted towards red
Incidence = 1/12 males 8%
Blue Yellow colour blindness
Autosomal
Caused by defect in blue-yellow decoder
Blue + yellow are confused
Both are perceived as greyish
Incidence = rare <1%
Total colour blindness
Incidence = very rare ) <0.003%)
5. Sound is also a very important communication
medium for humans and other animals
Explain why sound is a useful and versatile form of communication
Você também pode gostar
- Aloka Prosound Alpha6 UserDocumento346 páginasAloka Prosound Alpha6 UserGiovanni Gil Martodimedjo100% (7)
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications 1st Edition Wentworth Solutions ManualDocumento35 páginasFundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications 1st Edition Wentworth Solutions Manualhoy.guzzler67fzc100% (44)
- CommunicationDocumento16 páginasCommunicationbitchass niggaAinda não há avaliações
- WPR 2Documento5 páginasWPR 2ishika mohanAinda não há avaliações
- General Psychology Module on the Human BrainDocumento7 páginasGeneral Psychology Module on the Human BrainLawrence Jim BongstarAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic Eye Restores VisionDocumento19 páginasBionic Eye Restores VisionYellaReddy TarigopulaAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic EyeDocumento6 páginasBionic EyeChandu GudeAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of Vision PDFDocumento14 páginasPhysiology of Vision PDFJana Bayot100% (2)
- Soumya Bionic EyeDocumento17 páginasSoumya Bionic EyePriti ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic Eyes: Towards Creating The Joy of Sight For The BlindDocumento9 páginasBionic Eyes: Towards Creating The Joy of Sight For The BlindVed Shekhar GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- The Physics of Light and Color - Human Vision and Color Perception - Olympus LSDocumento14 páginasThe Physics of Light and Color - Human Vision and Color Perception - Olympus LSmarialopezmartinez424Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Paper: The Future of Retinal Implants and The Bionic EyeDocumento7 páginasFinal Paper: The Future of Retinal Implants and The Bionic EyePatrick Tice-CarrollAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology of SightDocumento3 páginasPhysiology of SightDevendra RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocumento6 páginasStructure and Function of The Human EyeAljhon DelfinAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and Function of EyesDocumento11 páginasStructure and Function of EyesSamar Ameen SialAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Retina: Presented byDocumento6 páginasArtificial Retina: Presented bySai KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial RetinaDocumento6 páginasArtificial RetinavenkateshmukharjiAinda não há avaliações
- Medical PhysicsDocumento34 páginasMedical Physicsn0tsewAinda não há avaliações
- Model Science The Human EyeDocumento27 páginasModel Science The Human EyeMansoor AliAinda não há avaliações
- G-10 Biology, 3.2 Sense OrgansDocumento10 páginasG-10 Biology, 3.2 Sense OrgansYohannes NigussieAinda não há avaliações
- Krishna VeniDocumento7 páginasKrishna VeniPrinlova PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocumento52 páginasOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababAinda não há avaliações
- Special Sensors PDFDocumento45 páginasSpecial Sensors PDFSwarna JayarathnaAinda não há avaliações
- Onisha Biology Project 14 10 15Documento14 páginasOnisha Biology Project 14 10 15Jelani GreerAinda não há avaliações
- Biology IPDocumento17 páginasBiology IPIshika RajputAinda não há avaliações
- ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSINGDocumento83 páginasELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSINGshellyAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 5Documento3 páginasLecture Notes 5Carol RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Author 1: K.Dinakar (2 B.Tech, ECE) Author 2: P.Jagadish Babu (2 B.Tech, ECE)Documento8 páginasAuthor 1: K.Dinakar (2 B.Tech, ECE) Author 2: P.Jagadish Babu (2 B.Tech, ECE)Jagadish BabuAinda não há avaliações
- How the Human Eye WorksDocumento16 páginasHow the Human Eye WorksRahul ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Eye Disorders-1Documento11 páginasIntroduction To Eye Disorders-1bhavani GAinda não há avaliações
- The Sense of SightDocumento7 páginasThe Sense of SightRosy SantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Functions: Anatomy and AssessmentDocumento88 páginasVisual Functions: Anatomy and AssessmentsharenAinda não há avaliações
- Human EyeDocumento4 páginasHuman EyeLit Central DreamsAinda não há avaliações
- Human Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition4865Documento8 páginasHuman Organ Systems and Bio Designs - 1: at Myintuition48651NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKAAinda não há avaliações
- EYESSDocumento43 páginasEYESSsalwanaseer9999Ainda não há avaliações
- Presented by Carmelita Ramos, RNDocumento81 páginasPresented by Carmelita Ramos, RNMela De Jesus RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Communication Study GuideDocumento5 páginasUnit 2 Communication Study GuideviviannAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial EyeDocumento31 páginasArtificial Eyeapi-19937584Ainda não há avaliações
- A Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byDocumento13 páginasA Project On " Human Eye": Submitted To-Submitted byaman1990100% (1)
- Chapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocumento3 páginasChapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful WorldSahil AnsariAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic EyesDocumento15 páginasBionic Eyespavan96Ainda não há avaliações
- Eye PDFDocumento19 páginasEye PDFDebbie MeyerAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful World Revision NotesDocumento3 páginasChapter 11 - Human Eye and Colourful World Revision NotesNancy GiriAinda não há avaliações
- I. Structures Involved in Detecting Changes and Producing ResponsesDocumento9 páginasI. Structures Involved in Detecting Changes and Producing ResponsesholdonpainendsAinda não há avaliações
- Vision ResearchDocumento4 páginasVision ResearchMichael SmithAinda não há avaliações
- How Vision Works: The Science Behind SightDocumento6 páginasHow Vision Works: The Science Behind SightmwxAinda não há avaliações
- DIP Lecture 5 - Elements of Visual Perception.Documento8 páginasDIP Lecture 5 - Elements of Visual Perception.Samrat BorkarAinda não há avaliações
- Anjie S. Bispat and Adeline C. Y. Sung: Biochemistry of VisionDocumento35 páginasAnjie S. Bispat and Adeline C. Y. Sung: Biochemistry of VisionMonesa Christy VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Eye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BDocumento11 páginasEye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BCR7STUDIO 7100% (1)
- SightDocumento26 páginasSightapi-703497157Ainda não há avaliações
- The Eye - Grade11Documento4 páginasThe Eye - Grade11joshua NaulthyAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Eye Anatomy and TypesDocumento36 páginasArtificial Eye Anatomy and TypesEng-Alaa ShararAinda não há avaliações
- Bionic Eye: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Kle Institute of Technology HubliDocumento25 páginasBionic Eye: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Kle Institute of Technology HubliAbhishek MatAinda não há avaliações
- Final TouchDocumento49 páginasFinal TouchmalathiAinda não há avaliações
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsAinda não há avaliações
- Occupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthNo EverandOccupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthAinda não há avaliações
- The World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!No EverandThe World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!Nota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- Visual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsNo EverandVisual Field Loss in the Real World: A Book of Static Perimetry Test Targets for Eye Health ProfessionalsAinda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management Plan: CEIC8204 Business Management in Chemical EngineeringDocumento13 páginasProject Management Plan: CEIC8204 Business Management in Chemical EngineeringCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- BirdbrainDocumento1 páginaBirdbrainplastoneAinda não há avaliações
- BirdbrainDocumento1 páginaBirdbrainplastoneAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes Vs AlkenesDocumento1 páginaAlkanes Vs AlkenesCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Acetone and Water DistillationDocumento17 páginasAcetone and Water Distillationinvincible111100% (1)
- Explain The Significance of The TreeDocumento1 páginaExplain The Significance of The TreeCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Hominid EvolutionDocumento2 páginasHominid EvolutionJosephine TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Past HSC QuestionsDocumento2 páginasPast HSC QuestionsCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Tips ModulesDocumento3 páginasTips ModulesCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- As You Like It Reveals How A Connection To Place Allows Individuals To Enrich Their Sense of Belonging and Their Relationships With Each OtherDocumento2 páginasAs You Like It Reveals How A Connection To Place Allows Individuals To Enrich Their Sense of Belonging and Their Relationships With Each OtherCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Explain The Significance of The TreeDocumento1 páginaExplain The Significance of The TreeCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- One Disadvantage It Produce Large Amounts of Coke. Two Process That Superseded Are Visbreaking, Catalytic Cracking and Steam CrackingDocumento4 páginasOne Disadvantage It Produce Large Amounts of Coke. Two Process That Superseded Are Visbreaking, Catalytic Cracking and Steam CrackingCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- As You Like It Reveals How A Connection To Place Allows Individuals To Enrich Their Sense of Belonging and Their Relationships With Each OtherDocumento2 páginasAs You Like It Reveals How A Connection To Place Allows Individuals To Enrich Their Sense of Belonging and Their Relationships With Each OtherCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Belonging PieceDocumento2 páginasCreative Belonging PieceCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Prelim 2010 2U QuestionDocumento10 páginasPrelim 2010 2U QuestionCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- 3U Parametric TopicDocumento7 páginas3U Parametric TopicCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- ValidityDocumento1 páginaValidityCindy VoAinda não há avaliações
- Stereo Microscopes enDocumento32 páginasStereo Microscopes entomichelAinda não há avaliações
- Intel RealSenseDocumento119 páginasIntel RealSenseRicardo De La PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Term 3 Week 2 - 2020Documento7 páginasLife Sciences Grade 12 Term 3 Week 2 - 2020paballorandomaccAinda não há avaliações
- Iscience: Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Displays: Perspectives and ChallengesDocumento13 páginasIscience: Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Displays: Perspectives and ChallengesfarihAinda não há avaliações
- Developing Hardware Capabilities for Mobile ManipulationDocumento13 páginasDeveloping Hardware Capabilities for Mobile ManipulationCodrut MoldovanAinda não há avaliações
- Sony 4K Ultra HD WhitePaper v2TGDocumento26 páginasSony 4K Ultra HD WhitePaper v2TGJaimichu07Ainda não há avaliações
- Mura Tore 2007Documento8 páginasMura Tore 2007Lepaca KliffothAinda não há avaliações
- EVAN-Toolbox IntroductoryManual V1.8Documento37 páginasEVAN-Toolbox IntroductoryManual V1.8Ivan JerkovićAinda não há avaliações
- The Carillon - Vol. 54, Issue 22Documento24 páginasThe Carillon - Vol. 54, Issue 22carillontechnic9873Ainda não há avaliações
- Pinnacle Studio Readme: Technical NotesDocumento5 páginasPinnacle Studio Readme: Technical NotesAhtasham ul haqAinda não há avaliações
- Audio For HD and 3D - UEFA Champions League FinalDocumento4 páginasAudio For HD and 3D - UEFA Champions League FinalCalrecCommunityAinda não há avaliações
- VidPIV Particle Image Velocimetry SoftwareDocumento22 páginasVidPIV Particle Image Velocimetry SoftwareSiamakAinda não há avaliações
- Stereo Imaging Techniques and ApplicationsDocumento47 páginasStereo Imaging Techniques and ApplicationsRavi GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Stereo AnalystDocumento312 páginasStereo AnalystMatt TenneyAinda não há avaliações
- 3D TechnologyDocumento2 páginas3D TechnologyPradeep YenAinda não há avaliações
- Instant Download Human Resources Management in Canada Canadian 13th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocumento33 páginasInstant Download Human Resources Management in Canada Canadian 13th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdylanyoung2tlm100% (9)
- Lecture 5 StereoscopicDocumento13 páginasLecture 5 StereoscopicHedaeturRahmanAinda não há avaliações
- An Intuitive and Interactive Holographic Instructional Support SystemDocumento4 páginasAn Intuitive and Interactive Holographic Instructional Support SystemMelvin LeyvaAinda não há avaliações
- Photogrammetry QADocumento21 páginasPhotogrammetry QAVyle SabadoAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Televisor LG PDFDocumento80 páginasManual Televisor LG PDFRené Arangua MasseranoAinda não há avaliações
- 00 CourseDocumento15 páginas00 CourseSaurabhAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Vision Improvement Habits for AllDocumento7 páginasNatural Vision Improvement Habits for Allelizabeta_radeska@commander.com100% (1)
- Optical 3 D Scanner TechnologyDocumento9 páginasOptical 3 D Scanner TechnologySantiago Marcelo ReinaAinda não há avaliações
- Screenless DisplayDocumento21 páginasScreenless DisplayAbhishek Raj100% (3)
- Thesis ProjektDocumento100 páginasThesis Projektsef370Ainda não há avaliações
- Transformarea Hartii Din Format Analog in Format DigitalDocumento8 páginasTransformarea Hartii Din Format Analog in Format Digitali_like_surfAinda não há avaliações
- SliceViewer and VoxelViewer - enDocumento55 páginasSliceViewer and VoxelViewer - enemadhsobhyAinda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full Accounting For Decision Making and Control 9th Edition Zimmerman Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 páginasDwnload Full Accounting For Decision Making and Control 9th Edition Zimmerman Solutions Manual PDFdietzbysshevip813100% (14)